Five Facts You May Not Know About Brain Tumors
by Laura Hegwer, Rush University Medical Center
Brain tumors scare most people, but there are still reasons to be hopeful if you learn you have an abnormal growth in your braineven if it’s cancer, says Sean Grimm, MD, chief of the Section of Medical Neuro-Oncology at RUSH.
Here, Grimm shares five facts about brain tumors you may not knowand discusses why doctors are encouraged by advances that may help many people with brain tumors live longer, fuller lives.
Fact: Headaches are not always the main symptom of a brain tumor
Daily headaches that get worse over time can be a sign of a brain tumor, but “it’s rare that headaches are the only symptom,” Grimm says. Other warning signs include:
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Difficulty walking
- Trouble with speech, vision or hearing
People with brain tumors may have symptoms like seizures or confusion without having headaches at all. If you’re concerned about any symptoms, Grimm recommends making an appointment with your primary care doctor or a general neurologist.
Fact: Cell phones aren’t to blame for brain tumors, based on current evidence
Incidencethe number of cases diagnosed each yearof malignant brain tumors has remained fairly stable in recent years, even dipping a bit in 2019. Although some have speculated that cell phones could cause brain tumors, research suggests that’s not likely.
Fact: More people are surviving brain tumors today, compared with just a few years ago
Citation
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
The primary goal of surgery for Parkinson’s disease is to reduce the motor symptoms and tremors of the disease, as well as the side effects that can come from some of the medications used to treat it, such as dyskinesia or motor fluctuations . Another goal of surgery is to increase the number of hours of on time each day and in many cases, to reduce the amount of medication needed each day to maintain the best condition.
Deep brain stimulation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat neurological symptoms of Parkinsons disease, including tremors, rigidity, and movement control.
Dr. Kaplitt and Dr. Stieg talked about DBS for Parkinson’s disease on an episode of This Is Your Brain With Dr. Phil Stieg. Listen to that podcast episode below:
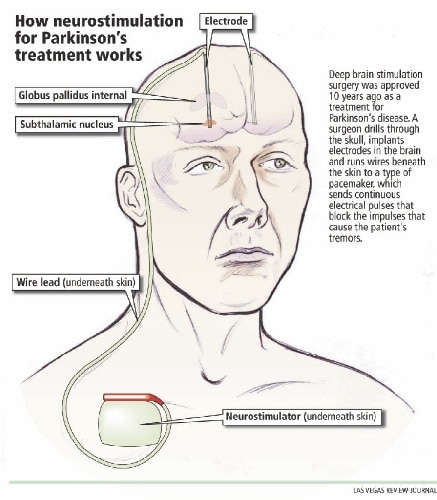
The procedure involves placing battery-operated neurotransmitters under the collarbone. The devices are connected to a wire under the skin that runs up the length of the neck into the scalp, where it is placed into the brain through a small hole in the skull. The tip of this wire sends the electrical impulses generated by the neurotransmitter into the precise spot in the brain that regulates activity of the key circuits in Parkinsons disease.
The procedure can be done in one or two stages, which can be performed in a single day or on consecutive days.
Hear from patients who have been treated with focused ultrasound for essential tremor:
How Effective Is Brain Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease surgery known as deep brain stimulation is one of the possible treatment options for Parkinson’s disease. Deep brain stimulation was initially approved to ease tremors in PD patients in 1997, but it was later used to treat patients in the advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease. The surgery is also offered to patients in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease who do not respond to medication. Learn more about the effectiveness of Parkinson’s disease surgery and what it involves.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Treatment For Parkinson’s
Am I A Good Candidate For Dbs
To determine if you are a good candidate, you:
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Amelia Heston, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Life After Dbs Surgery
Once the neurotransmitter has been programmed, you are given a handheld controller to make adjustments.
With the controller, you can turn the simulator on or off, select the signal strength, and move across different program types.
If your DBS neurotransmitter has a rechargeable battery, then it will take about two hours for the device to recharge completely.
Make sure to carry your Implanted Device Identification card if you are traveling by air, as Airport Security will detect the device.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Big Movement Exercises
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation And How Does It Work
DBS is a therapy that we have for various neurological conditions, said Dr. Sheth. It’s a system that you can think of like a pacemaker. But rather than being a pacemaker for the heart, it’s for the brain.
Dr. Sheth describes the brain as having many circuits that govern everything we do, including how we move.
If the movement circuit is not working properly, we may have a movement disorder like Parkinson’s, he said. If we can identify the circuit within the brain that is not working properly, we can use this device to reset the rhythms in the brain and restore the balance so that our movements can be better controlled or without a tremor.
