Finding The Right Medication
Finding the right medication to treat your Parkinson’s symptoms is a process that takes time and effort from you and your doctor. Parkinson’s medications work in different ways. Many are pills that you swallow, but some can be given through skin patches or intestinal infusions. It can sometimes feel like “trial and error” to figure out the best medication, dose and schedule to treat your symptoms. Over time, as symptoms progress or complications arise, your doctor may adjust your medications. This might mean changing your dose or how often you take a drug, or adding or switching medications. Staying in tune with your symptoms and which are most bothersome, and keeping track of how well medication is or is not working can help direct adjustments to your treatment regimen.
Here we describe the different categories of Parkinson’s medications how they work, their potential benefits and common side effects. We also give examples and highlight therapies that have been approved in the last few years with an asterisk.
Your Parkinson’s Drug Treatment
Dopamine is a chemical messenger made in the brain. The symptoms of Parkinsons appear when dopamine levels become too low. This is because many of the cells in your brain that produce dopamine have died or are dying. Taking dopamine as a drug doesnt work because it cannot cross the blood brain barrier. To get around this, doctors use other medication that can act in a similar way.
Which Medications Are Used In The Treatment Of Parkinson Disease
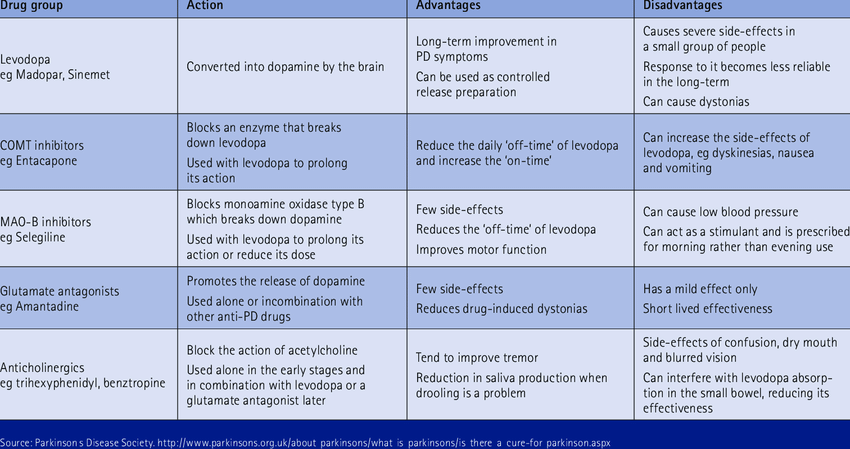
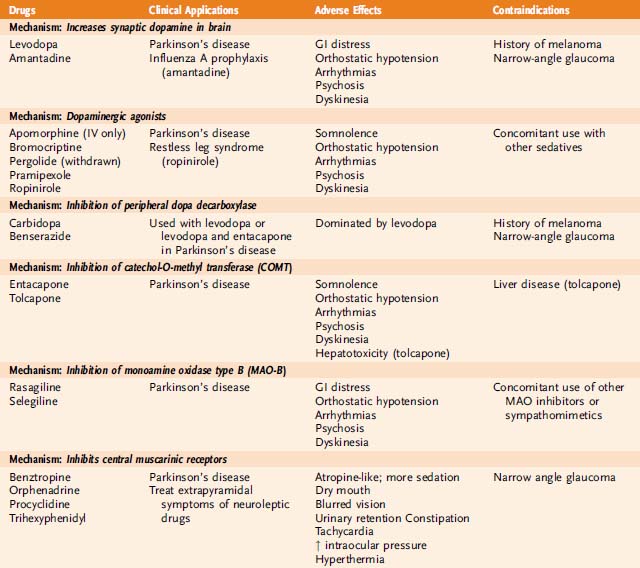
The cornerstone of symptomatic treatment for Parkinson disease is dopamine replacement therapy. The criterion standard of symptomatic therapy is levodopa , the metabolic precursor of dopamine, in combination with carbidopa, a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor . This combination provides the greatest symptomatic benefit with the fewest short-term adverse effects.
Dopamine agonists such as pramipexole and ropinirole can be used as monotherapy to improve symptoms in early disease or as adjuncts to levodopa in patients whose response to levodopa is deteriorating and in those who are experiencing fluctuations in their response to levodopa.
Monoamine oxidase -B inhibitors provide symptomatic benefit as monotherapy in early disease and as adjuncts to levodopa in patients experiencing motor fluctuations.
Catechol-O -methyl transferase inhibitors inhibitors such as entacapone and tolcapone may be used to increase the peripheral half-life of levodopa, thereby delivering more levodopa to the brain over a longer time.
Anticholinergic medications can be used for the treatment of resting tremor. However, they are not particularly effective for bradykinesia, rigidity, gait disturbance, or other features of advanced Parkinson disease and cognitive side effects are common. Therefore, anticholinergics are usually reserved for the treatment of tremor that is not adequately controlled with dopaminergic medications.
