What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
All cases of parkinsonism regardless of the specific condition involved slowed movements plus other related symptoms. What you can expect depends on the specific condition you have and what treatments if any that you receive. Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you more about what you can expect if you have parkinsonism.
How long does parkinsonism last?
How long parkinsonism lasts depends on the specific condition. Nearly all conditions that fall under parkinsonism are life-long conditions. One condition that isnt always a life-long problem is drug-induced parkinsonism.
Because parkinsonism includes so many different conditions, its best to talk to your healthcare provider about how long your condition will last. They can best explain what you can expect, including the likely timeline for how this condition will affect you.
Whats the outlook for this condition?
The outlook for parkinsonism depends on your condition, how severe it is, and whether or not its treatable. Many forms of parkinsonism arent deadly on their own but can contribute to deadly complications. An example of this is trouble swallowing, a common symptom of Parkinsons disease and other forms of parkinsonism, and how this increases your risk of developing pneumonia.
You May Like: Current Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
Stage One Of Parkinsons Disease
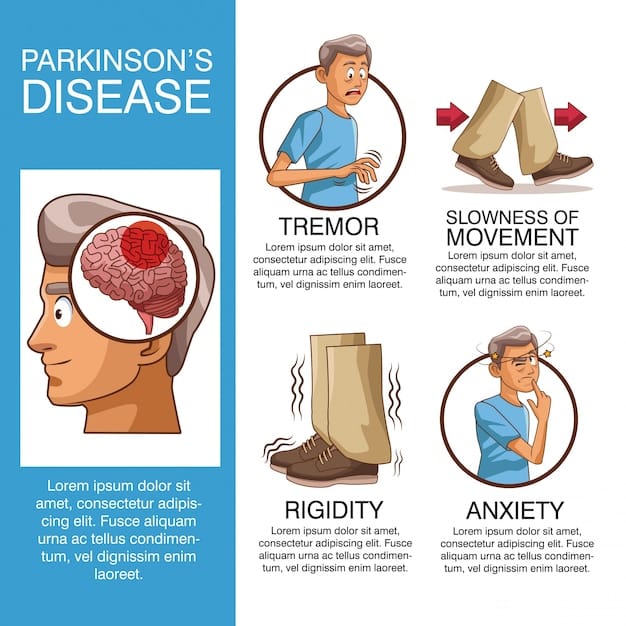
In stage one, the earliest stage, the symptoms of PD are mild and only seen on one side of the body , and there is usually minimal or no functional impairment.
The symptoms of PD at stage one may be so mild that the person doesnt seek medical attention or the physician is unable to make a diagnosis. Symptoms at stage one may include tremor, such as intermittent tremor of one hand, rigidity, or one hand or leg may feel more clumsy than another, or one side of the face may be affected, impacting the expression.
This stage is very difficult to diagnose and a physician may wait to see if the symptoms get worse over time before making a formal diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Changes In Cognition And Parkinsons Disease
Some people with Parkinsons may experience changes in their cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and the ability to plan and accomplish tasks. Stress, depression, and some medications may also contribute to these changes in cognition.
Over time, as the disease progresses, some people may develop dementia and be diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia, a type of Lewy body dementia. People with Parkinsons dementia may have severe memory and thinking problems that affect daily living.
Talk with your doctor if you or a loved one is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease and is experiencing problems with thinking or memory.
Recommended Reading: Is Restless Legs A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Research Roundup: Two Types Of Parkinson’s Disease And More
Every week there are numerous scientific studies published. Heres a look at some of the more interesting ones.
Parkinsons Disease is Actually Two Diseases
Researchers from Aarhus Universityin Denmark indicating that Parkinsons disease is actually two types of the disease. This helps explain why there are so many different symptoms and pathways. Parkinsons is marked by slow deterioration of the brain from accumulation of alpha-synuclein, a protein that damages nerve cells. This causes slow, stiff movements. Some patients apparently have damage to the brains dopamine system before damage in the intestines and heart occurs. Other patients have damage to the nervous systems of the intestines and heart before the damage in the brains dopamine system. The research was published in the journal Brain.
With the help of advanced scanning techniques, weve shown that Parkinsons disease can be divided into two variants, which start in different places in the body, said Per Borghammer, professor of clinical medicine at Aarhus University. For some patients, the disease starts in the intestines and spreads from there to the brain through neural connections. For others, the disease starts in the brain and spreads to the intestines and other organs such as the heart.
