Epidemiology And Natural History Of Dlb And Pdd
Approximately 12% of those aged above 65 years are diagnosed with DLB worldwide , affecting approximately 5% of all dementia cases in those over the age of 75 . Its incidence is 0.71.4 new cases/100,000 person-years or 3.5/100,000 person-years . For PDD, the cumulative prevalence is of 75% of PD patients surviving more than 10 years , 83% after 20 years , and up to 95% by age 90 years , with an overall prevalence of 31.1% and incidence rates from 0.43 to 1.13/100,000 person-years , indicating that, annually, approximately 10% of a PD population will develop dementia . The data concerning age at disease or dementia onset are highly variable. Whereas in the Olmsted County study DLB patients were younger at symptom onset than those with PDD and had more hallucinations and cognitive fluctuations, others have reported younger age at disease onset in PDD , or no essential differences between disorders .
What Does Lewy Body Dementia Look Like
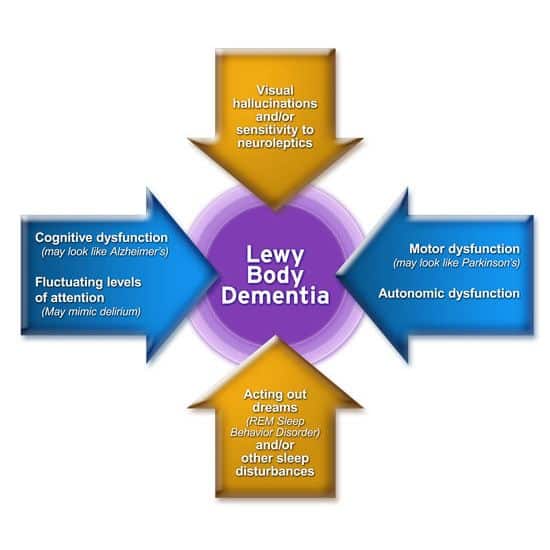
Lewy body dementia affects a persons ability to think and process information and it can negatively impact memory and alter personality. Though it shares aspects of other forms of dementia, there are distinct hallmarks of LBD. Lewy body dementia symptoms include:
- Fluctuating attention/alertness: These shifts can last hours or go on for days. The person may stare into space, appear lethargic or drowsy, and have hard-to-understand speech, appearing a lot like delirium. At other times, the person may have much more clarity of thought.
- Visual hallucinations: Often, these are very detailed hallucinations and visions of people or animals, and they can recur.
- Movement disorders: Parkinsons-like movement issues, such as muscle rigidity, tremors, falls, or a shuffling gait or way of walking, may occur.
Pd Dementia And Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone and try to:
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Look into medical alert systems. These systems can be critical in the event of a fall or if your loved one wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smartwatches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider bringing it up with their doctor and taking additional safety precautions.
Read Also: Why Do People Get Parkinson’s
Causes Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is caused by clumps of protein forming inside brain cells. These abnormal deposits are called Lewy bodies.
These deposits are also found in people with Parkinsons disease, and they build up in areas of the brain responsible for functions such as thinking, visual perception and muscle movement.
Its not clear why the deposits develop and how exactly they damage the brain. Its thought that part of the problem is the proteins affecting the brains normal functions by interfering with signals sent between brain cells.
Dementia with Lewy bodies usually occurs in people with no family history of the condition, although there have been very rare cases that seem to run in families.
