What The Experiments Showed
Initially, the researchers tested the nanobody on mouse brain tissue in vitro. They found that PFFNB2 could bind to aggregates of alpha-synuclein, but could not prevent the formation of clumps.
Further experiments revealed that the nanobody could bind to and disrupt fibrils of alpha-synuclein that had already formed, destabilizing the misshapen proteins.
The researchers then tested this in live mice and found that the nanobody prevented alpha-synuclein from spreading to the cortex of the brain. The cortex is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for most higher brain functions.
Dr. Petrossian explained for MNT that he results showed that they were able to specifically target the preformed fibrils of alpha-synuclein in cell and mouse models, that they were able to reduce the clumping of alpha-synuclein in cell models, and they were able to reduce alpha-synuclein pathology in mouse models.
Changing The Course Of Parkinsons
As a world-leading Parkinsons research supporter since 1957, trailblazing discoveries aimed at easing, curing and preventing the disease drive us forward. While the cause of Parkinsons is still unknown, through a history of strategic research investments of more than $400 million, we steer transformative progress to help uncover the mystery of this disease.
Parkinsons Foundation research funding has led to breakthroughs, including:
- The discovery of alpha-synuclein the first gene associated with Parkinsons.
- The first standard tools to measure Parkinsons progression the Hoehn and Yahr scale.
- Publishing the first double-blind clinical trial of carbidopa/levodopa in collaboration with Merck, Inc.
- Developing the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale, now widely used in PD research and clinical trials.
The PD community continues to fuel the Foundations growth. Support of the Reach Further initiative helps us boost investments in leading-edge PD research and allows us to build on 60 years of funding pioneering scientific progress, a legacy that includes:
- Our work to uncover the origins of Parkinsons using the power of genetics through the groundbreaking, PD GENEration: Mapping the Future of Parkinsons Disease initiative.
- The Parkinsons Foundation landmark Parkinsons Outcomes Project a nearly 15,000 participant-strong study of people across five countries who live with PD that has led to best care practices and accelerating PD research.
The Parkinsons Disease Medication Pipeline
The pipeline for Parkinsons disease medications is extremely crowded these days, with multiple medications at various stages of research development. This is very exciting news for the PD community and is a perfect example of the hope in progress part of our organizations motto. It is thrilling to see the research that is underway, especially the potential treatments that have already made it to the clinical trial phase of development. However, this progress brings with it the welcome challenge of keeping track of all the potential compounds that are in research development! Recently, a review was published in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease which cataloged the 145 compounds that are currently being studied in humans via clinical trials for PD. This is a staggering number and is even more exceptional when you consider the many more compounds that are not quite yet ready for human trials, but are currently being studied in the laboratory in test tubes, cell culture or animal models of PD. The number also does not account for compounds that have been studied in small clinical trials, garnered promising data, and will be studied in larger clinical trials in the near future but are not being tested in clinical trials right now.
Some background on the review
Recommended Reading: Large 10 Parkinson’s Exercises
Cambridge Researchers Will Play A Key Role In Clinical Trials Of A New Treatment That Involves Transplanting Healthy Nerve Cells Into The Brains Of Patients With Parkinsons Disease
This could transform the way we treat Parkinsons disease
Roger Barker
The Swedish Medical Products Agency has granted approval for the trial to proceed ethical approval has already been obtained from the Swedish Ethics Review Authority. The team, led from Lund University in Sweden, is poised to begin recruitment.
STEM-PD uses human embryonic stem cells, a type of cell that can turn into almost any type of cell in the body. The team has programmed the cells to develop into dopamine nerve cell, which will be transplanted into the brains of patients to replace cells that are lost in Parkinsons disease. The product has already been shown to be safe and effective at reverting motor deficits in animal models of Parkinsons disease.
The trial is a collaboration with colleagues at Skåne University Hospital, the University of Cambridge, Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust , and Imperial College London.
Professor Roger Barker from the Wellcome-MRC Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge and CUH is clinical lead on the project. The use of stem cells will in theory enable us to make unlimited amounts of dopamine neurons and thus opens the prospect of producing this therapy to a wide patient population. This could transform the way we treat Parkinsons disease
The cells to be used in the trial have been manufactured under good manufacturing practice at the Royal Free Hospital in London and have undergone rigorous testing in the lab.
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
You May Like: What Does Parkinson’s Do To The Brain
Parkinsons Disease: A Hopeful Future
Parkinsons disease is the fastest growing neurological condition in the world. Between 1990 and 2015, the number of people with this disease doubled to over 6 million . This number is predicted to double again to 12 million by 2040, primarily because of an ageing population . In the UK, the lifetime risk of developing Parkinsons disease is 2.7%, with approximately 17,300 new diagnoses made every year in people aged 45 and above .
