Differences Between Pdd And Dlb
So, how are PDD and DLB different from each other? That depends on whom you ask. Some clinicians feel that these two conditions are simply different versions of the same disorder. In fact, some professionals use the terms interchangeably. Yet, according to currently agreed-upon diagnostic guidelines, there are some differences.
Managing The Effects Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
A person with dementia with Lewy bodies might:
- have recurring visual hallucinations – see things that are not there
- experience disturbed sleep– known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep disorder, in which people are restless and can experience intense dreams/nightmares
- experience sudden changes and fluctuations in alertness – people may stare blankly into space for periods of time, seem drowsy and lethargic and spend a lot of time sleeping
- have slowed movement, difficulty walking, shuffling or appear rigid
- experience tremors – usually in the hands whilst at rest
- have problems with balance and be prone to falls
- bladder and bowel problems
- difficulties with swallowing
Memory is often less affected than with other types of dementia but people may be at more risk of mood and behaviour changes such as apathy, anxiety, depression, delusions and paranoia. One type of delusion, known as Capgras syndrome, in which the person believes that a friend or relation has been replaced by an imposter can be particularly difficult for families. Other symptoms may include changes in blood pressure, body temperature and impaired sense of smell.
Which Medicines Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Guidelines released by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network recommend starting with a dopamine agonist, levodopa with a dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor or a monoamine-oxidase inhibitor. Other medicines are also sometimes used, usually in addition to one of these three main types of medication.
The Relationship Between Parkinsons Disease And Sleep
It’s unclear whether poor sleep causes parkinsonian symptoms to worsen or whether worsening parkinsonian symptoms cause poor sleep. In many cases it’s likely a case of bidirectionality, with each one exacerbating the other.
Fragmented sleep and sleep deprivation appear to leave the brain more vulnerable to oxidative stress, which has been tied to the development of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s disease is not usually diagnosed until individuals have developed sufficient motor symptoms, by which time a significant portion of brain cells have already been damaged. If poor sleep quality or having sleep disorders foreshadows the development of parkinsonian symptoms, these could be useful in early diagnosis of the disease.
More research is needed to clarify the multifaceted relationship between Parkinson’s disease and sleep. A better understanding of this connection may offer medical experts the unique opportunity to screen at-risk individuals and perhaps delay the onset of the disease.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Early stage
Advanced stage
Read Messages From Our Community Related To Mental Health In Advanced Pd:
“My Dad fights aggressively when his aides try to get him to do something he doesn’t want to. He gets so angry and is so strong it can take many people to restrain him.”
“My Mom lives at home, but constantly thinks that she is somewhere else and wants to go home. She becomes irritated and angry with the family because she says that we are holding her hostage.”
“My husband is verbally abusive towards me. This is an entirely new aspect to his personality. He was always very loving. Now he is aggressive.”
“My wife is severely depressed. Although she can get out of bed with help, she would rather stay in bed and do nothing. She also doesn’t seem to mind that she is doing nothing all day.”
“Often, my brother doesn’t recognize me when I visit. Last week, I saw my brother in the morning, but when I spoke with him on the phone later on in the evening, he mentioned that he had not seen me in a long while.”
These quotes highlight a set of very problematic issues in advanced PD which include cognitive decline/dementia, , , anxiety, , and behavior problems . One person often has a mixture of these symptoms and the symptoms can be inter-related.