Dont Miss: Foods That Prevent Parkinsons Disease
What Causes Dementia With Lewy Bodies
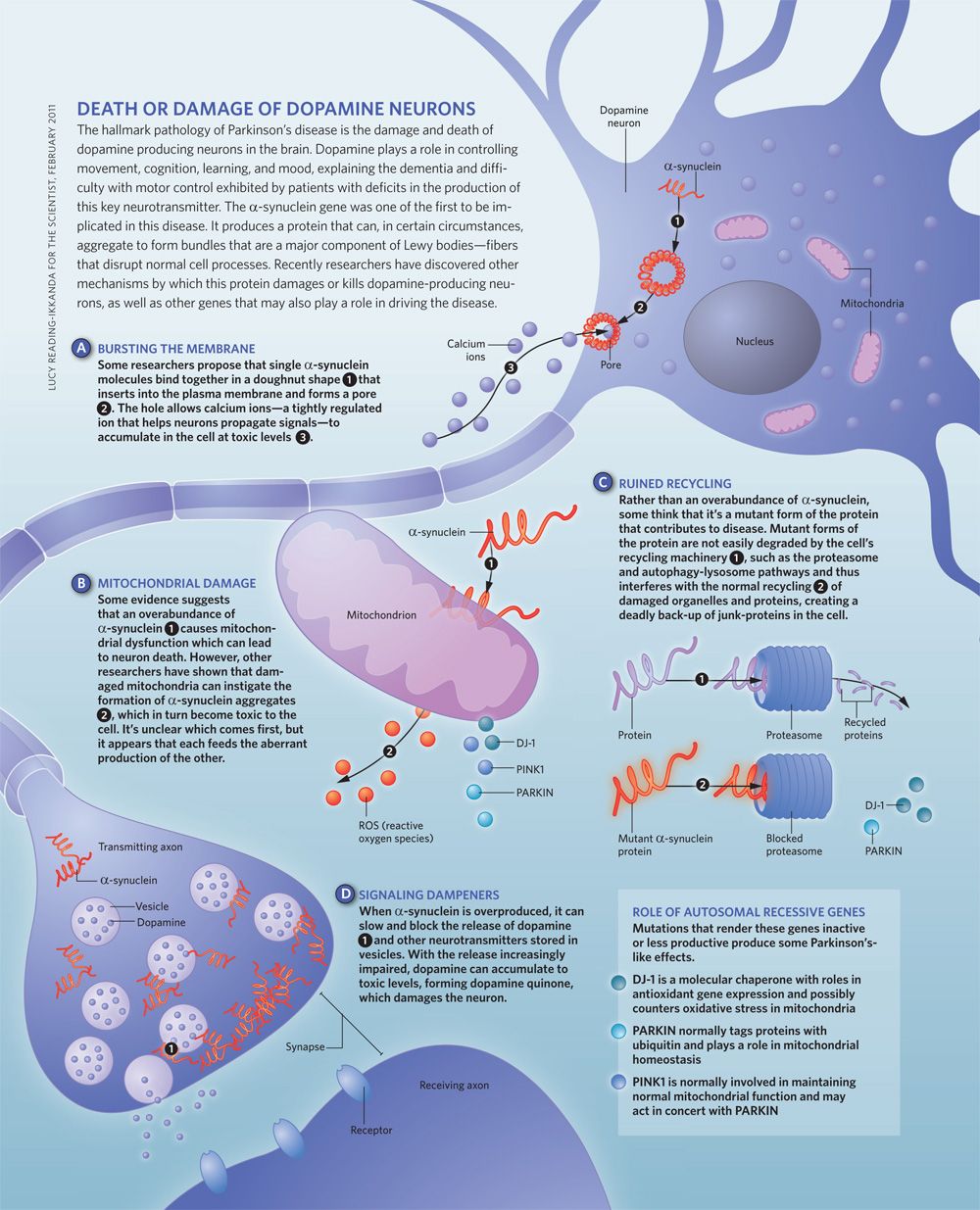
It is not yet known why Lewy bodies develop in the brain or exactly how they cause dementia. But we do know that Lewy body disease:
- can cause different symptoms depending on what parts of the brain have the biggest build-up of faulty proteins
- reduces the levels of important chemicals needed to send messages around the brain
- breaks the connections between nerve cells, eventually causing these cells to stop working
- usually develops over a period of many years typically when a person is approaching old age. Lewy bodies can be developing in the brain for a long time before any symptoms show.
