Scientifically Backed Ways To Prevent Parkinsons Disease
Dopamine plays a major role in a variety of mental and physical functions, including:
- Voluntary movement
- Memory
- General behavior
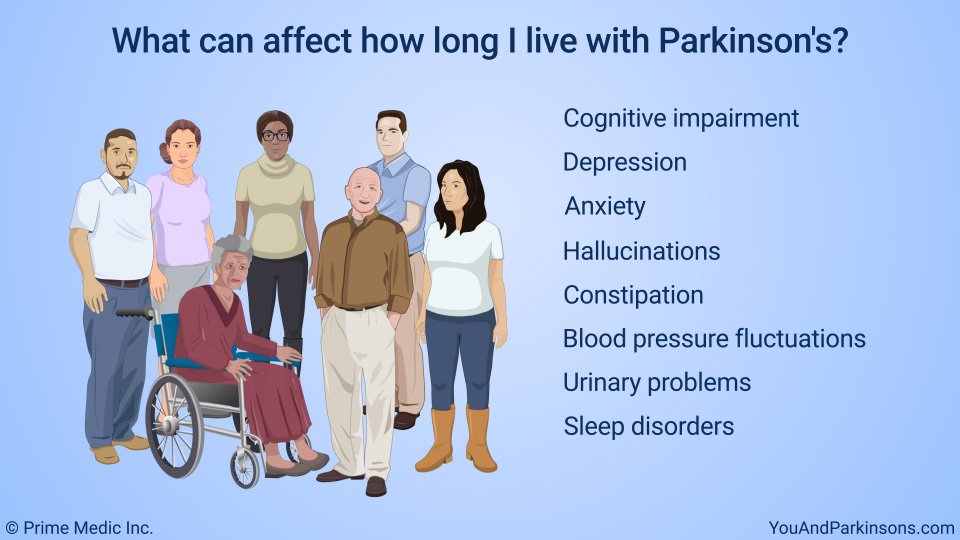
Parkinsons now afflicts roughly 1.5 million people in the United States alone, with primary symptoms being body tremors, slow movement, rigid limbs, reduced memory, a shuffling gait and speech impairment. So we have to ask:
1.) What causes it?
2.) How do we prevent it?
Currently there isnt a known cure, and its not fully understood what causes the dip in dopamine however, we know that aging is the single most important risk factor for PD, with inflammation and stress contributing to cell damage. And we now know enough about the disease to understand the preventative measures that counter the aging and death of the neurons under attack.
Because there is no known cure, its critical that we prevent the disease before symptoms arise. Granted, thanks to recent advancements in modern surgical procedures, there are some safe surgeries that can mitigate some of the more severe symptoms associated with PD. The most common one now is deep brain stimulation, in which they implant an electrode into the brain that can stop some of the more severe symptoms of Parkinsons.
But this article will try to keep it from getting to that point. The less drugs and surgery we can have in our lives, the better.
What Is A Datscan
A DaTscan is an imaging drug, also called Ioflupane I 123 or phenyltropane, that acts as a radioactive tracer for dopamine transporters within the brain. This drug was approved by the FDA in 2011. It may help distinguish the diagnosis of essential tremor from Parkinson’s syndromes, like Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease dementia.
The drug is administered during the SPECT scan. This scanning technique gathers images of a particular area in the brain called the striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum helps facilitate the transportation of dopamine.
DaTscan is injected into the patients bloodstream and eventually circulates to the brain. The tracer attaches itself to a molecule found on dopamine neurons in the striatum called the dopamine transporter . The patient then undergoes a SPECT scan which will produce an image of the dopaminergic neuron terminals that remain available in the striatum.
In patients with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or parkinsonism , this area of the brain will show dark. This indicates the loss of dopamine-containing nerve cells within the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
Imaging And Lab Tests
Your doctor may order some imaging tests and laboratory tests. Imaging tests can include computed tomography scans and magnetic resonance imaging scans. Laboratory tests can include blood tests and urine tests.
While these tests and scans will not help diagnose Parkinsons disease, they can help rule out other conditions that have similar symptoms.
Your doctor may also suggest that you get a dopamine transporter scan . This scan requires a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner. It involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug so that your doctor can study the dopamine systems in your brain .
