Complications In Advanced Pd
While worsening of motor function and drug-induced motor complications represents a major challenge in patients with mid-stage to advanced disease, in the advanced stage of PD the most troublesome and distressful complications are usually nonmotor symptoms, including psychiatric and cognitive disorders, autonomic disturbances, and sleep disorders that significantly increase the need for supportive care. Unfortunately, these symptoms are frequently neglected in clinical practice due to limited consultation time, perception of the patient and caregivers that their symptoms are unrelated to the disease, or insufficient awareness of the clinicians, who generally focus on motor symptoms .
Proper supporting care becomes increasingly important in advanced PD. Rehabilitative and support services for patients and family become key interventions as the disease reaches its more debilitating stages and pharmacologic or surgical treatment becomes less relevant. Management of motor and nonmotor complications in advanced PD requires careful and ongoing assessment of whether symptoms are a side effect of medication or related to the progression of the disease .
Medication Issues
Also Check: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Symptoms
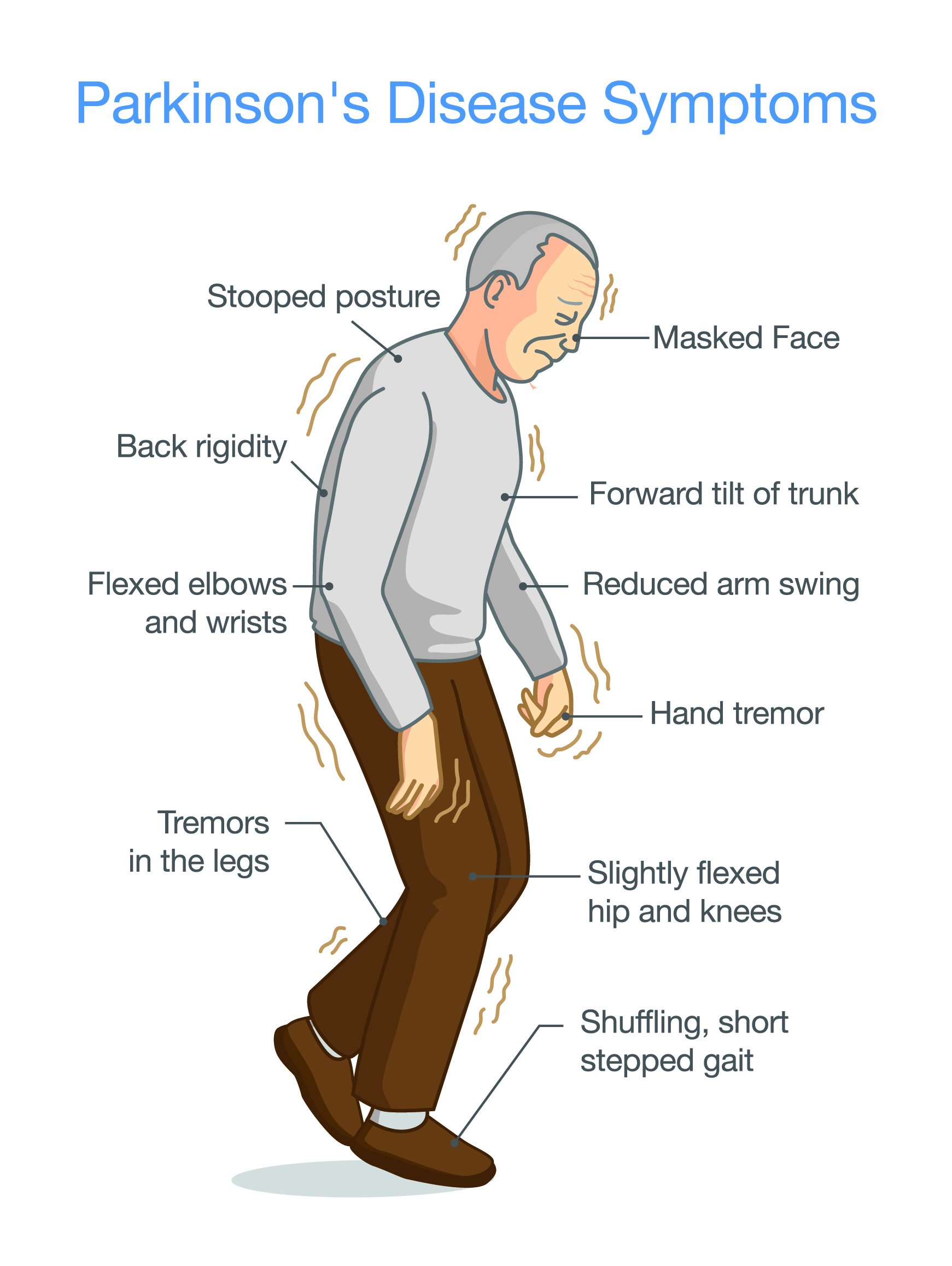
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Tips For Living With Hallucinations
It is important for people with PD to talk about hallucinations with their family and care team, because they are manageable and can be troublesome if not treated. Discuss all possible symptoms with your doctor, no matter how minor, rare or bizarre you may think they are.