One Of The Most Difficult Neurological Disorder Symptoms Of Parkinsons
How Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia Different From Alzheimers Disease
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Parkinson’s Disease
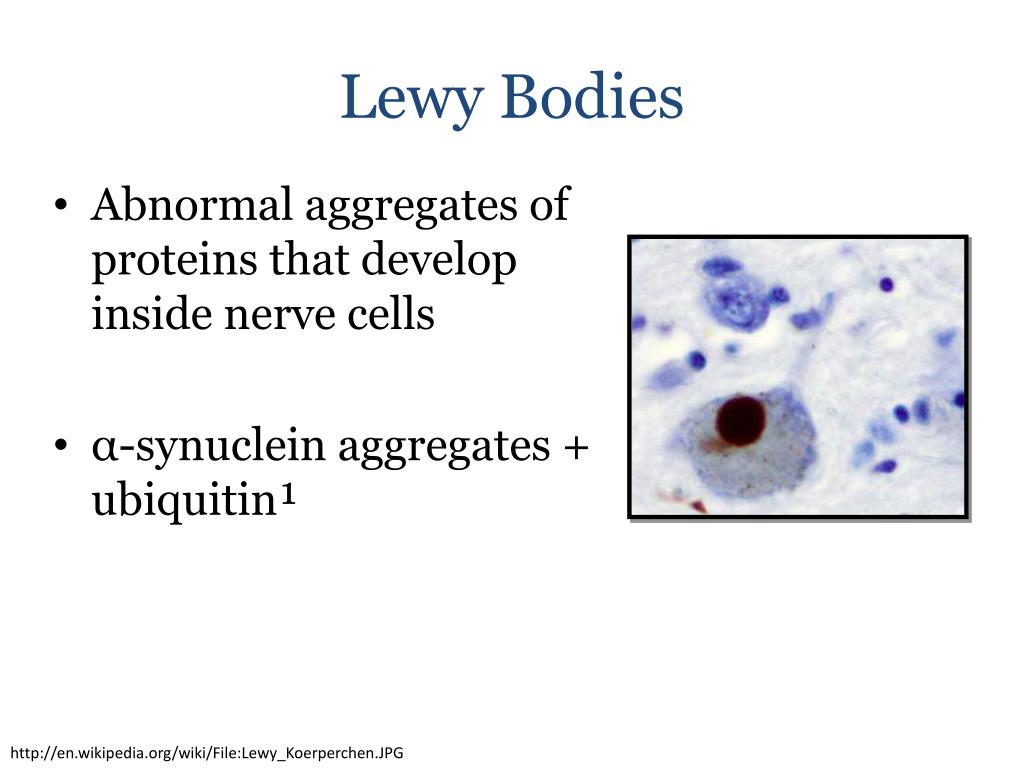
Lewy Bodies In The Pathophysiology Of Disease
Currently the neuropathological diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies is based on the detection and quantification of Lewy bodies . These are insoluble protein aggregates forming fibrils and composed mainly but not exclusively of ?-synuclein . In Parkinson’s disease, Lewy bodies are mainly found at predilection sites of neuronal loss, i.e. the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus. This has led to the conclusion that Lewy bodies are somehow related to nerve cell loss. The number of Lewy bodies in patients with mild to moderate loss of neurons in the substantia nigra is higher than in patients with severe neuronal depletion. It was thus interpreted that Lewy body-containing neurons are the dying neurons . On the other hand, Lewy bodies may not always accompany nerve cell degeneration and it is indeed unlikely that every dying nerve cell goes through a stage of Lewy body formation . It was shown that the presence of Lewy bodies does not predispose substantia nigra neurons to undergo apoptotic cell death to a greater degree than the general population of substantia nigra neurons and most neurons that undergo cell death do not contain Lewy bodies . Substantia nigra neurons, whether they contain Lewy bodies or not, are similarly affected, for example, by morphological dendritic abnormalities or biochemical changes, indicating that the neurons in general are involved in the disease process .
What Does Lewy Body Dementia Look Like
Lewy body dementia affects a person’s ability to think and process information — and it can negatively impact memory and alter personality. Though it shares aspects of other forms of dementia, there are distinct hallmarks of LBD. Lewy body dementia symptoms include:
- Fluctuating attention/alertness: These shifts can last hours or go on for days. The person may stare into space, appear lethargic or drowsy, and have hard-to-understand speech, appearing a lot like delirium. At other times, the person may have much more clarity of thought.
- Visual hallucinations: Often, these are very detailed hallucinations and visions of people or animals, and they can recur.
- Movement disorders: Parkinson’s-like movement issues, such as muscle rigidity, tremors, falls, or a shuffling gait or way of walking, may occur.
Tests For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
There’s no single test for dementia with Lewy bodies.
