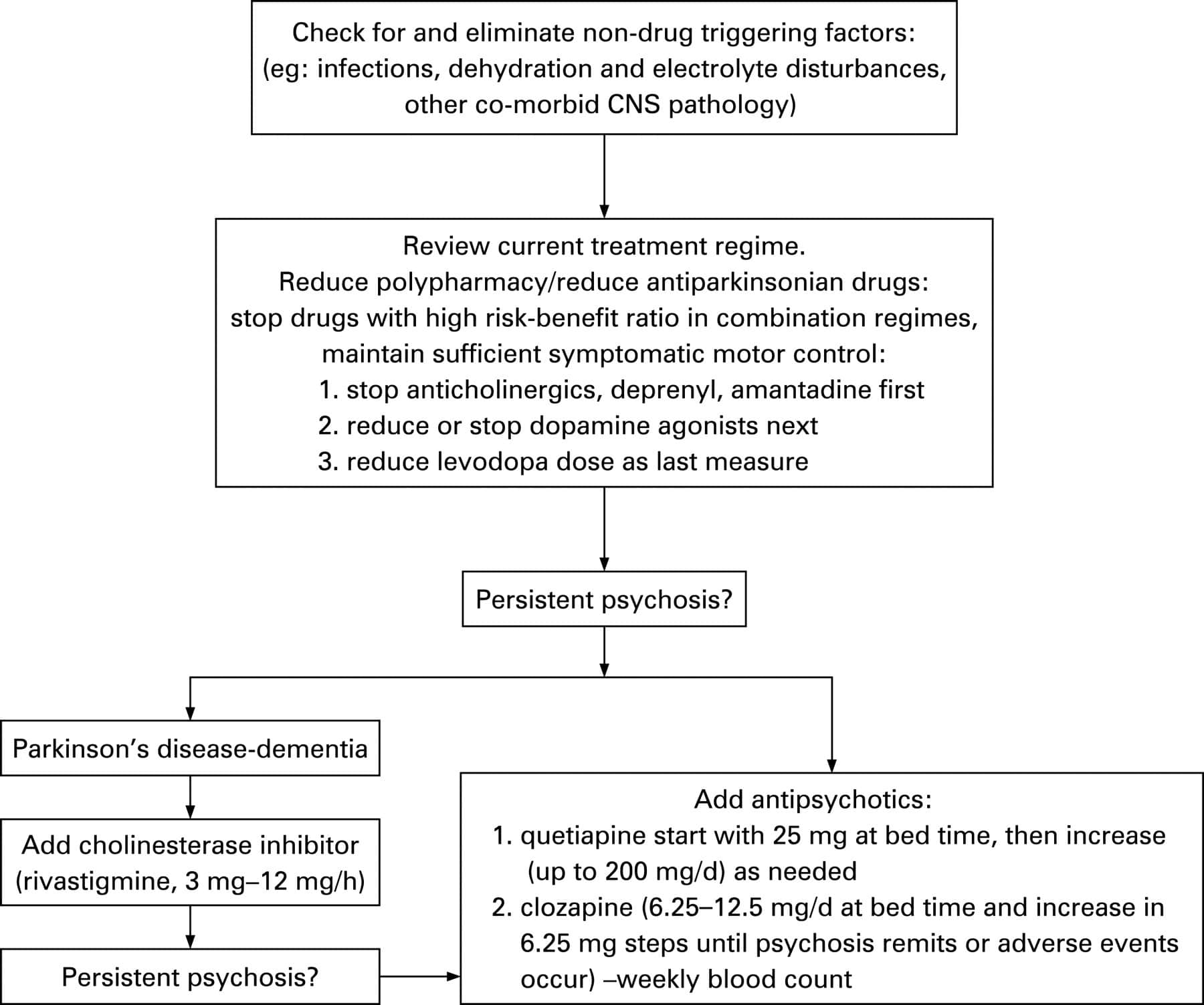
Predictive Factors And Pathophysiology
Minor hallucinations/illusions
Patients with isolated minor hallucinations/illusions differed from patients without hallucinations only by the presence of more depressive symptoms on the CES-D rating scale, suggesting that depressive symptoms are a facilitating factor. Indeed, depression may sometimes trigger or aggravate hallucinations associated with deafness or ocular pathology . However, when we analysed depression according to CES-D cut-off scores, the difference between the Parkinsons disease patients with minor hallucinations/illusions and those with no hallucinations was not significant. Interestingly, hallucinations involving the deceased spouse have been reported in up to half of widowed persons, with a higher frequency in the elderly . In the present study, the `presence was that of a deceased relative in only three cases bereavement cannot therefore explain the bulk of the cases.