- Good lighting and stimulating activities in the evening can help keep hallucinations at bay.
- While a hallucination is occurring, caregivers can help their loved one by reassuring them that they will be safe and validating their partners experience. For example, say, Ill take the cat outside instead of arguing that there is no cat.
You May Like: Are Intention Tremors Common In Parkinson’s
Medications Used For Treating Psychosis
Antipsychotic agents are designed to balance abnormal chemical levels in the brain. Up until the 1990s, the use of antipsychotics in PD was controversial because the drugs used until that time work by reducing excess dopamine. This alleviated psychosis but caused dramatic worsening of PD motor symptoms.
Fortunately, medications that are better tolerated by people with PD are now available. Today, there are three antipsychotic medications considered relatively safe for people with PD: quetiapine , clozapine and the newest agent, pimavanserin . They cause limited worsening of PD while treating hallucinations and delusions.
Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal
Parkinsons disease itself doesnt cause death. However, symptoms related to Parkinsons can be fatal. For example, injuries that occur because of a fall or problems associated with dementia can be fatal.
Some people with Parkinsons experience difficulty swallowing. This can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This condition is caused when foods, or other foreign objects, are inhaled into the lungs.
Also Check: When Do Parkinson’s Symptoms Start
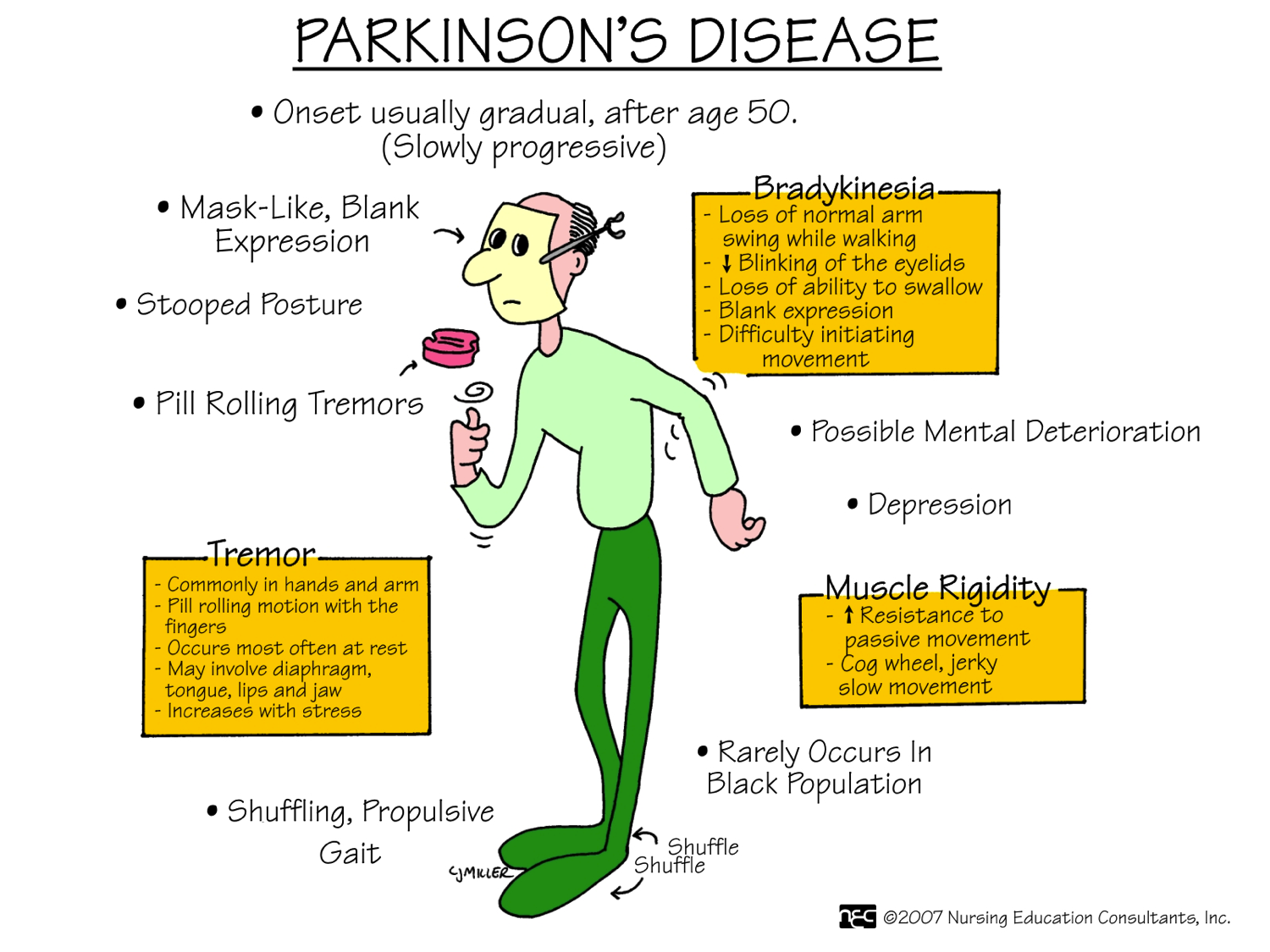
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease:
- tremor
- bradykinesia
- postural instability
Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinsons.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinsons disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinsons. If you suspect Parkinsons, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Introducing an easier way to track your symptoms and manage care.
Micrographia Or Small Hand Writing
