Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Is Deep Brain Stimulation Right For Me
If you get DBS, a surgeon puts electrodes into your brain to prevent the abnormal signals that cause Parkinson’s symptoms.
The procedure might be an option for you if:
- You’ve had Parkinson’s disease for more than 5 years.
- You have “off” and “on” periods where your symptoms come and go, even though you take medicine every day.
- Symptoms like tremor, stiffness, and slowness get in the way of your daily life.
- Your medicine dose wears off before it’s time to take the next one.
- You have side effects from your medicine that bother you.
What To Expect During Surgery
You’ll get DBS surgery in two parts. During the first part, the surgeon puts in the electrodes. You’ll be awake while this is going on, but you’ll get medicine to relax you and prevent pain.
First, your doctor will place a special frame around your head to keep it still. They’ll use magnetic resonance imaging to map out the areas in your brain where they’ll do the operation.
Your surgeon will place electrodes into areas on one or both sides of your brain that control movement. They’ll ask you to do certain tasks during the procedure to help them put the electrodes in the right spots.
On the same day or at a later time, you’ll have a second surgery to put in a device called an impulse generator. It’s battery-operated and sends impulses to the electrodes in your brain.
You will be asleep for this procedure. The surgeon will place the generator under the skin of your upper chest, just below your collarbone. Wires will connect the generator to the electrodes in your brain.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Sites Of Deep Brain Stimulation And Symptom Control
While both subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus stimulation help improve the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, studies have found a few differences.
DBS of the third target, the ventral intermediate nucleus, can be beneficial for controlling tremors but does not work as well at addressing the other motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
In a Canadian study, targeting the subthalamic nucleus allowed people to reduce the doses of their medications to a greater degree, while targeting the globus pallidus internus was more effective for abnormal movements .
In another study, STN deep brain stimulation also led to a greater reduction in medication dosages. However, GPi stimulation resulted in greater improvement in quality of life, and also appeared to help with the fluency of speech and depression symptoms.
Side effects of DBS can sometimes include subtle cognitive changes . A different study compared these effects with regard to these different areas.
GPi showed smaller neurocognitive declines than STN, though the effects were small with both. On a positive note, both procedures seemed to reduce symptoms of depression following surgery.
Review Of Empirical Research

Against this complicated backdrop, we examine empirical evidence pertaining to personality change following DBS. We evaluate the types of methods used to study this question, and we summarize and integrate research findings across personality characteristics. Finally, we list a number of strategies for advancing research.
Recommended Reading: When Was Muhammad Ali Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
What To Expect After Dbs
Surgery to implant the leads generally entails an overnight stay, while the IPG is usually implanted as same-day surgery. During recovery, your surgeon will talk to you about caring for your wounds, when you can shower, and any activity restrictions. Its usually recommended that any heavy lifting be avoided for a few weeks.
After another two to four weeks, youll return to have your device programmed. This process will continue for several weeks to ensure the stimulation settings are optimal to control your symptoms. During these visits, you will be shown how to turn the device on and off with the handheld device and check the battery level.
Once the programming has been completed, you will have regular follow-up visits to check and adjust the stimulation to maintain the most benefit for your symptoms.
What Does Dbs Do
Used for the first time in 1986, DBS primarily helps with motor symptoms, specifically severe motor fluctuations or tremor in advanced stages, according to one studys description.
During the procedure, a surgeon places electrodes in the brain. These electrodes transmit impulses that either interrupt or change abnormal brain activity. The wires can be placed in multiple areas of the brain, which impacts the potential effects of the pulse interruptions. For example, Dad struggles most with dyskinesia and hopes to alleviate those symptoms. But if tremors are inhibiting someone, a surgeon can adjust the placement of electrodes to benefit that persons body optimally.
A surgeon places a device thats similar to a pacemaker under the skin beneath the collarbone. This piece of hardware transmits signals to the electrodes, allowing them to moderate adverse brain activity. The procedure generally causes minimal or no tissue damage. Ultimately, DBS is not a cure, but it can significantly impact quality of life, according to various studies and anecdotal evidence.
Read Also: Color For Parkinson’s Awareness
Deep Brain Stimulation Doctors
Our expert restorative neurosurgeon Dr. JP Langevin has many years of experience with DBS. He was the first to implant and program PerceptTM PC with BrainSenseTM technology DBS system to treat patients with Parkinsons disease among Providence hospitals, the 3rd largest healthcare system in the United States.
S For Assessing Personality Changes Following Dbs
Supplementary Table 1 gives detailed descriptions of studies included in our review, grouped according to primary methods. Most research used quantitative methods, while qualitative methods are growing increasingly common. There is an emerging trend for studies to assess patient valued characteristics using a mixed-methods approach. Across methods, most studies relied only on self-reports, though a few assessed caregiver or clinician perspectives.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative research on personality change comes from meta-analyses and primary studies employing retrospective, cross-sectional, prospective, and randomized clinical trial designs. This research has some general limitations. Meta-analyses focused mainly on clinical measures of psychiatric symptoms rather than scales assessing normal range personality. Most retrospective, cross-sectional, and prospective studies included small sample sizes, limiting power to detect small- to moderate effect sizes. And there has been one RCT to date, which decreases the confidence with which causal claims can be made. Additionally, quantitative studies focused almost exclusively on dispositional traits rather than characteristic adaptations and narrative identity.
