Let’s Talk: Discussing The Diagnosis And Navigating Family Dynamics
In this hour long talk at the 2019 CurePSP Family Conference, Jessica Shurer, MSW, LCSW discusses how to explain your diagnosis to people unfamiliar with it in understandable terms, and how family members and caregivers can help with this conversation. While the diagnosis referred to in this talk is progressive supranuclear palsy , which is a parkinsonism with similarities to Parkinson’s Disease, the concept is the same.
Ms. Shurer gave a similar half-hour talk at the CurePSP Family Conference in Nov. 2020. That talk is posted on the CurePSP YouTube channel.
What Is Essential Tremor And How Is It Different To A Parkinsons Tremor
A tremor is a rhythmical, involuntary movement that affects a part of the body, such as the hand.
Essential tremor is the most common type of tremor. Its most noticeable when your hands are doing something and it usually affects both the right and left sides of the body equally. Essential tremors often lessen when your body is resting.
Unlike an essential tremor, a Parkinsons tremor is most obvious when the affected body part is resting and tends to be less noticeable with movement. It usually starts on one side of the body and may progress to the other side as Parkinsons develops.
The time it takes to get a diagnosis can vary from person to person. Some people may receive a diagnosis of Parkinsons quite quickly, but for others it may be a long process. This can be due to a number of things, including your medical history, your age and what symptoms you have.
Your specialist may wish to rule out other causes of your symptoms first and see how you respond to treatment. This may take some time, and, as already mentioned, there is currently no definitive test for Parkinsons.
How you respond to treatment may help your specialist make a diagnosis. Keeping a diary or record of your symptoms will give the specialist more information to guide their decision.
Because the symptoms of Parkinsons are sometimes similar to other forms of parkinsonism, people can sometimes be misdiagnosed.
Is A Diagnostic Error Possible
About 25% of people who are diagnosed with Parkinsons disease do not have it. If your diagnosis was made by your general practitioner, it is important to see a neurologist.
If it was a general neurologist who made the diagnosis, you might be interested in meeting with a neurologist who specializes in movement disorders. Because they are trained to specifically diagnose and treat movement disorders. They are better equipped to distinguish Parkinsons disease from other related diseases with similar symptoms.
Read Also: Life Expectancy After Parkinson’s Diagnosis
When Does Parkinsons Start
Many people live with Parkinsons for years before being officially diagnosed. Early symptoms are called pre-motor symptoms and effects like constipation, depression and loss of smell can begin anywhere from a few months to multiple decades before a diagnosis or more visible motor symptoms like tremor appear. Looking back after diagnosis, some people can pinpoint the onset of their Parkinsons or recognize seemingly disconnected symptoms that in hindsight were really the start of what they can now identify as Parkinsons symptoms.
For younger people with Parkinsons or those without the more classic symptoms of tremor, rigidity and slow movement, the diagnosis can be more difficult and take longer to confirm.
Parkinsons is complex, multifaceted and not to be faced alone. Putting together a strong care team among your family and community, friends and mentors in the Parkinsons community and various healthcare professionals will help you best manage symptoms and enjoy the best possible quality of life.
A care team can range from your family members to your acupuncturist, and include just about everyone in between! Since Parkinsons impacts each person so differently, your care team will be unique to you and it will change and evolve as your symptoms do the same. Healthcare providers, complementary therapy specialists and even emotional well-being professionals should all be considered as you evaluate who best fits on your personal care team.
Tips For Caring For Someone With Parkinsons Disease
Caring for a loved one with early onset Parkinsons can be difficult. If youre a caregiver for someone with this condition, its important that you remember your own emotional and physical health.
Not only are you dealing with a difficult diagnosis, youre also managing an increased number of responsibilities. Burnout is common in caregivers, so make sure youre checking in with your own needs.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation Center for Parkinsons Research recommends these tips for caregivers:
You May Like: Parkinson’s Life Expectancy After Diagnosis
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s Disease And Parkinson’s Syndrome
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Who Do I Contact For A Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
If you are worried, see your GP. He will be able to support you and refer you to appropriate specialists.