The following may be needed to make a diagnosis:
- an assessment of symptoms – for example, whether there are typical symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies
- an assessment of mental abilities – this will usually involve a number of tasks and questions
- blood tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms
- brain scans, such as an MRI scan, CT scan or a SPECT scan – these can detect signs of dementia or other problems with the brain
How Can We Support The Sleep/wake Cycle Of Dlb
For people with DLB who are confused about the day-night cycle, some daily strategies can be helpful. At night, starting a “lights out” routine that happens at the same hour every day, where all curtains are closed and lights are turned off, can help the person understand that it is sleep time. During the day, opening the curtains, allowing patients to spend as much time in the daylight as possible, avoiding naps, and organizing stimulating activities, can be helpful. Having lots of calendars and clocks in every room might also help a person with DLB be less confused about the time of day.
How Can A Person Diagnosed With Lewy Body Dementia Live The Best Life Possible
First, it’s important to interact with others as much as possible. Plus exercise and eat a healthy diet to keep mind and body as strong as possible.
Use music and aromatherapy to reduce anxiety and improve mood.
Other things you can do involve seeking the help and assistance of others. Therapists can improve the quality of life of someone living with Lewy body dementia. Therapists include:
- Physical therapists: These therapists can help improve physical strength, flexibility, balance and walking mechanics.
- Occupational therapists: These therapists can teach skills and methods to maintain your ability to perform activities of everyday life and remain independent.
- Speech therapists: These therapists can improve swallowing difficulties and ability to speak more clearly.
Persons with Lewy body dementia and their families can also benefit from counseling with a psychotherapist. This counselor teaches how to manage emotional and behavioral problems. Finally, joining a support group – there are support groups for persons with LBD and for the caregivers of persons with LBD. Support groups help solve day-to-day problems and frustrations through sharing similar experiences. See the resource section of this article for links to support groups.
Is There Treatment Available
At present there is no cure for Lewy body disease. Symptoms such as depression and disturbing hallucinations can usually be reduced by medication. However, medications to relieve hallucinations may increase muscle tremors and stiffness. Conversely, anti-Parkinson drugs may make hallucinations worse.
Emerging evidence suggests that cholinesterase inhibitor drugs may be quite helpful for some people with this condition.
People with this form of dementia are very sensitive to the side effects of neuroleptic drugs such as antipsychotic medications. It is essential all medications are supervised by a specialist to avoid these severe side effects.
Are The Presynaptic
From neurophysiological studies it is known that the formation of postsynaptic dendritic spines is associated with presynaptic activity. Spine shapes are regulated dynamically by synaptic activity and changes in shape play an important role in synaptic plasticity. Long-term potentiation induces formation of new dendritic spines and deprivation causes a reduction . We assumed that the huge amount of presynaptic tiny ?-synuclein aggregates have a pathological impact on dendritic spines. Analysing pre- and post-synaptic markers in DLB cases, we found a 50% reduction of the presynaptic markers synuclein and syntaxin as compared to controls . This is in line with previous reports showing a reduction of presynaptic structures in DLB and Parkinson’s disease . Looking at postsynaptic markers, there is a decrease in the postsynaptic scaffold protein PSD95 but the most considerable changes were seen in an almost complete loss of drebrin . Drebrin is an f-actin-binding postsynaptic protein that is known to be involved in organizing the dendritic pool of actin for the formation of spines . It is reported to modulate spine size and its content correlates with the spine head size . In double transgenic mice serving as an Alzheimer’s disease model , a drebrin loss in the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex precedes the onset of the AD pathology .
