How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinsons disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinsons is caused by a combination ofenvironmental and geneticfactors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
Findings On Medication Use And Motor Complications
The results showed that deep brain stimulation was effective at reducing motor complications from Parkinsons disease for more than 15 years.
The researchers also found that the therapy reduced the amount of time a person experienced dyskinesia by a whopping 75%. Dyskinesia is a side effect of a common Parkinsons medication called levodopa that results in rapid, involuntary body movements, like twisting, squirming, and head bobbing.
Whats more, participants spent about 59% less time in an off state, when medication stopped being as effective, and reduced their use of medications to manage dopamine levels by 51%.
Historical Perspective Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Prior to the discovery of levodopa, surgical interventions were the most efficacious treatment for PD symptoms, but primarily focused on the reduction of bothersome tremor. Early approaches targeted the pyramidal tracts, with lesioning either at the point of origin in the cortex or the descending pathways through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord . Although tremor was reliably improved following surgery, hemiparesis was an inevitable consequence. However, in 1952, Dr. Irving Cooper inadvertently interrupted the anterior choroidal artery while performing a mesencephalic pedunculotomy in a patient with PD. Ligation of the vessel was required, though what resulted was a serendipitous reduction in rigidity and tremor with preservation of motor and sensory function. Cooper reasoned the favorable outcomes were due to infarction of the medial globus pallidus. An expansion of ablative stereotactic surgery followed, aided by the earlier development of the stereotactic frame and methods of targeting deep brain structures, including the basal ganglia and thalamus. However, the success of these approaches was limited, partly because of inaccurate, imprecise, and inconsistent targeting. Moreover, intentionally created bilateral brain lesions frequently led to irreversible deficits in speech, swallowing, and cognition.
You May Like: Risk Factors For Parkinson Disease
Side Effects And Problems With Dopamine Agonists
Common side effects of dopamine agonists include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hallucinations or delusions and confusion
- Existing dyskinesias becoming more troublesome initially
If you are taking Cabergoline , Pergolide or Bromocriptine your neurologist or GP will have to arrange a chest CT scan or ultrasound of your heart yearly as over time these medications may effect heart or lung tissue.
This precaution does not apply to the other dopamine agonists available in Australia.
Recommended Reading: Effective Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications arent as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Also Check: What Are The First Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
A Stanford Neurosurgeon Answered Questions About Deep Brain Stimulation
Stanfords Parkinsons Community Outreach Program hosts a quarterly deep brain stimulation support group meeting for those wanting to learn more about this surgical treatment for Parkinsons disease . The June 2020 meeting featured Dr. Daniel Kramer, a neurosurgeon and clinical instructor at Stanford, who answered audience questions pertaining to DBS.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinsons
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Risk factors for PD include:
- Age. The average age of onset is about 70 years, and the incidence rises significantly with advancing age. However, a small percent of people with PD have early-onset disease that begins before the age of 50.
- Sex. PD affects more men than women.
- Heredity. People with one or more close relatives who have PD have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. An estimated 15 to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease. Some cases of the disease can be traced to specific genetic mutations.