References
You May Like: How Parkinson’s Affects The Nervous System
What Other Information Should I Know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain lab tests to check your response to levodopa and carbidopa.
Before having any laboratory test, tell your doctor and the laboratory personnel that you are taking levodopa and carbidopa.
Levodopa and carbidopa can lose its effect completely over time or only at certain times during the day. Call your doctor if your Parkinson’s disease symptoms worsen or vary in severity.
As your condition improves and it is easier for you to move, be careful not to overdo physical activities. Increase your activity gradually to avoid falls and injuries.
Levodopa and carbidopa can cause false results in urine tests for sugar and ketones .
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Contraindicated Drugs For Parkinson’s Patients
More than two dozen drugs should not be taken by Parkinsons patients because they alter the brains dopamine system. Always let your neurologist know before you have surgery, so he or she can work with your medical team to keep your Parkinsons in control. View a list of drugs that Parkinsons patients should not take.
You May Like: How Do They Test For Parkinson’s
Some Disadvantages Of Mao
When selegiline is taken together with levodopa, side effects such as dyskinesias , hallunications or vivid dreaming may sometimes occur or worsen.
When people have taken rasagiline on its own , the most commonly reported side effects have been:
- Headache
- Depression
When taken with levodopa, the most common reports have been of uncontrolled movements and accidental falls.
Many of these side effects may be due to the increase in dopamine caused by rasagiline or selegiline. Your doctor or consultant can alter the dosage to correct these effects.
If youre taking some types of antidepressant, you might not be able to take MAO-B inhibitors, as these drugs can interact with each other to raise blood pressure to a dangerous level.
Your neurologist or pharmacist is the best person to advise on potential interactions with other medications.
Impulsive And Compulsive Behavior
Some people taking dopamine agonists may experience problems with impulsive or compulsive behaviours. For example an increased desire to gamble or engage in sexual activity. These behaviours often develop slowly so may not seem to be a problem immediately. It is important for both the person living with Parkinsons and their family to be aware of this side effect. If affected by this side effect, a reduction in dose or stopping the medication will stop the behaviour.
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Cause Seizures
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Other PD medications work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. One such class is the MAO-B inhibitors. As is discussed above, MAO-B is one of the main enzymes involved in the breakdown of dopamine, and reducing the activity of this enzyme therefore results in increased dopaminergic activity within the striatum, mediated by endogenous dopamine . Their use relieves motor symptoms in PD patients, and as with dopamine agonists they may be used as an initial treatment option, to delay the need for levodopa therapy, to reduce the risk of levodopa-induced motor complications . While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose.
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patient’s symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
Don’t Miss: What’s The Cause Of Parkinson’s Disease
Withdrawal Syndrome With Levodopa
Research has shown that withdrawal symptoms can happen when someone very suddenly stops taking levodopa, perhaps because they are experiencing impulsive and compulsive behaviour. It can lead to symptoms such as depression, anxiety and pain. Any withdrawal from Parkinsons medications needs to be done gradually, under the supervision of a health professional, to avoid the risk of developing this syndrome.
Other Medications For Parkinsons Disease And How To Manage Medication
Medication is the main treatment for Parkinsons disease. It is used to try and increase the levels of dopamine in the brain or to mimic the action of dopamine on receptors in the brain. The two main types of drugs used levodopa and dopamine agonists All the other drugs are used occasionally alone but usually together with levodopa or a dopamine agonist. They reduce the breakdown either of levodopa in the general circulation before it reaches the brain, or of dopamine in the brain. However, they are only used with great caution because they have other possible effects in the body, some of which may be dangerous.
The MAO-B inhibitors delay the breakdown of dopamine so helping to reduce the end-of-dose deterioration for people who are taking a levodopa preparation. Selegiline may also be used on its own in the early stages of treatment when the body is still itself making reasonable amounts of dopamine. It is not recommended for use by people who have postural hypotension as it can make this worse. Andrew takes selegiline as part of a cocktail of drugs including levodopa a dopamine agonist , and another drug to counteract the hyperacidity which is a known side effect of selegiline. Penny was on ropinirole when she was prescribed rasagiline and she believes this helped to clear the fog in her brain.
You May Like: What Helps Parkinson’s Tremors
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
Recent research has discovered dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome, which can happen when someone very suddenly stops taking dopamine agonists, perhaps because they are experiencing impulsive and compulsive behaviour. It can lead to symptoms including depression, anxiety or pain . Any withdrawal from Parkinsons medications needs to be gradual, under the supervision of a health professional, to avoid the risk of this syndrome.
Injections of apomorphine are taken in a similar way to insulin for diabetes. There is a ready-to-use injection pen that works within 10 minutes and is often used as a rescue measure. This is very useful if you have a sudden off period.