The diagnosis of Parkinsons disease is based on your doctors description of symptoms and his neurological examination. There is no blood test or x-ray examination to confirm the diagnosis.
The first symptoms of the disease are not specific. Taken one by one, they do not make it possible to rule on the disease. However, it is the general portrait of the symptoms that will concern your doctor.
If your doctor suspects that you have Parkinsons disease, they will put you on a waiting list to get an appointment with a neurologist. Depending on the availability of resources in your area, you should get an appointment within 6 months. If you have had a fall in the past few weeks, tell the doctor. This could reduce your wait time.
Keep a symptom diary and bring it to your appointment. This will help you describe the changes you have observed.
- What are your concerns?
- What medications do you take?
- What changes have you observed?
- Are there any situations that make your symptoms worse?
- Are your daily activities affected? Which ones?
- Do you have difficulty smelling certain smells?
- Do you have trouble sleeping?
- Have you noticed any changes in your memory or mood?
Have someone accompany you to your appointment. Not only will your loved one be able to provide important information during the meeting, but will also be able to support you in the process of accepting the diagnosis.
Read Also: 10 Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease That Doctors Often Miss
What Parkinsons Diagnosis Criteria Do Doctors Use
Until the 1980s, there was no formal diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons disease. Beginning with James Parkinsons 1817 article, An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, and Margaret Hoehn and Melvin Yahrs description of the five stages of motor progression in 1967, scientists focused on the unique ways Parkinsons disease affects movement. A few scientists also noted non-motor symptoms like issues with automatic body functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
With the discovery in the 1950s of levodopa, a drug that gets turned into dopamine in your brain and thus replaces some of the dopamine that is lost due to PD, and the discovery of how dramatically levodopa improves motor symptoms, the medical community continued to focus more of their efforts on defining and treating Parkinsons as a motor condition.7
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Diagnosing Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
There is no single test to detect Parkinsons. A diagnosis may be difficult and take a while. The condition is usually diagnosed by a neurologist based on a review of your symptoms and a physical exam.
A DaTscan to visualize your brains dopamine system may help confirm diagnosis. Blood tests and other imaging tests, such as an MRI scan, dont diagnose Parkinsons. However, they may be used to rule out other conditions.
Physical Examination And Tests
A trip to the neurologists office often includes what seems like dozens of questions, along with multiple tests.
There currently are no diagnostic blood tests for Parkinson’s disease, but your doctor may do some routine blood and urine tests to assess your overall health. Your blood pressure will be taken sitting and standing to look for orthostatic hypotension.
A movement disorder specialist will do a variety of physical tests to assess you as well.
Also Check: How Much Mucuna Pruriens To Take For Parkinson’s
How Many People Does Parkinsons Disease Affect
Parkinsons disease affects 1 in every 500 people in Canada. Over 100,000 Canadians are living with Parkinsons today and approximately 6,600 new cases of PD are diagnosed each year in Canada . Most are diagnosed over the age of 60 however, at least 10% of the Parkinsons population develops symptoms before the age of 50. Approximately four million people worldwide are living with the condition.
Medications For People With Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain and other organs such as the gut, which produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This causes a deficiency in the availability of dopamine, which is necessary for smooth and controlled movements. Medication therapy focuses on maximising the availability of dopamine in the brain. Medication regimes are individually tailored to your specific need. Parkinsons medications fit into one of the following broad categories:
- levodopa dopamine replacement therapy
- dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine
- COMT inhibitors used along with levodopa. This medication blocks an enzyme known as COMT to prevent levodopa breaking down in the intestine, allowing more of it to reach the brain
- anticholinergics block the effect of another brain chemical to rebalance its levels with dopamine
- amantadine has anticholinergic properties and improves dopamine transmission
- MAO type B inhibitors prevent the metabolism of dopamine within the brain.
Recommended Reading: Effects Of Missing Parkinson’s Medication
Who Are The Specialists In The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease In Quebec
The doctors who treat Parkinsons disease are neurologists. Some of them are specialized and work in clinics for movement disorders.