Parkinsons patients often experience a sudden change in their handwriting and the medical term is known as Micrographia. A person with PD may begin with regular handwriting but, gradually they end up writing in smaller font, and letters may look cramped. Note how the handwriting becomes progressively smaller even in signing. The first letter R is big and the last letter A is barely legible. Also the same becomes normal in ON phase of medication
Also Check: What Is Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s Disease
How Do I Know If I Have A Swallowing Problem
- I have recently lost weight without trying.
- I tend to avoid drinking liquids.
- I get the sensation of food being stuck in my throat.
- I tend to drool.
- I notice food collecting around my gum line.
- I tend to cough or choke before, during or after eating or drinking.
- I often have heartburn or a sore throat.
- I have trouble keeping food or liquid in my mouth.
*Please note that not all content is available in both languages. If you are interested in receiving Spanish communications, we recommend selecting both” to stay best informed on the Foundation’s work and the latest in PD news.
Lifestyle Factors That Increase The Risk Of Parkinson’s
Prescott explains, “Maintaining a healthy lifestyle has been shown to play an important part in overall brain and body health. However, there is no definitive research that shows direct correlation between risk factors and incidence of Parkinson’s Disease. Some research has supported the benefits of exercise and use of caffeine to lower risk for Parkinson’s Disease.”
Read Also: Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Seizures
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
A Guide To Understanding End
Crossroads Hospice & Palliative Care created guidelines to help family caregivers better understand the physical changes of the end-of-life process, as well as the emotional and spiritual end-of-life changes taking place.
The following describes the physical symptoms you may observe. Here are end-of-life signs and helpful tips:
Also Check: Do People Die From Parkinson’s Disease
What You Can Expect
Parkinson does follow a broad pattern. While it moves at different paces for different people, changes tend to come on slowly. Symptoms usually get worse over time, and new ones probably will pop up along the way.