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinson’s disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Etiology Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
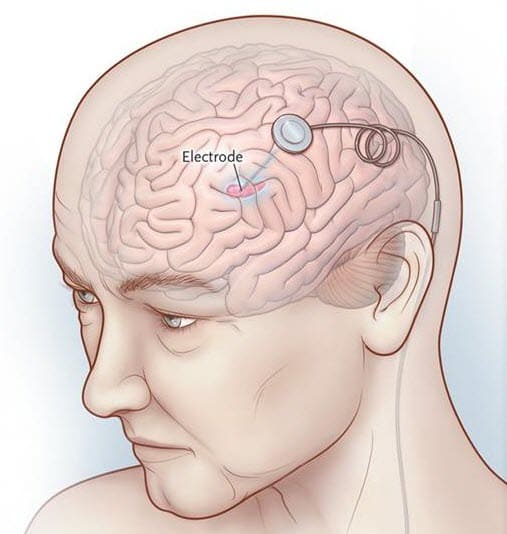
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease: Deep Brain Stimulation And Lesioning
When we refer to surgery in Parkinsons disease it usually refers to Deep Brain Stimulation .Deep Brain Stimulation involves placing a wire with electrodes at its tip into one of three target sites in the brain the thalamus, the globus pallidus or the subthalamic nucleus. A few days after they are connected to an implantable pulse generator . This small unit is inserted under the skin on the chest wall. When the IPG is turned on the electric pulses stimulate the target area and produce a change in the Parkinsonian symptoms..
Before DBS was introduced in the 1980s the only operation available for Parkinsons disease involved selectively damaging certain cells in the thalamus and the gobus pallidus called lesioning. While this sometimes relieved symptoms the damage was irreversible and the operation was risky. With DBS the insertion of the electrodes can be checked to confirm that they have been sited correctly and there are further opportunities for fine tuning through the IPG. The technical advances which have made this operation possible have been the development of CT and MRI scanning which allow the surgeon to locate the target site with great accuracy. While it is not essential, it is usual for the electrodes to be inserted with the patient awake so that they can provide evidence that the target has been reached.
Last reviewed May 2017.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Disease And Essential Tremor
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
Who Is Suitable For Deep Brain Stimulation
Not everyone will be suitable for deep brain stimulation, and it wont work for everyone who has the operation. If you have responded well to tablet-based medication you may be a suitable candidate. Discussing the options with your neurologist or a DBS specialist neurologist will help identify your suitability.
About The Dbs Procedure
Deep brain stimulation therapy uses a small, pacemaker-like device to send electrical signals to an area in the brain that helps fine-tune and control movement. The electrical brain stimulation may, in some cases, block some of the brain messages that cause involuntary and disabling motor symptoms. The device is implanted under the skin in the chest. Small, thin wires connect the device to electrodes placed in your skull, allowing the signals to reach the areas of your brain that are causing your symptoms.
After the DBS system is implanted, your expert DBS programmer adjusts the settings to personalize your DBS therapy. You may need several programming sessions to find your optimal settings. The settings can be adjusted in the future if your symptoms change. Most people do not feel the stimulation, though some may sense a brief tingling when the stimulation is first activated.
A few weeks after the procedure, most patients can resume normal daily activities. Your DBS clinician will let you know when you can try activities that had been difficult for you prior to deep brain stimulation surgery.
DBS surgery recovery and healing
Patients are usually able to return home the day after DBS surgery. Healing can take several weeks, and we will give you medication to manage any pain. Typically, we will not activate your device until your first programming session.
DBS programming sessions
Risks of DBS surgery
You May Like: Coconut Oil And Parkinson Disease
Being Prepared & Anticipating Problems
Because of the concerns that we will discuss below, it is prudent to have your neurologist speak to your surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the surgery so he/she can discuss the potential issues that may arise during and after the surgery. It is also very useful to have your neurologist write a letter with all the necessary information so it can be dispersed to other members of the medical team who will be responsible for your day-to-day care after the surgery.
Depending on the type of surgery, there may be more than one option for anesthesia. General anesthesia may not be the only option, and a more localized form of anesthesia may be possible. Local anesthesia typically causes fewer side effects. Discuss what anesthesia options you have with the surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the surgery.
In addition, if the surgery requires you to stay in the hospital overnight, consider having a family member or friend stay with you. This person can provide a calming presence, helping to prevent agitation or distress. He or she can keep an eye on whether you are taking your own medications correctly and what additional medications you are bring given.
What Are The Next Steps Following A Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
Once you have a diagnosis of Parkinsons, your doctor can begin developing a treatment plan. Parkinsons treatments aim to minimize symptoms and slow down progression.