Having Lewy body disease doesnt mean that a persons dementia is only caused by the build-up of Lewy bodies in their brain.
Many people with DLB also have a build-up of other proteins that cause Alzheimers disease. This is common in people over about 80 years old. For people with both DLB and Alzheimers, dementia symptoms are often more severe and progress more quickly.
Also Check: What Causes Parkinson’s Syndrome
Mild Cognitive Impairment And Dementia In Parkinson Disease
Contrary to Dr James Parkinsons introduction to An Essay on the Shaking Palsy,18 the intellect is not uninjured in PD. Although patients with PD first come to medical attention because of characteristic motor signs, including rest tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and gait abnormality, specific cognitive impairments in executive function, visual-spatial skill, and even memory function in patients with PD are common and have been known for more than 40 years.19 PD hastens deterioration of these cognitive abilities over time, with the incidence and prevalence of cognitive impairments increasing with duration and severity of illness.20,21 In this sense, PD can be considered a risk factor for dementia. Formal criteria have been developed for mild cognitive impairment in PD .22,23 These criteria attempt to account for the contribution of motor impairment to functional decline and are now being validated.
How Is Lewy Body Dementia Diagnosed
Diagnosing Lewy body dementia can be challenging. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with symptoms found in other brain or psychiatric conditions.
There are no medical tests that can diagnose Lewy body dementia with 100% accuracy. A diagnosis may require a group of specialists, including:
- Neuropsychologists.
Together, they can make the diagnosis of probable LBD based on the combined results of tests and symptoms.
Along with a history of progressive cognitive decline that interferes with daily activities, a diagnosis of LBD is considered probable if two of the following four core features are present and is considered possible if only one is present:
- Fluctuations in cognition and behavior.
- Recurrent visual hallucinations.
- Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder.
Some people with Parkinsons disease who develop cognitive symptoms less than a year after the onset of movement problems may be diagnosed with Lewy body dementia.
Healthcare providers use the following strategies to help diagnose LBD and to rule out conditions that cause similar symptoms:
Recommended Reading: Does John Lithgow Have Parkinson’s
What Is Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies inhibits everyday activities by causing memory and thinking problems, specifically targeting problem-solving, planning, and visual learning abilities. In contrast to PDD, dementia usually always appears first or around the same time as parkinsonism) in patients with DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons come as the disease progresses.
The main difference between Parkinsons disease and dementia with Lewy bodies is the timeline of the symptom onset. With Parkinsons, onset of symptoms usually happens gradually over years of having the illness. However, with Lewy body dementia, the onset of symptoms is much more aggressive, rapidly affecting patients within a year of diagnosis.
You May Like: Aqua Hydration Formula For Parkinsons
The Difference Between Parkinson’s Disease And Lewy Body Dementia
One of the most confusing concepts to explain in the clinic is the difference between Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease Dementia and Lewy Body Dementia. Ultimately people with Parkinson’s can look very similar with motor and non-motor problems. This is particularly tricky when PwP first present but the easiest way to consider Lewy Body Dementia is like having a very aggressive progression of Parkinson’s where patients are dementing in the first year of their condition whereas this process is much slower when patients develop Parkinson’s Disease Dementia. Indeed, clinically Lewy Body Dementia patients look like they have a cross between Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, which is actually close to what is seen down the microscope when researchers study the brain. Understanding the differences between Parkinson’s Disease and Lewy Body Dementia is not only difficult for patients and their families but has led some professional groups to try and lump all of these patients together under one umbrella, which probably does little to help individual families appreciate what the future holds.
Hopefully this video will help you to gain a more complete understanding of the differences between Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease Dementia and Lewy Body Dementia.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Foundation Center Of Excellence
What Is The Prognosis Of Lewy Body Dementia
The prognosis of LBD is generally fair to poor because it gets worse over time.
People with LBD can die from several different complications, such as:
- Swallowing issues.