- Exposure to pesticides. Studies show an increased risk of PD in people who live in rural areas with increased pesticide use.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Sleep Disorder Treatment
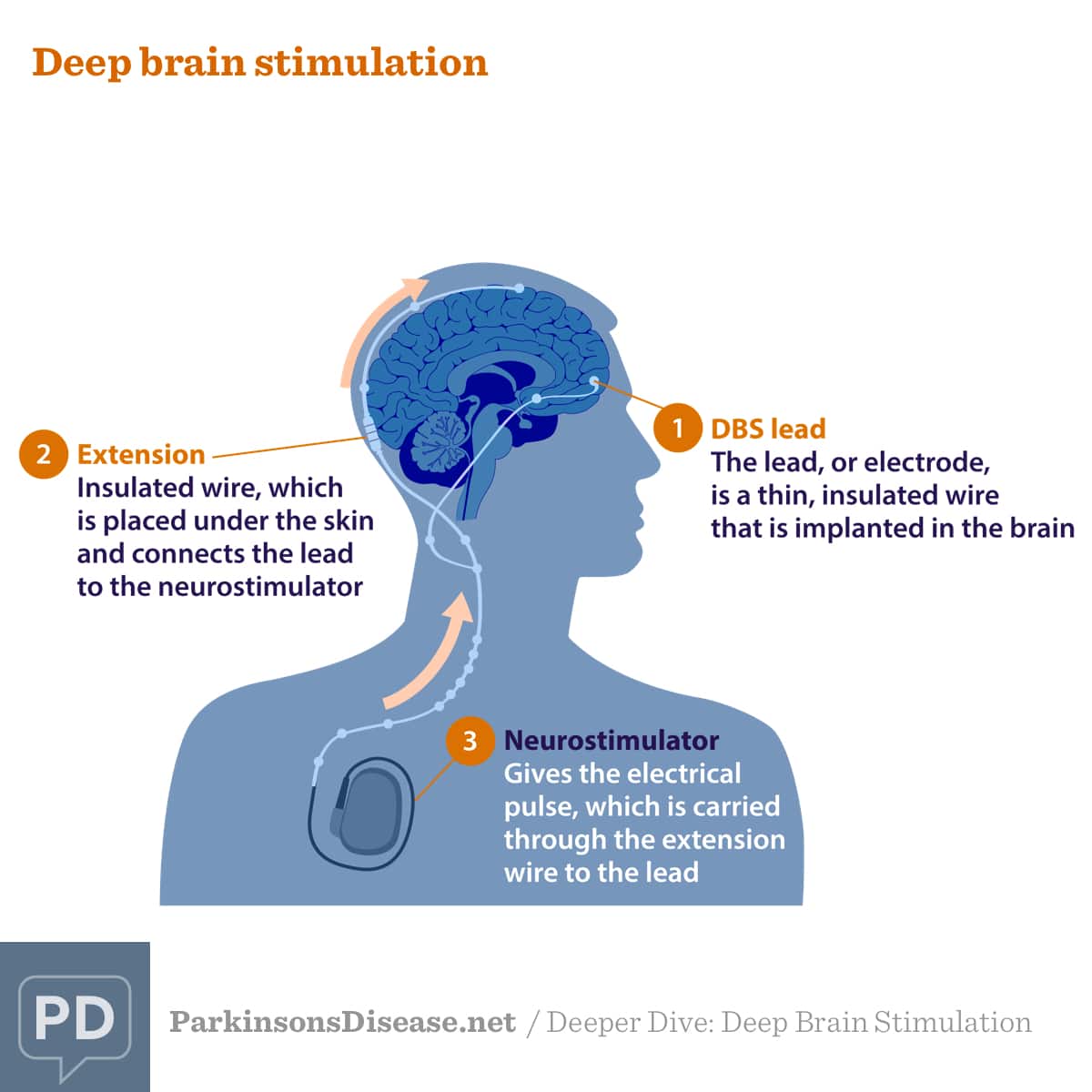
What Happens During Deep Brain Stimulation
This procedure actually involves two to three surgeries that usually happen at different times. The first one or two procedures are to insert the stimulation leads into each side of your brain at the same or separate times. The second procedure is to implant the stimulator battery known as a pulse generator under the skin of your upper chest.
Before these surgeries happen, your healthcare provider will usually insert an intravenous line to give you IV fluids. An IV also allows them to give you medications during the procedure as needed.
Lead placement
This procedure usually starts with your healthcare provider shaving the hair on your scalp. This makes it easier to place your head into a special frame that will hold your head still. The frame is set with four pins in your skull. This is done while youre under sedation, and you likely wont remember this part.
Once the frame is set, theyll bring in an intra-operative CT scanner to take images of your brain and identify the trajectory used for the electrode placement. Once the CT scan is complete, the entry point is identified, sedation is turned back on and your head is cleaned with surgical prep. Local anesthetic is then injected to numb that area of your scalp and skull. Your neurosurgeon will then make a small cut .