Treatment plans will take into account such factors as symptoms, overall health, and response to treatment. Although theres no cure for Parkinsons, treatment can improve your quality of life.
Common treatments for Parkinsons include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength and balance.
- Speech therapy: Speech therapy can help reduce communication difficulties.
- Lifestyle changes: People with Parkinsons often benefit from adding exercise to their daily lives.
- Medication: There are several medications approved to treat the symptoms of Parkinsons. You might need to change medications as Parkinsons progresses.
- Deep brain stimulation:Deep brain stimulation is a surgical procedure. Surgeons place electrodes in your brain that are connected to a generator placed in your chest. These electrodes can help reduce the symptoms of Parkinsons.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons And Stiff Neck
Recommended Reading: How To Check If You Have Parkinson Disease
Living With A Stimulator
Once the DBS has been programmed, you are sent home with instructions for adjusting your own stimulation. The handheld controller allows you turn the stimulator on and off, select programs, and adjust the strength of the stimulation. Most patients keep their DBS system turned on 24 hours day and night. Some patients with essential tremor can use it during the day and turn off the system before bedtime. Your doctor may alter the settings on follow-up visits if necessary.
If your DBS has a rechargeable battery, you will need to use a charging unit. On average charging time is 1 to 2 hours per week. You will have a choice of either a primary cell battery or a rechargeable unit and you should discuss this with you surgeon prior to surgery.
Just like a cardiac pacemaker, other devices such as cellular phones, pagers, microwaves, security doors, and anti theft sensors will not affect your stimulator. Be sure to carry your Implanted Device Identification card when flying, since the device is detected at airport security gates.
Who Is A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is more than just a surgical procedure. It involves a series of evaluations, procedures, and consultations before and after the actual operation, so people interested in being treated with DBS should be prepared to commit time to the process.
For example, those who do not live close to a medical center that offers DBS surgery may need to spend significant time traveling back and forth to appointments.
The procedure, as well as the pre-operative evaluation and post-operative follow-up, can be expensive depending on the persons insurance coverage. DBS surgery is an FDA-approved treatment for Parkinsons disease, and Medicare and most private insurers cover the procedure, but the extent of coverage will depend on each persons individual policy.
Prospective patients should have realistic expectations about DBS results. Although DBS can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease and greatly improve quality of life in properly selected patients, it is not likely to return anyone to perfect health.
Also Check: How Do You Get Tested For Parkinson’s Disease
There Are No Laboratory Tests To Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
Currently there are no laboratory tests that can diagnose Parkinsons disease. This can make it difficult to accurately diagnose because PD resembles other movement disorders. In order to diagnose PD, a physician will take a complete medical history and perform a neurological exam. Additional testing may be done simply to rule out other neurological conditions that may resemble Parkinsons.
Read Also: The 4 Classic Features Of Parkinsons Disease Are
Risks Of Deep Brain Stimulation
As with any medical procedure, there are genuine risks of getting the DBS procedure done.
General risks are seizures, infections, blood clots, excessive bleeding, and anesthesia reactions.
There is a risk that DBS may lead to speech and balance-related afflictions from Parkinsons to worsen.
DBS can also worsen depression in some people with Parkinsons.
Recommended Reading: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Dont Miss: How To Tell Difference Between Parkinsons And Essential Tremor
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurological condition that mainly affects your bodys movement. The disease is progressive and has symptoms like tremors, slow movement, stiffness, and speech difficulty. Most people develop the disease around or after the age of 60. But 10% to 20% of people with Parkinsons develop it at age 50 or younger. Men are more likely to develop this condition than women.
Parkinsons symptoms are caused by a decrease in the cells in your brain that produce dopamine. Its the lower dopamine levels that cause the movement-based symptoms of this disease.
Experts are not 100% sure what exactly causes this disease. They believe most cases of Parkinsons dont have one single cause but may have multiple components interacting with each other.
Genetics. Between 10% and 15% of all Parkinsons cases are caused or influenced by at least 1 of 12 genetic mutations that can be passed down from a parent to a child.
Some of these gene mutations are more common in specific cultural groups. For example, Ashkenazi Jews and North African Berbers are more likely to have the G2019S mutation on the LRRK2 gene, which can cause Parkinsons. However, even having a genetic tendency for Parkinsons doesnt mean you will get it. Studies show that only between 25% and 35% of people with the G2019S mutation will get Parkinsons disease.
Head injury. People who have had a traumatic brain injury have a higher risk of developing Parkinsons, but experts dont know exactly why.
Also Check: What Is Rigidity In Parkinson’s Disease