Epigenetic Changes May Explain Why Humans Live Longer than Other Primates
Biomarker for Neurodegeneration Identified in the Eye
Children and Adults Have Two Distinct Immune Responses to COVID-19
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Mutation
Lifestyle And Other Protective Factors
Cigarette smoking and caffeine consumption are the two most consistent protective factors associated with a reduced risk of PD. Other reported associations include higher serum urate, ibuprofen use and exercise, among others. The negative association between cigarette smoking and PD is most intriguing. This inverse relationship is not easily explained, but some have suggested that PD-related cautious personality predisposes some individuals to quitting neuroprotective smoking as the biological mechanism involved in PD. The other hypothesis links nicotine to dopaminergic neuronal protection since it has been shown to stimulate the release of dopamine in the striatum and preserve dopaminergic function in experimental models. It is also possible that there are other unidentified neuroprotective components in cigarette smoke.
The relative risk reduction of PD among caffeine drinkers is between 0.5 and 0.8 and, similar to smoking, a dose-dependent effect has been consistently demonstrated in most studies. Caffeine, an antagonist of adenosine A2a receptor, has been postulated to exert neuroprotective role by blocking this receptor. In addition to caffeine, it is possible that antioxidants present in some beverages may contribute to a protective effect among black tea drinkers, independent of caffeine.
Whats The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinsons
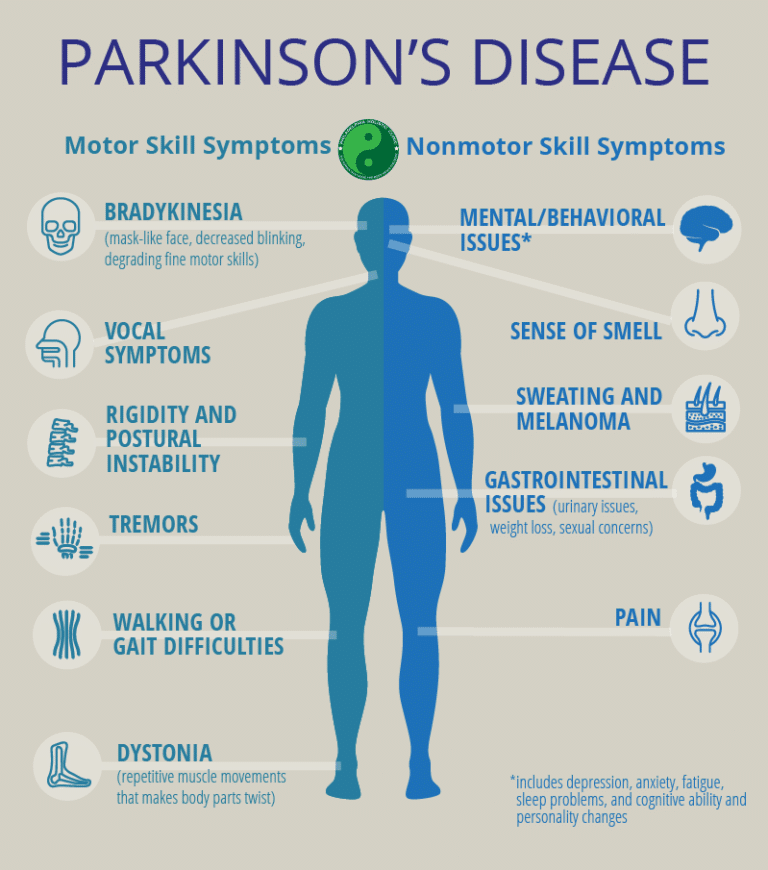
People with PSP generally progress more rapidly than people with Parkinsons. A person with Parkinsons tends to lean forward while a person with PSP tends to lean backward. Tremors are common in people with Parkinsons and rare in people with PSP. Speech and swallowing abnormalities are more severe and show up sooner in those living with PSP.
For more information on progressive supranuclear palsy, read this fact sheet and insights from the CurePSP organization website.
Don’t Miss: How Can A Neurologist Help With Parkinson’s
Every Person With Parkinsons May Experience Different Movements
There are multiple types of movements that a person with Parkinsons disease can experience. Some people may have just one or two of these symptoms, while another may experience all of them. Likewise, the degree of severity can vary from person to person, and symptoms that may bother some people may not bother others at all.
