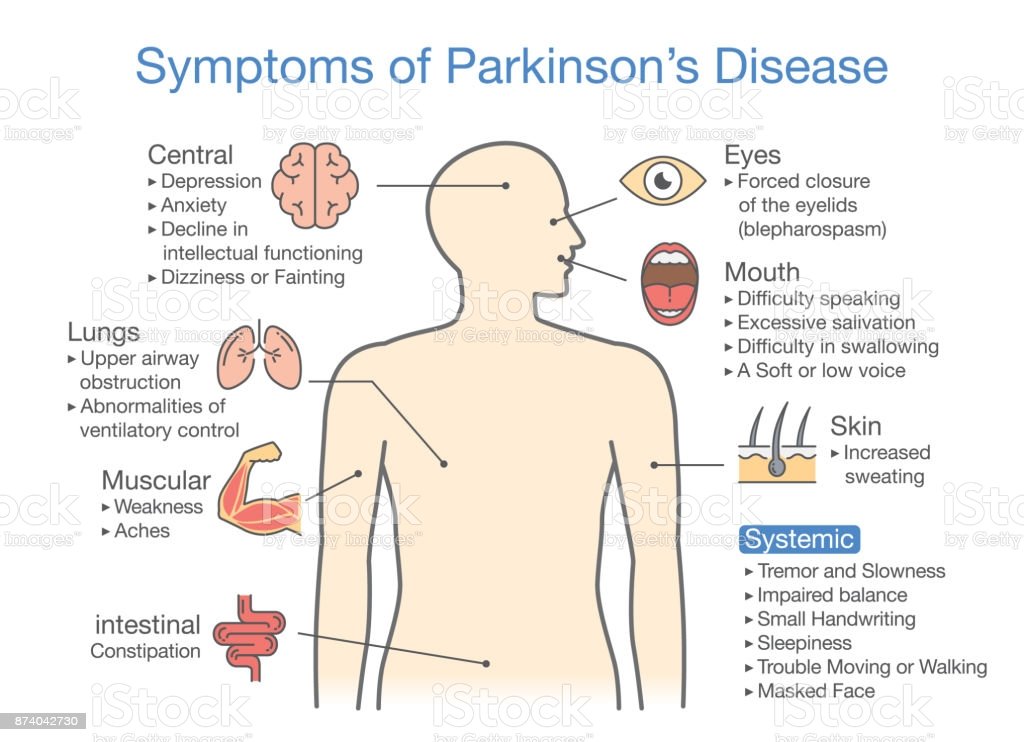
Insight In Brain Activation Studies For Motor Functions
This is an overview of brain activation studies which describes findings that help in our understanding of the pathophysiology of motor, cognitive, and behavioral symptoms seen in Parkinsons disease PD and the underlying neuronal changes. Activation studies of PD patients have been utilized to see the basal-ganglia-thalamocortical circuit function. Several types of motor tasks have been used in conjunction with different neuroimaging techniques to study the motor circuit in PD.
Most common tests included the repetitive tasks, involving either of these two, one was repeated thumb to other finger opposition movements second was manipulation of a joystick in different directions. When normal subjects did repetitive right-hand joystick movements in different directions while they underwent H2O PET, an increase in regional cerebral blood flow was noted in the contralateral primary sensorimotor cortex and lentiform nucleus. Activation was also noted in the bilateral anterior cingulate gyrus, supplementary motor area , lateral premotor cortex, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Opposite to that, PD patients showed a more complex activation pattern, which showed impaired rCBF changes in the lentiform nucleus, anterior cingulate gyrus, SMA, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. However normal activation was seen at the level of sensorimotor cortex, lateral, and parietal premotor cortex when compared with healthy controls .
What Is A Datscan
A DaTscan is an imaging drug, also called Ioflupane I 123 or phenyltropane, that acts as a radioactive tracer for dopamine transporters within the brain. This drug was approved by the FDA in 2011. It may help distinguish the diagnosis of essential tremor from Parkinson’s syndromes, like Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease dementia.
The drug is administered during the SPECT scan. This scanning technique gathers images of a particular area in the brain called the striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum helps facilitate the transportation of dopamine.
