Bladder And Bowel Problems
Bladder and bowel problems are common in men and women of all ages, but people with Parkinsons are more likely to have these problems than people who dont have the condition.
If you have Parkinson’s, you may be more likely to have problems with your bladder or bowels than people of a similar age without the condition.
Some of these problems are common in men and women of all ages, whether they have Parkinson’s or not.
Bowel problems are very common in the general public. But any change in bowel habit, particularly if you see blood in your bowel motions, should be reported to your GP.
Whatever the reason for your bladder and bowel problems, you can usually do something to help. It may be that the problem can be cured completely. But if that isnt possible, there are many different ways of managing the symptoms so they dont rule your life.
Mild Memory And Thinking Problems
Mild memory and thinking problems can be a normal part of getting older. But sometimes, these symptoms are caused by Parkinsons.
This is when you have symptoms such as forgetfulness, problems concentrating and difficulty making decisions, but you can still manage your day-to-day life.
Mild memory and thinking problems are common in Parkinsons and can happen at any stage of the condition, but not everyone with Parkinson’s has these symptoms.
If you do experience these symptoms, your doctor may describe it as mild cognitive impairment .
Its normal to worry if youre experiencing memory and thinking problems, but it doesnt necessarily mean you have dementia, or that you will develop it in the future.
Dementia in Parkinsons is diagnosed when thinking and memory problems are steadily getting worse over time and affect everyday life and daily tasks such as cooking, cleaning and dressing.
A New Toilet Or An Alternative
If you have real difficulties getting to the toilet, it may be possible to get a grant to build a new one, perhaps downstairs. An occupational therapist can advise you on this.
Not all homes are suitable for building new toilets, so a commode might be needed. A commode is a moveable toilet that doesnt use running water. It looks like a chair, with a container underneath that can be removed and cleaned after someone has used it. They can be very discreet.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s Disease
Addressing Practical Aspects Of Eating And Drinking
Some people with Parkinsons have problems chewing and swallowing. This can make it difficult to eat a diet with plenty of fibre. A speech and language therapist can give advice about this. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral. If it takes a long time to eat and your meal goes cold, eat smaller portions and go back for seconds that have been kept warm. You can also get special plates that keep your meals hot the Disabled Living Foundation has more information.
An occupational therapist will also be able to give you some tips and practical advice.
There Are Many Simple Non
- Wearing compression socks
- Elevating your legs when sitting
- Drinking more fluids
- Increasing your salt intake
- Elevating the head of your bed by 30 degrees
A physical therapist can also show you exercises to reduce the problems of dizziness when you stand. Since your heart also helps control blood pressure, it is important to discuss lightheadedness or dizziness with your physician.
While psychosis is usually associated with mental disorders like schizophrenia, sometimes Parkinsons itself or side effects of medications can change your perception of reality resulting in Parkinsons psychosis. Estimates suggest as many as 40% of people living with Parkinsons may experience some type of psychosis.
Parkinsons psychosis typically takes the form of hallucinations , delusions or both. Hallucinations and delusions are more common in people who have been living with Parkinsons for a long time. Some people are aware that what they are experiencing is not actually real, while others are not.
Hallucinations in Parkinsons can be common, especially during later stages of living with it. Often, they are non-threatening visual hallucinations or visions of things that are not really there.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Parkinson’s On The Rise
Tips For Living With Hallucinations
It is important for people with PD to talk about hallucinations with their family and care team these are manageable and can be troublesome if not treated. Discuss all possible symptoms with your doctor, no matter how minor, rare or bizarre you may think they are.
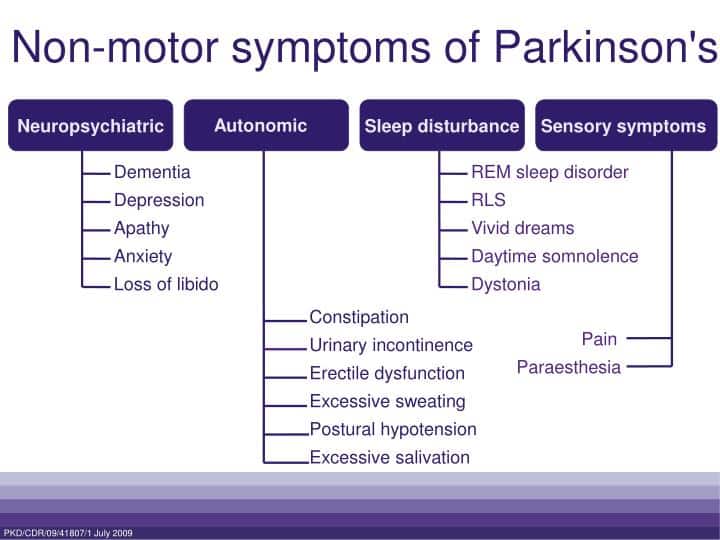
Nonmotor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder of the brain and central nervous system that most people recognize by its motor symptoms, which include tremors, muscle rigidity, impaired balance, and slowness of movement . Many Parkinsons patients, however, also develop nonmotor symptoms, which ultimately may be even more disabling.
