New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Nonmotor Symptoms And The Premotor Phase Of Pd
PD has been traditionally regarded as a motor disorder, perhaps because the original account of the clinical features emphasized these symptoms, while failing to recognize the important nonmotor aspects of the disease. In addition, motor symptoms often meet the eye straightaway, even for untrained observers. However, in recent years there has been an increasing interest in nonmotor symptoms of PD , because their recognition is useful for diagnostic purposes, but also because they are a major source of deterioration in quality of life, and warrant specific management .
Hereditary Forms Of Parkinson’s Disease And Their Clinical Features
A small but significant number of PD patients have a family history compatible with Mendelian autosomal inheritance , either dominant or recessive. Many of these are classified as young-onset or juvenile-onset PD . A number of levodopa-responsive parkinsonian syndromes have been described and linked to a specific locus or gene in the last few years, and some of them have been classified as PARK syndromes . Some of these denote true PD, whereas others represent more complex phenotypes and dissimilar diseases. Only the former group will be briefly approached here, as the clinical phenotype may be a useful pointer for the diagnosis in daily practice, guiding subsequent molecular testing. For more details on the genetics of PD please refer to Klein and Westenberger .
You May Like: Medication Used For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease And Movement Disorders Center
Our center provides compassionate and timely treatment to patients with movement disorders, such as dystonia, ataxia, essential tremor and similar conditions. But our mission goes beyond patient care excellence. By offering educational events and support groups, we empower patients and caregivers to become better partners in their health.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication

If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: How To Slow The Progression Of Parkinson Disease
Symptom History Of Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosis of PD is most often made when a doctor identifies the primary motor symptoms in a patient. Diagnostic criteria for PD called the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale recommend that the physician assess for symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, balance impairments, freezing episodes , posture, changes in handwriting, difficulty swallowing, and reduced facial expression.3,4
In addition to these primary motor symptoms, the symptom history for diagnosing PD should include investigating the presence of non-motor symptoms of PD, such as constipation, a frequent and urgent need to urinate, sleep disturbances, pain, orthostatic hypotension , reduced sense of smell , sexual dysfunction, and fatigue. In addition, many people with PD experience mood disorders like depression or anxiety and cognitive changes, such as memory difficulties, slowed thinking, or confusion.4,5
Physical Exam For Parkinson’s
During a physical exam, the doctor examines the patients body for signs of disease. The doctor will include a visual inspection , palpation , ascultation , and percussion . The physical exam for PD is generally conducted by a neurologist and may also be called a neurological exam. It is recommended that a patient see a neurologist with special training in movement disorders as these specialists have the most knowledge about the symptoms and medications. During a neurological exam, the patient may be asked to sit, stand, walk, and extend their arms as the doctor evaluates balance and coordination. Most neurologists recommend a spouse or caregiver attend the exam with the patient to help with answering important questions.1,2
Don’t Miss: Is Essential Tremors A Form Of Parkinson’s Disease
Comparison Of Patients In Whom A Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease Was Maintained Or Rejected
Patients in whom a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was confirmed had more severe disease as measured by the Hoehn and Yahr stage , more often had a tremor at rest or a classical pill rolling tremor , and more often reported a good initial and sustained response to levodopa than those in whom it was rejected.
Patients in whom the diagnosis was changed to non-parkinsonian tremor had no other parkinsonian features such as rigidity, bradykinesia, hypomimia, or monotonous speech. They also reported falls significantly less frequently and had higher mini-mental state scores . Those in whom the diagnosis was changed to atypical parkinsonism had more severe akinesia , rigidity , and postural instability , less commonly reported an initially or currently good response to levodopa , but more often had incontinence and additional features incompatible with Parkinson’s disease. Those in whom the diagnosis was changed to vascular parkinsonism were older than those in whom a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was confirmed , had a larger number of smoking years , more often had gait difficulties as their first complaint , and had more severe postural instability they never had a rest tremor.
How I Examine My Patient: The Art Of Neurological Examination For Parkinson’s Disease
Article type: Other
Authors: Bloem, Bastiaan R. | Brundin, Patrik
Affiliations: Radboud University Medical Center, Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior, Department of Neurology, Nijmegen, The Netherlands | Laboratory of Translational Parkinson’s Disease Research, Center for Neurodegenerative Science, Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA
Note: Correspondence to: Bastiaan R. Bloem, Department of Neurology , Radboud University Medical Center, PO Box 9101, 6500 HB, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Tel.: +31 24 3615 202 E-mail:
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-149006
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 563-565, 2014
Don’t Miss: How Does Sinemet Help With Parkinson’s
Testing For Parkinsons Disease
There is no lab or imaging test that is recommended or definitive for Parkinsons disease. However, in 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging scan called the DaTscan. This technique allows doctors to see detailed pictures of the brains dopamine system.