DaTscan is injected into the patients bloodstream and eventually circulates to the brain. The tracer attaches itself to a molecule found on dopamine neurons in the striatum called the dopamine transporter . The patient then undergoes a SPECT scan which will produce an image of the dopaminergic neuron terminals that remain available in the striatum.
In patients with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or parkinsonism , this area of the brain will show dark. This indicates the loss of dopamine-containing nerve cells within the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
Tests To Rule Out Other Conditions
Blood tests can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
An MRI or CT scan can check for signs of a stroke or brain tumor, which may cause similar symptoms.
Hydrocephalus due to atrophy can occur with some types of dementia and would be visible with one of these imaging tests. If the person has neurologic symptoms but a normal scan result, Parkinsons disease may be present.
The doctor a lumbar puncture to rule out inflammation or a brain infection.
Don’t Miss: Stage 4 Parkinson’s Life Expectancy
Ethics Safety And Dissemination
The study will be conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and in accordance with the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act . All unwanted and harmful outcomes spontaneously reported by the participants, that may or not be related to this study, will be recorded. In case of a serious adverse event, the Ethics committee and relevant authorities will be notified immediately.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Committee of the Maastricht University Medical Centre and written informed consent will be obtained from all participants prior to inclusion. Also, participants are given the choice to provide additional consent for the use of study data and biological specimens in ancillary studies. Before consenting, all participants will be extensively informed about the study. During the study patients have the right to withdraw from the study without explanation at any time.
Monitoring of the study will be performed at random moments by employees of CTCM. Those employees are trained and certified in monitoring studies and are not in any way involved in the study.
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as;stroke, tumors,;hydrocephalus;, and Wilsons Disease .
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy With Parkinsons
How Can Magnetic Resonance Imaging Help
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to monitor a large variety of disorders and diseases throughout the body. the images produced during an MRI scan may show tissue structures and organs in excellent detail. Functional MRI is one technique that can provide information about the body during certain activities. Both conventional and functional MRI may help show the progress of diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, and may show the response to treatments.
Functional MRI may be used to image the brain during movement. Research for Parkinson’s disease has included fMRI to monitor what regions are activated during automatic motion.4 This study of 12 patients with Parkinson’s disease practiced sequences of finger movement until they were able to be done automatically. Then, they underwent fMRI to compare their scans before and after they had learned the sequences. The results showed that the most of the same areas of the brain were active while performing the sequences before or after they became automatic. Subjects without Parkinson’s had significantly reduced activity in the brain after automaticity. This means that patients with Parkinson’s disease had more trouble performing the actions than the people without.
Exclusion Of Symptomatic Parkinsonism
Structural brain imaging using cMRI with visual assessment of T2- and T1-weighted sequences including contrast-enhanced T1 imaging is usually normal in patients with early PD; thus, its traditional role is the detection/exclusion of other underlying basal ganglia or brainstem pathologies . These include vascular, space-occupying or demyelinating lesions within the basal ganglia or brainstem, drug- or toxic-induced parkinsonism, e.g. due to manganism, or neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation , normal pressure hydrocephalus, or infectious causes . Typical MR findings in patients with symptomatic parkinsonism are summarized in Table;.
Also Check: How To Treat Parkinson’s Naturally
Clinical Application Of Brain Mri In The Diagnostic Work
aDepartment of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, The NetherlandsbDepartment of Diagnostic Imaging, Medical Center of Postgraduate Education, Warsaw, PolandcDepartment of Neurology, Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Keywords: Atypical parkinsonism, brain, magnetic resonance imaging, Parkinsons disease
ABSTRACT
Background: Differentiating Parkinsons disease and atypical parkinsonism on clinical parameters is challenging, especially in early disease courses. This is due to large overlap in symptoms and because the so called red flags, i.e. symptoms indicating atypical parkinsonism, have not developed. Brain MRI can aid to improve the accuracy and confidence about the diagnosis.Objective and Methods: In the current paper, we discuss when brain MRI should be performed in the diagnostic work-up of parkinsonism, our preferred brain MRI scanning protocol, and the diagnostic value of specific abnormalities.Results and Conclusions: The main purpose of brain MRI is to assess cerebrovascular damage, and to exclude other possible and sometimes treatable causes of parkinsonism, such as normal pressure hydrocephalus. Furthermore, brain MRI can support the possible or probable diagnosis of a specific form of atypical parkinsonism.