Qualitative Methods
Patient Valued Characteristics: A Mixed Methods Approach
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Memory Issues
Why A Doctor May Choose Deep Brain Stimulation
According to the National Parkinson Foundation, the ideal Parkinsons disease candidate for DBS surgery has:
-
PD symptoms that interfere with activities of daily living.
-
Fluctuations in mobility due to PD medications with or without dyskinesia .
-
Continued good response to PD medications, even if the medication effects may wear off sooner than they have in the past.
-
A history of several different combinations of PD medications while under the supervision of a neurologist specializing in movement disorders.
These factors* may make a person a less than ideal candidate for DBS surgery:
-
Difficulty with balance, walking, or freezing as the main disabling symptom.
-
A primary symptom of speech difficulty.
-
Continuous confusion and problems with memory and thinking.
-
A psychiatric condition such as depression or anxiety that has not improved or stabilized with other treatment.
-
Another condition that increases the risk for surgery complications.
*Some of these factors may be treatable. Having one or more does not disqualify a person for future DBS surgery, but the doctor may recommend more aggressive therapy focused on these issues before surgery takes place.
Improves Quality Of Life
75% of patients preferred DBS to medical therapy alone considering the PDQ-39.*2DBS therapy improves quality of life by 13% to 26% compared to before receiving DBS.**2,5 Improved quality of life includes things such as feeling better emotionally, feeling less embarrassed in public, moving about more easily, and having less physician discomfort. In the same studies, patients receiving best medical therapy without DBS showed no improvement in quality of life compared with their baseline.
*Per protocol analysis** Based on PDQ-39 single indexine
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Stereotactic Dbs Vs Interventional Image
Stereotactic DBS surgery requires the patient to be off their medication. During the procedure, a frame stabilizes the head and provides coordinates to help the surgeons guide the lead to the correct location in the brain. The patient gets local anesthesia to keep them comfortable throughout each step along with a mild sedative to help them relax.
During image-guided DBS surgery, such as with interventional MRI or CT scan, the patient is often asleep under general anesthesia while the surgeon uses images of the brain to guide the lead to its target.
Some advanced centers offer both the stereotactic and iMRI-guided options for DBS surgery. In this case, the doctor and patient will discuss which procedure is better based on a number of factors.
For instance, the doctor may recommend an image-guided procedure for children, patients who have extreme symptoms, those who are especially anxious or fearful or those whose leads are going into certain parts of the brain.
Generally, DBS surgery follows this process:
Placement Of The Neurostimulator
This procedure takes place under general anesthesia so that the person is asleep. The surgical team inserts the neurostimulator under the outer layers of skin, usually just under the collarbone, but sometimes in the chest or abdomen. The extension wire from the lead is attached to the neurostimulator.
Read Also: Lifespan Parkinson’s
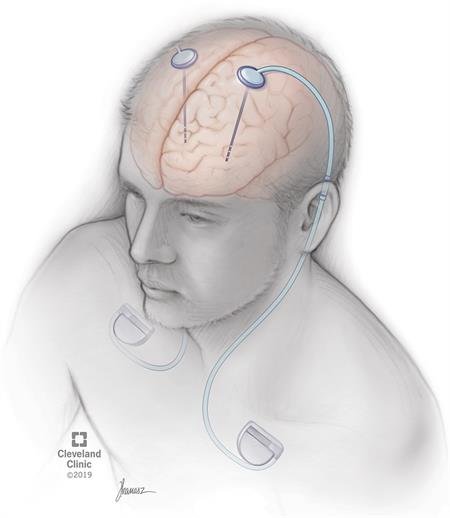
What Does The Dbs System Look Like
A DBS system has three parts:
- The electrode Your neurosurgeon places this thin wire in the brain. Before your DBS surgery, the surgeon decides on the best place to put it. This place is called the target area.
The DBS system in the picture has two electrodes, but some just have one.
- The extension This wire connects the electrode to the pulse generator, or IPG. The extension goes under the skin of the shoulder, neck and head.
- The IPG, also called the stimulator This is the small square device shown in the picture. It is about the size of a tea bag. It creates low-voltage electrical pulses. Your neurosurgeon usually puts it under the skin near the collarbone, but it can also go lower on the chest or near the belly.
The IPG runs on a battery. This battery lasts three to five years and can be replaced.
In “asleep” DBS, developed by OHSU’s Dr. Kim Burchiel, the patient is placed under general anesthesia. The patient is not aware of any part of the procedure. The neurosurgeon uses high-resolution scans taken before and during surgery to precisely place the tiny electrodes in the brain. “Asleep” DBS is faster and safer. Patients can also take their medication on the day of surgery.
