What Is The Clinical Relevance Of These Findings
Stratification, or defining different subcategories, is key to better understanding disease mechanisms and kinetics in PD, predicting disease course and ultimately delivering personalised management strategies. The emerging focus of PD trial design is on early motor disease, including novel immunomodulatory therapies that require intensive and invasive monitoring. Traditionally, little account has been taken of disease heterogeneity in early PD when selecting patients for randomised, placebo-controlled studies. However, our results show that baseline phenotype is associated with variable rates of subsequent motor progression, although confounded by potential medication response effects. The mean difference in UPDRS motor scores between the fastest and slowest motor progression subtypes in Tracking Parkinsons was 2.6 points, equivalent to the primary hierarchical endpoint of several studies, including the ADAGIO study. Recruitment without taking into account heterogeneity and potential sources of recruitment bias may lead to less efficient designs, though there are various trade-offs between the cost of selecting patient subgroups, the sample size required for demonstrating a reduction in disease progression and increasing the length of follow-up.
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
A Way To Slow Parkinsons
Blocking Specific Form of a Brain Chemical Could Slow Brain Cell Loss, Researchers Find
Sept. 12, 2006 Blocking a specific form of a brain chemical slows brain cell loss in an animal model of Parkinsons disease, Texas researchers report.
In the animal model, the researchers found they could slow the death of affected brain cells by about half by blocking the chemical, called soluble TNF.
The finding offers a target for new drugs that could slow the progression of the debilitating and deadly disease. And it may apply to Alzheimers diseaseAlzheimers disease as well, suggest University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center researchers Melissa K. McCoy, Malú G. Tansey, PhD, and colleagues.
The finding may unveil opportunities for development of new therapeutics to treat human neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease, McCoy and colleagues say.
The researchers report their study in the Sept. 13 issue of The Journal of Neuroscience.
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Read Also: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Feel Like
Enhancing Neuronal Survival Processes
An alternative to stopping the spread of pathology, is to try and help neurons continue to function despite the presence of pathological alpha synuclein, i.e., to provide some form of trophic support. There are several classes of drugs being repurposed , which may achieve this.
There has been a lot of publicity surrounding the potential of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in PD . These drugs are licensed for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes and have neuroprotective properties across the whole range of animal models of PD, including 2 alpha synuclein models. There is some evidence that this action may relate to an improvement in brain insulin signaling which enhances Akt activity while additional data indicate these drugs may also act in parallel through a positive effect on neuroinflammation . Indeed, the increased risk of developing PD among T2DM patients may be ameliorated according to the choice of anti-diabetic agent used .
You May Like: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Cured
No, Parkinson’s disease is not curable. However, it is treatable, and many treatments are highly effective. It might also be possible to delay the progress and more severe symptoms of the disease.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Parkinson’s disease is a very common condition, and it is more likely to happen to people as they get older. While Parkinson’s isn’t curable, there are many different ways to treat this condition. They include several different classes of medications, surgery to implant brain-stimulation devices and more. Thanks to advances in treatment and care, many can live for years or even decades with this condition and can adapt to or receive treatment for the effects and symptoms.
Don’t Miss: How Effective Is Parkinson Medication
Onset Of The Classic Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
It is only in Stage 3 that the classic motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, including tremor and dyskinesias, begin to appear. This may be many years after the onset of the disease, as measured by loss of dopamine nerve cells. Motor symptoms are related to the loss of dopamine-containing neurons in a specific part of the brain called the substantia nigra. It is estimated that 50% or more of these cells must be lost before the motor symptoms begin to manifest. The loss of these dopaminergic neurons disrupts the function of the striatum, a part of the brain controlling movement. By Stage 4, cell loss has spread to the mesocortex.
Reprogramming For Compound Validation
Since their initial work focused on patients skin cells, the team needed to validate their findings in dopaminergic brain cells, which are lost in Parkinsons. This can be particularly challenging because we cant easily take a brain biopsy from a patient, says Dr Mortiboys. The team therefore used a reprogramming technique utilising the patients skin cells to generate induced neuronal progenitor cells. We used a slightly modified protocol, which doesnt take the cells all the way back to being stem cells, explains Dr Mortiboys. Our method takes them to an intermediate, which can only become brain cell types. Crucially for us, it doesnt take them back to the embryonic state. The reason for this is that age is one of the biggest risk factors for Parkinsons and many other neurodegenerative conditions. We didnt want to wipe all the age-associated changes in the cell so, with this reprogramming technique, we retained the changes that had happened throughout the cells lifetime while still producing a high percentage of dopaminergic cells.