Parkinsons disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder of the brain . It is characterised by the death of certain brain cells , particularly in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra . A high proportion of neurons within this part of the brain use a chemical called dopamine to transmit signals between themselves and throughout the brain these signals act to coordinate movement .
As the neurons in the substantia nigra die off, the amount of dopamine falls, which results in some of the major features of Parkinsons disease, such as slowness and stiffness of movement .
Adapted from International Society for Stem Cell Research 2022.
These symptoms increase in severity over time as more neurons are lost, and eventually patients may experience a resting tremor and have problems walking . Approximately 80% of patients also develop dementia within 20 years of disease onset .
Current treatment options target the symptoms, but not the cause
A new era: Targets for the Parkinsons disease medication pipeline
Lewy body accumulation
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
The causes of Parkinsons disease are still greatly unknown. Scientists who have studied this disorder estimate that 10-15% of cases come from genetics after seeing a series of genetic mutations that were common in Parkinsons patients.
Doctors suspect that environmental factors and lifestyle choices may have effects on the severity of Parkinsons disease symptoms. Exposure to chemicals like pesticides may increase the likelihood of developing Parkinsons disease. On the other hand, a good diet and regular exercise may decrease your chances.
You May Like: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Smell Like
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes shaking and muscle stiffness, and slows movement. It develops when neurons in a particular part of the brain stop working properly and are lost over time. These neurons produce an important chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is used by the brain to send messages across brain areas to help control movement. Eventually, the brain cannot make enough dopamine to control the movement properly.1,2
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease Dementia Prognosis
When To Contact A Doctor
If you have a family history of Parkinsons disease, you may wish to talk with a doctor about your potential risks or even explore genetic testing. However, its important to remember that not all people with a family history of Parkinsons disease will be affected.
Signs of Parkinsons disease can be different for every person. Parkinsons is usually separated into premotor, motor, and cognitive stages. These dont necessarily occur in a particular order, and not everyone will experience them all.
As explained by the Parkinsons Foundation, common early symptoms include:
- tremor, or involuntary shaking of the hands
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Headaches
How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Body
The telltale symptoms all have to do with the way you move. You usually notice problems like:
Rigid muscles. It can happen on just about any part of your body. Doctors sometimes mistake early Parkinson’s for arthritis.
Slow movements. You may find that even simple acts, like buttoning a shirt, take much longer than usual.
Tremors. Your hands, arms, legs, lips, jaw, or tongue are shaky when you’re not using them.
Walking and balance problems. You may notice your arms aren’t swinging as freely when you walk. Or you can’t take long steps, so you have to shuffle instead.
Parkinson’s can also cause a range of other issues, from depression to bladder problems to acting out dreams. It may be a while before abnormal movements start.
Changes In Cognition And Parkinsons Disease
Some people with Parkinsons may experience changes in their cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and the ability to plan and accomplish tasks. Stress, depression, and some medications may also contribute to these changes in cognition.
Over time, as the disease progresses, some people may develop dementia and be diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia, a type of Lewy body dementia. People with Parkinsons dementia may have severe memory and thinking problems that affect daily living.
Talk with your doctor if you or a loved one is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease and is experiencing problems with thinking or memory.
Also Check: When Was Linda Ronstadt Diagnosed With Parkinson’s
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases
While there have been significant advances in the symptomatic management of these diseases that improve quality of life and at times survival, the available medications likely only slow the progression of neuronal death by a few months. The idea of using cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases has been around for decades, most notably in Parkinson’s Disease where a variety of cell transplant investigations have been performed with success.
According to a recent study conducted by Nathan P. Staff et al,
“The precise mechanism by which MSCs may exert beneficial effects in neurological disease is still being elucidated, but it appears that multiple different mechanisms may contribute. First, MSCs have been shown to secrete neurotrophic growth factors, including glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor , vascular endothelial growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor ,which can be further enhanced under specific culture conditions.Neurotrophic growth factors have been shown to improve neuronal survival in a number of preclinical models of neuron injury, including ALS, PD, and MSA transgenic animalsand nerve injury models. â Second, MSCs strongly modulate the immune system and can aid wound healing, and this mechanism has been exploited in disorders such as graft versus host disease and Crohnâs disease. From a neurodegenerative perspective, it has become increasingly recognized that neuroinflammation plays a significant pathomechanistic role.”
