When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
Finding The Right Treatment
The long list of Parkinsons non-motor symptoms includes constipation, memory and thinking changes, low blood pressure, depression or anxiety, sleep problems and others. A number of therapies are available to treat Parkinsons disease non-motor symptoms, but many patients are left wanting not responding well to therapies or seeing enough relief. Some drugs are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat these conditions in people with PD. Most, however, are FDA-approved for the general population but have not been studied in large numbers of people with PD. Still, doctors commonly prescribe them, and people with Parkinsons often find them beneficial.
Here we describe Parkinsons non-motor symptom treatments. With all Parkinsons symptoms, discuss treatment options with your doctor and work together to find a regimen that fits your needs.
Dementia
Parkinsons disease dementia is when memory or thinking changes interfere with a persons job, daily activities or social interactions.
What Are The Causes
Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications that reduce dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that works to control bodily movements.
Dopamine is also part of the brains reward system. It helps you feel pleasure and enjoyment, and it supports your ability to learn and focus.
Medications that bind to and block dopamine receptors are called dopamine antagonists. These medications arent used to treat Parkinsons disease. Rather, theyre used to treat other conditions that might seriously impact your quality of life.
If your doctor has prescribed a medication that causes unwanted side effects, you may have options. You may also decide that the side effects are worth it if the medication effectively treats your condition.
Some medications that cause drug-induced parkinsonism include:
Also Check: What Are The First Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
What Is The Prognosis
Tremor is not considered a life-threating condition. Although many cases of tremor are mild, tremor can be very disabling for other people. It can be difficult for individuals with tremor to perform normal daily activities such as working, bathing, dressing, and eating. Tremor can also cause social disability. People may limit their physical activity, travel, and social engagements to avoid embarrassment or other consequences.
The symptoms of essential tremor usually worsen with age. Additionally, there is some evidence that people with essential tremor are more likely than average to develop other neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinsons disease or Alzheimers disease, especially in individuals whose tremor first appears after age 65.
Unlike essential tremor, the symptoms of physiologic and drug-induced tremor do not generally worsen over time and can often be improved or eliminated once the underlying causes are treated.
Is It Okay To Use Parkinsons Disease Medicine Together
First used as a remedy, levodopa has tremendous effect and is quick to work. However, since the duration of the effect is short, wearing-off is likely to appear when used alone. Also, even if you are using a drug with a long duration of action, you may combine it with other drugs due to the appearance of motor complications caused by the therapeutic drug. In other words, Parkinsons disease is often treated with multiple drugs.
Regarding the concomitant use, caution is required when concomitantly using drugs other than antiparkinsons disease drugs, such as when treating non-motor symptoms . As mentioned above, there are many aspects that rely on empirical treatment and various drugs are used. Therefore, it is advisable to ask the prescribing doctor or pharmacist from time to time whether adverse events may occur with the combined use of the drug.
References
Also Check: How Do I Stop Drooling In Parkinson’s
If Levodopa Causes Dyskinesia Then Why Should I Take It
At present, treatment with levodopa is the most effective way to relieve tremor, stiffness, and slow movement associated with Parkinsons. In the early stage of Parkinsons, levodopa may not be necessary and there are other medications available to treat this stage of the disease. However, as the disease progresses and symptoms begin to interfere with daily living, your doctor will prescribe levodopa.
- It typically doesnt develop immediately Its important to note that there is usually a time lag of roughly 4 to 10 years from the start of treatment with levodopa to when dyskinesia emerges, and its severity will vary among different individuals.
- Younger people are at a greater risk People who get Parkinsons in their later years may not show signs of dyskinesia or may have only mild symptoms within their lifetime. Being diagnosed with Parkinsons at a younger age is associated with a greater chance of developing dyskinesia.
- As with every aspect of Parkinsons, there is variability in dyskinesias Some do not develop dyskinesias at all. For those who do get them, not all experience them the same. Dyskinesia in its milder form may not be bothersome, and the mobility afforded by taking levodopa may be preferable to the immobility associated with not taking levodopa. People with Parkinsons must weigh the benefits from using levodopa versus the impact of dyskinesia on their quality of life.
What Are The Symptoms
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Recommended Reading: How Do People Get Parkinson’s Disease
Explain The Medicines Used For Each Symptom
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease can be broadly divided into motor and non-motor symptoms.
: Exercise symptoms are mainly akinesia, tremor, and muscle rigidity , and posture maintenance disorder , forward leaning posture, and freezing legs may also appear. I have. In other words, it can be said that the motor symptom of Parkinsons disease is immobility.
: It is said that most people develop non-motor symptoms, and there are a wide range of disorders such as sleep disorders, mental / behavioral / cognitive disorders, independence neuropathy, and sensory disorders. It is said that this is because the effects of neurodegeneration spread not only to the dopamine nervous system but also to other nervous systems .
In addition to the symptoms of Parkinsons disease, treatment-induced motor complications may also occur.
Below, we will introduce the therapeutic agents and treatment policies for motor and non-motor symptoms, as well as motor complications, as specified in the Parkinsons Disease Practice Guidelines 2018.
