Can You Boost Levels Of Acetylcholine
There is no proven way to increase acetylcholine levels. However, some evidence suggests that consuming choline, a nutrient, could help.
The body requires choline for proper brain and nervous system function. It is also necessary for muscle control and to create healthy membranes around the bodys cells.
Choline is also a building block of acetylcholine. People must get enough choline from their diets to produce adequate levels of acetylcholine.
Studies in animals have found that a high intake of choline during gestation and early development improves cognitive function and helps prevent age-related memory decline.
The confirm that some animal studies have shown that higher intakes of choline could lead to better cognitive function. However, they caution, other studies have found it to be unhelpful.
Many foods contain choline, including:
recommended amount of choline is 425 milligrams per day for women and 550 mg for men.
A person can take choline supplements, but high doses can cause side effects such as vomiting, a fishy body odor, and liver damage.
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons And Myasthenia Gravis
Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterized by a decline in the dopamine level of the brain whereas myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of antibodies that block the transmission of impulses across the neuromuscular junction. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease but Parkinsons is not considered as an autoimmune disease. This is the main difference between Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis. The appearance of Lewy bodies and loss of dopaminergic neurons in pars compacta of the substantia nigra region of midbrain are the hallmark morphological changes in Parkinsons disease. In contrast, the block of the transmission of nervous impulses at the neuromuscular junction due to the action of autoantibodies is the pathological basis of myasthenia gravis.
In addition, there is no laboratory test for the exact identification of Parkinsons disease. However, investigations such as Anti ACh receptor antibodies in the serum, tensilon test, imaging studies, ESR and CRP can help to diagnose myasthenia gravis. Furthermore, anticholinesterases such as pyridostigmine, immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids, Thymectomy, Plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulins can help to manage myasthenia gravis. On the other hand, drugs such as dopamine receptor agonists and levodopa, which restore the dopamine activity of the brain, can alleviate motor symptoms in Parkinsons.
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world.
Although there is no cure for myasthenia gravis, management of the disorder has improved over the past 30 years. There is a greater understanding about the causes, structure and function of the neuromuscular junction, the fundamental aspects of the thymus gland and of autoimmunity. Technological advances have led to more timely and accurate diagnosis of myasthenia gravis and new and enhanced therapies have improved treatment options. Researchers are working to develop better medications, identify new ways to diagnose and treat individuals, and improve treatment options.
Medication
Some people with myasthenia gravis do not respond favorably to available treatment options, which usually include long-term suppression of the immune system. New drugs are being tested, either alone or in combination with existing drug therapies, to see if they are more effective in targeting the causes of the disease.
Diagnostics and biomarkers
Assistive technologies, such as magnetic devices, may also help people with myasthenia gravis to control some symptoms of the disorder.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Parkinson’s To Kill You
What Are The Symptoms Of Myasthenia Gravis
The hallmark of myasthenia gravis is muscle weakness that worsens after periods of activity and improves after periods of rest. Certain muscles such as those that control eye and eyelid movement, facial expression, chewing, talking, and swallowing are often involved in the disorder.
The onset of the disorder may be sudden, and symptoms often are not immediately recognized as myasthenia gravis. The degree of muscle weakness involved in myasthenia gravis varies greatly among individuals.
People with myasthenia gravis may experience the following symptoms:
- weakness of the eye muscles
- drooping of one or both eyelids
- blurred or double vision
- a change in facial expression
- difficulty swallowing
- impaired speech
- weakness in the arms, hands, fingers, legs, and neck.
Sometimes the severe weakness of myasthenia gravis may cause respiratory failure, which requires immediate emergency medical care.
