Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
What Tests Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
There currently are no tests that can definitively diagnose Parkinsons Disease. A diagnosis is based on the clinical findings of your physician in combination with your report on the symptoms you are experiencing.
In situations where an older person presents with the typical features of Parkinsons and they are responsive to dopamine replacement therapy, there is unlikely to be any benefit to further investigation or imaging.
What Tests Might I Have
Your doctor may want to start by testing your blood or doing a brain scan to rule out other conditions.
People who have Parkinsonâs disease donât make enough of a brain chemical called dopamine, which helps you move. If those first tests donât show a reason for your symptoms, your doctor may ask you to try a medication called carbidopa-levodopa, which your brain can turn into dopamine. If your symptoms get much better after you start the drug, your doctor probably will tell you that you have Parkinsonâs disease.
If the medication doesnât work for you and thereâs no other explanation for your issues, your doctor might suggest an imaging test called a DaTscan. This uses a small amount of a radioactive drug and a special scanner, called a single photon emission computed tomography scanner, to see how much dopamine is in your brain. This test can’t tell you for sure that you have Parkinson’s disease, but it can give your doctor more information to work with.
It can take a long time for some people to get a diagnosis. You may need to see your neurologist regularly so they can keep an eye on your symptoms and eventually figure out whatâs behind them.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Techniques For Visualization And Segmentation Of Brain Regions
MRI sequences for visualization of the basal ganglia and the cortex
The anatomy of the cortex is usually better depicted using conventional three-dimensional T1-weighted sequences which present high grey/white matter contrast.
Segmentation and volume calculation
Small structures such as the SN are usually outlined and segmented manually. Some cortical regions can be segmented manually, but automated techniques are preferred as exploratory tools to detect grey and white matters changes in the cortex . These techniques are designed for group studies, are automated, whole brain and rater independent. They include voxel-based, deformation-based and tensor-based morphometry, cortical thickness and sulci measurements. Voxel-based morphometry is now a standard technique, sensitive to differences in grey and white matter . VBM provides metrics such as the concentration, density and volume of grey matter. A major limitation of VBM is the nonspecificity with respect to the underlying tissue changes. Deformation-based and tensor-based morphometry provide information about global or local differences in shape, respectively . Other software allows measurements of topographic differences in thickness, surface area and curvature of the cortex .
What Are The Symptoms
Each person is affected differently by Parkinsons disease and no two people will experience exactly the same symptoms. The impact of Parkinsons disease can be unpredictable and it is common for people to have good days and bad days.
The main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are:
- tremor
- rigidity
- balance problems
- problems with posture
Other possible symptoms include difficulty initiating movement , a shuffling gait when walking, and freezing when trying to move . People might experience a loss of facial expression, speech problems , swallowing problems, bowel and bladder problems, difficulties at night and tiredness during the day. Skin can become greasy and people might experience excessive sweating. Sexual problems are common. People often experience depression and anxiety. Another common symptom is small handwriting .
Other less common symptoms can include pain and memory problems.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
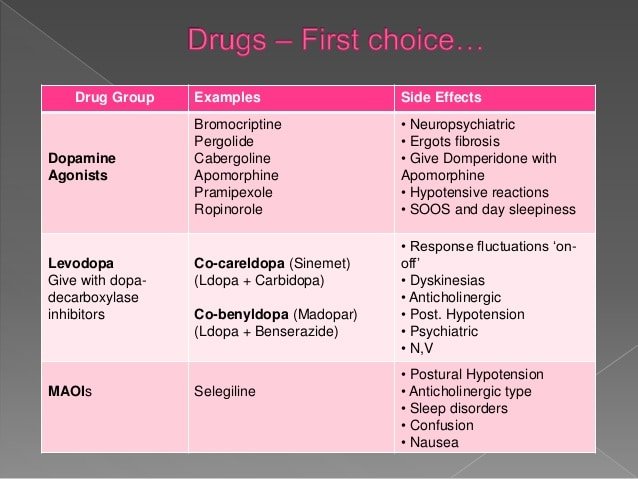
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
What Are The Limitations Of The Test
Currently, DaTscan that is in clinical use is not quantitative, which means that the test is not designed to determine how impaired the dopamine system is just whether it is or not. This means that the test is not used to tell you whether the disease has progressed over time and is not used to follow a patients disease. It also is not used currently as a clinical test to screen for the disease before motor symptoms are evident. Because of these limitations, the search continues for additional measurable indicators, known as biomarkers, to help diagnosis and manage PD.
Tips and Takeaways
- DaTscan is a test that can help in the diagnosis of PD, although in most situations a clinical exam done by a neurologist offers the same information.
- Neurologists are skilled to diagnose PD through a clinical exam. While the exam to some may seem very basic and thus a PD diagnosis subjective or questionable, neurologists are well-trained to assess and diagnose with confidence.