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Don’t Miss: Does Pot Help Parkinson’s
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
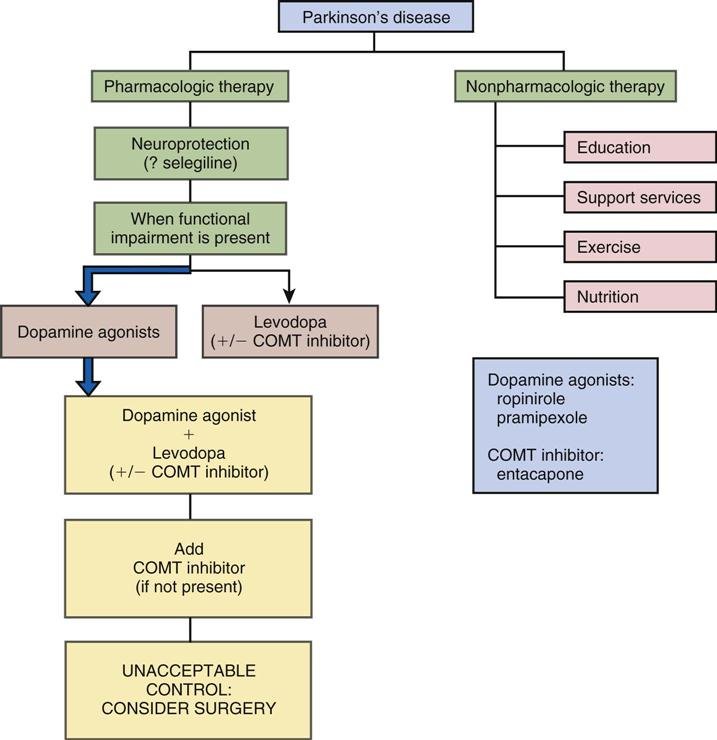
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson Disease Affect The Immune System
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
When Should I Start Taking Medication

If you have been diagnosed with Parkinsons, you may be wondering when you should start treatment and with what medication. There is no single strategy that applies to everyone. The timing will differ from person to person. It depends on a variety of factors, such as:
- your age
- the nature of your symptom
- your lifestyle
- your overall physical health
- whether you experience balance problems with walking
- changes in intellectual abilities, and
- your own attitude toward taking medication
When to start taking medication can be decided in consultation with your neurologist or movement disorder specialist. The decision to delay taking medication requires close monitoring and evaluation for risks of falls and injuries, especially if you are older. The older you are, the more you are at risk for a fall, and Parkinsons medication, when used appropriately, may reduce this risk.
You May Like: What Is Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
What Is A Parkinsons Tremor
Other health issues can also cause tremors, like multiple sclerosis or essential tremor. But Parkinsonâs tremors are different because theyâre usually:
- Resting. Parkinsonâs tremors happen when your muscles are still. They go away when you move. They also lessen while you sleep. For example, if youâre sitting in a chair with your arm relaxed, you may notice that your fingers twitch. But if youâre using your hand, like when you shake someone elseâs hand, the tremor eases or stops.
- Rhythmic. Parkinsonâs tremors are slow and continuous. They arenât random tics, jerks, or spasms.
- Asymmetric. They tend to start on one side of your body. But they can spread to both sides of the body.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Feet
What Is The Latest Treatment For Parkinsons
Research for new Parkinsons drugs and therapies is ongoing. Most people live a long time with Parkinsons disease, which means you might take medications for a long time. All of these main treatments cause side effects that are hard to live with, so new drugs to treat those side effects are also being studied.
Adenosine A2a antagonists
This medication was approved by the FDA in 2019 for Parkinsons disease as additional treatment alongside levodopa. It works by blocking a protein called the adenosine A2 receptor, which increases dopamine signaling. These medications lower off time and uncontrollable, jerky movements.
Other therapies
There are clinical trials and research happening for other therapies, including:
- Stem cell therapy that uses healthy cells to repair damage from Parkinsons
- Growth factors, which are proteins that support nerve cells and promote growth and survival
- Gene therapy to reprogram cells to stay healthy and work better for longer
- Drugs for side effects like NLX-112 that targets certain serotonin receptors
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Also Check: What Foods Should Be Avoided With Parkinson’s
How Do Wearable Tremor
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
In this type of system, electrical stimulation is applied to the skins surface to stimulate the sensory nerves, the nerves that carry information about pain, temperature, and body positioning from the limbs to the brain. The exact mechanism of how this stimulation suppresses tremor is not completely worked out. It is known that sensory nerves connect from the arms and legs to a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is also implicated in tremor. It is thought that stimulating the sensory nerves can disrupt pathological circuits in the thalamus that are responsible for tremor.
Cala One was the first transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation system approved by the FDA in 2018 for tremor control. A newer version, Cala TrioTM, is designed to replace Cala One. Cala-Trio is FDA-cleared and is available with a prescription from your doctor. The device is worn on the wrist and applies electrical stimulation to the median and radial nerves. Of note, someone with a DBS system in place is not able to use Cala One or Cala Trio. A randomized controlled trial of Cala One showed mixed results, with improvements on some tremor measures, but no improvements on others. However, self-rated improvements on activities of daily living were 50% in the treatment group and 27% in the control group.
Functional electrical stimulation
Energy dissipation
Readi-Steadi® is a customizable weighted glove which can help dissipate tremor.
Active orthoses