What Is A Myasthenic Crisis
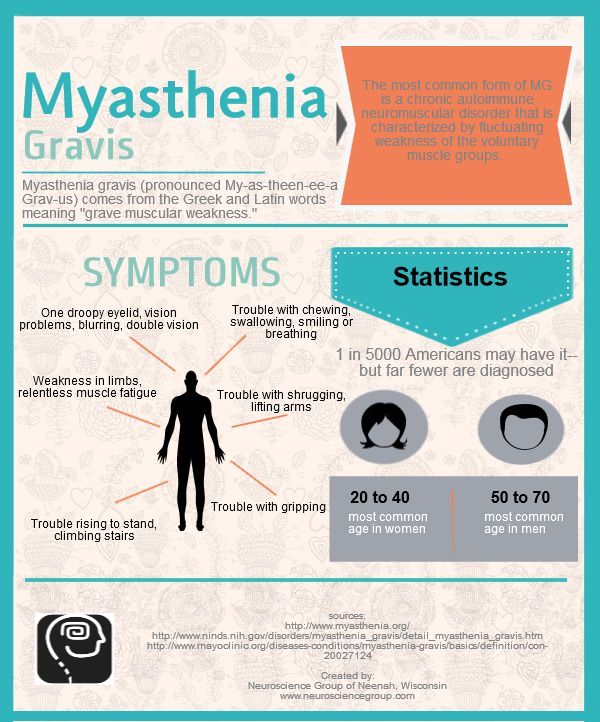
A myasthenic crisis is a medical emergency that occurs when the muscles that control breathing weaken to the point where individuals require a ventilator to help them breathe. It may be triggered by infection, stress, surgery, or an adverse reaction to medication. Approximately 15 to 20 percent of people with myasthenia gravis experience at least one myasthenic crisis. However, up to one-half of people may have no obvious cause for their myasthenic crisis. Certain medications have been shown to cause myasthenia gravis. However, sometimes these medications may still be used if it is more important to treat an underlying condition.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Caregiver Guide
How Are They Alike
MS and Parkinsonâs both affect your central nervous system, which includes your brain and spinal cord. Thatâs why they both can affect how you move, sleep, feel, and talk.
These diseases both affect your nerves. MS can break down the coating, called myelin, that surrounds and protects your nerves. In Parkinsonâs, nerve cells in a part of your brain slowly die off.
Both can start out with mild symptoms, but they get worse over time.
Common symptoms of both diseases include:
- Shaky fingers, hands, lips, or limbs
- Slurred speech thatâs hard for others to understand
- Numb or weak limbs that make your walk unsteady
- Loss of muscle control that often affects one side of your body at first, then later both
- Spastic limb movements that are hard to control
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
- Dementia with Lewy bodies is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder in which abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein build up in multiple areas of the brain.
- DLB first causes progressive problems with memory and fluctuations in thinking, as well as hallucinations. These symptoms are joined later in the course of the disease by parkinsonism with slowness, stiffness and other symptoms similar to PD.
- While the same abnormal protein is found in the brains of those with PD, when individuals with PD develop memory and thinking problems it tends to occur later in the course of their disease.
- There are no specific treatments for DLB. Treatment focuses on symptoms.
avainero välillä Parkinsonin ja myasthenia gravis on se vaikka myasthenia on autoimmuunisairaus, joka johtuu auto-vasta-aineiden tuotannosta kehossa, Parkinsonin taudin patogeneesissä ei ole autoimmuunikomponenttia.
Sekä Parkinsonin että myasthenia gravis ovat neurologisia häiriöitä, joilla on erittäin heikentyvä vaikutus potilaan elämänlaatuun. Parkinsonin tauti on liikuntahäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista aivojen dopamiinitason lasku. Myasthenia gravis on sitä vastoin autoimmuunihäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista sellaisten vasta-aineiden tuottaminen, jotka estävät impulssien siirron neuromuskulaarisen liitoksen kautta.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Affect Eyesight
Getting It Right: Parkwest Physicians Are Committed To Accurate Diagnoses
After eight years of treatment for an illness he didnt have, Mercer Granade, 71, is finally on the right track. His myasthenia gravis was misdiagnosed as Parkinsons disease in 2013 before he and his wife moved to Knoxville, but the further he progressed in his illness, the more doubtful he became about the diagnosis. It took a visit to the emergency department at Parkwest Medical Center and an examination by board-certified neurologist Robert Malka, MD, to find out what was really wrong.
Im just so grateful for my entire team that continues to take care of me, Granade says. I just cant put it into words I get emotional about it. Dr. Malka says diagnosing an illness can be challenging, and any time a patient has a very sudden spike in symptoms, a reevaluation is in order. Thats where you have to step back and start over ground zero, square one, Dr. Malka says.
My partner at Parkwest has the same mindset, and were going to listen and were going to pull out all the stops we can to get an accurate diagnosis, Dr. Malka says. My partners at Fort Sanders Regional Medical Center are also of that mindset. Between our facilities, I think we have the top two facilities for neurologic care in the region. I dont say that lightly. I truly mean it.
Mik On Ero Parkinsonin Ja Myasthenia Gravisin Vlill
Parkinsonin tauti on liikuntahäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista aivojen dopamiinitasojen lasku, kun taas myasthenia gravis on autoimmuunihäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista vasta-aineiden tuottaminen, jotka estävät impulssien siirtymisen neuromuskulaarisen liittymän yli. Myasthenia gravis on autoimmuunisairaus, mutta Parkinsonin tautia ei pidetä autoimmuunisairautena. Tämä on tärkein ero Parkinsonin ja myasthenia gravisin välillä. Lewy-elinten esiintyminen ja dopaminergisten hermosolujen menetykset keskiaivojen justi nigra -alueen Pars Compactassa ovat Parkinsonin taudin tunnusomaisia ââmorfologisia muutoksia. Sitä vastoin autoantuneiden vaikutuksesta johtuvien hermoimpulssien siirtymisen esto neuromuskulaarisessa risteyksessä on myasthenia gravis -patologinen perusta.