- DaTscan may be useful in distinguishing PD from certain conditions, but not from others, so talk with your neurologist about whether DaTscan would be useful in your specific situation.
- DaTscan is not a test used for monitoring PD progression. It can be used to help clarify a PD diagnosis, but it is not a test you would undergo multiple times during the course of your disease.
Do you have a question or issue that you would like Dr. Gilbert to explore? Suggest a Topic
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Imaging And Other Tools To Aid Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
In addition to taking a history and performing a detailed neurologic examination, physicians sometimes use brain imaging to help support a particular diagnosis. However, these studies have their limitations in the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease and are typically used only in select patients. Brain imaging is not routinely performed by neurologists or movement disorder specialists when they are considering a diagnosis, especially if the persons symptoms strongly suggest to the physician that idiopathic Parkinsons disease is the correct diagnosis.
Helping diagnose Parkinsons with DaTscan and other tests
Rather, use of imaging is most helpful when the diagnosis is uncertain, or when physicians are looking for changes in the brain that are more typical of one of several Parkinsonian syndromes and other conditions that can mimic Parkinsons. Imaging studies to evaluate Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonian syndromes include magnetic resonance imaging , which examines the structure of the brain, and DaTscan, an imaging test approved by the Food and Drug Administration to detect the dopamine function in the brain. A DaTscan may help differentiate idiopathic Parkinsons disease from certain other neurologic disorders. Most physicians offices will have access to MRI; however, DaTscan imaging may only be available at larger hospitals or medical centers.
Conditions Misdiagnosed As Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease, especially in its early stages when symptoms are mild, is not an easy disease to diagnose. The non-specific, and easily overlooked nature of the signs of Parkinsons make it difficult to spot, and unlike many illnesses, there is no one laboratory test or radiological exam that will provide a definitive diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
Patients exhibiting Parkinsons-like symptoms may undergo blood and urine tests, or CT or MRI scans to exclude other conditions, but none of these will provide a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. The best way to test for Parkinsons disease is to conduct a systemic neurological examination that includes tests to gauge a patients reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, balance, gait, and overall movement. Even so, according to information presented on The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research, up to 25 percent of Parkinsons disease diagnoses are incorrect.
So, why is there confusion about diagnosing Parkinsons disease? The simple answer is that symptoms of Parkinsons disease are not clear cut, and therefore, it is easy to mistake them for other conditions, or to classify them as parkinsonian when they are not.
Here is a brief overview of the top ten conditions mistaken for Parkinsons disease:
Beyond those top three, there are other conditions that are often confused with Parkinsons disease, including:
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
How Can Magnetic Resonance Imaging Help
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to monitor a large variety of disorders and diseases throughout the body. the images produced during an MRI scan may show tissue structures and organs in excellent detail. Functional MRI is one technique that can provide information about the body during certain activities. Both conventional and functional MRI may help show the progress of diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, and may show the response to treatments.
Functional MRI may be used to image the brain during movement. Research for Parkinson’s disease has included fMRI to monitor what regions are activated during automatic motion.4 This study of 12 patients with Parkinson’s disease practiced sequences of finger movement until they were able to be done automatically. Then, they underwent fMRI to compare their scans before and after they had learned the sequences. The results showed that the most of the same areas of the brain were active while performing the sequences before or after they became automatic. Subjects without Parkinson’s had significantly reduced activity in the brain after automaticity. This means that patients with Parkinson’s disease had more trouble performing the actions than the people without.
When Brain Mri Is Recommended To Help Diagnose Parkinsonism
Differentiating atypical parkinsonism from Parkinsons disease can be a challenge in patients presenting with symptoms in early disease stages. A diagnosis cannot be made from a brain magnetic resonance imaging scan, but brain MRI can be of added value when there is uncertainty about the clinical diagnosis.
The appropriateness of and the added diagnostic value of a brain MRI scan in the work-up of parkinsonism is described in a newly published article in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease. Lead author Frederick J.A. Meijer, MD, PhD, a neuroradiologist in the department of radiology and nuclear medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, offers advice on the scanning protocol to use, and also discusses its diagnostic value with respect to specific abnormalities that can be seen.
The authors of the article, who also include neurologists from the Radboud University Medical Center and Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior, conducted a 3-year long prospective study on the contribution of routine brain MRI to the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism.1 Based on this research, the authors refuted clinical guidelines recommending standard use of cerebral MRI for all patients presenting with parkinsonism.;
3T brain MRI including DTI tractography in a patient presenting with parkinsonism.
