What Is The Difference Between A Parkinson’s Disease Patient With Dystonia And A Dystonia Patient With Parkinson’s Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological movement disorder with a wide array of symptoms that includes slowness of movement, rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes, and others. The movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be called parkinsonism. Parkinsonism is one aspect of Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms of dystonia and parkinsonism can occur in the same patient because both of these movement disorders seem to arise from involvement of the basal ganglia in the brain. Both parkinsonism and dystonia can each be caused by a great many disorders, and some of these disorders includes features of both parkinsonism and dystonia.
For example, there are the disorders known as dopa-responsive dystonia and x-linked dystonia-parkinsonism . DRD commonly begins in children as a dystonia predominately affecting the feet and being first manifested by an abnormal gait. In these children, features of parkinsonism tend to develop such as slowness of movement and also decreased muscle tone.
When DRD begins in adults, it usually appears first as parkinsonism and can be mistaken for Parkinson’s disease. XDP can also first develop as either dystonia or parkinsonism, and the symptoms of other disorder may occur.
Is Dystonia A Form Of Parkinson’s
Dystonia can be one of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease . PD is a long-term neurological movement disorder with various symptoms ranging from slowness of movement , rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes and others. In young-onset PD, foot dystonia may be the first feature. Later, other symptoms such as personality changes and memory impairment become noticeable.;
Dystonia may sometimes develop as an isolated symptom in individuals who do not have PD. It may be seen in people who suffer from Huntingtons chorea, birth injury, stroke, brain infections, etc. Sometimes, a person with Parkinsons may develop dystonia due to the drug Leva Dopa that is given as a part of PD treatment.
Dystonia is a neurological disorder that purely affects movement and is characterized by involuntary contractions of the muscles causing repetitive or twisting movements or abnormal postures. Dystonia can occur in isolation or as a symptom of PD. It, however, does not affect everyone with PD.
Both PD and dystonia seem to occur due to the involvement of a part of the brain called the basal ganglia. Thus, the symptoms of both can occur in the same person.
Experiencing Pain Or Symptoms That Concern You
Call: 310-582-7433
While it is relatively uncommon, cervical dystonia is by no means rare. Exact prevalence rates are not available, but an estimated 60,000 160,000 Americans are living with cervical dystonia. In one study, only half of these patients reported being treated for their condition. Cervical dystonia often comes on in mid-life but can begin at any age, and typically affects women twice as frequently as men.
In addition to neck pain, many patients may manifest with a head tremor. Often patients assume that tremor is due to more common causes, such as Parkinsons disease and essential tremor. However, isolated head tremor should be considered undiagnosed cervical dystonia until proven otherwise.
A tremor in cervical dystonia tends to be jerky and irregular and often is worse in the direction of the head away from the abnormal positioning. So, if cervical dystonia is causing a head turn to the right, tremor may be worst when the patient attempts to turn their head to the left.
Cervical dystonia is known by many names, and the terminology can get confusing at times. The most common alternate name is spasmodic torticollis, but;torticollis;may also refer to the specific position of head turning to left or right, whereas head tilt is known as laterocollis. When the neck is extended it is known as retrocollis, whereas neck flexion is known as anterocollis.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Evidence On Actual And Illusory Tactile Information Processing In Pd And Dystonia
In conclusion, STDT abnormalities in dystonia may reflect defective inhibitory activity at both the cortical and subcortical levels and create a permissive background for the development of other pathophysiological processes in dystonia. Which of these pathophysiological processes are directly linked to motor symptoms remains unknown.
When the Aristotle illusion paradigm was applied to PD patients, patients and healthy controls were found to experience the same illusory doubling perception . Hence, tactile perception involving an inter-digit functional relationship appears to be preserved in PD .