Pulse generator placement
Who May Benefit From Deep Brain Stimulation
A number of criteria can help identify people who are good candidates for deep brain stimulation. This includes people who:
- Have been living with Parkinsons disease for at least five years, though the procedure was approved for early symptoms in 2016 and is now being evaluated to see if it offers benefits for people earlier in the disease
- Have symptoms that are not well controlled on medications
- Are responding to Parkinsons medications : The procedure should only be done for people who are responding to this treatment, but the medication effects fluctuate during the day and the effectiveness of the medication is getting shorter.
- Find that the uncontrolled symptoms are lowering their quality of life
- Are doing relatively well cognitively
At the current time, there is no set age limit for DBS, but the effectiveness may be lower in older people.
You May Like: Charity Navigator Parkinson’s Foundation
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery And Implantation
DBS consists of two surgeries, spaced approximately three to six weeks apart to ensure the patient has adequate time to recover. Throughout your experience, you will be attended to by a top team of physicians and other medical experts including a neurosurgeon, an electrophysiologist, and an anesthesiologist.
It should be noted that DBS offers many benefits. The generator can be programmed by a neurologist, and customized to each individual patient. The procedure is also reversible. Most patients experience a significant improvement of symptoms. However, as with any brain surgery, there are risks. With DBS, the risk of stroke is 1 in 100 and infection is 1 in 50.
Today, many more patients could be helped by DBS than are currently benefiting from the procedure. Statistics show only 7 percent of Parkinsons disease and 1 percent of tremor patients in Michigan who would benefit from the procedure have undergone DBS. At U-M, we are proud to have one of the superior DBS programs in the country. We have developed a wide array of ways to improve DBS, including special imaging tools that help doctors more accurately place the electrodes, and lead intraoperative motor and speech testing that result in fewer side effects for the patient.
U-M is also home to an active research program, where our team of experts is always working on ways to make DBS faster and more accurate. We also regularly have clinical trials available for patients interested in participating.
Changes In Cognition And Parkinsons Disease