In these clinics, interdisciplinary teams made up of health professionals, such as physiotherapists, speech therapists, specialist nurses, can help you manage the symptoms of the disease as they appear.
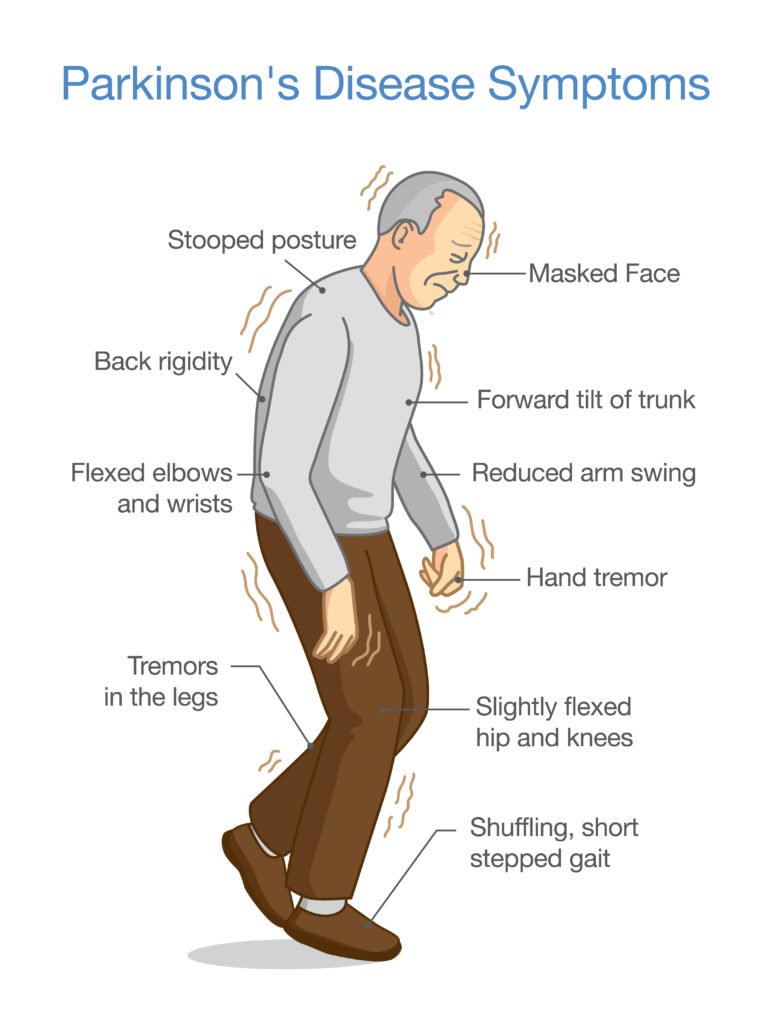
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
- tremor or shaking, often when resting or tired. It usually begins in one arm or hand
- muscle rigidity or stiffness, which can limit movement and may be painful
- slowing of movement, which may lead to periods of freezing and small shuffling steps
- stooped posture and balance problems
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary from person to person as well as over time. Some people also experience:
- loss of unconscious movements, such as blinking and smiling
- difficulties with handwriting
- drop in blood pressure leading to dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
- sweating
Many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease could be caused by other conditions. For example, stooped posture could be caused by osteoporosis. But if you are worried by your symptoms, it is a good idea to see your doctor.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
What Is The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
There is currently no treatment to cure Parkinson’s disease. Several therapies are available to delay the onset of motor symptoms and to ameliorate motor symptoms. All of these therapies are designed to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain either by replacing dopamine, mimicking dopamine, or prolonging the effect of dopamine by inhibiting its breakdown. Studies have shown that early therapy in the non-motor stage can delay the onset of motor symptoms, thereby extending quality of life.
The most effective therapy for Parkinson’s disease is levodopa , which is converted to dopamine in the brain. However, because long-term treatment with levodopa can lead to unpleasant side effects , its use is often delayed until motor impairment is more severe. Levodopa is frequently prescribed together with carbidopa , which prevents levodopa from being broken down before it reaches the brain. Co-treatment with carbidopa allows for a lower levodopa dose, thereby reducing side effects.