INTRODUCTION OF THE CLINICAL DILEMMA
DESCRIPTION OF THE TEST
DISCUSSION
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
What Tests Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
There currently are no tests that can definitively diagnose Parkinsons Disease. A diagnosis is based on the clinical findings of your physician in combination with your report on the symptoms you are experiencing.
In situations where an older person presents with the typical features of Parkinsons and they are responsive to dopamine replacement therapy, there is unlikely to be any benefit to further investigation or imaging.
Read Also: How To Deal With Parkinson’s Disease
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
This study will be conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and in accordance with the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act . The handling of personal data will comply with the EU General Data Protection Regulation and the Dutch Act on Implementation of the GDPR. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Committee of the Maastricht University Medical Centre , and registered in the Dutch Trial Register . Written informed consent is obtained from all participants prior to inclusion. Participants who are not able to provide informed consent due to limitations in their cognitive status, will be excluded from participation. During the study, patients have the right to withdraw from the study without explanation at any time.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a disorder that affects the nervous system and movement.2,3 The symptoms typically begin gradually, and it may take a while for patients to notice them. These symptoms may include tremors, slow movement, rigid muscles as well as speech and writing changes. Patients may also experience impaired posture and balance or loss of automatic movements, such as blinking, smiling or swinging their arms.
Parkinson’s has a variety of risk factors that should be considered. In many cases, Parkinson’s usually affects people who are 50 years of age or older.2,3 However, some patients may experience young onset Parkinson’s disease, also called early-onset Parkinson’s disease, which affects roughly 2-10% of the population with Parkinson’s in the United States.3 Men may be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease than women.2 If a close relative has Parkinson’s disease, a patient may be more likely to develop the disorder. The risk may still be small unless there are a large number of relatives with Parkinson’s disease. Finally, long-term exposure to herbicides and pesticides may slightly increase a patient’s risk.2
Once the disease has begun to progress, there are five stages that patients may experience.
Don’t Miss: Do Lewy Bodies Cause Parkinson’s
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
Coming to terms with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s and living with the disease is challenging and will take a lot of adjustment. There are still things you can do that can help you to feel more in control of your situation and to stay positive. Some things that might help could include:
- choosing to lead a healthy lifestyle
- making informed decisions related to your treatment
- keeping a diary of your symptoms in preparation for meetings with health and social care professionals
- attending a self-management course
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
A diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is likely if you have at least 2 of the 3 following symptoms:
- shaking or tremor in a part of your body that usually only occurs at rest
- slowness of movement
- muscle stiffness
If your symptoms improve after taking a medication called levodopa, it’s more likely you have Parkinson’s disease.
Special brain scans, such as a;single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases;to try to;rule out;other causes of;your symptoms.
Also Check: Where Is The Lesion In Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a disorder that affects the nervous system and movement.2,3 The symptoms typically begin gradually, and it may take a while for patients to notice them. These symptoms may include tremors, slow movement, rigid muscles as well as speech and writing changes. Patients may also experience impaired posture and balance or loss of automatic movements, such as blinking, smiling or swinging their arms.
Parkinsons has a variety of risk factors that should be considered. In many cases, Parkinsons usually affects people who are 50 years of age or older.2,3 However, some patients may experience young onset Parkinsons disease, also called early-onset Parkinsons disease, which affects roughly 2-10% of the population with Parkinsons in the United States.3 Men may be more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.2 If a close relative has Parkinsons disease, a patient may be more likely to develop the disorder. The risk may still be small unless there are a large number of relatives with Parkinsons disease. Finally, long-term exposure to herbicides and pesticides may slightly increase a patients risk.2
Once the disease has begun to progress, there are five stages that patients may experience.
The Importance Of Early Diagnosis
Early detection and diagnosis is important because the treatments for PD are more effective in the early stages of the disease. In addition, physical therapy and , which greatly improve symptoms and delay progression of the disease, are much easier to perform in the early stages.