While a DaTscan cannot conclusively prove that you have Parkinsons, it can help confirm your doctors diagnosis and eliminate other conditions.
Don’t Miss: Non Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
How I Reversed My Parkinsons Disease Symptoms
- SAVE
Being diagnosed with Parkinsons disease is a life-altering event. Youre presented with all these drugs to take to help ward off the unpleasant symptoms but these drugs cause unwanted side effects.
Its not a no-win situation. You can manage and possibly reverse Parkinsons disease and live a full life.
Its time to find out what you can do to help your body deal with this disease naturally and effectively. Just keep reading.
Collection Of The Sdata And Gdata Sets
One core requirement was to capture data passively, so as to enable unobtrusive screening for PD. To that end, data were recorded automatically when subjects performed certain actions with their personal smartphones. Specifically, accelerometer data were captured whenever a phone call was received or made by the subject. An upper threshold of 75s was set for this type of recording in order to preserve battery life. Keystroke timing data were recorded by a custom software keyboard, developed for the needs of the study and bundled with the Android application. Whenever the subject used the custom keyboard to type, two timestamps were captured per key tap, one indicating the down time and the other indicating the uptime . The typed content was never captured. Data captured from both modalities, along with some pseudo-anonymised metadata, were temporarily stored on the smartphone database and eventually uploaded to a remote server, when the phone was deemed to be idle.
Table 4 Clinically-assessed subjects that contributed typing data. All values refer to the population mean, with the standard deviation given inside parentheses.
You May Like: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
When Is Datscan Helpful
There are situations in which DaTscan can be very helpful in securing a diagnosis when neurologic exam findings are not clear-cut. Although DaTscan cannot distinguish PSP, CBGD, and MSA from PD, studies suggest that it may be able to distinguish drug-induced parkinsonism and vascular parkinsonism from PD.
The FDA indication for DaTscan is for distinguishing between PD and essential tremor . Usually it is quite straightforward for a neurologist to distinguish between the tremors of ET and the tremors of PD. PD tremors occur at rest and are accompanied by slowness and stiffness of the limb, whereas ET tremors occur with action and are not accompanied by slowness and stiffness of the limb. However, some people may have mixed tremor features making the diagnosis more difficult. In those cases, a DaTscan can be very useful.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Parkinsons affects nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
Also Check: L Dopa Dyskinesia
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
What Helps Parkinsons Disease
There is no official cure for Parkinsons Disease.
As the disease progresses, patients often suffer from cognitive decline. Existing treatments can help ease symptoms, but over time, the drugs themselves can cause debilitating side effects.
Carbidopa is most commonly used for Parkinsons disease. However, there can be a number of negative side effects and problems associated with the administration of carbidopa during treatment of Parkinsons disease. This is thought to be because the administration of carbidopa will deplete the body of vitamin B-6, l-tyrosine, l-tryptophan, 5-hydroxytryptophan , serotonin, and sulfur amino acids.
The properly balanced administration of Mucuna pruriens , and not carbidopa, in conjunction with 5-HTP, l-tyrosine, l-cysteine, and other supportive nutritional supplements can improve symptoms.
A research study, led by Dr. Marty Hinz and printed in the International Journal of Internal Medicine, was done with 254 Parkinsons patients who were newly diagnosed with no previous treatment and those who were diagnosed more than 20 years before and had tried many other medical treatment options. It showed that these supplements were helpful in the treatment of Parkinsons Disease.