Lisäksi ei ole laboratoriotestiä Parkinsonin taudin tarkkaksi tunnistamiseksi. Kuitenkin tutkimukset, kuten anti-ACh-reseptorivasta-aineet seerumissa, tensilon-testi, kuvantamiskokeet, ESR ja CRP, voivat auttaa diagnosoimaan myasthenia gravis. Lisäksi antikoliiniesteraasit, kuten pyridostigmiini, immunosuppressantit, kuten kortikosteroidit, tymektoomia, plasmafereesi ja laskimonsisäiset immunoglobuliinit, voivat auttaa hallitsemaan myasthenia gravis -bakteeria. Toisaalta lääkkeet, kuten dopamiinireseptoriagonistit ja levodopa, jotka palauttavat aivojen dopamiiniaktiivisuuden, voivat lievittää motorisia oireita Parkinsonin.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Fatal
Fda Designates Myasthenia Gravis Agent Rozanolixizumab Application For Priority Review
UCBs rozanolixizumab received priority review on its biologic license application by FDA and expects feedback during the second quarter of 2023.
UCB Pharma announced that the FDA has granted priority review for the biologic license application for its agent rozanolixizumab), a potential treatment for adults with generalized myasthenia gravis who are anti-acetylcholine receptor or anti-muscle-specific tyrosine kinase antibody positive.1 If the FDA approves the review, it could deliver significant improvements for the safety and effectiveness of the treatment, diagnosis, or preventative care for this patient population.
The application is based on data from the phase 3 MycarinG study which showed that rozanolixizumab significantly reduced Myasthenia Gravis-Activities of Daily Living score over a 43-day period. Notably, rozanolixizumab 7-mg/kg and 10-mg/kg had a least-square mean change on MG-ADL of 3.370 and 3.403 compared with 0.784 for those on placebo.
Two hundred patients were randomized 1:1:1 in the MycarinG study and given weekly rozanolixizumab 7 mg/kg , 10 mg/kg or placebo for 6 weeks,followed with an observation period for 8 weeks. In the active treatment arm group, a higher proportion of treatment emergent adverse events occurred in comparison with placebo . Reports of the most common TEAEs were headache, diarrhea, pyrexia, and nausea although, a higher incidence of headache was observed in the rozanolixizumab groups versus placebo.
What Is Corticobasal Syndrome
Corticobasal syndrome is a form of atypical parkinsonism , which means that it shares some features with Parkinsons disease such as stiffness , tremor at rest, slowness of movement and postural instability . It may also cause problems with memory and thinking. Corticobasal syndrome, however, is distinct from Parkinsons disease in regards to other clinical features and its response to treatment.
There are some variations of the name of corticobasal syndrome. The name implies the parts of the brain are damaged. Corticobasal syndrome results in gradual loss of nerve cells in the surface of the brain as well as deep structures . These brain regions are heavily involved in the control of movement, so corticobasal syndrome causes problems with mobility. In contrast to other types of atypical parkinsonism, the neurodegeneration in corticobasal syndrome is markedly asymmetrical, thus the symptoms usually start on one side of body and remain worse on that half throughout the course of the disease.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Seizures
Advice On Parkinsons Disease
- The diseases characterized by slow motor impairment of the movements and poor response, cognitive loss with difficulty in the reactivity, are disabling for driving.
- The patient should visit his physician for any doubt, and if the presence of symptoms of secondary parkinsonism is confirmed, although it is beginning, he should be advised against driving until the clinical condition subsides.
- In evolutive diseases with movement and position disorders, it is advised against driving on a permanent basis.
- When the patient is diagnosed of Parkinsonâs disease, the symptoms characteristic of the disease will be disabling for driving.
- Furthermore, the drugs used can cause adverse reactions that would hinder driving further, and should be noticed.
With your help, we can multiply the scope of our initiatives.
Join our Foundation.
Parkinsons And Mental Well

The impact on mental and cognitive health is real. Parkinsons cognitive changes, depression, and anxiety can disrupt social life, careers, hobbies, and interests. They can uproot our sense of identity and how we relate to others. If you experience any of these symptoms, you are not alone. While they can feel isolating at times, people with Parkinsons understand the mental toll.