Some people with Parkinsons may experience changes in their cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and the ability to plan and accomplish tasks. Stress, depression, and some medications may also contribute to these changes in cognition.
Over time, as the disease progresses, some people may develop dementia and be diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia, a type of Lewy body dementia. People with Parkinsons dementia may have severe memory and thinking problems that affect daily living.
Talk with your doctor if you or a loved one is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease and is experiencing problems with thinking or memory.
Read Also: Parkinsons And Gut Health
You May Like: Fun Activities For Parkinson’s Patients
What Care Is Needed After
On top of the wound care required with any surgery, DBS calls for special follow-up and ongoing care. Depression, falls, nausea, and problems with motor skills and swallowing can occur after DBS. In a follow-up appointment, doctors can address these issues and any other side effects of the device and/or the stimulation.1,2
Some follow-up care will last only a short time, depending on the issue. For instance, DBS can alter a persons mood, personality, and speech. Counseling, drugs, and speech therapy may help with these issues. A doctor can help find the best course of action in each case.1,2
People treated with DBS will need some extra care for the rest of their lives. Each persons device must be maintained and adjusted to meet their unique needs. Dosages of other drugs used to treat PD may also need to change over time.1,2,4
New And Emerging Targets
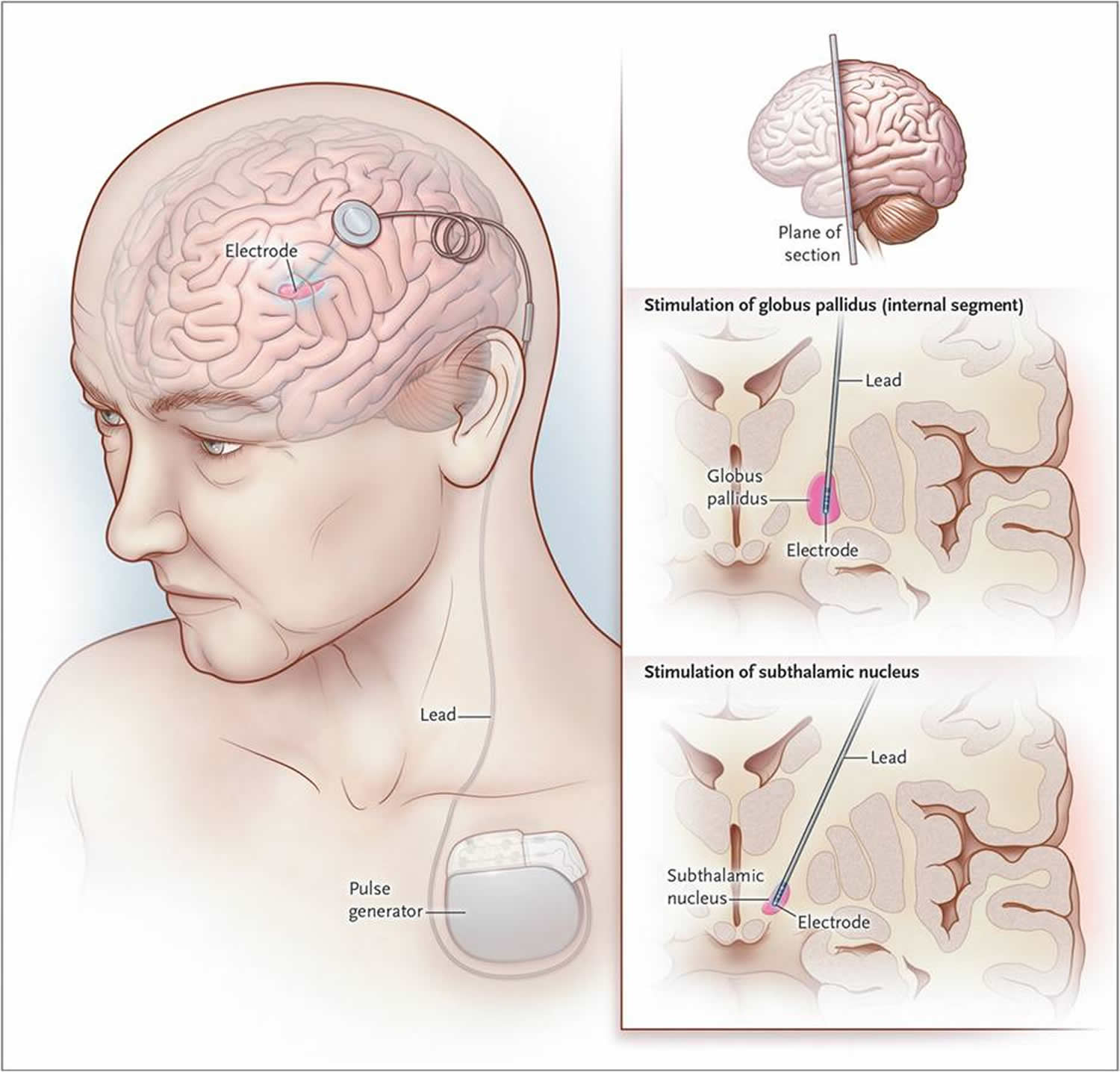
Since, there is no consensus on the best target for DBS in PD and because no target is able to effectively manage all the patients symptoms and QoL over a prolonged period, newer targets and dual target stimulation is being investigated to improve PD outcomes in patients with refractory motor and non-motor symptoms.11 Stimulation of caudal zona incerta is associated with better motor control than best medical treatment .46 Dual stimulation of STN and cZI has been tried with better results that targeting individual regions.47 Also, Vim, PPN, and PSA are the newer targets found to be effective in different PD patient populations .11
Also Check: Therapeutic Regimen For Parkinson’s Disease
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider will schedule visits to see you after your procedures. Programming visits occur with your neurologist, and youll need to make appointments to see them. The goal of those visits is to find the settings that work best and don’t cause side effects that disrupt your life.
