What Are The Symptoms Of End
Stage four for Parkinsons disease is often called advanced Parkinsons disease because people in this stage experience severe and incapacitating symptoms. This is when medication doesnt help as much and serious disabilities set in.
Theres an increased severity in:
- How you speak a softer voice that trails off.
- Falling and trouble with balance and coordination.
- Freezing a sudden, but temporary inability to move, when you start to walk or change direction.
- Moving without assistance or a wheelchair.
- Other symptoms such as constipation, depression, loss of smell, low blood pressure when going to stand up, pain, and sleep issues.
Many times someone with advanced PD cant live on their own and needs help with daily tasks.
Stage five is the final stage of Parkinsons, and assistance will be needed in all areas of daily life as motor skills are seriously impaired. You may:
- Experience stiffness in your legs. It may make it impossible to walk or stand without help.
- Need a wheelchair at all times or are bedridden.
- Need round-the-clock nursing care for all activities.
- Experience hallucinations and delusions.
As Parkinsons disease progresses into these advanced stages, its symptoms can often become increasingly difficult to manage. Whether you or your loved one with end-stage Parkinsons lives at home, in an assisted living facility or a nursing home, hospice services can optimize your quality of life and that of your family members as well.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Challenges To Classify Disease Stages At The Boundary Of Advpd And Atypical Parkinsonism
During disease progression and based on the predominant motor and non-motor features associated with advPD, the separation from atypical parkinsonism may be difficult and overlap syndromes like minimal change multiple system atrophy or progressive supranuclear palsy with predominant parkinsonism have been described . AP includes a heterogeneous bunch of syndromes, all characterized by clinically manifest parkinsonism in combination with other clinical features and a poor therapeutic response to dopaminergic medication. Only post-mortem analyses can clearly differentiate from advPD, as their neuropathology is characteristically different: in MSA, alpha-synuclein accumulation is found and defines an alpha-syncleinopathy as PD, but mainly in glial cells as cytoplasmic inclusions . In contrast, PSP and corticobasal degeneration are referred to as tauopathies due to characteristic intraneuronal tau aggregation and some TDP-43 proteinopathies might also develop clinical parkinsonism .
In this context, technical tests might further improve the quality of differential diagnosis. Autonomous tests, such as tests for cardiovascular, urinary, thermoregulatory or gastrointestinal dysfunction can be helpful for the diagnostic differentiation PD versus AP. Due to a marked overlap, the combination of several tests such as urodynamic investigation, tests for orthostatic dysregulation, RR-intervals and sympathetic skin response can contribute to support the correct diagnosis.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Having Parkinsons Is Not A Death Sentence
Parkinsons disease is not fatal, and your life expectancy depends highly on the type of Parkinson’s you have. If the type of disease isn’t causing issues with brain function, you can potentially live as long as people without the disease.
However, if someone has an atypical case of the condition that occurs at the same time as other conditions such as dementia, this can negatively affect their life expectancy.
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Parkinson’s Disease
The severity of Parkinson’s disease symptoms and signs vary greatly from person to peson, and it is not possible to predict how quickly the disease will progress. Parkinson’s disease itself is not a fatal disease, and the average life expectancy is similar to that of people without the disease. Secondary complications, such as pneumonia, falling-related injuries, and choking can lead to death. Many treatment options can reduce some of the symptoms and prolong the quality of life.
Also Check: Does Parkinson Cause Memory Loss
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
How Fast Does Parkinson’s Disease Progress
People tend to move through the Parkinson’s disease stages slowly, usually over the course of years. Research has shown that the disease tends to progress less rapidly in people who are diagnosed at a younger age than those diagnosed later in life.
What’s more, Parkinson’s disease may begin decades before a patient even notices a single motor symptom.
“We know that Parkinson’s disease actually starts many, many years before you see that tremor or that shuffling,”Lynda Nwabuobi, MD, assistant professor of clinical neurology at Weill Cornell Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Institute, tells Health. “We think at least 30 years.”
Also Check: Parkinson Life Expectancy Early Onset
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Early Signs Of Parkinsons Disease Dementia
In the beginning, PDD can be subtle. Early on, there may be memory loss and difficulties with daily activities, says Michael S. Okun, M.D., executive director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases at University of Florida Health in Gainesville. Delusions or hallucinations may also start to happen. Dr. Petrossian points out that there can be an overlap between the early signs of dementia and mild cognitive impairment due to Parkinsons disease, which can make it difficult to learn new skills and recall information or conversations.