How does my neurosurgeon test the electrodes if I am asleep?
For Parkinsons, the leads go in one of three brain areas:
- The subthalamic nucleus, or STN
- The globus pallidus internus, or GPi
- The thalamus
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinson’s disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Cognitive Test
Mechanism Of Action Of Dbs
Current hypotheses on the action mechanism of DBS include depolarization blockade , synaptic inhibition , synaptic depression , stimulation-induced disruption of pathological network activity , and stimulation of afferent axons projecting to the STN . Depolarization blockade and synaptic inhibition are likely to explain the similarity between the therapeutic benefit of DBS and lesional surgery. Recordings of decreased somatic activation in the stimulated nucleus favor these hypotheses . However, the increased output of projection neurons does not seem to be mediated by these phenomena . Another and currently favored hypothesis is that DBS overrides abnormal spike train patterns by an unphysiological, high-frequency pattern, and thereby masks pathological signals, which cause dysfunction of the remaining elements of the basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical and brainstem motor loop . The exact nature of the abnormal signals and the interaction between stimulation-induced neuronal responses and intrinsic brain activity remains elusive, but abnormalities of the firing rate and pattern of basal-ganglia neurons, changes in oscillatory activity and excessive synchronization at multiple levels of the motor loop have been proposed as pathophysiological correlates of motor symptoms in PD .
A General Rule Is That Dbs Will Likely Improve Parkinsons Symptoms That Respond To Medication
The Evaluation prior to DBS Surgery
A team of experts, including a movement disorder specialist and a neurosurgeon , conduct an extensive assessment when considering DBS for someone. The evaluation consists of medication and symptom review, examination both on and off Parkinsons drugs, brain imaging, and oftentimes also detailed memory/thinking testing . If DBS is offered, its important to discuss the expected benefits as each persons experience is unique. Its also critical to discuss the potential surgical risks, including bleeding, stroke and infection.
The DBS Procedure and Device Programming
In DBS surgery, thin wires called electrodes are placed into one or both sides of the brain in specific areas that control movement. Usually a person remains awake during surgery so that he or she can answer questions and perform certain tasks to make sure that the electrodes are positioned correctly. However, some medical centers now are using brain imaging to guide the electrodes to the right spot while a person is asleep. Each method has its pros and cons and may not be suitable for everyone or available everywhere.
Once the electrodes are situated, they are connected to a battery-operated device that is typically placed under the skin below the collarbone. This device, called a neurostimulator, delivers continuous electrical pulses through the electrodes to decrease Parkinsons symptoms.
How DBS Works
Research on DBS
Recommended Reading: What State Has Highest Rate Of Parkinson’s
Potential Psychological Effects Of Dbs
The past 15 years have seen an increasing amount of research devoted to whether DBS causes psychological changes in PD patients. Such effects are plausible for at least three reasons. First, DBS may impact cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and neuropsychiatic networks because these functional networks are adjacent to the motor fronto-subcortical networks targeted by DBS . Second, living with technological equipment in the brain that alters functioning may present profound challenges to identity . Third, the potential lifestyle changes that occur following DBS may relate to shifting patterns of psychosocial functioning .
Excellent review articles touch upon the psychological effects of DBS, focusing on issues such as impulsivity , psychological variables relevant to neuroethics , acute and enduring psychiatric and neuropsychiatric changes , and measurement of these and other complex changes . Some of these articles reviewed individual studies that assessed variables relevant to the field of personality psychology, such as personality traits , and personality disorders , however, none of the reviews focused primarily on personality changes. Thus, our central aim is to provide a brief but relatively comprehensive evaluation of this research. Before doing so, it is important to frame our review within the context of three relevant issues: defining personality and offering a putative neurobiological basis for personality change following DBS.
How Effective Is Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation provides excellent relief for most patients symptoms including tremor, stiffness , slowed movement , freezing of gait and dyskinesias. Long-term studies have shown continued improvement in tremor, bradykinesia, and dyskinesia. Many patients are able to reduce their medications and maintain their level of function including independent participation in activities of daily living required to care for oneself. One of the distinct advantages, is that after DBS, patients on average improve their daily on timewhen they are at their best, without troublesome dyskinesiaby half a day.
Also Check: Sugar And Parkinson’s Disease
Adjusting A Deep Brain Stimulation Device To Meet A Patients Needs Takes Time
Four to six weeks after the surgery, patients begin meeting with Orcutt and her colleagues to program the deep brain stimulation device. Together, the patient and care team tune the device so that it delivers the right amount of stimulation to minimize symptoms. Orcutt will see patients regularly until they have identified the appropriate DBS settings. During this time, Orcutt also adjusts patients medications.
This process takes time, she said. There is no formula because everyone is unique. It all depends on a patients condition, where the electrodes are in the brain and what they can tolerate.
Typically, patients will establish their optimal stimulation settings in two to three months following surgery, according to Cooper. Sometimes it happens faster, and sometimes it takes longer, Cooper said. In some cases it may take a year to find the correct DBS settings.