Soreness or nodules can develop where the needle enters your skin. If this happens, do not stop the treatment and quickly seek advice from your specialist or Parkinsons nurse. It is important to change injection site to minimise scarring or infection. Simple massage, silicone gel patches or ultrasound can help to reduce any nodules that form.
Side Effects And Problems With Levodopa
In the early days of taking levodopa, you may feel sickness or nausea. In most people this will pass as your body adjusts to the medication.
Overtime as Parkinsons progresses the levodopa dose will need to be adjusted. Many people will become more aware that symptoms sometimes return between doses of medication. This is called wearing off and is a sign your dose needs to be adjusted.
As levodopa is absorbed through the gut, constipation or other stomach problems may impact on uptake of the medication. In some people who have had Parkinsons for sometime extra involuntary movements can occur. Your neurologist will be able to help adjust medications to minimise dyskinesia.
Other side effects may include:
- Confusion
- Psychological changes
- Sleepiness, fainting or dizziness
Side effects of levodopa can sometimes be improved by changing your dose, the form of the drug or how often you take it. If this doesnt work, other types of drug may be combined with levodopa.
Speak to your GP or specialist about the right treatment for you.
You May Like: What Can Help With Parkinson’s Disease
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Side Effects Of Levodopa:
Levodopa preparations are not without side effects. The most common include nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, involuntary movements, and, at higher doses in the elderly and frail, confusion.
- Nausea and vomiting can be a problem as the drug is being introduced. This is because the dose of carbidopa is not large enough to control these side effects. Ironically, the nausea and vomiting often get better as the levodopa/carbidopa dose is increased. The controlled-release preparation, Sinemet CRTM, is absorbed more slowly and far less likely to cause early side effects. Taking the drug with a light meal or snack can also help these side effects.
- Involuntary movements writhing, jerking, or free flowing movements and nodding can occur. The rate at which dopamine “turns over” in a person’s brain cells may determine whether or not they will develop dyskinesia . Dyskinesia can only be controlled effectively by lowering the dose of levodopa or, in some severe cases, surgery.
:2747-2754, 2004).
Other drug side effects include:
:888-899, 2004).
These can usually be improved with lower, more frequent doses of the drug, the use of a controlled release drug or with the addition of a dopamine agonist.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Come On Suddenly
Full List Of Medications Approved For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease In The Usa
Below is a full list of Parkinsons medications that have been approved to treat Parkinsons in the United States. This material is intended to provide you with information. It should not be used for treatment purposes, but rather as a source for discussion with the patients own physician. Work with your physician to determine which medications are best for you, and know the risks and benefits of each.
Side Effects And Problems Of Anticholinergics
Another reason these drugs are not a first choice for treating Parkinsons are their side effects. Some people may experience confusion, a dry mouth, constipation and blurred vision when taking anticholinergics.
Anticholinergics may interfere with levodopa absorption in the small bowel, which reduces the effectiveness of Madopar or Sinemet, forms of the drug levodopa.
Anticholinergics are not usually prescribed to older people with Parkinsons because there is an increased risk of memory loss and, in men, problems urinating.
You May Like: Why Does Parkinson’s Affect Speech
Why Is This Medication Prescribed
The combination of levodopa and carbidopa is used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s-like symptoms that may develop after encephalitis or injury to the nervous system caused by carbon monoxide poisoning or manganese poisoning. Parkinson’s symptoms, including tremors , stiffness, and slowness of movement, are caused by a lack of dopamine, a natural substance usually found in the brain. Levodopa is in a class of medications called central nervous system agents. It works by being converted to dopamine in the brain. Carbidopa is in a class of medications called decarboxylase inhibitors. It works by preventing levodopa from being broken down before it reaches the brain. This allows for a lower dose of levodopa, which causes less nausea and vomiting.
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinson’s disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
Also Check: What Medicine Do You Take For Parkinson’s Disease
Medication Management For Parkinson’s Disease
As Parkinsons disease progresses, some individuals may need to increase the dosage of their medication to control symptoms. With time, patients may notice that, throughout their day, they have periods of good symptom control , periods in which symptoms are much more noticeable , and even periods in which peak medication levels produce involuntary movements . When people experience these various states throughout the day, they are said to have motor fluctuations .
When assessing a patients response to medication, the Parkinsons neurologist may ask the patient to come to the clinic off meds, usually foregoing their Parkinson medications for 12 to 24 hours. The doctor will then perform the usual exam utilizing the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale , gaining valuable information on the patients baseline Parkinsons disease in the drug-free state.
After this first exam, the neurologist will give a dose of medication , wait 30 to 60 minutes and re-examine the patient. At that point, the doctor may give another dose, followed by re-examination. This cycle repeats until the doctor can determine that a) the patient is a responder or b) a non-responder to medications. It also allows for monitoring of potential side effects, like nausea, dizziness, low blood pressure, etc.