Once these cells had been cultured, the team studied their mitochondrial function and observed that they were far more defective in the patients brain cells than in their skin cells. This showed us that it did matter which cells we were looking at it really was a problem with the mitochondria in the dopaminergic brain cells, explained Dr Mortiboys.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Infectious Or Noninfectious
Changes In Sleeping Patterns
As Parkinsons progresses, you can also develop problems with sleep patterns. These may not happen in the early stages, but can be noticeable later. You might wake up often in the middle of the night or sleep more during the day than you do at night.
Another common sleep disturbance for people with Parkinsons is rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. This is when you start acting out your dreams in your sleep, such as verbally and physically, which can get uncomfortable if someone is sharing your bed. Dr. Rundle-Gonzalez says many times a bed partner will be the one to notice sleep problems.
REM sleep behavior disorder can also happen in people who dont have Parkinsons. However, if this isnt something youve dealt with before, its likely related to your disease. There are medications your doctor can prescribe to help you sleep comfortably through the night.
What Are The Symptoms
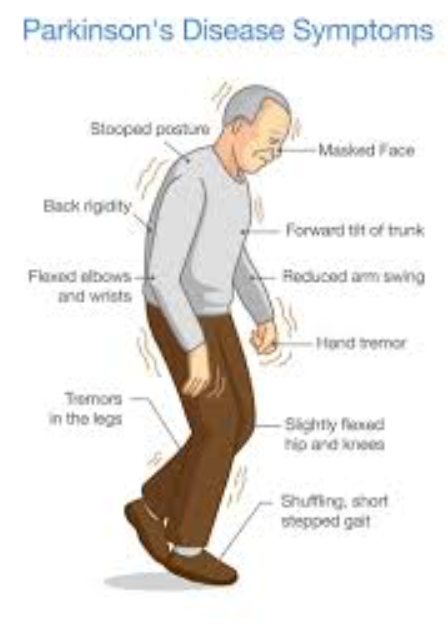
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Don’t Miss: What Are The Common Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
In 1817, Dr. James Parkinson published An Essay on the Shaking Palsy describing non-motor, as well as, motor symptoms of the illness that bears his name. Parkinsons is not just a movement disorder, explained Dr. Shprecher. Constipation, impaired sense of smell, and dream enactment can occur years before motor symptoms of Parkinsons. The latter, caused by a condition called REM sleep behavior disorder, is a very strong risk factor for both Parkinsons and dementia . This has prompted us to join a consortium of centers studying REM sleep behavior disorder.
You May Like: Does Resting Tremor Always Mean Parkinson’s
How Do Symptoms Progress
The most common symptoms of Parkinsons are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
Not everyone with Parkinsons experiences the same combination of symptoms they vary from person to person.
Also, how Parkinsons affects someone can change from day to day, and even from hour to hour. Symptoms that may be noticeable one day may not be a problem the next.
Many of the symptoms can be treated or managed with medication and therapies.
Many people with Parkinsons lead active and fulfilling lives. An important part of coping with Parkinsons is understanding how it affects you and how to work around it.
It may not always be easy to maintain a positive outlook, especially immediately after diagnosis. But we can give you help and support.
Dont Miss: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinsons
How Does Parkinsons Progress
Parkinsons is a chronic and slowly progressive disorder. This means that symptoms normally appear slowly and develop gradually over time. The stage at which symptoms appear, speed at which they progress and the severity of those symptoms will vary from person to person. The most important point is that Parkinsons affects everyone differently.
There are a wide range of symptoms, but it is highly unlikely that you will experience every possible symptom. Some of the early symptoms of Parkinsons include handwriting changes, reduced sense of smell, tiredness and constipation. As Parkinsons progresses symptoms will change over time, and new symptoms will emerge. It can take many years for symptoms to progress to a point where they cause problems.
Ultimately symptoms will begin to impact on your day-to-day life. Many symptoms are related to physical movement, so you may find that walking becomes difficult. You may also experience non-movement symptoms such as mood changes, disrupted sleep or difficulty communicating. As these symptoms worsen it may become difficult to manage all of your daily activities.
Currently, there is no known way to slow the progression of Parkinsons. However, medications and other treatments can help to effectively manage your symptoms. To ensure the effectiveness of medications, they will need to be reviewed regularly by your specialist or doctor.
Also Check: Are Adjustable Beds Good For Parkinson’s Patients
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
Associations Between Gait Changes And Change In Levodopa Dose Over Time
LEDD increased by 106 mg/day each year. Ninety-three percent of people with PD had increased LEDD compared to baseline assessment . Only one gait characteristic was related to LEDD change larger increases in step width variability related to greater increases in LEDD over time . Inclusion of the LEDD × Time interaction resulted in no significant change in step width variability , indicating that step width variability change is at least partially explained by a change in LEDD. All other gait characteristics meeting criteria 1 and 3 did not show associations between gait change and LEDD change and therefore exhibited disease-specific change that was not related to levodopa adjustments .