A DaTscan involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug and a machine called a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner, similar to an MRI.
The drug binds to dopamine transmitters in the brain, showing where in the brain dopaminergic neurons are.
The results of a DaTscan cant show that you have Parkinsons, but they can help your doctor confirm a diagnosis or rule out a Parkinsons mimic.
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
Also Check: Does Weed Help Parkinson’s Disease
Incident Neurologic Disorders In Covid
To test the robustness of study results, we evaluated the associations between COVID-19 and the prespecified neurologic outcomes in analyses considering a historical control group as the referent category the demographic and health characteristics before and after weighting are presented in Supplementary Tables , , and 9, examination of standardized mean differences suggested that covariates were balanced after application of inverse weighting . The results showed increased risks and associated burdens of the prespecified outcomes in comparisons of COVID-19 versus the overall historical control group , in subgroup analyses and by age as continuous variable and by care setting of the acute phase of the disease . Both the direction and magnitude of risks were consistent with analyses using the contemporary control as the referent category.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
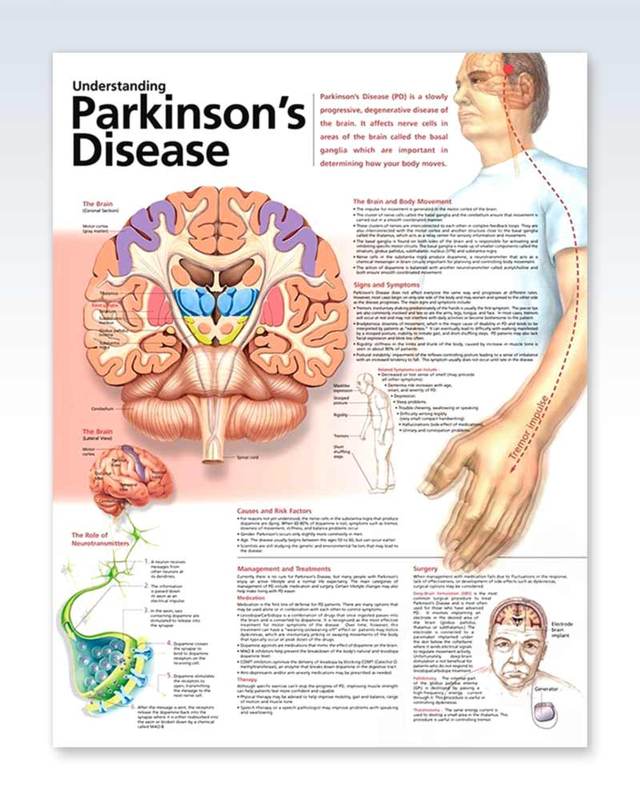
Parkinsons Disease is a neurodegenerative disorder marked by a loss of dopaminergic neurons in the area of the brain known as the substantia nigra. It affects an estimated one million people in the United States and 10 million worldwide. While the exact cause is largely unknown and there currently is no cure, Parkinsons Disease is not fatal. However, untreated, it may lead to life-altering complications.
Also Check: Are There Any New Treatments For Parkinson Disease
Other Tests Used To Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosis of PD is generally made using a medical history and a physical/neurological exam. Imaging tests, such as MRI , PET scans, or DaTscans are expensive and are not routinely used.1,7
An active area of research is the development of biomarkers which are molecules in the blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid that can reliably indicate PD. Imaging tests that can detect aggregates of a molecule called synuclein, which is linked to PD, are also being actively researched.
Gait & Balance Abnormalities
Parkinsons Disease Exam
Patients with Parkinsons disease can develop an alteration of the postural reflexes that causes instability in gait and balance control. Such alterations usually develop later in the course of the illness and are a major cause of disability, especially because of the high risk for falls that derives.
Using the exam to pick up postural instability is of the utmost importance for the management of patients with PD, since it will trigger either a medication adjustment or a physical therapy intervention both aimed at falls prevention.
We have three tests for this part of the PD exam:
1) Standing up from a chair
2) Free walking
3) Provoked pull test maneuver for balance
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Prognosis With Treatment
I Have Pd And Several Symptoms Should I Get A Datscan
Likely no. There is no need for DaTscan when your history and exam suggest Parkinsons disease and you meet the diagnostic criteria. Occasionally, if signs and symptoms are mild or you dont meet the diagnostic criteria, your doctor will refer you for a DaT scan. Keep in mind that ultimately the diagnosis is based on your history and physical exam. The DaT scan is most commonly used to complete the picture and is not a test for a diagnosis.
Is Parkinsons Disease Treated By A Neurologist
People with Parkinsons disease will usually require a team of healthcare professionals to help them manage the condition.
A neurologist, a doctor specializing in conditions of the brain and nervous system, will be one of the main people involved in treating Parkinsons.