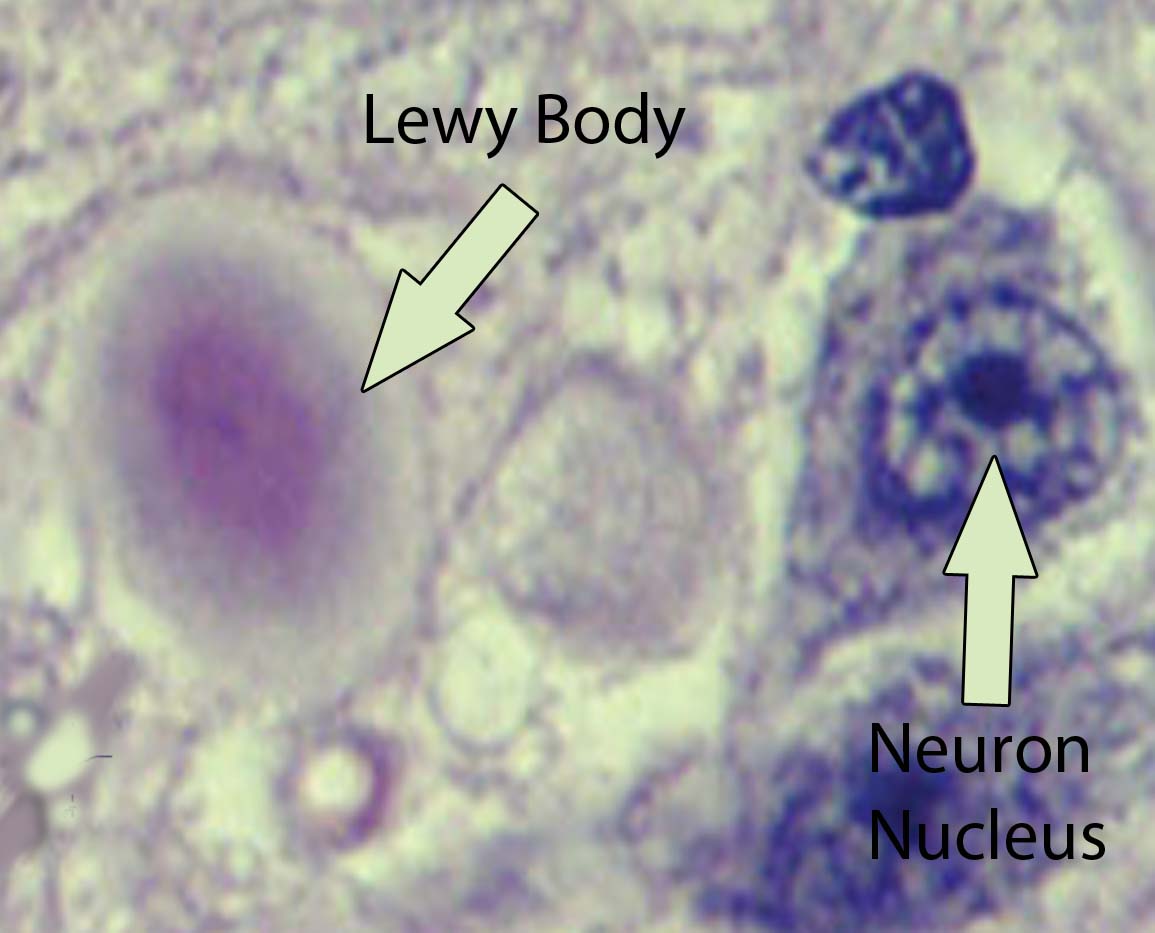
What Is Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia is not a single disorder but rather a spectrum of closely-related disorders involving disturbances of cognition, behavior, sleep, movement and autonomic function.
In these progressive disorders, Lewy bodies build up in the brain. Lewy bodies in the brain stem cause a disruption in the production of chemical messengers called dopamine. Too little dopamine can cause parkinsonism, a clinical syndrome that’s characterized by tremor, bradykinesia , and postural instability. Parkinsonism can be caused by Parkinson’s disease itself as well as by other underlying neurological conditions such as LBD. These Lewy bodies are also found throughout other areas of the brain, including the cerebral cortex. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is also depleted, causing disruption of perception, thinking and behavior.
A German neurologist, Friederich H. Lewy, first discovered the abnormal protein deposits in the early 1900s as he was conducting research on Parkinson’s disease.
Outlook For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
How quickly dementia with Lewy bodies gets worse varies from person to person.
Home-based help will usually be needed, and some people will eventually need care in a nursing home.
The average survival time after diagnosis is similar to that of Alzheimer’s disease – around 6 to 12 years. But this is highly variable and some people live much longer than this.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with dementia, remember that you’re not alone. The NHS and social services, as well as voluntary organisations, can provide advice and support for you and your family.
Parkinsons Disease With Dementia Versus Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Some patients with Parkinson’s disease experience no or only subtle cognitive decline, and their primary limitation is their motor disorder. However, other patients with Parkinson’s disease develop dementia as a consequence of the disease. When dementia develops after an established motor disorder, we call the disease Parkinson’s disease with dementia . In contrast, when dementia develops prior to or at the same time as the motor disorder, we call the disease DLB. Although the initial sequence of symptoms differs in PDD and DLB, as the disorders progress, the symptoms and the underlying brain changes are much more similar than they are different. As such, many researchers and clinicians think of PDD and DLB as being on a continuum of a similar disease process rather than as two distinct entities.