Regular visits with your healthcare provider are also common to monitor your condition, symptoms and to adjust medications or other treatments as needed. The schedule for these visits is something that your provider will discuss with you.
Prevention Of The Breakdown Of Endogenous Dopamine Medications
MAO-B Inhibitors work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose. Commonly used MAO-B inhibitors include selegiline and rasagiline . More recently, the drug safinamide was also approved for use in PD, which appears to have multiple modes of action, one of which is thought to be inhibition of MAO-B . MAO-B inhibitors are generally well tolerated, with gastrointestinal side effects being the most common problem. Other adverse effects include aching joints, depression, fatigue, dry mouth, insomnia, dizziness, confusion, nightmares, hallucinations, flu-like symptoms, indigestion, and headache.
Catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitors: another enzyme that is involved in dopamine degradation is COMT. These drugs are predominantly used as adjunctive therapy to levodopa, prolonging its duration of action by increasing its half-life and its delivery to the brain. COMT inhibitors come in the form of tablets and are not generally prescribed as monotherapy, as on their own they offer only limited effect on PD symptoms. Examples of COMT inhibitors include entacapone , tolcapone , and opicapone .
Recommended Reading: What’s Good For Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation At Michigan Medicine
For carefully selected patients with Parkinsons disease, Essential Tremor, and Dystonia, deep brain stimulation offers a therapeutic surgical option that can reduce or eliminate movement-related problems and greatly improve quality of life. At the University of Michigan Health System, our STIM program brings together a team of medical experts who are leaders in their respective fields and on the cutting-edge of the latest research.
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Parkinson’s Hallucinations
Placement Of The Neurostimulator
This procedure takes place under general anesthesia so that the person is asleep. The surgical team inserts the neurostimulator under the outer layers of skin, usually just under the collarbone, but sometimes in the chest or abdomen. The extension wire from the lead is attached to the neurostimulator.
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
You May Like: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: What Is Parkinson’s Dementia
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider Or Go To The Hospital
Because DBS involves surgery especially the procedure on your brain there are some warning signs you shouldn’t ignore. You should call your healthcare provider immediately or go to the hospital outside of business hours if you have the following symptoms:
- Severe headache that happens suddenly or wont go away.
- Bleeding from your incisions.
- Redness, swelling or unusual warmth which are signs of infection around your incisions.
- Sudden changes in your vision, such as seeing double, blurred vision or loss of vision.
- Fever of 101 degrees F or higher.
What Happens During Surgery
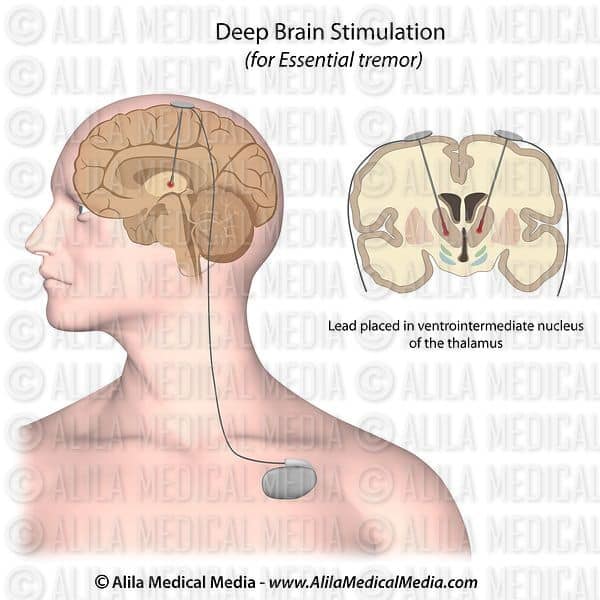
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Read Also: Is There Memory Loss With Parkinson’s Disease