Interestingly, the same paradigm applied to patients with dystonia revealed a different pattern of results. The illusion was found not to occur in focal hand dystonia when the non-affected fingers of the affected hand were touched, whereas it did occur when the object came into contact with the affected fingers . This study thus demonstrated a very specific tactile alteration that was present in the affected hand of patients with focal hand dystonia though not in patients with other types of dystonia, such as cervical dystonia and blepharospasm . This finding suggests that the impairment in inter-digit tactile perception is, unlike other kinds of tactile deficits, specific to focal hand dystonia.
Can You Get Dystonia Before Parkinsons

Can you get dystonia BEFORE parkinsonsPyr2
Pyr2
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Study Protocol And Follow Up Analysis
Patients with idiopathic CD were assessed preoperatively and at defined follow up visits according to a standard protocol including a modified Toronto western spasmodic torticollis rating scale , as used earlier, consisting of subscores for the severity of CD , functional disability , and pain ; mini mental state examination ; Hamilton depression scale; and a standard videotape protocol. The TWSTRS could not be used for the patient with bilateral oscillating phasic torticollis. All formal assessments were performed by the neurologists on the study team.
Patients with cervical dyskinesias and cervical myelopathy were assessed with a cervical dyskinesia rating scale adapted from the Burke-Fahn-Marsden scale. This scale has not been validated thus far. The severity of dyskinesias at rest and during movement was graded on a scale of 0 to 4. An overall score was then calculated according to the following formula: ×)+×). Thus, the maximum possible overall CDRS score was 28.
Clinical assessments were made preoperatively, 1 week, and 3 months after the operation, and at subsequent 3 month intervals up to 1 year postoperatively. Long term follow up assessments were planned at 6 month intervals subsequently. New assessments were also made preoperatively in those patients who needed replacement of implantable pulse generators because of depletion of the batteries. For statistical analysis the paired t test and the Wilcoxon signed rank test were used.
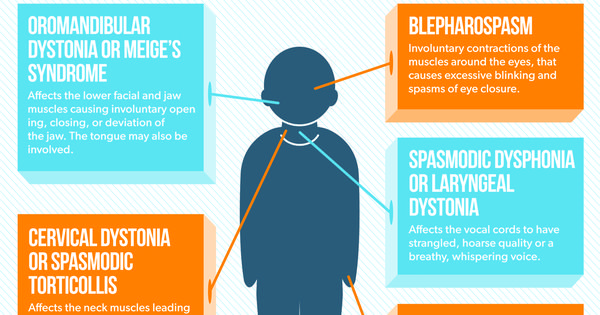
What Dystonia Looks Like In Pd
The involuntary muscle movements of dystonia can be subtle or very noticeable. They may manifest as:
-
Blepharospasm , squinting or repeated blinking
-
Grimacing or repeated jaw clenching
-
Thin, hoarse or shaky voice
-
Twisting of the neck into an abnormal posture
-
Twitching and cramping of the hands, fingers, feet or toes
If you experience symptoms of cervical dystonia, you should notify your doctor right away. Keeping a log of your dystonia symptoms can be helpful in finding the right treatment.
You May Like: Mds Cancer Ribbon Color
Dystonia Or Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps and dystonia occur when one of your muscles, or a group of muscles, tightens or shortens involuntarily.
Muscle cramps and dystonia can be confusing as they can feel very similar. You may not always be able to tell the difference between them, but they are caused by separate problems and are therefore treated differently.
Muscle cramps in Parkinsons are generally caused by muscular rigidity and reduced movement rather than by muscles contracting. But, like dystonia, cramps can also be painful and very distressing.
Normal painkillers do not usually relieve them, but cramps often respond well to massage and the use of a hot water bottle or heated pad. Movement and exercise may also help to release cramps and reduce stiffness. If these do not help, then your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants.
Potential Factors Driving The Occurrence Of Parkinsonian Features
Neither TWSTRS torticollis severity on stimulation nor the percentage reduction of torticollis severity upon stimulation correlated with the MDS-UPDRS motor scores or any of its subscales . Similarly, upon switching stimulation off, the percentage increase in torticollis severity did not correlate with the decrease in MDS-UPDRS motor scores or any of the subscales . The duration of stimulation and stimulation amplitude did not correlate with the MDS-UPDRS motor or any of the subscores .