Dopaminergic agents and other treatments
In the present study, non-hallucinators were more likely to be on anticholinergics or selegiline than patients with hallucinations. A similar paradoxical, negative association between anticholinergics and hallucinations was found by Sanchez-Ramos and colleagues . This reflects the recommendation whereby the use of these drugs in patients with cognitive impairment is avoided because of the well-known risk of cognitive worsening and/or hallucinations in this population.
Cognitive impairment
Dont Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
Hallucinations And Delusions In Pd
Hallucinations and delusions are collectively referred to as psychosis.
Visual hallucinations are the most common type of hallucination. In a visual hallucination, someone sees things that are not actually there. There can also be auditory and olfactory hallucinations. Often hallucinations are not alarming to the person experiencing them.
Delusions are when there is an alternative view of reality: an entire irrational story is created. Paranoia is a common type of delusion. Capgras delusions are a specific type of delusion where the person believes that a spouse, adult child, or other family member has been replaced by an imposter.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Copay Assistance Program
What Causes Psychosis In Parkinsons
Currently, there is not a clear understanding of the exact cause of Parkinsons disease psychosis, although certain brain chemicals and receptors are believed to play a role. In general, the condition is believed to be caused by either one of the following:
Side effect of dopamine therapy:
Although an exact causal relationship has not been established, some believe that this condition may be a side effect of dopaminergic therapy .2Dopaminergic therapy increases dopamine levels, helping improve motor symptoms in patients with Parkinsons disease. However, increasing dopamine levels can also cause chemical and physical changes in the brain that inadvertently lead to symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions.
Natural outcome of the disease:
This condition can be triggered by changes in the brain that occur regardless of taking dopamine enhancing medication. Some of these changes occur naturally as Parkinsons disease progresses.2
Recommended Reading: How Does Caffeine Affect Parkinson’s Disease
Practical Tips For Caregivers Of People With Parkinson’s Psychosis
This 2-page tip sheet has bullet point suggestions for what to do if the person you care for experiences hallucination, delusions or confusion, or becomes agitated or aggressive. In addition, there are tips for how to best be prepared for a doctors appointment when you bring this behavior to the attention of your medical team.
Treatment And Management Of Hallucinations
You should discuss any hallucinations or delusions with your doctor, or Parkinsons nurse if you have one, so that all treatment options can be considered.
In mild cases no specific action may be required and simple reassurance that the images, sensations or sounds are harmless may be all that is needed.
Also Check: Can Young Adults Get Parkinson’s Disease
Australia Continues To Forge Ahead
Its not the first time Australian researchers have been involved in potentially groundbreaking treatments for Parkinsons disease.
In November, The New Daily reported that researchers at the University of Queensland partly funded by the Michael J Fox Foundation had developed a world-first pill that could stop the death of brain cells in Parkinsons sufferers rather than just managing symptoms.
Phase one tests of this drug are expected to take place this year, and all going well, phase two will follow in 2020.
You May Like: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Hallucinations In Parkinsons Disease: Approach And Management
Babak Tousi, MD, and Thayagaran Subramanian, MD
Risk Factors
Risk factors that have been reported include dementia, duration of therapy with dopaminergic medications, duration of disease, age of patients,10,11 anticholinergic medications, and sleep disorders.12-15 The mnemonic SADDAD can be used to recall these risk factors for hallucinations in PD:
Sleep disorders Anticholinergic medications Duration of disease
Severe cognitive impairment or dementia is a major and independent predictive factor for visual hallucinations.4,9,16 In one study, the prevalence of visual hallucinations was reported as 70% in patients with PD who have dementia.9 It is not clear whether cognitive impairment and hallucinations occur independently as the natural progression of disease or if they have causative links. Studies using positron emission tomography have shown marked occipital hypometabolism in patients with PD who have dementia.17 This suggests that degenerative process in the visual cortex can be a cause for visual hallucinations.
