Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
There is currently no proven disease-modifying or neuroprotective therapy for PD. A summary of previous neuroprotection trials is given in a recent review article. Current evidence-based treatment for PD is symptomatic and mainly based around dopaminergic replacement or modulation . The evidence base is summarised in recent guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are all licensed for use as initial therapy in PD. Anticholinergics are no longer routinely used due to the risk of cognitive decompensation.
Pharmacological therapies currently used for initial and adjunctive treatment of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
What Tests Might I Have
Your doctor may want to start by testing your blood or doing a brain scan to rule out other conditions.
People who have Parkinsonâs disease donât make enough of a brain chemical called dopamine, which helps you move. If those first tests donât show a reason for your symptoms, your doctor may ask you to try a medication called carbidopa-levodopa, which your brain can turn into dopamine. If your symptoms get much better after you start the drug, your doctor probably will tell you that you have Parkinsonâs disease.
If the medication doesnât work for you and thereâs no other explanation for your issues, your doctor might suggest an imaging test called a DaTscan. This uses a small amount of a radioactive drug and a special scanner, called a single photon emission computed tomography scanner, to see how much dopamine is in your brain. This test can’t tell you for sure that you have Parkinson’s disease, but it can give your doctor more information to work with.
It can take a long time for some people to get a diagnosis. You may need to see your neurologist regularly so they can keep an eye on your symptoms and eventually figure out whatâs behind them.
Read Also: Should Someone With Parkinson’s Drive
Testing For Parkinsons Disease
There is no lab or imaging test that is recommended or definitive for Parkinsons disease. However, in 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging scan called the DaTscan. This technique allows doctors to see detailed pictures of the brains dopamine system.
A DaTscan involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug and a machine called a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner, similar to an MRI.
The drug binds to dopamine transmitters in the brain, showing where in the brain dopaminergic neurons are.
The results of a DaTscan cant show that you have Parkinsons, but they can help your doctor confirm a diagnosis or rule out a Parkinsons mimic.
Molecular Imaging In Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD relies on the clinical manifestation of cardinal motor symptoms, bradykinesia, and tremor at rest or rigidity . A positive response to dopaminergic drugs is supportive of the diagnosis. Single photon emission computed tomography or PET ligands that are specific for dopamine transporters indirectly enable the quantification of the deficit of dopaminergic nigrostriatal projections and can provide further support of diagnosis . Deficiencies of monoamine synthesis can be measured with dihydroxyphenylalanine which is a substrate for the enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in all monoaminergic neurons including noradrenergic neurons .
The role of deficits of noradrenaline in motor and non-motor symptoms is not clear and research on the noradrenergic system in PD patients has been hindered by lack of specific methods to visualize the noradrenergic neurons and projections in vivo. We have recently carried out PET studies to investigate the role of noradrenaline in non-motor symptoms in PD patients and these studies will form the basis of discussions in the paragraphs below.
Paul Johns BSc BM MSc FRCPath, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Dry Mouth And Parkinson’s
Sensitivity Specificity And Predictive Value Of A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
Of 126 patients with a pre-existing clinical diagnosis of probable and possible Parkinsons disease in the overall sample , 111 were confirmed as having Parkinsons disease, resulting in a sensitivity of 88.1% similarly, it was confirmed that 54 of 74 patients did not have Parkinsons disease, resulting in a specificity of 73.0% . The positive and negative predictive values of a previous clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons disease were 84.7% and 78.3% . In other words, in 85% of patients with a previous diagnosis of Parkinsons disease this diagnosis was confirmed, and 78% of patients with a diagnosis other than Parkinsons disease did not have the disease .
When this was broken down by a specialist or other doctor diagnosis, the diagnostic validity was as follows. Neurologists and geriatricians had a sensitivity and specificity of 93.5% and 64.5% , respectively, compared with 73.5% and 79.1% for non-specialists. The positive predictive values were greater for specialists than for other doctors , but the negative predictive values were equivalent v non-specialist 79.1% ).