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Standard Treatments Partially Normalise Ssrt
Although SSRT did not correlate with disease severity, when patients were treated SSRT was reduced. In PD patients, the SSRT was significantly reduced by levodopa treatment. This is in agreement with past work which showed an improvement in response inhibition in the ON phase, although two previous studies failed to find a decrease specifically in SSRT with dopaminergic medications,. It is possible that our improved approach to estimation of SSRT allowed us to detect a relation, which could otherwise be masked by measurement variability.
It is perhaps not unexpected that treatment with a centrally-acting drug such as levodopa could modulate response inhibition. Interestingly, the patients with more prolonged OFF ocSSRT demonstrated a positive correlation with change in ocSSRT after levodopa administration. This differential correlation could suggest that RT and ocSSRT may be measuring underlying processes which are differently affected by the disease.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dystonia
The symptoms of dystonia may vary from person to person. Various types of dystonia can affect only one muscle, groups of muscles or muscles throughout the body. In childhood or early-onset dystonia, the symptoms often start in the limbs and may progress to involve other parts of the body. Symptoms may occur after periods of exertion. They may fluctuate throughout the course of the day.
In adult-onset dystonia, the symptoms usually affect one or adjacent parts of the body, most often involving the neck and/or facial muscles.
Involuntary muscle contractions may affect a single area such as the leg, jaw or arm.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Ribbon Color
How Can I Help Myself
You will need to try a variety of sensory tricks to see what works for you as dystonia affects everyone differently.
Spasms may be reduced by touching the affected part of the body either before or during any movement known to trigger dystonia. Although this may not prevent or stop a spasm, touching can distract or trick the brain and reduce the length and intensity of a muscle contraction.
Simple massage exerting pressure on the foot, or the use of a hot water bottle or heated pad can also help, as can movement and exercise – see Coping Strategies – Tips & Tricks.
For eye spasms, some people find lying down, singing, yawning, laughing, chewing, putting pressure on the eyebrows or just talking can help. Spasms in the vocal cords may respond to yawning or sneezing.
Simply relaxing may also help so try taking a bath, having a massage or a calming activity such as yoga.
Clinical Outcome Of Patients With Cervical Dystonia
All patients were available for regular follow up examinations. The dystonia improved gradually over the next 6 months during adaptation of the stimulation settings. Phasic components improved earlier, and dystonic postures improved later. A representative example is shown in figure 2. The subtle dystonic movements of body parts other than the neck disappeared after prolonged stimulation. Anticholinergic medication was tapered off in all patients during follow up, and benzodiazepines in two patients were reduced. The first patient in this series had several exacerbations of CD in the late follow up . Two such episodes were due to unilateral electrode fractures, and two to implantable pulse generator battery depletion. Each time, CD had become worse within a few hours. After replacement of the non-functioning hardware, clinical improvement was noted to occur with much less delay than before. Patient 5, with bilateral oscillating phasic torticollis, had a more variable course. The dystonic movements were minimal during the first 3 months after surgery, but later recurred on several occasions and finally improved only after extensive reprogramming of the stimulator. Improvement has been stable in the other three patients.
Figure 3
Radiography of patient 1 showing a fracture of the left lead just above the connection to the extension wire. The electrode was replaced stereotactically. The connector was placed behind the ear in subsequent procedures.
Don’t Miss: Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s
Optimal Combination Ssrt As A Measure Of The Stopping Process
In this study we introduced ocSSRT as an improved method for estimating SSRT. Most of the literature has reported results based on the avSSRT. The ocSSRT was in agreement with the avSSRT when measured from the same experiment, thus validating this newly-developed statistical measure. However, the test-retest reliability for a group of healthy participants who performed the trial on two separate days over an interval of one month showed a much stronger agreement between ocSSRT compared with avSSRT. Either SSRT measure could therefore be used interchangeably in cross-sectional studies where the aim is to compare stopping process among various groups, although the decreased variability of ocSSRT will increase the statistical power of comparisons and there would be more chance for the differences to reach significance with fewer subjects. For a prospective study, ocSSRT would also have advantages over avSSRT due to its higher test-retest reliability.