You May Like: Does Amy Klobuchar Have Parkinson’s
Caregiving In The Late Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
In late-stage PD, patients have significant mobility challenges. Caregivers likely need to provide more hands-on assistance to help them get around the house. Its important that caregivers learn safe and effective methods to provide help without injuring themselves. Physical therapists can be a great resource to assess an individual situation and teach effective ways of giving assistance.3
Freezing, a sudden but temporary inability to move, can become more common in late-stage PD. Freezing often happens when initiating movement or navigating around obstacles, and freezing episodes contribute to falls. Caregivers can help their loved one overcome freezing by providing a visual cue to step over, like a laser pointer, or using music or rhythm for the person with PD to walk to.3
Late stage PD can make daily activities, such as getting dressed, much more challenging. Caregivers can make getting dressed easier by ensuring adequate time to account for slow movement, choosing a time when medications are “on” and working well, and assembling all necessary items close to the person. Allowing the person with PD to do as much as they can gives them a sense of participation in the process.3
Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal
Parkinsons disease itself doesnt cause death. However, symptoms related to Parkinsons can be fatal. For example, injuries that occur because of a fall or problems associated with dementia can be fatal.
Some people with Parkinsons experience difficulty swallowing. This can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This condition is caused when foods, or other foreign objects, are inhaled into the lungs.
Read Also: Parkinsons Disease Deaths
Typical Timescale For Pdd
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, PDD is typically diagnosed when a person living with Parkinsons disease experiences cognitive decline after a year or more of motor symptoms. But in most cases, people experience many years of tremors, slowness of movement, and muscle cramps before showing signs of significant cognitive decline. The Weill Institute for Neurosciences estimates the average time from onset of movement problems to developing dementia is 10 years. An estimated 50% to 80% of people with Parkinsons will eventually experience Parkinsons disease dementia, says the Alzheimers Association.
Treating Parkinsons Disease Dementia

A treatment plan for PDD typically includes medications that boost the brains level of certain neurotransmitters and help improve memory and processing speed, Dr. Petrossian says. Exercise is also an important part of the treatment planDr. Petrossian recommends skill-based activities like boxing or dance to boost cognitive function as well as fitness. PDD symptoms should be monitored long-term by a neurologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, says Dr. Okun. In many cases, physical, occupational, speech, and social work therapy can also be useful since PPD affects all aspects of life.
Read Also: Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder Parkinson’s
What Are The Non
Parkinson’s disease stages are defined by the severity of a patient’s motor symptoms and how much those symptoms impact one’s ability to function every day. But there are non-motor symptoms that are more likely to develop later in the disease, too, and a doctor may take those into consideration when assessing someone with the disorder.
For example, people with late-stage Parkinson’s disease might have difficulty chewing, eating, speaking, or swallowing , which is considered both a motor and non-motor symptom. Dysphagia in particular can lead to serious health problems like malnutrition, dehydration, and aspiration.
In the final stages of Parkinson’s disease, a person might develop cognitive changes, including slowness of memory or thinking, trouble planning and accomplishing tasks, and difficulty concentrating. Or they might notice changes in their bone health or vision.
But there’s no telling for sure if or when these symptoms will occur in any individual because Parkinson’s disease symptoms vary from person to person.
How Can Hospice Help Your Loved One In The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Hospice care is an extra layer of support to help you care for your loved one with end-stage Parkinsons disease. It is a special kind of care that provides comfort, support, and dignity at the end of life.
The comprehensive program focuses on physical, emotional, and spiritual quality of life through the help of a team of experts. The team includes a board-certified physician, nurse, social worker, certified home health aide , spiritual support counselor, and volunteer.
The nurse will explain the prognosis and what to expect in the upcoming days or weeks. They will also monitor pain and other symptoms. The CHHA helps with personal care needs like bathing and changing bed linens. The social worker helps address social, emotional and practical challenges including complex and inter-related needs. The spiritual support counselor helps explore spiritual concerns.
Most importantly, the hospice team will be there for you during this difficult time, bringing you peace of mind. The team is on call 24 hours a day even at 2:00 am.
Hospice is about making your final months and weeks as good as possible. This means focusing on what really matters to you.
Don’t Miss: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
The Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease, otherwise known as Parkinsonism, is marked by some distinct symptoms. These include symptoms like:
- Uncontrollable tremors
- Slowed movements
- And more
Parkinsons disease is a disorder that becomes more severe over time, usually. Many doctors rely on the Hoehn and Yahr rating scale when it comes to classifying the severity of symptoms. In todays guide, we will be reviewing the five stages of Parkinsons according to that scale.