Also Check: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
Imaging And Differential Diagnosis
The core clinical signs of PD include resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Most patients also experience nonmotor symptoms such as cognitive and emotional changes , dysautonomia, sleep disorders, and sensory disturbances. Many experience prodromal nonmotor symptoms such as anosmia, depression, constipation, and REM sleep behavior. Clinical subtypes of the disease have been identified, including tremor dominant and postural instability gait difficulty . Atypical features may be clues that there are other etiologies that can be differentiated with imaging studies.1 Structural brain imaging is frequently ordered to investigate these cases. In addition, SPECT imaging with DaT may be useful to confirm central nervous system dopamine signaling deficiency in select cases . On DaT scans, normal radiotracer uptake in the striatum forms 2 crescent-shaped regions of activity, mirrored around the median plane. In contrast, in PD, there is asymmetrically decreased activity in the putamen, often with preserved uptake in the caudate nucleus.2,3 A DaT scan is FDA approved for differentiating essential tremor from PD, and is also frequently useful for differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from PD.
Cerebrovascular Disease
Corticobasal Degeneration
Multiple System Atrophy
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Neoplasms
Neurotoxicity
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Where To Get A Parkinsons Mri
Your two main choices if youre thinking about a Parkinsons MRI are a hospital and a free-standing imaging center. An imaging center offers you a comfortable environment with the highest quality equipment and technicians who are extremely experienced and focus exclusively on imaging. Imaging centers are also more affordable than hospitals.
Do you need a Parkinsons MRI? Are you a doctor who wants to schedule a Parkinsons MRI for a patient? Then, contact us today. At American Health Imaging, we focus on imaging, and we would love to help you.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Sleep Attacks
Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Conventional Mri Sequences
Due to its high spatial and contrast resolution, cMRI with assessment of T1-, T2-, proton density-weighted as well as T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences offers in vivo visualization of regional, disease-specific tissue alterations and certain cMRI patterns that are typical for APDs. Atrophy patterns are better demonstrated by T1-weighted images, displaying anatomical details and providing an excellent grey and white matter contrast. More recently, advanced T1 sequences were developed to improve detection of nigral changes in PD patients. These include a variety of inversion recovery images and a recently developed neuromelanin-sensitive T1-weighted sequence . On NM-MRI, neuromelanin acts as a paramagnetic agent because of its iron-binding potential. On these images, neuromelanin-containing tissues appear as loci of high signal intensity allowing measurements of volume and concentration of neuromelanin in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus . Moreover, it seems that visual inspection of NM-MRI sequences by experienced neuroradiologists provides results comparable to quantitative analyses in the detection of SN changes in early stage PD .
Datscan: A Test To Help In The Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
In 2011, the Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging test to help diagnose PD. In this test, a radioactive tracer, Ioflupane 123I, also known as DaTscan, is injected into the blood, where it circulates around the body and makes its way into the brain. It attaches itself to the dopamine transporter, a molecule found on dopamine neurons. Several hours after the tracer has been injected, special imaging equipment scans the head to detect the presence of DaTscan.
People with PD will typically have a smaller signal in a part of the brain called the striatum, where the ends of the dopamine neurons are meant to be. Here is a normal scan on the left, which would indicate a healthy dopamine system, next to an abnormal scan on the right, which would indicate an unhealthy dopamine system.
It is important to note that conventional MRI imaging will appear normal in PD and is therefore not helpful in confirming the diagnosis. Other atypical parkinsonian conditions, such as vascular parkinsonism however, can have abnormalities on MRI, so the test may be done to rule out other diagnoses.
Read Also: Average Life Expectancy For Parkinson Disease
Differences Between Parkinsons Disease And Atypical Parkinsonism
The symptoms of Parkinsons disease and atypical parkinsonism overlap, and in a clinical setting, it can be hard to tell if a patient has one or the other. Atypical parkinsonism is diseases that present some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons Disease but do not respond well to drug treatment. With an MRI, your doctor can help to make the diagnosis more accurate, which is essential for quality treatment. Additionally, an MRI can also help your medical team to determine if you have a certain type of atypical parkinsonism. This can help to create a prognosis and guide your treatment options.
Tractography And Anatomical Connectivity
Tractography is a technique based on the anisotropy of water diffusion that allows reconstructing fibre tracts in the brain. Tracks are reconstructed by assuming that the main direction of diffusion in a voxel indicates the local orientation of white matter fibres . Using tractography, diffusion measures and connectivity measures can be calculated within the specific fibre tracks. Tractography has also been successfully used to parcel out the SN and the basal ganglia into specific territories .
In PD, reduced connectivity was observed between the SN and ipsilateral putamen and thalamus as well as in the sensorimotor circuit of the basal ganglia . Automated diffusion-based parcellation of SN subregions showed that the SNr and SNc in PD patients showed a general atrophy . Tractography is therefore used to investigate changes in anatomical connectivity in PD patients .
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Genetic Link