Such nonmotor symptoms can include depression and anxiety, sleeping problems, fatigue, and cognitive changes.
While these symptoms do not affect movement, coordination, or physical tasks, they usually worsen over time and can make managing the disease more difficult. Some nonmotor symptoms of Parkinsons also can begin years before a person is diagnosed with the disease.
Parkinsons motor and nonmotor symptoms often are considered as separate problems. But its important to note that these symptoms can overlap and affect each other, informing each persons disease experience. For example, problems with the muscles that control the mouth and throat a motor symptom can lead to complications that arent directly motor-related, such as excessive drooling and difficulties with speech.
Sudden drops in blood pressure another nonmotor symptom can lead to dizziness and, in extreme cases, to a loss of balance that can cause falls.
The following are the main nonmotor symptoms of Parkinsons:
Don’t Miss: How Does Dopamine Affect Parkinson’s Disease
Clinical Evaluation Of Non
The following symptoms were assessed: hyposmia, neuropsychiatric disorders , autonomic dysfunctions , and sleep disturbances . A clinical interview was conducted to determine the presence of each NMS at the time of the examination. Informations on the current use of medications, such as laxatives, hypnotics, or antidepressants to treat some of these NMS, were also collected.
Smell loss was assessed by the validated Argentina Hyposmia Rating Scale starting by asking the subjects whether they noted a change in their ability to smell. Patients with factors that could impair odor identification, such as: current smokers, medical history of nasal surgery , allergic rhinitis, and traumatic nasal injuries were eliminated. According to these criteria, our sample for this test was restricted to 51 patients . Hyposmia was considered to be present if the AHRS score was lower than 22.
To evaluate the presence of depression and its severity, we used the MontgomeryAsberg Depression Rating Scale . The cut-off scores we used were: < 7 absent signs, mild signs = 718, moderate = 1834, and 35 reflects severe depression. This scale consistently has the highest Cronbachs alpha levels reaching 0.92 . Patients with severe depression were excluded from the study. Patients with scores 7 were considered having depression.
What To Expect From Diagnosis
Theres no single test for Parkinsons, so it can take some time to reach the diagnosis.
Your doctor will likely refer you to a neurologist, who will review your symptoms and perform a physical examination. Tell your doctor about all the medications you take. Some of these symptoms could be side effects of those drugs.
Your doctor will also want to check for other conditions that cause similar symptoms.
Diagnostic testing will be based on your symptoms and neurologic workup and may include:
- blood tests
Recommended Reading: Is A Runny Nose A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Tips For Achieving A Healthy Weight
Whether you wish to gain weight or lose it, diet and exercise are key.
- Eat a balanced diet, with a variety of foods from all the food groups: whole grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products and sources of protein like meat, fish and beans.
- Exercise helps keep people mobile and strong and can improve mood. Being active stimulates appetite and burns calories.
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
Don’t Miss: Do You Have Hallucinations With Parkinson’s
Difficulty Moving The Eyes
You may have difficulties when starting to move your eyes or when trying to move them quickly. This might be more noticeable when looking at fast-moving objects, such as cars. Sometimes, instead of a smooth movement, your eyes move in a slow and jerky way. Difficulties in moving the eyes up or down are more common in progressive supranuclear palsy than Parkinson’s.
What Are Delusions

Delusions are illogical, irrational, dysfunctional views or persistent thoughts that are not based in reality. They are not deliberate and are very real to the person with PD. People with delusions who feel threatened may become argumentative, aggressive, agitated or unsafe.
- Delusions are less common in PD than visual hallucinations. They affect about 8% of people with PD.
- Compared to hallucinations, delusions tend to be more complicated, present a greater risk for behavioral disturbances and safety concerns, are typically more difficult to treat and represent a more obvious deterioration or decline in ones condition.
- Delusions can begin as generalized confusion at night. Over time, confusion can develop into clear delusions and behavioral disturbances during the day.
- Paranoia can lead to medication noncompliance a person refusing to take medications, believing they are poisonous or deadly.
- Delusions can be associated with dementia. As a result, people with delusions are often confused and extremely difficult to manage. In these cases, many caregivers require outside assistance.
All forms of delusions can be seen with PD, although delusions of jealousy and persecution are most widely reported and represent a greater challenge for treatment. These delusions can lead to aggression, which can pose a serious safety risk to the person with PD, family members and care partners.
You May Like: Are Shaky Hands A Sign Of Parkinson’s
What Are The Non
Parkinsons is officially classified as a movement disorder because it involves damage to the areas of the brain, nerves and muscles that influence the speed, quality, fluency and ease of movement. While the effects of Parkinsons on movement are often the most visible symptoms, like tremor, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons, like emotional and cognitive challenges, can sometimes have an even greater effect on your quality of life.
The effects of Parkinsons not related to movement are called non-motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons may actually outnumber motor symptoms and can appear years before motor symptoms.
In this article, we will help you identify and learn about the various non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons so you can take the first steps to living well.
Non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons are effects not related to movement.