- Depression leading to suicide
- Reactions to first-generation antipsychotic medications used to treat and manage symptoms of many psychiatric disorders, such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with LBD, its important to learn about the condition and all the medications and therapies that can help you be as comfortable and safe as possible.
How Can We Manage Hallucinations
It may not be necessary to treat all hallucinations of a person with DLB. Hallucinations are often harmless, and it is okay to allow them to happen, as long as they are not disruptive or upsetting to the person or his/her surroundings. Sometimes, recognizing the hallucination and then switching the topic might be an efficient way of handling frustrations that occur because of a hallucination. If hallucinations need medical treatment, your provider may be able to discuss and suggest some options. However, most medications used to treat hallucinations may make movement symptoms worse.
Don’t Miss: What Medications Should Parkinson’s Patients Avoid
Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons Disease
A person with Parkinsons disease may develop dementia and have problems with reasoning and thinking. Lewy bodies are a feature of several brain disorders, including Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease, and they may cause rigid muscles and problems with movement and posture.
Research suggests that the similarity of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia may be indicative of a shared link to how the brain processes alpha-synuclein.
It is not possible to test for the presence of Lewy bodies, so researchers must try to determine their effects by carrying out postmortem studies.
There is currently no cure for dementia. However, medication can alleviate the symptoms, while a team of medical professionals and therapists may help a person develop strategies to manage their daily activities.
Lewy Body Dementia Vs Alzheimer’s Disease
Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are similar but not the same. This starts with how the features of dementia differ for each disorder:
- Lewy body dementia is a form of dementia with characteristics of Parkinson’s disease that affects executive function , speed of thinking, memory, movement, and moods. LBD can cause visual hallucinations, problems with attention and alertness, and movement problems such as tremors and stiffness.
- Alzheimer’s disease is the more common form of dementia that primarily affects language, behavior, and memory. It mainly manifests with profound memory loss, such as trouble recalling events, recognizing people, naming objects, or learning new information.
LBD and Alzheimer’s disease can appear similar in the early stages, and it is not uncommon for someone with LBD to be mistakenly diagnosed with Alzheimer’s at first.
The underlying causes of Alzheimer’s and LBD can and often do overlap. As a result, a person with LBD might experience Alzheimer-type changes in their brain, resulting in shared characteristics and symptoms referred to as mixed dementia.
The main differences between LBD and Alzheimer’s can be summarized in the following chart:
| Survival time is between three and five years after symptoms appear. | Survival time ranges from four to 10 years after symptoms appear. |
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Foot Cramps
Some Examples Of Delusions And Their Impact In Pd Include:
- Belief: Your partner is being unfaithful.
- Behavior: Paranoia, agitation, suspiciousness, aggression
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder
REM sleep behavior disorder refers to a syndrome in which the normal paralysis of REM sleep is impaired. As a result, patients bed partners may report that they act out their dreams with behaviors such as kicking, punching, and yelling. The observation that most REM sleep behavior disorder behaviors are violent suggests that the impairment of paralysis may be relative, with a reduction in threshold that is overcome by only the most emotionally salient dreams, perhaps on the basis of catecholamine or amygdala drive.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Body Temperature Regulation
Differences Between Pdd And Dlb
So, how are PDD and DLB different from each other? That depends on whom you ask. Some clinicians feel that these two conditions are simply different versions of the same disorder. In fact, some professionals use the terms interchangeably. Yet, according to currently agreed-upon diagnostic guidelines, there are some differences.
Treatment Of Hallucinations Delusions And Agitation
Visual hallucinations, delusions, and other productive-psychotic symptoms may occur early on in the disease course in dementia with Lewy bodies. In Parkinsons disease, these often develop only during the course of the disease, and in a scenario where new hallucinations or psychoses occur for the first time after a change in medication, the most recent change in medication should be reversed . If this does not yield the desired success or if hallucinations occur without prior change of medication, the medication for Parkinsons disease should be changed according to the treatment algorithm provided in the guidelines .