Its important to note that theres not a single answer that works for every person with Parkinsons, says , a neurologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and an instructor in neurology at Harvard Medical School in Cambridge, Massachusetts. You have to ask the person, What bothers you, and how much does it affect you? What the caregiver or the even the physician observes as the most severe symptoms may not feel that way to the person with Parkinsons.
Here are eight types of movements that people with Parkinsons may experience. Learn more about what these symptoms are and what can be done to prevent them.
Different Types Of Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism can be categorized into four different types. These are:
Primary parkinsonism, Familial neurodegenerative conditions causing parkinsonism.
What is Primary parkinsonism?Primary parkinsonism is due to idiopathic Parkinsons disease. It includes sporadic and familial cases and accounts for about 80% of parkinsonism cases.
What is Secondary parkinsonism?This form of parkinsonism, can be caused by a variety of issues. These include drug induced, infections, toxins, vascular, trauma to brain, hemi-atrophy hemi-parkinsonism, brain tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, hypoxia, and metabolic dysfunction.
What is atypical parkinsonism?Most experts include Parkinson plus conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy, and corticobasal degeneration in atypical parkinsonism. The response of these conditions to the dopaminergic medications is usually poor. These cases of parkinsonism may be difficult to distinguish from idiopathic Parkinsons disease especially early in the course the disease.
Two other Parkinson plus conditions are progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasilar degeneration . They differ from Parkinsons disease in that:
i. their neurons do not contain Lewy bodies, but rather a series of intertwined fragments of tau protein ii. target neurons in the globus pallidus and putamenin addition to those in the substantia nigraare destroyed iii. levodopa, typically, elicits no response in these patients.
Notice44
Read Also: How Do You Find Out If You Have Parkinson Disease
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Page last reviewed: 03 November 2022 Next review due: 03 November 2025
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinsons. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
You May Like: Yopd Life Expectancy
Don’t Miss: Foods Not To Eat If You Have Parkinson’s Disease
Deterrence And Patient Education
Parkinsonism in any form is debilitating. Preventive measures should be taken to reduce future consequences.
- Patients with parkinsonism are at an increased risk of falling, and thus, appropriate measures like installing handles and bars are necessary
- Adequate driving safety should be maintained – if symptoms get worse patients should refrain entirely from driving
- Patients and families can gain assistance by joining local support groups with similar individuals
- A regular follow-up with the speech therapist is essential
Multiple System Atrophy Formerly Called Shy
As predicted by the name of this parkinsonism, multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems of the body. It affects both the motor skills movement system and the involuntary system of the body. Though the symptoms can often be treated with medications, there is no cure. In addition, there are no drugs that are able to slow the progress of MSA.
You May Like: Masked Facies Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinsons. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinsons also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Parkinsonism Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Often confused as one and the same, Parkinsons disease is actually the most common kind of Parkinsonism, accounting for nearly 80% of all cases.2 PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the same motor conditions as Parkinsonisms including tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and impaired balance. Other contributing causes of Parkinsonism include multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration. PD has no directly attributable cause or cure.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Parkinsonism
Symptomatic Treatment Of Levodopa
Levodopa-resistant symptoms
There are many levodopa-resistant motor symptoms such as dysarthria and dysphagia, freezing of gait, postural instability and dysautonomia. Freezing, sudden immobility of the feet when attempting to walk, often associated with falls, may be seen in either the off or the on period. Although off-period freezing may improve with optimisation of medications, on-period freezing is usually resistant to pharmacologic treatment.
Physical therapy, including strategies that utilise sensory cues, such as stepping over a horizontal laser beam, may be helpful. Dysarthria and dysphagia are often treated by speech and voice therapists. Injection of botulinum toxin has been found to be effective in controlling high-amplitude rest and postural hand tremor which may be resistant to levodopa. Botulinum toxin may be also beneficial in the treatment of a variety of other non-levodopa responsive parkinsonian symptoms such as blepharospasm, apraxia of eyelid opening, anterocollis, camptocormia, bruxism, sialorrhea, seborrhea, hyperhidrosis, overactive bladder and constipation.
Non-motor symptoms
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Also Check: Wolff-parkinson-white Syndrome Treatment
How Is Psp Diagnosed
Currently there are no tests or brain imaging techniques to definitively diagnose PSP. An initial diagnosis is based on the persons medical history and a physical and neurological exam. Identifying early gait problems, problems moving the eyes, speech and swallowing abnormalities, as well as ruling out other similar disorders is important. Diagnostic imaging may show shrinkage at the top of the brain stem and look at brain activity in known areas of degeneration.