Auditory and Tactile Hallucinations
Treatment
Summary
AcknowledgmentThe authors acknowledge the help of Dr. Robert Palmer, Chief of Geriatric Section, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, in the preparation of this paper.
Don’t Miss: How To Sleep Better With Parkinson’s
Section Header Managing Psychosis With Medication
Dont keep hallucinations or delusions a secret from your doctor. Medications — or changes to the medications you take — can help manage Parkinsons psychosis.
Streamlining your meds. The first thing your doctor may want to do is stop or lower your Parkinsons medication dose. They may boost dopamine levels in your brain. That improves motor symptoms but can also cause changes in your emotions or the way you act.
Antipsychotics. These medications balance your brain chemicals. Only a few are considered safe for people with Parkinsons disease. These include quetiapine and clozapine .
Pimavanserin . Another antipsychotic, this first-in-class drug was approved by the FDA in 2016 to treat hallucinations and delusions in Parkinsons disease linked with psychosis.
If you see a doctor who isnt part of your usual care team — say, in the emergency room or an urgent care setting — tell them you have Parkinsons disease and what medications you take for it.
What Makes Some People With Parkinsons More Susceptible To Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Not everyone living with Parkinsons will experience hallucinations and/or delusions, but there are several things that can increase your risk. Here are a few to look out for. Be sure to speak to your doctors and care partners if you notice any changes.
- Increased sleep disturbances such as REM Sleep Behavior Disorder, sleep apnea, vivid dreaming and sleep interruptions
- Vision problems such as blurry or double vision
- Hearing problems
Also Check: Can Probiotics Help Parkinson’s Disease
Support Your Loved One And Yourself
PDP is also associated with increased caregiver stress and burden, nursing home placement and increased morbidity and mortality. But, your loved one is certainly not alone in living with PDP, and an effective management plan can improve the complications. Seek out the support that he or she needs, but also make sure that you are getting the emotional care you personally need in order to be an effective advocate for your loved one.
Visual Hallucinations In Parkinsons Disease: Towards Better Understanding And Treatments
Parkinsons disease is a common neurodegenerative disease, affecting more than 2% of people over 75, with estimated 7 to 10 million affected people worldwide. Although traditionally Parkinsons disease is thought of as a disorder of movement, with tremor and slowing of movement being the cardinal features, it can cause a wide range of other non-motor symptoms and frequently leads to dementia. These non-motor symptoms, are common, can occur even before motor symptoms become evident and are often the most troubling for patients.
Visual hallucinations, the sensation of seeing objects that are not really there, are a common non-motor symptoms in PD, affecting up to 70% of individuals over the course of the disease. As well as causing distress, visual hallucinations have a significant impact on the quality of life of patients and their families: hallucinations often herald the cognitive decline and are a strong predictor for nursing home placement.
The wide variety of visual hallucinations
The experience of visual hallucinations vary from person to person and can change across the course of the disease. Commonly, people with Parkinsons disease experience one or more of the following hallucinations:
Figure 1. Giuseppe Archimboldo, Portrait with Vegetables . A famous example of pareidolia. The same painting is seen as a collection of vegetables or a face .
Visual hallucinations are challenging to treat
A better understanding of hallucinations is needed
Next Post
You May Like: Can Parkinsons Be Cured If Caught Early
New Drug Shows Promise In Treating Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Off-label drugs have been used to manage psychotic-related symptoms in Parkinsons disease patients, but they worsen motor symptoms by reducing dopamine levels. Nuplazid is the only FDA-approved drug that treats Parkinsons disease psychosis without impairing motor function.