Algorithm for the treatment of psychosis PDD, Parkinsons disease dementia DLB, dementia with Lewy bodies
If this does not improve the productive-psychotic symptoms to a satisfactory degree, the use of antipsychotics may be considered. This is particularly the case when a reduction in the Parkinson medication is followed by a substantial deterioration in motor functioning, so that a minimum dose of levodopa is a definite requirement.
It is in particular the productive-psychotic symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia that place a heavy burden on relatives and carers they are also responsible for a multitude of admissions to residential care homes, so that medication treatment is absolutely essential.
In acute situations, patients may be given a short course of clomethiazole and lorazepam .
Don’t Miss: Photobiomodulation Therapy For Parkinson’s
What Is Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
Both conditions relate to decline in cognitive thinking and reasoning, loss of brain cells and abnormal alpha-synuclein protein clusters termed as Lewy bodies.
Both disorders have very similar symptoms, but the symptoms usually happen in a different order dependant on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Major similarities between Parkinsons and Lewy Body Dementia include
- Both disorders affect approximately one million people in the United States
- They both cause an impact to the brain nerve cells
- There is no cure for both of these conditions
- Symptoms that impact the body include stiffness, weakness and slowness in movements
- Symptoms that affect brain include: memory loss, attention span and impaired executive functioning
The protein alpha-synuclein unusually builds up in the brain in aggregates, or clumps, called Lewy bodies. The location of those clumps makes a difference.
Also, people who have Lewy bodies dementia tend to exhibit greater variation in brain function ability than those with PD dementia.
Fluctuations Of Attention And Arousal
Attention and alertness may fluctuate, leading to episodes of staring and perturbed flow of ideas, or to frequent daytime drowsiness and naps during the day. These episodes can be hard to quantify and need to be disentangled from toxic metabolic processes such as medication side effects or infections. A recent fluctuations scale vetted for this purpose is the Dementia Cognitive Fluctuation Scale,13 which aggregates prior scales. The fluctuations screen requires a positive response to at least three of the following: Does the patients inability to organize thoughts in a coherent way vary significantly over the course of the day? Does the patient spend more than 1 hour sleeping during the waking day? Is the patient drowsy and lethargic for more than 1 hour during the day, despite getting the usual amount of sleep the night before? Is the patient difficult to arouse on a usual day? This approach had a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 76% in differentiating clinical syndromes of DLB and PDD from AD and vascular dementia, but has yet to be neuropathologically validated.
Also Check: What Brain Structure Is Affected By Parkinson’s
Building A Lewy Body Dementia Care Team
After receiving a diagnosis, a person with LBD may benefit from seeing a neurologist who specializes in dementia and/or movement disorders. Your primary doctor can work with other professionals to follow your treatment plan. Depending on an individuals particular symptoms, physical, speech, and occupational therapists, as well as mental health and palliative care specialists, can be helpful.
Support groups are another valuable resource for people with LBD and their caregivers. Sharing experiences and tips with others in the same situation can help people find practical solutions to day-to-day challenges and get emotional and social support.
Causes Of Lewy Body Dementia Vs Alzheimer’s
![Lewy Body Dementia Symptoms [Infographic]](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/lewy-body-dementia-symptoms-infographic.jpeg)
Lewy body dementia is caused by the abnormal buildup of proteins, called Lewy bodies, in the brain. When clumps of these proteins accumulate, nerves in the brain start to lose their function and eventually die. The damage in the brain is widespread and affects many domains of thinking and functioning.
Alzheimer’s is caused by the abnormal buildup of proteins called amyloid that leads to the formation of plaques in the brain. The abnormal twisting of another protein called tau causes neurofibrillary tangles that block signals between nerve cells. Over time, the progressive damage will kill the cells.
Don’t Miss: Best Mushroom For Parkinson’s Disease