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Death
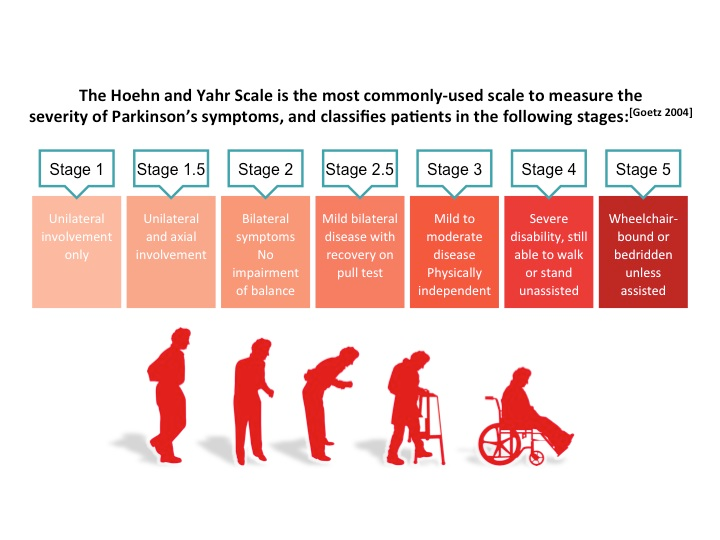
Are There Limitations To The Hoehn And Yahr Scale
One of the main limitations of the Hoehn and Yahr scale is that it focuses solely on motor symptoms. While Parkinsons primarily affects movement functions, it can have other symptoms such as sleep changes and restless leg syndrome, or cognitive changes such as mood changes, fatigue, loss of smell, and micrographia . Some patients with Parkinsons disease may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
To account for non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, there is another rating scale known as the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale . Neurologists developed the UPDRS in 1987 as a gold standard for monitoring the response to medications used to decrease the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The scale contains four parts:
- Part I: Mentation, Behavior, MoodThe first part scores intellectual impairment, thought disorder, depression, and motivation/initiative.
- Part II: Activities of Daily LivingThe second part scores activities such as hygiene, dressing, walking, tremor, and sensory complaints.
- Part III: Motor ExaminationThe third part scores speech, facial expression, tremor at rest, hand movements, and other motor functions.
- Part IV: Complications of Therapy The final part scores whether and how often the patient experiences symptoms such as painful dyskinesias, dystonia , nausea, vomiting, or sleep disturbances.
The 5 Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Getting older is underrated by most. Its a joyful experience to sit back, relax and watch the people in your life grow up, have kids of their own and flourish. Age can be a beautiful thing, even as our bodies begin to slow down. We spoke with David Shprecher, DO, movement disorders director at Banner Sun Health Research Institute about a well-known illness which afflicts as many as 2% of people older than 65, Parkinsons Disease.
You May Like: What Does Parkinson’s Medication Do
Prevalence Of Parkinsons State
Western and Southern states appear to have lower rates of Parkinsons disease, while Northeastern and many Midwestern states have higher rates . Mississippi and Montana have the lowest rates of Parkinsons, at 5.1 per 10,000. Vermont has the highest rate of Parkinsons at 9.9 per 10,000.
Exhibit 2: Prevalence of Parkinsons Disease, by geography
Parkinsons Disease Late Stage Complications
During the most advanced stage of Parkinsons typically between stages four and five a persons symptoms and medication regime become more complex.
Supporting care becomes especially important in advanced Parkinsons, with an estimated 50 to 80% of people eventually experiencing dementia and an increased number of falls.
Read Also: Does A Dat Scan Confirm Parkinson’s
Stage Five Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage five is the most advanced and is characterized by an inability to rise from a chair or get out of bed without help, they may have a tendency to fall when standing or turning, and they may freeze or stumble when walking.
Around-the-clock assistance is required at this stage to reduce the risk of falling and help the patient with all daily activities. At stage five, the patient may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
While the symptoms worsen over time, it is worth noting that some patients with PD never reach stage five. Also, the length of time to progress through the different stages varies from individual to individual. Not all the symptoms may occur in one individual either. For example, one person may have a tremor but balance remains intact. In addition, there are treatments available that can help at every stage of the disease. However, the earlier the diagnosis, and the earlier the stage at which the disease is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment is at alleviating symptoms.