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor, and postural instability. While therapeutic advances have been made to improve motor-related symptoms, many older adults affected by this disease also develop Parkinsons disease psychosis . Psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions develop in more than 50% of PD patients and can lead to severe impairments in cognitive, behavioral, and emotional function.1
PDP Drives Nursing Home Placement According to the Parkinsons Disease Foundation, 1 million people have been diagnosed with PD in the United States, and between 7 million and 10 million people worldwide have the condition. Hallucinations and delusions drive the nursing home placement and hospitalization of patients diagnosed with PDP, says Jason Kellogg, MD, chief of staff at Newport Bay Hospital in Newport Beach, California.
He adds that the delusions and hallucinations observed in PDP tend to be more dramatic in nature. For instance, these patients are usually high-functioning, well-dressed men and women. But their hallucinations are quite striking because they have delusions of persecution and visual hallucinations.
What Are Hallucinations Like With Parkinsons
Hallucinations are when you see, hear, or feel things that arent actually there, explains Jennifer S. Hui, M.D., a neurologist with Keck Medicine of University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They can run the gamut in terms of how they manifest in different people with psychosis. In specifically, hallucinations tend to share some common characteristics.
Typically, hallucinations in Parkinsons patients are very specific, explains Ling Pan, M.D., clinical assistant professor of neurology and neurosurgery at NYU Langone Health in New York City. They are visual hallucinations, often of small animals or objects, strangers in the home, or seeing family members who arent there, whether living or deceased.
Earlier on in the disease, visual hallucinations may be milder. They may be more like illusions, rather than a fully formed hallucination, she adds. For example, patients may see a shape morphing on the floor or think they see something passing by them.
While researchers still dont know why psychosis can occur with Parkinsons, medications for the condition can sometimes play a role. If we are treating with dopamine agonists, these can sometimes lead to hallucinations and be a culprit in worsening that symptom if you are already prone to it and if your Parkinsons disease is enough to cause that symptom to manifest, says Dr. Hui.
Recommended Reading: Can I Take Ibuprofen With Parkinson’s Medication
How Can You Improve Aggressiveness And Hallucinations In Parkinsons
Hallucinations may spark anger or aggression in a person with Parkinsons disease. Some ways to help include:
- Reassure them, tell them they are safe.
- Speak slowly and calmly.
- Ask questions about the persons feelings.
- Listen to the person, dont interrupt.
- Avoid sudden movements.
- Give the person space and a way out, so they dont feel cornered or threatened.
- Make an emergency plan ahead of time for what you and others in the house will do if the person experiencing hallucinations becomes a danger to themselves, you, or anyone else.
- When it is safe, help the person speak with their healthcare provider about making a plan to address the hallucinations.
Pathology Of Neurotransmitter Pathways In Pd Psychosis And Relevance Of Medications
The distribution of pathology in PD involves key components of dopaminergic and other important neurotransmitter pathways implicated in PD psychosis. Dopamine is synthesized in the substantia nigra, with projections to the striatum, limbic system and frontal lobe , and five recognized dopamine receptors with broad distribution throughout the brain and peripheries at varying levels of expression . It is known that dopaminergic medications have differential actions across these receptors, and, similarly, antipsychotic medications display different binding affinities for individual dopamine receptors .
While loss of dopaminergic neurons within the substantia nigra is a central pathological feature of PD , neuronal loss also occurs in multiple other subcortical nuclei with projections to cortical, limbic, and basal ganglia regions. These include the dopaminergic nuclei of the ventral tegmentum, noradrenergic locus coeruleus, serotonergic raphe nuclei, histaminergic tuberomammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus, and cholinergic nucleus basalis of Meynert and the pedunculopontine nucleus . LB deposition and neuronal loss in the locus coeruleus occurs earlier and is more prominent than PD pathology in the substantia nigra, with some evidence that pathology in this region may contribute to subsequent dopaminergic cell loss, because noradrenergic neurons directly innervate the substantia nigra .