Current diagnosis is made through the presence of motor symptoms; however, researchers have found that by the time motor symptoms occur, over 60% of all dopamine neurons in the basal ganglia of the brain have been damaged. Non-motor symptoms become apparent in people with PD long before motor symptoms, including sleep disturbances and loss of the sense of smell.3
Active areas of include looking for markers in the blood, urine, or cerebral spinal fluid that reliably detect PD, called . In addition, brain imaging tests that have high sensitivity for detecting PD are also being actively researched.4
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Personality
What Is Essential Tremor And How Is It Different To A Parkinsons Tremor
A tremor is a rhythmical, involuntary movement that affects a part of the body, such as the hand.
Essential tremor is the most common type of tremor. Its most noticeable when your hands are doing something and it usually affects both the right and left sides of the body equally. Essential tremors often lessen when your body is resting.;
Unlike an essential tremor, a Parkinsons tremor is most obvious when the affected body part is resting and tends to be less noticeable with movement. It usually starts on one side of the body and may progress to the other side as Parkinsons develops.
The time it takes to get a diagnosis can vary from person to person. Some people may receive a diagnosis of Parkinsons quite quickly, but for others it may be a long process. This can be due to a number of things, including your medical history, your age and what symptoms you have.
Your specialist may wish to rule out other causes of your symptoms first and see how you respond to treatment. This may take some time, and, as already mentioned, there is currently no definitive test;for Parkinsons.
How you respond to treatment may help your specialist make a diagnosis. Keeping a diary or record of your symptoms will give the specialist more information to guide their decision.
Because the symptoms of Parkinsons are sometimes similar to other forms of parkinsonism, people can sometimes be misdiagnosed.;
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Participants are eligible for participation in this study if they meet the following criteria: 1) All patients have to be diagnosed with PD by a neurologist, within the last 3years before inclusion. 2) A score of 24 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment at baseline. 3) Able to read and understand Dutch. 4) 18years of age or older. 5) Providing written informed consent.
Participants with advanced cognitive impairment, defined as a score of <24 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment , or a diagnosis of dementia according to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders criteria at baseline, will be excluded from participation. The presence of a clear diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases other than PD is also an exclusion criterion. Lastly, potential participants cannot take part if there are any contra-indications for a 7T MRI scan, such as claustrophobia, permanent makeup or the presence of incompatible metallic devices in their body. These exclusion criteria are also in place for the HC group.
Also Check: What Causes Hallucinations With Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease Early Stages Detected With ‘simple’ Mri; Up To 85% Accurate
Detecting a life-threatening disease could give researchers the power of earlier diagnosis, treatment approaches, and innovative therapies a power that could one day possibly lead to cure a disease like Parkinsons. Researchers from Oxford University published their findings in the journal of Neurology, which reveal a promising new diagnostic approach for the early stages of Parkinsons disease.
At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinson’s disease in the vast majority of cases, said Dr. Clare Mackay, the studys co-author and professor of the Department of Psychiatry at Oxford University. Oxford researchers are turning the tables on that bleak risk evaluation now that they have developed an expediently simple technique to diagnose early Parkinsons stages with a magnetic resonance imaging machine with 85 percent accuracy. A normal MRI scan cannot detect the early signs, which is why researchers used restating state functional MRI to look at how strong the brain connections were in the basal ganglia, where important dopamine nerves are located.
We think that our MRI test will be relevant for diagnosis of Parkinson’s, said Dr. Michele Hu, the studys co-author and professor of the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences at Oxford University and the Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust.
Why Doctors Consider Mri To Detect Dementia
Medical experts will advise on the use of MRI when they suspect that a person has dementia.
MRI uses focused radio waves and magnetic fields to detect the presence of hydrogen atoms in tissues in the human body.
MRI scans also reveal the brains anatomic structure with 3D imaging allowing doctors to get a clear view of the current state of the organ.
This way, the doctor is able to rule out other health problems like hydrocephalus, hemorrhage, stroke, and tumors that can mimic dementia.
With these scans, physicians can also detect loss of brain mass that relates to different types of dementia.
fMRI records blood flow changes that are linked to the activities of the brain. This may help physicians differentiate dementia types.
Verywellhealth.com also suggests that MRI scans can at times identify reversible cognitive decline.
In such a case, a doctor will recommend appropriate treatment that will reverse this decline and restore cognitive functioning.
You May Like: Can Anxiety Cause Parkinson’s Symptoms