Conflict Of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer MP declared a shared affiliation, with no collaboration, with one of the authors, AC, to the handling editor at time of review.
Read Also: Parkinsons And Alzheimers Life Expectancy
General Summary And Hypotheses For Potential Therapeutic Strategies
In this narrative review we have described a number of abnormalities in somatic sensory input processing that have been reported in PD and dystonia. We have also shown that these abnormalities are not limited to unimodal sensory processing but are also very evident in somatosensory and sensorimotor integration processes.
The cerebral network underlying these abnormal processes of integration is likely to include the basal ganglia and the sensorimotor areas of the cerebral cortex for PD, and to extend to the cerebellum in dystonia. Although the extent to which somatic sensory processing and integration mechanisms contribute to the mechanisms underlying motor disturbances in PD and dystonia has only partially been investigated to date, the possibility of manipulating sensory information to improve motor deficits in PD and dystonia deserves further attention.
Sensorimotor retraining may serve as a therapeutic strategy in movement disorders. There is some evidence that the modulation of somatosensory cortical activity by means of non-invasive brain stimulation improves motor symptoms and induces self-perceived improvement . Furthermore, in patients with PD as well as in patients with focal dystonia muscle vibration, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and kinesio-taping used for sensory retraining purposes seems to improve sensory and motor disturbances .
What Treatment Is Available
For treatment to be effective, it is essential to understand the trigger or cause of the dystonia. Certain medications may be effective for some people but not for others. Some work by interfering with neurotransmitters in the brain and disrupting the messages they send to muscles. Others work by relaxing the muscles to reduce shaking and improve muscle control.
Depending on the cause and severity of your dystonia, your doctor may suggest the following strategies:
Remember that not all of these strategies will work for everyone so it is important to communicate well with your doctor so that, together, you can find the best solution for you.
Keeping a diary: If the dystonia is levodopa-related, it is a good idea to keep a ‘motor diary’ to record when dystonic spasms occur and how they relate to the timing of medications. This information can help your doctor adjust dosage and/or timings of medication to better manage your dystonia. For more information, see;Keeping a diary.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Prognosis Life Expectancy
Dystonia Classification By Body Part
Focal Dystonia
Focal dystonia is limited to one area of the body and can affect the neck , eyes , jaw/mouth/lower face , vocal cords or arms/legs . Other less common types of focal dystonias can cause unusual stretching, bending or twisting of the trunk or sustained contractions and involuntary, writhing movements of the abdominal wall .
Focal dystonia more commonly affects people in their 40s and 50s and is frequently referred to as adult-onset dystonia. Women are affected about three times more frequently than men. In general, focal dystonias are classified as primary and are not hereditary.
Symptoms Of Cervical Dystonia
Pain is the most frequent and challenging symptom of cervical dystonia. The pain is usually on the same side of the head as the tilt.
The most common abnormal movement in cervical dystonia is a twisting of the head and chin sideways, toward your shoulder, called torticollis. Other abnormal movements include the head:
- tipping forward, chin downward, known as anterocollis
- tilting backward, chin upward, called retrocollis
- tilting sideways, ear to shoulder, known as laterocollis
Some may have a combination of these movements. Also, the symptoms may vary over time and by individual.
Stress or excitement may aggravate symptoms. Also, some physical positions may activate symptoms.
The symptoms usually begin gradually. They may get worse and then reach a plateau. Other symptoms may include:
- neck pain that radiates to the shoulders
- a raised shoulder
Pain is a main symptom of cervical dystonia. People respond individually to different types of drugs and combinations of treatments. What works for others may not work for you.
Also Check: Which President Had Parkinson’s Disease
