Are There Side Effects From Dopamine Agonists
Side effects from DA medications can vary depending on the medication , dose, how long the medication is used, and individual traits.
If youre experiencing side effects which are bothersome, dont stop taking the medication on your own. Talk to your doctor about treatment options available to help improve your condition. This includes non-medication options too.
Side effects might be mild and go away after a few days or they may be important enough to need either a dose change or to stop the medication. DA medications can cause withdrawal symptoms or worsening of the condition if theyre suddenly stopped.
This is not a full list of side effects. Ask your pharmacist or doctor about specific concerns related to your medication.
side effects
Side effects for dopamine agonists include:
- drowsiness
- heart valve problems, heart failure
- trouble with memory or concentration
- movement-related problems
Advantages Of Dopamine Agonists
Dopamine agonists have several benefits:
- They can cross the blood-brain barrier on their own and do not need any carriers to reach the brain
- They act directly on the dopamine receptors found on the nerve cells and do not require any metabolic modification, release, or storage
- They have longer half-lives than levodopa and therefore produce more persistent dopamine receptor stimulation than levodopa
- The metabolism of levodopa produces free radicals that are toxic to nerve cells and especially dopamine-producing nerve cells. However, the metabolism of dopamine agonists does not generate any toxic byproducts
- Patients with early Parkinsons disease can be treated with dopamine agonists for several years before they require levodopa treatment. This reduces exposure to levodopa and therefore minimizes the impact of side effects such as levodopa-induced dyskinesia
- When dopamine agonists are taken alongside levodopa, they lower the dosage of levodopa required and smoothen out the on-off effects of levodopa that are responsible for dyskinesia
- Dopamine agonists can also have a positive effect on non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, such as sleep problems, mood changes, and pain.
Other Medications And Supplements
The combined use of antidepressants plus demonstrates improved effectiveness when compared to antidepressants alone, but these effects may not endure. The addition of a benzodiazepine is balanced against possible harms and other alternative treatment strategies when antidepressant mono-therapy is considered inadequate.
may have a rapid antidepressant effect lasting less than two weeks there is limited evidence of any effect after that, common acute side effects, and longer-term studies of safety and adverse effects are needed. A nasal spray form of was approved by the FDA in March 2019 for use in treatment-resistant depression when combined with an oral antidepressant risk of substance use disorder and concerns about its safety, serious adverse effects, tolerability, effect on suicidality, lack of information about dosage, whether the studies on it adequately represent broad populations, and escalating use of the product have been raised by an international panel of experts.
You May Like: What Is Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Essential Tremor Become Parkinsons
How Could The Use Of The Medication Change Or Evolve In The Future

Pavese says that in the future there could be greater potential to personalise Parkinsons treatments based on the needs of individual patients.
In terms of dopamine agonists, improved molecules with properties and activities closer to those of dopamine itself could lead to better clinical improvements with less side-effects.
He adds: Pharmacological research is very active in this field, and a number of clinical trials with new promising medications for Parkinsons are currently ongoing. Participations in these trials might not bring a direct benefit to individual participants but might help the development of new effective treatments for the disease. I therefore encourage patients to consider the possibility to take part in these clinical trials, if available to them.
Need to know: Nicola Pavese
Professor Nicola Pavese studied at Pisa University, Italy, and Imperial College London, UK. He is currently a professor of clinical neuroscience and the director of the Clinical Ageing Research Unit at Newcastle University, UK, and is consultant neurologist at Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. His research focuses on neuroimaging in neurodegenerative conditions.
Quick guide to dopamine agonists
To find out more about dopamine agonists and other Parkinsons treatments, please visit the EPDA website here.