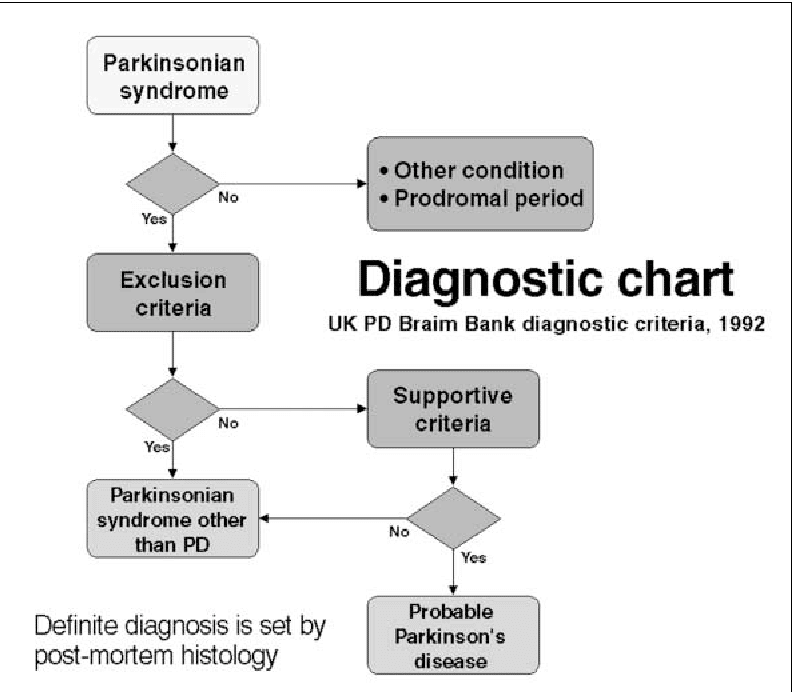
Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD is clinical and requires bradykinesia, defined as slowness of movement and decrement in amplitude or speed, usually assessed using finger tapping, foot tapping or pronationsupination hand movements. In addition, rest tremor or rigidity is required to confirm a parkinsonian syndrome. Tremor was absent at presentation in 30% in one series of pathologically proven PD. Patients with suspected PD should be referred quickly and untreated to a specialist in movement disorders for evaluation. Key points for discussion at diagnosis include the need to inform vehicle licensing agencies and insurers, signposting to written or web-based information on newly diagnosed PD, and provision of contact details for the local PD nurse specialist .
Current International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease adapted from Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2015 30:1591601. At least two supportive criteria and no red flags required for a diagnosis of clinically established Parkinson’s disease. Conditions in italics should be considered if the corresponding exclusion criteria or red flags are present.
Recommended Reading: What Medication For Parkinson’s Disease
The New Definition And Diagnostic Criteria Of Parkinsons Disease
@article, author=nther Deuschl and Thomas Gasser and Christopher G. Goetz and Glenda M. Halliday and Lawrence Joseph and Anthony E. Lang and Inga Liepelt-Scarfone and Irene Litvan and Kenneth Marek and Wolfgang Hermann Oertel and C. Warren Olanow and Werner Poewe and Matthew B. Stern}, journal=, year=, volume=, pages=}
- View 2 excerpts, cites methods and background
- Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- View 2 excerpts, cites background
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society
You May Like: Prevalence Of Parkinsons Disease In The Us
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: Rock Steady Boxing Parkinson’s Disease
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Testing For Parkinson’s Disease
The exam for Parkinson’s disease is based on the review of your medical history, but diagnostic imaging may be used to rule out other diseases that are easily mistaken for Parkinson’s disease.
CT and MRI scans can be used to rule out the possibility of other brain diseases besides Parkinson’s disease .Your doctor might also perform a test called an MIBG myocardial scintigraphy, which is used to examine the condition of sympathetic nerves in the heart. For this, you take a test agent containing a substance called metaiodobenzylguanidine, which is similar to norepinephrine . The degree to which this agent collects in the heart is then assessed using images. It is known that this agent does not collect in the heart in Parkinson’s disease patients, and this fact is used as a reference in making a diagnosis.
In January 2014, a testing procedure called dopamine transporter became available in Japan. DAT is a protein that encourages the recycling of the dopamine that is used to send signals in the brain. This test discriminates between conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies by visualizing the workings of DAT.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Considered An Autoimmune Disease
Response To Parkinsons Drugs
After examining you, and depending on the severity of your symptoms, your specialist may suggest you take medication for Parkinsons. If your symptoms improve after taking Parkinsons medication for a few weeks or months, your specialist may confirm a Parkinsons diagnosis. However, some people with other forms of parkinsonism will also respond well to these drugs.
Your specialist may suggest you have a scan to help make a diagnosis. However, scans alone cant make a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons, so they are not commonly used.
Pioneering Precision Neurology To Drive Early Accurate Diagnosis
At Altoida, we are dedicated to providing a reliable, affordable, and highly accurate way to measure and monitor brain health. We are building the worlds-first Precision Neurology platform and app-based medical devicebacked by 11 years of clinical validationto accelerate and improve drug development, neurological disease research, and patient care.
By completing a 10-minute series of and motor activities designed to simulate complex Activities of Daily Living on a smartphone or tablet, Altoidas device extracts and provides robust measurements of neurocognitive function across 13 neurocognitive domains. Our device measures and analyzes nearly 800 multimodal cognitive and functional digital biomarkers. Through the collection of highly granular data from integrated smartphone or tablet sensors, Altoidas device produces comprehensive neurocognitive domain scores. This data can be tracked longitudinally to reveal trends and patterns while flagging concerning ones.
This method, along with our innovative artificial intelligence, will pioneer fully digital predictive neurological disease diagnosis. Recently receiving Breakthrough Device designation by the FDA, Altoida’s platform has demonstrated ability to predict conversion from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s disease with a high degree of accuracy.
To learn more about if there is a test for Parkinsons disease or about utilizing Altoidas Precision Neurology platform, contact us today.