If you are suffering from Parkinsons, no matter if you were just diagnosed or are in Stage 5, contact the Texas Institute for Neurological Disorders in the Dallas-Fort Worth region today to get help from a movement disorder specialist along with the rest of our neurologists to create a highly personalized treatment for managing your specific symptoms. There is no cure for Parkinsons yet, but there are ways to significantly reduce negative symptoms. Contact us today to schedule your appointment.
Read Also: 10 Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease That Doctors Often Miss
Get Treatment For Your Parkinsons Today
Whatever stage your Parkinsons is in, our neurology staff, led by Dr. Sundaram, is prepared to give you our full support. We offer highly-personalized care, and will work with your other healthcare providers to deliver you the best solutions we can for managing your Parkinsons. If you are in North Texas or South Oklahoma, contact our providers at Texas Institute for Neurological Disorders to get the custom care you need. Schedule your appointment today.
Complications In Advanced Pd
While worsening of motor function and drug-induced motor complications represents a major challenge in patients with mid-stage to advanced disease, in the advanced stage of PD the most troublesome and distressful complications are usually nonmotor symptoms, including psychiatric and cognitive disorders, autonomic disturbances, and sleep disorders that significantly increase the need for supportive care. Unfortunately, these symptoms are frequently neglected in clinical practice due to limited consultation time, perception of the patient and caregivers that their symptoms are unrelated to the disease, or insufficient awareness of the clinicians, who generally focus on motor symptoms .
Proper supporting care becomes increasingly important in advanced PD. Rehabilitative and support services for patients and family become key interventions as the disease reaches its more debilitating stages and pharmacologic or surgical treatment becomes less relevant. Management of motor and nonmotor complications in advanced PD requires careful and ongoing assessment of whether symptoms are a side effect of medication or related to the progression of the disease .
Medication Issues
|
End of Dose Wears Off Symptoms in Advanced PD |
|---|
|
Systems affected |
|
Progression of motor symptoms Dystonia |
Fragmentation of Dosing
Dopamine Agonists Contraindicated
L-dopa and Dietary Proteins
Motor Issues
Dyskinesias
Dystonia
Freezing
Nonmotor Complications
Hallucinations, Delusions, Psychosis
Depression and Anxiety
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Disease Lifespan
What Is Parkinsons Disease
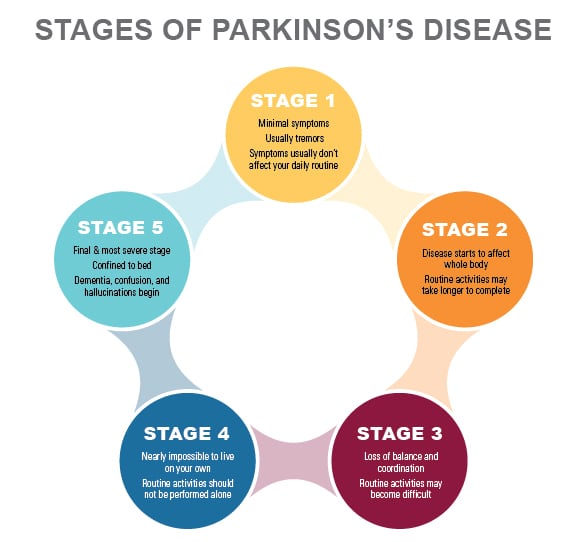
Parkinsons is a neurological illness caused by degeneration or breaking down of cells in the nervous system, explained Dr. Shprecher. The nature of Parkinsons Disease is progressive, meaning that it gets worse over time. To comprehend the natural progression of the disease, we should understand its five stages, as explained by the Parkinsons Foundation.
Stage One
Individuals experience mild symptoms that generally do not interfere with daily activities. Tremor and other movement symptoms occur on one side of the body only. They may also experience changes in posture, walking and facial expressions.
Stage Two
Symptoms worsen, including tremor, rigidity and other movement symptoms on both sides of the body. The person is still able to live alone, but daily tasks are more difficult and lengthier.
Stage Three
This is considered mid-stage. Individuals experience loss of balance and slowness of movements. While still fully independent, these symptoms significantly impair activities such as dressing and eating. Falls are also more common by stage three.
Stage Four
Symptoms are severe and limiting. Individuals may stand without help, but movement likely requires a walker. People in stage four require help with daily activities and are unable to live alone.
Stage Five