Diet And Lifestyle Changes

Additional therapies for Parkinsons disease treatment include eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise.
Some individuals may benefit from participating in physical and occupational therapy. These therapies often focus on balance, improving your gait, or tactics to allow you to complete your work.
Other alternative options center on promoting holistic well-being while living with Parkinsons disease. These are not shown to stop the diseases progression but can help you manage symptoms and stay hopeful:
Read Also: How Does Parkinson’s Develop
Foods High In Saturated Fat
The role that foods high in saturated fats play in Parkinsons progression is still under investigation and is often conflicting. We might eventually discover that there are certain types of saturated fats that actually help people with Parkinsons.
Some limited research does show that ketogenic, low-protein diets were beneficial for some with Parkinsons. Other research finds high saturated fat intake worsened risk.
But in general, foods that have been fried or heavily processed alter your metabolism, increase blood pressure, and impact your cholesterol. None of those things are good for your body, especially if youre trying to treat Parkinsons.
Recommended Reading: Asbestos And Parkinsons Disease
What New Treatments Are Being Developed
Thanks to the progress weve already made, new treatments are being tested in clinical trials that have the potential to slow, stop or even reverse Parkinsons.
These include:
- stem cell therapies, which aim to use healthy, living cells to replace or repair the damage in the brains of people with Parkinsons
- gene therapies, which use the power of genetics to reprogramme cells and change their behaviour to help them stay healthy and work better for longer
- growth factors , which are naturally occurring molecules that support the growth, development and survival of brain cells.
And were developing treatments that aim to improve life with the condition, including new drugs that can reduce dyskinesia.
Read Also: Loss Of Smell And Parkinsons
Also Check: Does Alcohol Affect Parkinson Tremors
Aiming For Timely Diagnosis
As with many chronic conditions, earlier recognition of Parkinsons disease can help people experience an enhanced quality of life.
2016 statistics reflect that around 6.1 million people worldwide had Parkinsons, more than double than in 1990. However, this increase doesnt necessarily mean that Parkinsons disease is more common now.
The rise could be the result of increasing awareness of the disease, causing more people to contact a doctor about potential symptoms. The global population is , meaning more adults are in the at-risk age category for Parkinsons disease.
A of research findings suggests a timely diagnosis of Parkinsons disease can provide the following benefits, among others:
- support your right to know about the disease as soon as possible
- enable you to take an active role in your health and well-being surrounding disease management and treatment options
- allow you to engage with ongoing research into Parkinsons disease
- help you understand that the symptoms of Parkinsons arent just part of aging but a specific health condition
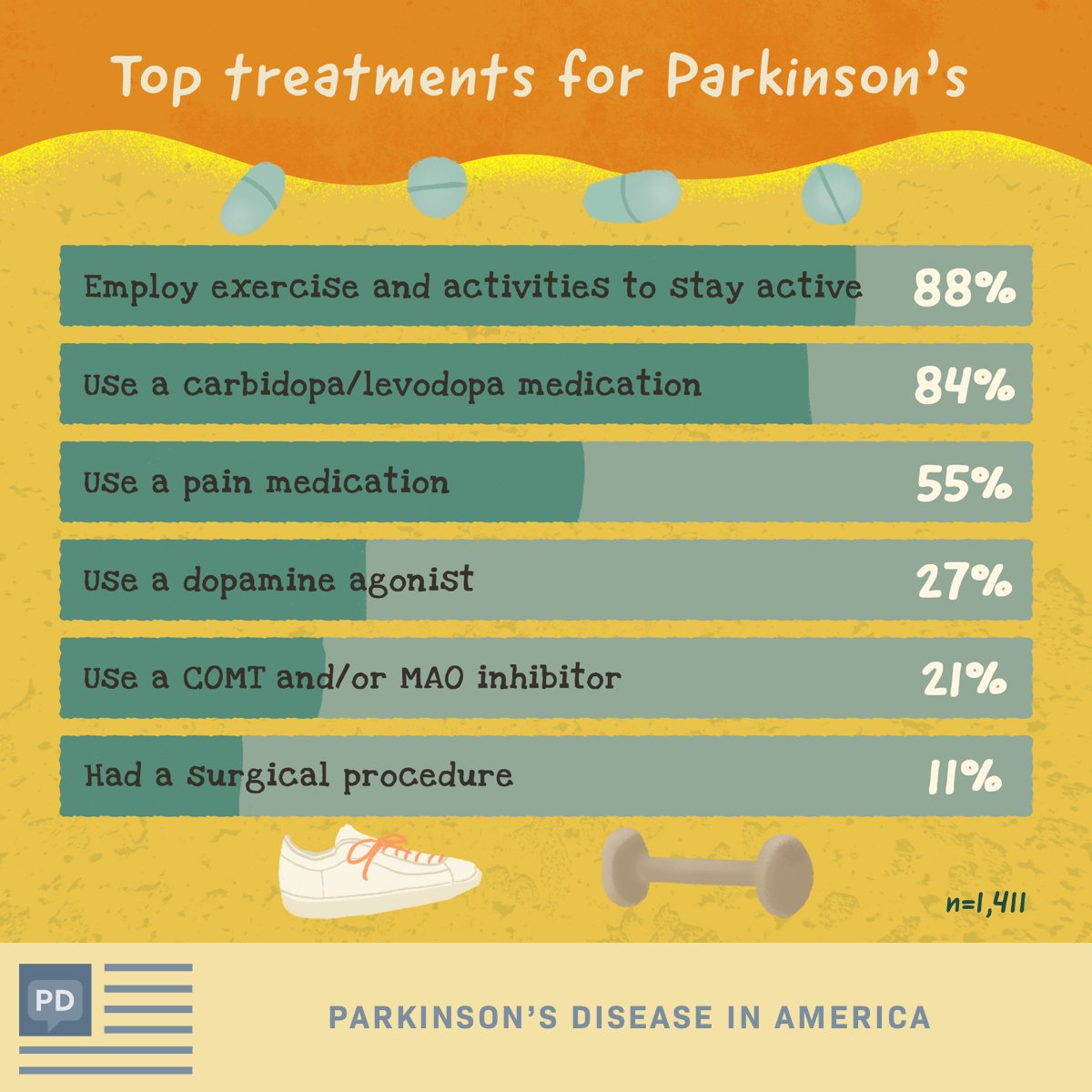
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Recommended Reading: A Typical Parkinson’s Progression