You May Like: How To Care For Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Patients With A Previous Diagnosis Other Than Parkinsons Disease
Among all patients seen, two were referred for diagnostic purposes without a previous diagnosis, and 69 of 202 patients had a previous diagnosis other than Parkinsons disease . Among these, 56 patients had been given a diagnosis of non-parkinsonian tremor, two of vascular parkinsonism, one of atypical parkinsonism, and 10 had been prescribed an antiparkinsonian drug for parkinsonian features without a specific diagnosis . Thirteen of the 69 patients with different diagnoses and the two patients referred for diagnostic purposes fulfilled strict clinical criteria for Parkinsons disease . In two additional patients who had a previous diagnosis of non-parkinsonian tremor, a diagnosis of possible Parkinsons disease was made . If only patients who had at some point in the past seen a specialist were considered, the diagnosis was changed to probable Parkinsons disease in five and to possible Parkinsons disease in one .
Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values for the overall sample* and by type of clinician
Recommended Reading: Michael J Fox On Parkinsons
Utility Of The New Movement Disorder Society Clinical Diagnostic Criteria For Parkinsons Disease Applied Retrospectively In A Large Cohort Study Of Recent Onset Cases
The MDS diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons Disease were tested retrospectively in a large cohort study.
-
Over 90% of cases diagnosed clinically as PD fulfilled MDS diagnostic criteria for PD.
-
Over 60% were categorized Clinically established PD under 30% were Clinically probable PD.
-
Cases categorized as not PD had more severe, less therapy responsive parkinsonism.
-
Categorization as PD by the MDS criteria was 85% stable after 2.5 years of follow-up.
Recommended Reading: What Is Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
From Prodromal To Overt Parkinsons Disease: Towards A New Definition In The Year 2040
Issue title: The Times They Are a-Changin: Parkinsons Disease 20 Years from Now
Guest editors: Patrik Brundin, J. William Langston and Bastiaan R. Bloem
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Berg, Danielaab* | Postuma, Ronald B.c*
Affiliations: Department of Neurology, Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, Kiel, Germany | Department of Neurodegeneration, Hertie-Institute for Clinical Brain Research Tuebingen, Germany | Department of Neurology, Montreal General Hospital, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Daniela Berg, MD, Department of Neurology, Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, Arnold-Heller-Str. 3 24105 Kiel, Germany. E-mail: . and Ronald B. Postuma, MD, MSc, Department of Neurology, L7-305 Montreal General Hospital, 1650 Cedar Ave, Montreal, Canada H3G1A4. E-mail: .
Keywords: Prodromal Parkinsons disease, higher-specificity markers, big data approaches, progression markers, subtypes, population-based screening, neuroprotective trials, gene-specific therapy, individual mechanism-specific therapy
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-181457
Journal: Journal of Parkinsons Disease, vol. 8, no. s1, pp. S19-S23, 2018
Abstract
Dont Miss: Fatigue Management And Parkinsons Disease
Likelihood Of Referral According To Final Diagnosis
Overall, 74% of all cases with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease had been seen by a specialist. However, when these cases were classified by final diagnosis , it was observed that, paradoxically, fewer cases with atypical disease had been seen by a specialist compared with those with classical Parkinson’s disease p = 0.02).
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Huntington’s Disease And Parkinson’s
Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Cured
No, Parkinson’s disease is not curable. However, it is treatable, and many treatments are highly effective. It might also be possible to delay the progress and more severe symptoms of the disease.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Parkinson’s disease is a very common condition, and it is more likely to happen to people as they get older. While Parkinson’s isn’t curable, there are many different ways to treat this condition. They include several different classes of medications, surgery to implant brain-stimulation devices and more. Thanks to advances in treatment and care, many can live for years or even decades with this condition and can adapt to or receive treatment for the effects and symptoms.
Is There A Test For Parkinsons Disease
Currently, there is no single test for Parkinsons diseaseno brain scan or lab test can provide a definitive diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Instead, doctors diagnose Parkinsons disease clinically, meaning a diagnosis is dependent on medical history, answers to certain questions, a physical examination, and the presence of specific physical symptoms.
Typically, the process for diagnosing Parkinsons disease follows these general steps:
Clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or any disease for that matter, relies heavily on the doctors judgment and expertise. Oftentimes, the patients symptoms, along with the neurological examination, are sufficient for determining the correct diagnosis, particularly for patients in the later stages of the disease. However, doctors may suggest further testing, such as brain imaging, to rule out any conditions that mimic the symptoms of Parkinsons disease .
Read Also: Lab Test For Parkinson’s Disease
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Patients In Whom A Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease Was Or Was Not Previously Made
![[PDF] 1 Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson â s Disease ...](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/pdf-1-diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-parkinson-atm-s-disease.png)
Patients in whom a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was previously made had a longer disease duration and greater disease severity , with more severe akinesia , postural instability, and rigidity than those in whom the diagnosis was not made before. They were also more likely to be depressed , to have experienced dyskinesias , and to live alone or with their family than in a nursing home .
Recommended Reading: Emotional Trauma And Parkinson’s Disease