The Process Of Lewy Body Formation Rather Than Simply
See allHide authors and affiliations
Lbs In Other Disorders
Incidental LBs
LBs are found in about 10% of brains from normal elderly individuals over age 65 years . These cases may represent the earliest stages of PD, and the distribution of LBs and the non-motor clinical manifestations in some cases seem to favor this argument . In particular, such cases have LBs, albeit in small numbers and not accompanied by neuronal loss or gliosis, in brain regions that are vulnerable to pathology in full-blown PD. Given the lack of overt parkinsonism, such cases have been referred to as being “incidental.” It is not known whether these individuals, who may or may not have non-motor prodromal features of PD, would have eventually progressed to PD, but preliminary evidence favors this hypothesis .
Pure Autonomic Failure
When the involvement of the autonomic nervous system in PD and prodromal PD was investigated, it was found that some individuals with pure autonomic failure have LB pathology at autopsy . In those cases, LBs were detected in brain and autonomic ganglia and LNs in sympathetic nerve fibers in epicardium and peri-adrenal tissues . It is of interest that PD and individuals with incidental LBS may also have adrenal ?-synuclein pathology .
Dementia with LBs
Dementia in PD
R.A. Armstrong DPhil, in, 2015
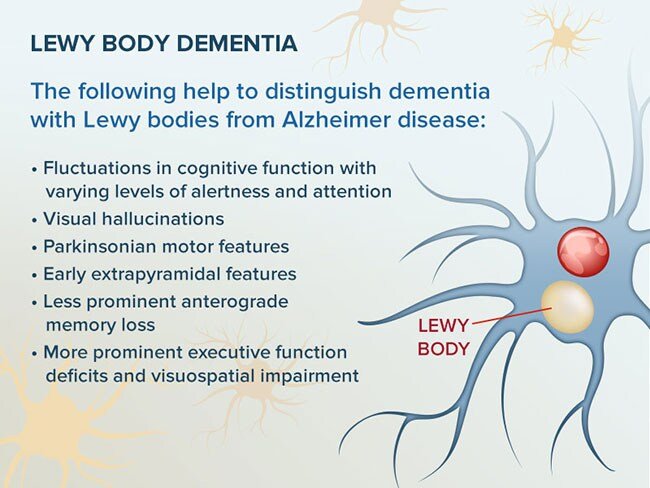
How Is Lbd Different From Parkinsons Or Alzheimers
These diseases are similar in a lot of ways. But there are some key differences in the symptoms that affect people with LBD and when those symptoms happen.
LBD may not cause short-term memory loss like Alzheimer’s. People with both conditions have trouble with thinking, alertness, and paying attention. But in LBD, those problems come and go. The disease can also cause hallucinations, often in the first few years someone has LBD. People with Alzheimer’s usually don’t have hallucinations until the later stages.
People with LBD also often act out their dreams and make violent movements when they’re asleep. It’s called REM sleep behavior disorder. Sometimes, it’s the first sign that someone has LBD.
LBD and Parkinson’s disease both cause movement problems, like stiff muscles and tremors. But most people with Parkinson’s don’t have problems with their thinking and memory until the very later stages of their disease. Sometimes, they don’t have it at all. In the type of LBD known as Parkinson’s disease with dementia, these problems begin much sooner.
People with LBD also need different drugs for their condition than the ones that treat Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s.
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Treatments for DLB are similar to PDD and are aimed at symptom control. The motor symptoms of slowness, stiffness and walking difficulties can be treated with Levodopa. However, Levodopa can cause or exacerbate hallucinations, making it difficult to use it as a treatment for patients who have or are at risk of having hallucinations. Sometimes, clinicians will need to treat the hallucinations more aggressively in order for a patient to tolerate Levodopa given to help the motor symptoms. On the flipside, anti-psychotic medications to control hallucinations can worsen motor symptoms, so treating all the symptoms of LBD simultaneously can be a tricky balancing act.