Our Research Achievements So Far
Thanks to more than 50 years of Parkinsons research, we understand more about the condition than ever before. Our research has led to major discoveries and improvements for people living with Parkinsons.
But we wont stop there. Together, we can find a cure.
Were collaborative. With your help, weve made research breakthroughs that have changed lives.
Were bold. Investing over £100m in research. Taking a stand against race inequality in research. Funding Dr Kirsty Bannisters research into pain that could see personal pain profiles become part of NHS practice.
Were ambitious. Funding world-first research to investigate whether cannabidiol could treat hallucinations and delusions in people with Parkinsons. Committing £800,000 to plan a new GDNF trial. Funding a pioneering study inspired by Joy Milne who can smell Parkinsons.
Collaborative. Bold. Ambitious. Its the only way weve been able to make life-changing discoveries.
Read Also: No Spill Coffee Cup Parkinsons
Funded By Leading Charities
Parkinsons UK and The Michael J. Fox Foundation , two leading charities have raised £1.5m to fund the phase 2 clinical trial, which is being sponsored by the biopharmaceutical company Neurolixis.
Dr Arthur Roach, Director of Research at Parkinsons UK, said: Were pleased to be supporting this study which aims to deliver a treatment that is desperately needed by many people living with Parkinsons. Its great that recruitment is now underway as this milestone brings us one step closer to results which could reveal an important new therapy for the millions living with this condition around the world.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Come And Go
First Patient Treated In Clinical Study Designed To Create New Brain Circuits Improve Symptoms
MORGANTOWN, W.Va. The West Virginia University Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute today announced the initiation of a clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a new innovative gene therapy in the treatment of Parkinsons disease. While surgical implants used in deep brain stimulation can treat Parkinsons disease, gene therapy can be of particular benefit without the need for implants in the brain.
This new study is the next step from a previous sham-controlled study that showed promise in Parkinsons disease,Ali Rezai, M.D., executive chair of the WVU Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute, said. In this study, AAV-GAD gene therapy is delivered to the subthalamic nucleus, a key area with dysfunction in a brain with Parkinsons disease. Over time, the gene therapy is intended to help Parkinsons disease by making new brain connections and improving symptoms.
The randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial is sponsored by MeiraGTx, a gene therapy innovation leader.
AAV-GAD is an experimental gene therapy to evaluate safety and treatment regimen using material manufactured with our proprietary production process that could support future commercialization, Alexandria Forbes, Ph.D., president and chief executive officer of MeiraGTx, said. We are excited to be working with the WVU Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute to move forward this innovative treatment for Parkinsons disease, and we look forward to reporting on the progress of the trial.