Recommended Reading: Early Signs Of Parkinson’s In Males
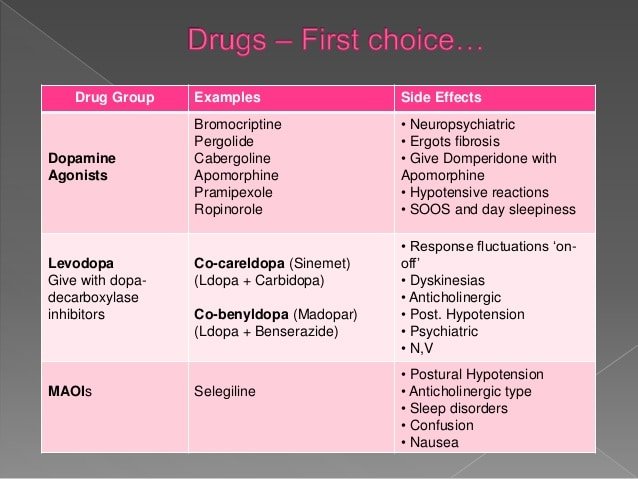
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
A diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is likely if you have at least 2 of the 3 following symptoms:
- shaking or tremor in a part of your body that usually only occurs at rest
- slowness of movement
- muscle stiffness
If your symptoms improve after taking a medication called levodopa, it’s more likely you have Parkinson’s disease.
Special brain scans, such as a single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases to try to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease can be complicated because there isnt a specific blood test or screening test that can determine whether or not you have it.
Instead, Parkinsons is diagnosed clinically, which means a doctor will examine you, review your symptoms and medical history, and diagnose accordingly.
Parkinsons disease is a neurological condition that can make movement difficult. If your general practitioner thinks you might have Parkinsons, they may refer you to a neurologist who specializes in movement disorders for a diagnosis.
It can be challenging to catch Parkinsons in the early stages because the symptoms may be too mild to notice or meet the diagnostic criteria. Also, early Parkinsons symptoms are often mistaken for typical signs of aging.
The symptoms of Parkinsons disease are also similar to those of other health conditions, which may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons at first. Your doctor may suggest specific tests and scans to help eliminate other conditions that can mimic the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Essential Oils For Parkinson’s
Get Predictions And Accuracy
The next and the final step is to get predictions for the testing dataset and estimating the accuracy of our model. The code to do the same is shown below.
predictions=model_obj.predictprint*100)
After running the code we come to know that the model is over 97.43% accurate which is pretty good right?! So there we go! We build our own Parkinsons Disease Classifier.
Physical And Neurological Examination
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
You May Like: Parkinson’s Icd 9
S For Detecting Parkinsons Disease:
1) Import Libraries
Firstly we will import all the required libraries which have been shared in the prerequisites section.
Code:
#load all modules for Parkinson's Disease Detection Projectimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_errorimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn import treefrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
2) Preprocessing
Read the parkinsons.csv file in dataframe using the pandas library
Code:
#read csv file of parkinson's datasetdf=pd.read_csv
dataset file :
Fetch the features and targets from the dataframe. Features will be all columns except name and status. Therefore we will drop these two columns. And our target will be status column which contains 0s and 1s
Code:
#extract features but we don't want 'name' and 'status' columns#so we will drop these two columns and store remainings#axis 1 is for columnsfeatures = df.drop#our target data will be 'status'target = df.loc
3) Normalization
We will scale our feature data in the range of -1 and 1. Scaling is important because variables at different scales do not contribute equal fitting to the model which may end up creating bias. For that we will be using MinMaxScaler to fit and then transform the feature data.
Code:
4) Training and Testing
Code:
5) Building the classifier model
Random forest example:
Code:
Tips For Caring For Someone With Parkinsons Disease
Caring for a loved one with early onset Parkinsons can be difficult. If youre a caregiver for someone with this condition, its important that you remember your own emotional and physical health.
Not only are you dealing with a difficult diagnosis, youre also managing an increased number of responsibilities. Burnout is common in caregivers, so make sure youre checking in with your own needs.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation Center for Parkinsons Research recommends these tips for caregivers:
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Parkinson’s Dementia
What Are The Symptoms
Each person is affected differently by Parkinsons disease and no two people will experience exactly the same symptoms. The impact of Parkinsons disease can be unpredictable and it is common for people to have good days and bad days.
The main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are:
- tremor
- rigidity
- balance problems
- problems with posture
Other possible symptoms include difficulty initiating movement , a shuffling gait when walking, and freezing when trying to move . People might experience a loss of facial expression, speech problems , swallowing problems, bowel and bladder problems, difficulties at night and tiredness during the day. Skin can become greasy and people might experience excessive sweating. Sexual problems are common. People often experience depression and anxiety. Another common symptom is small handwriting .
Other less common symptoms can include pain and memory problems.