Parkinsonâs doesnât always affect how long you live. But it can change your quality of life in a major way. After about 10 years, most people will have at least one major issue, like dementia or a physical disability.
What Surgeries And Therapies Can Treat Parkinson’s Disease
Surgery
In addition to drug treatment, specific surgical options are available that may be used in patients that have severe symptoms of the disease or when medication is no longer able to give symptomatic relief. Early surgical treatments involved removal or destruction of the thalamus to reduce tremors but had little or no effect on symptoms of bradykinesia or rigidity. Pallidotomy and subthalamotomy, two surgical operations that remove parts of the brain have shown improvements in many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. However, these techniques often do not reduce all of the symptoms which may continue to progress and may have many different complications when the brain tissue is destroyed in some patients, the outcomes versus the risks of these surgeries is still considered.
Parkinson’s Disease Gene Therapy
Parkinson’s Disease Other Therapies
Some studies claim that eating velvet or fava beans help with symptoms , but these studies were not deemed conclusive. Vitamin E and coenzyme Q have been claimed by some to be neuroprotective but are not a currently recommended treatment. A high fiber diet has been recommended to reduce the constipation that usually is seen in many Parkinson’s disease patients. Exercise has been suggested to help Parkinson’s disease patients studies suggest that many Parkinson’s disease patients benefit from exercises that stress flexibility, leg strength, and cardiovascular conditioning.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Parkinson Disease Naturally
Managing Depression In Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons, family members and caregivers may not always recognize the signs of depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing depression as a symptom of Parkinsons, it is important to know it can be treated.
Here are some suggestions:
- For information and support on living well with Parkinsons disease, contact our Information and Referral line.
- As much as possible, remain socially engaged and physically active. Resist the urge to isolate yourself.
- You may want to consult a psychologist and there are medications that help relieve depression in people with Parkinsons, including nortriptyline and citalopram .
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
The main motor symptoms of Parkinsons are:
- tremor
- slowness of movement
- problems with balance.
However, the condition does not only affect movement. People living with the condition can experience a range of non-motor symptoms that can often have a greater impact on their lives than movement difficulties.
Non-motor symptoms include:
- urinary urgency, frequency
- pain.
These non-motor symptoms are present at all stages of the condition but they can become more severe in the later stages of Parkinsons and have a major impact on quality of life.
Parkinsons gets worse over time and it can be difficult to predict how quickly the condition will progress. For most people, it can take years for the condition to progress to a point where it can cause major problems. For others, Parkinsons may progress more quickly.
Read Also: Can Physical Therapy Help Parkinson’s Disease
Depression And Parkinsons Disease
Depression is common in people with Parkinsons disease, occurring in about 40% to 50% of patients. Depression can worsen when the disease becomes more advanced and treatment becomes less effective. Mental health counseling and treatment options are available to help people living with APD. Seek help if you or a loved one is experiencing depression with their Parkinsons.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Towards The End Of Life
Parkinsons progresses in stages: diagnosis, maintenance, advanced and palliative. Professionals should have talk to people with Parkinsons about advance care planning in the earlier stages of the disease. This can allow them to express their wishes and preferences for their care in the later stages of the disease and make plans for the future.
Although the condition progresses differently and at a different speed for each person, the advanced stage can potentially cover a long period of time.
Problems that affect someone with advanced Parkinsons may include:
- medicines being less effective at managing symptoms than before
- having to take lots of medicines to manage symptoms and side effects
- more off periods when the effects of medication are reduced, and people experience movement fluctuations and involuntary movements
- increased mobility problems and falls
- swallowing difficulties
- less control of their Parkinsons symptoms, which become less predictable
- pain.
Some of the more advanced symptoms can lead to increased disability and poor health, which can make someone more vulnerable to infection, such as pneumonia. People with Parkinsons most often die because of an infection or another condition, usually caused by Parkinsons.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can A Parkinson Patient Live
What Is Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Advanced Parkinsons disease is a late stage of Parkinsons disease that is marked by limited mobility. Medications are used to control Parkinsons in early stages. When these medications lose their ability to work effectively and symptoms progress, physicians classify it as advanced Parkinsons disease.