Lewy Body Dementia: A Common Yet Underdiagnosed Dementia
While it’s not a household word yet, Lewy body dementia is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and , it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In fact, many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD.
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: “dementia with Lewy bodies” and “Parkinson’s disease dementia.” These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a person’s ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinson’s such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimer’s is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
What Is The Best Way To Communicate With A Person With Pdd
PD-related mood and motor changes can impact ; cognitive changes and Parkinson’s disease dementia can further these difficulties.
- It is not usually helpful to try to reason or argue with someone experiencing a hallucination or delusion. Stay calm and be patient. If the person is frightened by the hallucination or delusion, try to redirect their attention to something else.
- You may find acknowledging what the person is seeing, even if you do not see it, can reduce stress.
- Speak slowly and at eye level. Communicate in simple sentences.
- Ask one question at a time and wait for an answer.
- Limit distractions. Turn off the TV or radio before asking a person with PDD to do something.
- Consider causes behind disruptive behavior: the person may be hungry, thirsty, tired, in pain, frustrated, lonely or bored.
- If the person is stuck on an idea, try agreeing with them, then changing the subject.
- It’s OK to use humor to diffuse stressful situations but avoid negative humor or sarcasm ? these can be misunderstood.
Page reviewed by Dr. Jori Fleisher, MSCE, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurological Sciences at Rush University Medical Center, a Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence.
What Are Pd Dementia Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone.
- Evaluate privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementia’s early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Medical alert systems can be critical in case your loved one falls or wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smart watches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider speaking with their doctor about the subject and taking appropriate safety precautions.
Wait So What Is Parkinsonism
refers to the motor symptoms that are typically associated with PD, such as tremors, stiffness, and walking/ problems. Both PD and LBD are forms of Parkinsonism, meaning that PD patients and LBD patients may experience these motor symptoms.2 Because the Parkinsonism motor symptoms of PD and LBD can be very similar, it can be difficult to differentiate between the two conditions.
What Is Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
Both conditions relate to decline in cognitive thinking and reasoning, loss of brain cells and abnormal alpha-synuclein protein clusters termed as Lewy bodies.
Both disorders have very similar symptoms, but the symptoms usually happen in a different order dependant on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Major similarities between Parkinson’s and Lewy Body Dementia include;
- Both disorders affect approximately one million people in the United States
- They both an impact to the brain nerve cells
- There is no cure for both of these conditions
- Symptoms that impact the body include stiffness, weakness and slowness in movements
- Symptoms that affect brain include: memory loss, attention span and impaired executive functioning
The protein – alpha-synuclein unusually builds up in the brain in aggregates, or clumps, called Lewy bodies. The location of those clumps makes a difference.
Also, people who have Lewy bodies tend to exhibit greater variation in brain function ability than those with PD dementia.
What Can I Expect If I Or My Loved One Have A Diagnosis Of Lewy Body Dementia
Each person’s experience with Lewy body dementia is unique to them. How slowly or quickly the disease progresses is impossible to know, but may be influenced by your general health and any existing diseases you may have. Because LBD is a progressive disease, difficulties with mind and body functions get worse over time. Currently, there is no known way to stop the progression of the disease. After diagnosis, most people with LBD live between five and seven years. Some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis.
However, there’s always hope. Research on LBD, dementia with lewy bodies, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease with dementia are ongoing. New medications are being developed and new approaches to treatment are being investigated.
What Is Lewy Body Disease
Lewy body disease is caused by the degeneration and death of nerve cells in the brain. The name comes from the presence of abnormal spherical structures, called Lewy bodies, which develop inside nerve cells. It is thought that these may contribute to the death of the brain cells. They are named after the doctor who first wrote about them. It is sometimes referred to as Diffuse Lewy body disease.
Stages And Progression Of Lewy Body Dementia
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology. She is an associate professor of neurology at Tufts Medical School and medical director of the Lahey Clinic Multiple Sclerosis Center in Lexington, Massachusetts.
If you or someone you know has recently been diagnosed with Lewy body dementia, you might be wondering what to expect as the disease progresses. Is there a fairly typical progression like Alzheimer’s disease where it begins in early stages that are fairly uniform, then moves to middle stages and then to late stages? In Lewy body dementia, the answer is a bit more complicated.