Recommended Reading: Best Probiotic For Parkinson’s
Parkwest Provides Answers After Patients Eight
Mercer Granade was in a dramatic state of decline that was sudden and completely unexpected. It was absolutely terrifying, says Granade, 71. When he spoke, no one understood him. When he tried to eat, he couldnt. His muscles were failing him and he was desperately weak when he arrived in the emergency department at Parkwest Medical Center in March 2022.
Quina Diferncia Hi Ha Entre El Parkinson I La Myasthenia Gravis
La malaltia de Parkinson és un trastorn de moviment caracteritzat per un descens del nivell de dopamina del cervell mentre que la miastènia gravis és un trastorn autoimmune caracteritzat per la producció danticossos que bloquegen la transmissió dimpulsos a través de la unió neuromuscular. Myasthenia gravis és una malaltia autoimmune, però el Parkinson no es considera una malaltia autoimmune. Aquesta és la diferència principal entre el Parkinson i la miastènia gravis. Laparició de cossos Lewy i la pèrdua de neurones dopaminèrgiques en pars compacta de la regió de substància nigra del cervell mitjà són els canvis morfològics característics de la malaltia de Parkinson. En canvi, el bloqueig de la transmissió dimpulsos nerviosos a la unió neuromuscular a causa de lacció dels autoanticossos és la base patològica de la miastènia grava.
You May Like: Parkinson Silverware
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Vascular Parkinsonism
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public Liaison
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
National Institutes of Health
Bethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Impact On Quality Of Life
Parkinsons disease can be quite unpredictable. From the speed of progression to the symptoms experienced, PD affects everyone differently. The uncertainty of this condition, paired with the fact that there is no cure at this time, can lead to a major impact on quality of life. Parkinsons can bring on new worries, fears, and anxieties and that is completely understandable.
You May Like: How Long Does End Stage Parkinson’s Last
Loss Of Strength Of Central Origin
The most common cause is the vascular disease by infraction or hemorrhage.
- Hemispheric disorders: they cause paresis, and if the injuries are extensive and associated with focal neurological deficits such as dysphasia, contralateral homonymous hemianopsia, and oculocephalic deviation to the side of the injury.
- Injuries in the encephalic trunk: there occur as hemiparesis, tetraparesis, and less frequently monoparesis of contralateral localization. Some cranial pairs are affected and they are associated with a reduction of the level of consciousness.
- Spinal cord injuries: they cause ipsilateral hemiparesis, or else, tetraparesis in cervical injuries or paraparesis in dorsal injuries. They can be associated with spasticity of the extremities and sensory symptoms as paresthesia, that can start in one or both feet and rise. The motor involvement due to interruption of the corticospinal bundles causes tetraplegia or paraplegia, with increased muscle tone.
What Is The Opposite Of Myasthenia Gravis
The difference between LEMS and myasthenia gravis LEMS is a rare disorder of the nervous system caused by a disruption of how the nerve and muscle talk to each other. The disruptions are caused when antibodies bind to and attacks the nervous system. The reasons why this happens is currently unknown.
Also Check: Zhichan Capsule
Don’t Miss: Is There A Parkinson’s Test
How Effective Is Treatment For Mg And Als
As mentioned above, ALS treatment can only do so much. People with the disease can participate in many therapy methods only to improve their quality of life. However, a person with MG can go into remission with effective treatment and lead everyday, symptom-free lives.
Department Of Neurologyclinical Academic Building
About the department
The Department of Neurology faculty provides diagnostic and consultative services for all neurological disorders. The department serves as the major regional referral center for patients with movement disorders, including Parkinsons disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and dystonia epilepsy stroke multiple sclerosis neurogenetic disorders neuromuscular disorders such as ALS and myasthenia gravis nervous systems disorders affecting vision such as optic neuritis headache and neurobehavioral disorders such as dementia.
to visit the departments website.
Physicians & Professionals
Phone: Fax: 732-235-7041
The Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology Program at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School specializes in the evaluation, diagnosis and treatment of cognitive, psychiatric and behavioral syndromes within neurology. Conditions we treat include:
1. Diffuse and multifocal brain disorders affecting cognition and behavior .
2. Neurobehavioral syndromes associated with focal brain lesions .
3. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of neurological disorders .
Phone: Fax: 732-235-7041
Our Epilepsy Center consists of epilepsy neurologists, neurosurgeons, neuropsychologists, nurse practitioners, pharmacologists, psychiatrists, neuropathologist and research coordinators. We evaluate and manage new-onset or chronic seizure disorders.
Electrocorticography in assisting neurosurgeons for epilepsy resective surgery
About ALS
Also Check: On And Off Phenomenon
Read Also: Parkinson’s Physical Therapy Exercises