In earlier stages of Parkinson’s disease, substances that mimic the action of dopamine , and substances that reduce the breakdown of dopamine inhibitors) can be very efficacious in relieving motor symptoms. Unpleasant side effects of these preparations are quite common, including swelling caused by fluid accumulation in body tissues, drowsiness, constipation, dizziness, hallucinations, and nausea.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
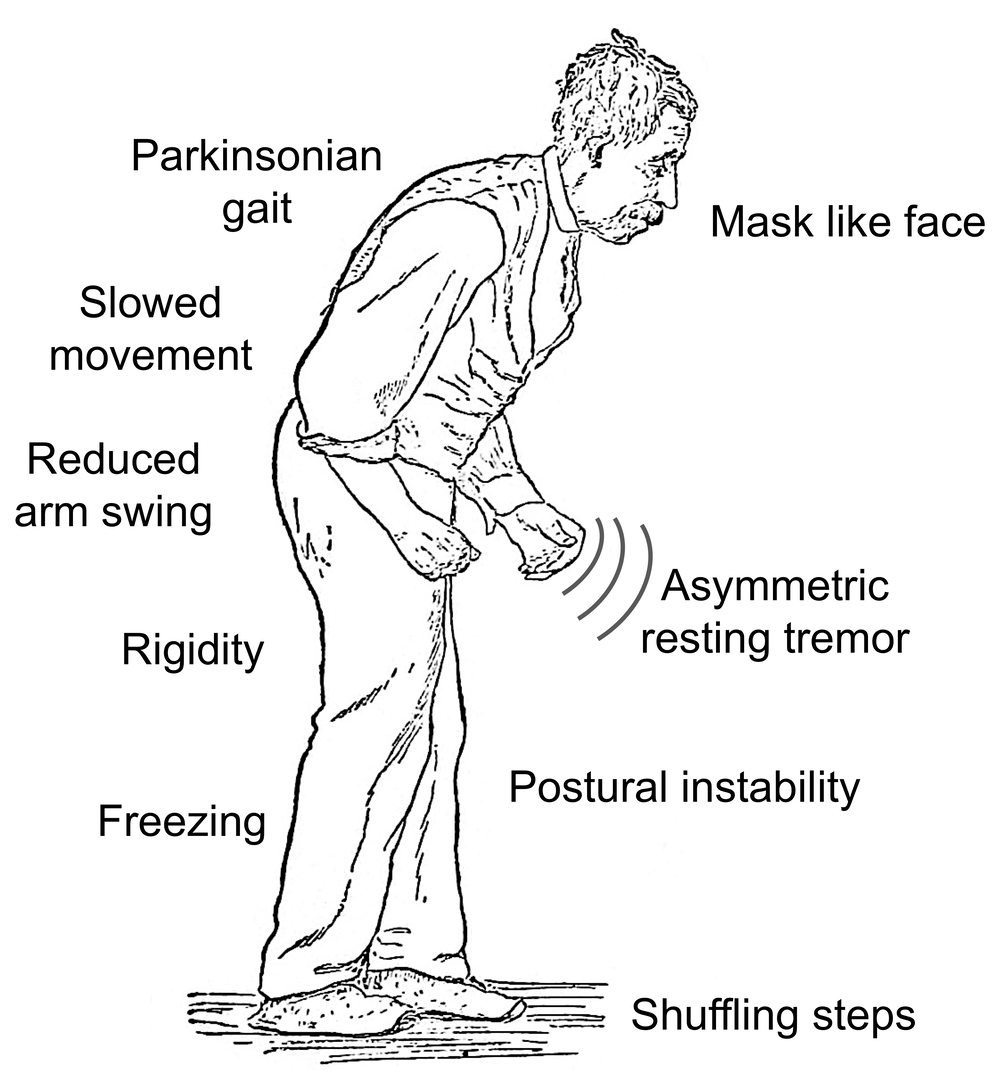
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