APD usually occurs after 10 years of living with Parkinsons, but can occur much later. Patients in this stage may require a wheelchair or other assistive devices, and they have a higher risk of falling, dementia, and other cognitive problems.
This article will discuss the symptoms, treatment, and prognosis for advanced Parkinsons disease.
Verywell / Nez Riaz
What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts don’t know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Parkinson’s
Late Stages Of Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative disorder that worsens over time. For some individuals, a long period of time may elapse between an initial diagnosis and the appearance of severe, disabling symptoms. For others, the disease may progress rapidly. Not much is known about why some people develop severe symptoms quickly, while others stay relatively healthy for much longer. However, there are a few commonly recognized stages of disease progression that are experienced by most individuals living with Parkinsons.
In the early stages of Parkinsons disease, symptoms like tremors, stiffness, and slow movement are usually mild, may be limited to one side of the body, and often present more of an annoyance than a true impediment to activities of daily living. In the middle stages of Parkinsons, these symptoms become more severe, and may be accompanied by urinary and gastrointestinal disorders, sleep problems, depression, and dementia. In late-stage Parkinsons, symptoms are very severe, and often disabling.
Edison Home Health Care is happy to advise and assist you or any loved one who seek appropriate care of Parkinsons disease. Give us a call at 888-311-1142, or fill out a contact form and we will respond shortly.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
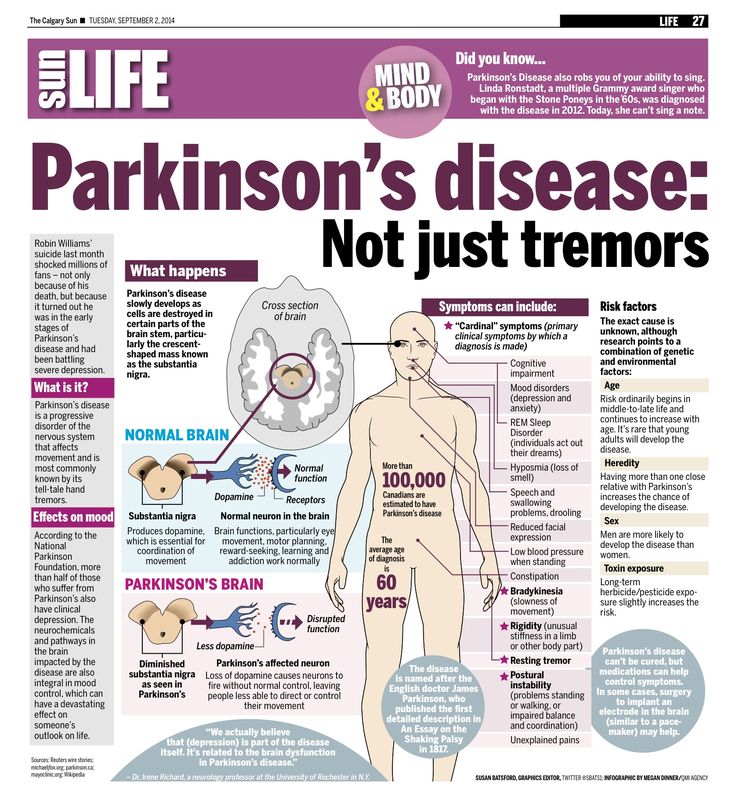
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Don’t Miss: Does Exercise Slow The Progression Of Parkinson’s
How Is It Treated And Is There A Cure
For now, Parkinsons disease is not curable, but there are multiple ways to manage its symptoms. The treatments can also vary from person to person, depending on their specific symptoms and how well certain treatments work. Medications are the primary way to treat this condition.
A secondary treatment option is a surgery to implant a device that will deliver a mild electrical current to part of your brain . There are also some experimental options, such as stem cell-based treatments, but their availability often varies, and many aren’t an option for people with Parkinsons disease.
Examples Of Delusions In Pd
- Jealousy
- Belief: Your partner is being unfaithful.
- Behavior: Paranoia, agitation, suspiciousness, aggression.
You May Like: How To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