Other healthcare professionals who may help treat Parkinsons can include:
- a persons regular doctor
- a physical therapist
- a speech or occupational therapist
- mental health professional
- other specialists, such as a gastroenterologist, if people experience other symptoms of Parkinsons such as digestive issues
You May Like: How Does Caffeine Affect Parkinson’s Disease
Definition Of Terms Used In The Analysis
Sensitivity: Proportion of patients with a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were previously diagnosed as having Parkinson’s disease: A/.
Specificity: Proportion of patients without a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were previously diagnosed as not having Parkinson’s disease: D/.
Positive predictive value: Proportion of patients with a previous diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who received a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: A/.
Negative predictive value: Proportion of patients with a previous diagnosis of not having Parkinson’s disease who received a final diagnosis of not having Parkinson’s disease: D/.
Parkinsons Disease Exam Presentation
How to present a patient with Parkinsonian symptoms for doctors, medical school exams, OSCEs, MRCP PACES and USMLE
- From the end of the bed, Mr Singh had hypomimia, decreased blinking, and a resting tremor, which disappeared on movement to shake my hand. This was more marked on the right than the left.
- On examination of the upper limbs there was increased tone, specifically cogwheel rigidity.
- Power was difficult to assess due to the rigidity.
- His movements were bradykinetic.
- Reflexes were normal bilaterally.
- His gait was slow to start and shuffling, with reduced arm-swing on the right and difficultly turning.
- In summary, the rigidity, bradykinesia, resting tremor and gait apraxia would be consistent with Parkinsonism.
- Though the most common cause would be Parkinsons Disease, I would like to take a full history as well as examining for autonomic instability and vertical gaze palsy that may be suggestive of a Parkinsons Plus syndrome.
Read Also: How Are You Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
Will I Be Contacted In The Future To Ask For Further Information
We may contact you at a later stage of our research. Researchers make new scientific discoveries each day. Thus, it is important to collect additional information about the health or lifestyle of participants that were not considered to be of importance when the collection was designed. If you agree to be contacted in the future, we shall contact you by e-mail for new scientific questions no more than once every 6 months.
Our research
What Happens During A Visit Which Examinations Can I Expect

If you are interested in joining the study and want to know more about what kind of examination you can expect during a visit, you can talk to your doctor or call us directly. The reception desk is open on weekdays from 08:00 to 16:30 and our secretaries can give you more information about the study and schedule an appointment with you. The appointment will take place when it suits you best.
After the phone call, you will receive a letter containing the confirmation of your appointment, instructions on how to get to our premises, as well as several questionnaires to fill in at home. The questionnaires are about the motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The purpose of the questionnaires is to gather more information about your personal situation. Filling out these questionnaires for the first visit will take a bit longer than in the follow-up visits because we want to know more about your familys medical history.
You will see a nurse during your visit. For our research, we ask you to donate blood, saliva and urine. The nurse will do the sampling and takes anthropometric measurements . You do not need to have fasted before the blood sampling and you can take your medication as usual.
Besides the neurological examination, you will also do neuropsychological tests with our neuropsychologist. Here, we test the motion of your hands, your attention, your memory, your concentration, language and sense of smell.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Male Vs Female
Patients With A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of probable Parkinson’s disease was confirmed in 109 of the 131 patients with this diagnosis , including three in whom atypical features were found but were insufficient to invalidate the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease . Two additional patients were found to have possible Parkinson’s disease. However, in 20 of the 131 patients the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was unequivocally rejected . The alternative diagnoses were non-parkinsonian tremor in four patients , vascular parkinsonism in six , progressive supranuclear palsy in four , and multiple system atrophy in three . Two patients received a diagnosis of idiopathic torsion dystonia, and one of dementia without parkinsonism. When only those patients who had seen a specialist at some point in the past were considered, the diagnosis was changed from Parkinson’s disease to a different diagnosis in 11%.
Patients with an initial diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
What Is A Datscan And What Role Does It Play In A Parkinsons Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved the use of a scan called a dopamine transporter scan . A DaTscan is an imaging technology that allows visualization of the dopamine system in the brain. It is similar to an MRI, but looks at the function of the brain rather than the structure.
A DaTscan involves injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug that is then measured by a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner . The SPECT scanner measures the levels and location of the drug in the brain.
It is important to know that a negative DaTscan does not rule out PD, especially early in the disease, but a positive DaTscan can help confirm it. A positive DaTscan can differentiate PD from essential tremor as there is no dopamine deficiency in the latter. However, DaTscan abnormalities can be seen in PD as well as other forms of atypical parkinsonism that cause a loss of dopamine . This means that a positive result does not differentiate Parkinsons disease from other forms of atypical parkinsonism.
Don’t Miss: Is Restless Leg Syndrome Related To Parkinson’s