You May Like: Similar To Parkinsons
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
Also Check: What Type Of Disease Is Parkinson’s
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A detailed cognitive assessment is essential for the detection of late-onset dementia. Regular exercise helps in maintaining physical health. Appropriate interprofessional physiotherapy and rehabilitation measures are necessary. A comprehensive approach from each specialty, including physicians and specialists, palliative care, social worker, physiotherapist, speech therapist, mental health nurse, and pharmacists, are of utmost importance to enhance patient care. These various disciplines need to collaborate across interprofessional lines to optimize care and outcomes for patients with parkinsonism.
Parkinsons Disease: Causes Symptoms And Treatments
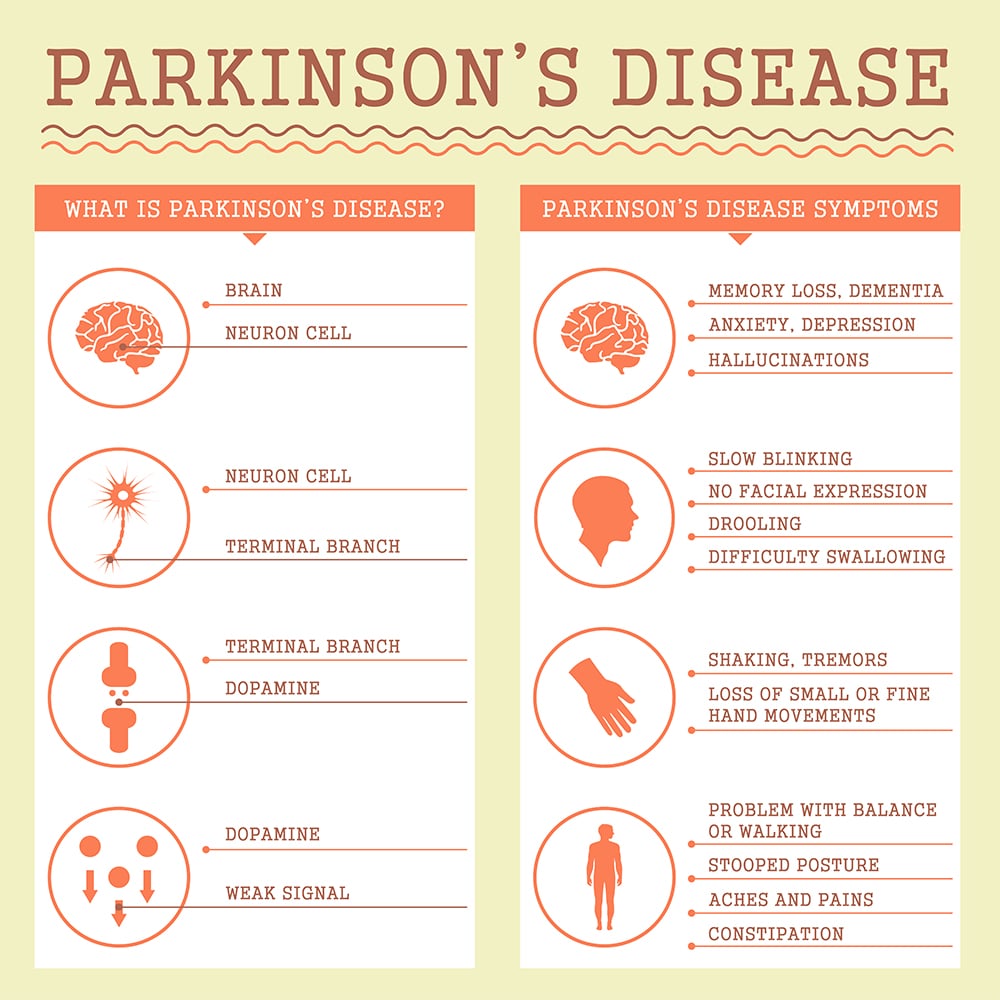
Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talking. They may also have mental and behavioral changes, sleep problems, depression, memory difficulties, and fatigue.
While virtually anyone could be at risk for developing Parkinsons, some research studies suggest this disease affects more men than women. Its unclear why, but studies are underway to understand factors that may increase a persons risk. One clear risk is age: Although most people with Parkinsons first develop the disease after age 60, about 5% to 10% experience onset before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinsons are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked to specific gene mutations.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Impairment