There is a wide variety of possible non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons, ranging from physiological effects like trouble swallowing, pain and fatigue, to mental and emotional impacts, such as mood changes, cognitive challenges and anxiety. Just as Parkinsons affects everyone differently, the type, frequency and severity of non-motor symptoms each person experiences vary. Remember, just because something is listed as a non-motor symptom of Parkinsons does not mean you will experience it.
Its a lot harder to explain the Parkinsons that people dont see. Paul
Problems Caused By Limited Mobility
Some people with Parkinsons might soil their underwear. This is because mobility problems can make it difficult to wipe after using the toilet. If this is the case, it might help to use wet wipes, a bidet, or an adapted bottom wiper. An occupational therapist or the Disabled Living Foundation can offer further advice.
Bowel problems are common. But you should tell your GP if there are any changes in your bowel habits, particularly if you see blood in your stool. Some problems are difficult to avoid, but there are things you can do to make them less likely to happen.
Don’t Miss: How Prevalent Is Parkinson’s Disease In The Population
There Are Different Types Of Incontinence That People With Parkinsons May Experience Such As:
- Urge incontinence: a frequent and urgent need to use the toilet.
- Stress incontinence: usually occurs in the presence of some kind of physical stressor such as coughing.
- Nocturia: the need to get up multiple times in the night to use the toilet.
Learn more about changes you can make to your diet and lifestyle to help manage an overactive bladder, as well as treatments to discuss with your doctor and other healthcare professionals with our Overactive Bladder Worksheet.
Many incontinence issues can be addressed by therapy with an incontinence specialist, practicing exercises such as Kegels on a daily basis and by taking certain medications.
Parkinsons can present a variety of problems related to swallowing, ranging from minor complaints when swallowing pills to severe difficulty chewing tough foods like steak and hard pieces of bread. Swallowing issues are important to address because of the potential risk of aspiration pneumonia. Aspiration pneumonia is caused when saliva, liquids or food is breathed into the lungs instead of being swallowed into the esophagus and stomach.
Many swallowing issues can be easily addressed with specific swallowing exercises and minor changes in diet. It is a good idea to consult with a licensed speech-language pathologist to identify problem areas and improve swallowing ability through intentional exercises.
Involuntary Closure Of The Eyelids
Eyelid apraxia occurs when the muscles that open the eyelids have trouble opening. This often happens during speech. Sometimes the eyelids might close completely and stop you being able to see properly. In mild cases of eyelid apraxia, simply rubbing the eyelids might help. Sometimes, injections of botulinum toxin are used to treat eyelid apraxia. Speak to your specialist for advice.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Pain
How Are Speech Problems Treated
There are many options to help improve your speech. A speech-language pathologist can help you pick the right approaches for you. SLPs are trained health care professionals who specialize in evaluating and treating people with speech, swallowing, voice and language problems.Ask your doctor for a referral to a speech-language pathologist. It is also important to contact your health insurance company to find out what therapy and procedures are eligible for reimbursement and to find a list of SLPs covered by your plan.Finally, visit a SLP who has experience treating people with PD. Call the Parkinsons Foundation Helpline at 1-800-4PD-INFO for help locating a speech-language pathologist in your area. Lee Silverman Voice Treatment, discussed below, is a specific voice therapy for PD but it is not the only way to obtain high quality speech therapy for PD.
Micrographia: Having Small Handwriting
Having small handwriting may seem like an unexpected aspect of Parkinsons, but it is quite common. Many people actually experience this symptom as one of their first signs of PD, years before other movement symptoms arrive. It is literally what the name describes: When you hold a pen or pencil and write on a sheet of paper, your numbers and letters are very small and cramped-looking. It is caused by a lack of dopamine in the part of your brain called the basal ganglia, which helps start and control your movements.25 Without dopamine, the neurons in the basal ganglia cannot communicate with each other to produce smooth, controlled movement.
You May Like: Do Parkinson’s Patients Sleep A Lot
Some Examples Of Delusions And Their Impact In Pd Include:
- Jealousy
- Belief: Your partner is being unfaithful.
- Behavior: Paranoia, agitation, suspiciousness, aggression
Managing Depression In Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons, family members and caregivers may not always recognize the signs of depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing depression as a symptom of Parkinsons, it is important to know it can be treated.
Here are some suggestions:
- For information and support on living well with Parkinsons disease, contact our Information and Referral line.
- As much as possible, remain socially engaged and physically active. Resist the urge to isolate yourself.
- You may want to consult a psychologist and there are medications that help relieve depression in people with Parkinsons, including nortriptyline and citalopram .
Read Also: How Are You Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
What Are Hallucinations
Hallucinations are when someone sees, hears or feels something that is not actually there. They are best described as deceptions or tricks played by the brain that involve the bodys senses. Hallucinations are not dreams or nightmares. They happen when the person is awake and can occur at any time of day or night.
When To See Your Doctor
Its easy to assume these problems have other causes, and they often do. But any of these non-motor symptoms can have a big impact on your overall quality of life.
Having one or more doesnt necessarily mean you have Parkinsons disease or that youll eventually develop it. But its worth consulting with your doctor.
Tell your doctor if youre concerned about having Parkinsons disease. Although theres no cure, there are medications to help control symptoms.
Also Check: What Gene Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