Don’t Miss: What Are The 5 Stages Of Parkinson Disease
Hallucinations And Rem Sleep Disorders In Parkinsons Disease
At timestamp 1:58 in this recording of Thrive: HAPS 2020 Caregiver Conference, you will find a one hour talk by neurologist Joohi Jimenez-Shahed, MD. In it she delves into what REM sleep behavior disorder is and is not, and the distinctions between hallucinations, delusions, and delirium. Managment options for RBD and hallucinations are included.
Also Check: Does Amy Klobuchar Have Parkinsons
Types Of Hallucinations In People With Parkinsons Disease
Hallucinations involve the five senses: sight, smell, touch, hearing, and taste.
People with hallucinations have sensory experiences that feel real to them, but are not actually happening and are not apparent to anyone else.
Types of hallucinations include:
- Auditory: Hearing things
- Gustatory: Tasting things
For people who experience Parkinsons-related hallucinations, the hallucinations are usually visual. They are typically non-threatening, but less commonly they can be of a threatening nature.
Often people with Parkinsons disease psychosis see small people or animals, or loved ones who have already died. They are not interacting with them, just being observed.
Auditory hallucinations are more common in people with schizophrenia, but can happen with Parkinsons disease. With Parkinsons disease, auditory hallucinations are usually accompanied by visual hallucinations.
More specific types of hallucinations experienced by people with Parkinsons disease include:
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Incontinence
How Common Is Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Between 20-40% of people with Parkinsons report the experience of hallucinations or delusions. When followed as the disease progresses over the years, this number increases. The increase does not mean that the hallucinations are persistent across the majority of patients. However, it is important to note that these statistics sometimes include delirium, in which the symptoms are temporary due to medication that needs to be adjusted or infection that needs to be treated, and isolated minor symptoms or minor hallucinations, including illusions, where instead of seeing things that are not there , people misinterpret things that are really there. These are the most common types of psychosis in people with PD, with different studies placing the occurrence between 25-70% of people with Parkinsons. Typically, if the person with PD only has these minor hallucinations, their doctor will not prescribe an antipsychotic medication, though more significant psychosis that requires medication may develop over time. In one study, 10% of those with minor hallucinations had their symptoms resolved within a few years, while 52% saw their symptoms remain the same and 38% saw their psychosis symptoms get worse.
We recommend that people with Parkinsons not use a single percentage to represent the prevalence of hallucinations and PDP. Parkinsons is a complex disease and as it progresses the percentages and risk of symptoms will change.
Also Check: Pfnca Wellness Programs
What Should I Do When My Loved One Is Experiencing A Hallucination
Most importantly, dont try to convince your loved one that what theyre experiencing isnt real. Theyll feel like youre putting down an experience that seems authentic to them.
Once a person has lost insight, itll be very difficult to convince them that what theyre experiencing isnt happening. Trying to argue with them may agitate and even enrage the person. Making them anxious could cause their hallucinations to get worse.
Instead, talk to the person gently and reassuringly. You might say something like, I understand that you see a dog in the corner of the room. Everything is going to be OK. Youre safe. You might even say that the dog must have left already.
Remember that the person cant control what theyre experiencing. Try to be as sympathetic as you can when you talk to them.
One approach that can help is to turn on all the lights in the room. Hallucinations are more likely to happen in dimly lit areas, and this can be caused by disease-related changes that affect the eyes.
Then, have the person really focus on what theyre seeing. That may reset their brain and help them see whats actually in front of them.
If the person doesnt have insight, try a distraction. Move them to a different room. Turn on the TV or play a game they like.
Try to keep your loved one as calm as possible. If they become very agitated or violent, call their doctor or 911.
Read Also: When To Take Parkinson’s Medication
Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis: The What When Why And How
Psychosis is a psychiatric term used in neurology to refer to a spectrum of abnormalities. Parkinsons disease psychosis is where people experience hallucinations or delusions. Hallucinations is seeing, hearing, or smelling things that dont exist. With tactile hallucinations, one can feel a presence that isnt there. Delusions are believing something that is not true, like that a spouse is being unfaithful or caregivers are stealing. In this one-hour talk, movement disorder specialist Christopher Goetz, MD, focuses on hallucinations and spends a little time on delusions.