Read more:
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Brain
Adverse Effects Of Dopamine Agonists
Side effects of dopamine agonists are common. Nausea occurs in up to 50% of patients nasal stuffiness, depression, and digital vasospasm occur, the latter more frequently with higher doses, as seen in patients with Parkinson disease. Postural hypotension can cause loss of consciousness, occurs infrequently, and is usually avoided by careful dosing. Signs and symptoms of psychosis or exacerbation of preexisting psychosis can be encountered in up to 1.3% of patients receiving bromocriptine.290 A history of psychotic symptoms should raise concerns about using these medications. If psychosis occurs in a patient in whom dopamine agonists are clearly the treatment of choice, the judicious combination of this agent and antipsychotic medication can be effective. A neuroleptic that is not a potent PRL stimulator, such as olanzapine, is preferred. CSF rhinorrhea occurs during dopamine agonist treatment in up to 6.1% of patients with macroadenomas, some of which are more resistant to dopamine agonists.291 Other rarely reported serious side effects include hepatic dysfunction and cardiac arrhythmias. Retroperitoneal fibrosis, pleural effusions and thickening, and restrictive mitral regurgitation have been reported in patients taking high doses of bromocriptine.292,293 Hypersexuality with disordered impulse control may occur with restoration of eugonadism or may be a direct dopamine effect.294
Philip A. Hanna MD, Joseph Jankovic MD, in, 2010
Ive Just Been Prescribed A Dopamine Agonist What Should I Be Aware Of
It is very important to mention the slightly higher risk of developing impulse control disorders, particularly pathological gambling, compulsive shopping, and hypersexuality as these could have important financial and social repercussions, says Pavese.
The possible occurrence of excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks should also be discussed, particularly with regards to driving.
I believe that it is very important for the patients, when possible, to take time to learn more about the different classes of medications that are available for Parkinsons and how they work so that they can participate in a discussion with their physicians and nurse specialists to choose the best treatment for their specific needs.
Recommended Reading: Do Parkinson’s Patients Get Mean
Involvement Of The Patients And The Public
No patients were involved in setting the research questions or the outcome measures, nor were they involved in developing plans for the design or implementation of the study. No patients were asked to advise on the study interpretation or write up the results. There are no plans to disseminate the results of the research to the study participants or the relevant patient community. It was not evaluated whether there was patient involvement with any of the studies included in the review.
What Are The Side Effects Of Dopamine Agonists
Dopamine agonists are associated with a number of side effects. Often these affect older patients, over the age of 65. These can include sleepiness, constipation, nausea and headaches, hallucinations and heart disease. Higher doses are associated with impulse control disorders.
The side effects of currently available dopamine agonists are generally mild and very similar to those caused by levodopa preparations, says Pavese. Compared to levodopa, there is a slighter higher risk to develop excessive daytime sleepiness, impulse control disorders, and, especially in elderly patients, hallucinations and psychosis. These side effects can be slightly different among the different types of dopamine agonists.
In these cases, the reduction of doses or the progressive weaning off of the implicated dopamine agonist improves the symptoms. Re-adjustments with possible increases in the doses of levodopa are then possibly required.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease And Muscle Spasms
Some Disadvantages Of Comt Inhibitors
These drugs can increase the side effects caused by levodopa, notably dyskinesias , nausea and vomiting.
If these side effects increase after starting the drug, people should raise the issue with their healthcare professional, as reducing the levodopa dose can often help.
COMT inhibtors will discolour urine making it a reddish-brown colour. Some people also experience diarrhoea which may occur some months after commencing the medication.
Be aware that other drugs for Parkinsons or other conditions can affect the action of COMT inhibitors. The combination of apomorphine and entacapone needs careful supervision.
Examples Of Dopamine Agonists
Following are the common dopamine agonists that are used to treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
- Bromocriptine
- Rotigotine
- Apomorphine
Bromocriptine and pergolide were widely used in the past but now rarely used mainly because of their adverse effects on the heart. They are linked to a heart condition called valvular heart disease.
Read Also: What Year Was Michael J Fox Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
Dealing With Side Effects Of Parkinsons Drugs
Its important to speak to your specialist or pharmacist if you notice anything unusual.
Changing or adding to your medication might help, and your specialist will be able to look into this.
For many people with advanced Parkinsons, medication may start to be reduced if side effects outweigh the benefits of taking medication.
But if some of the medication is reduced, you may find you get the benefits of the remaining ones, rather than the side effects.
If you experience side effects from your Parkinsons medication, you shouldnt stop taking it without guidance from your specialist.
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
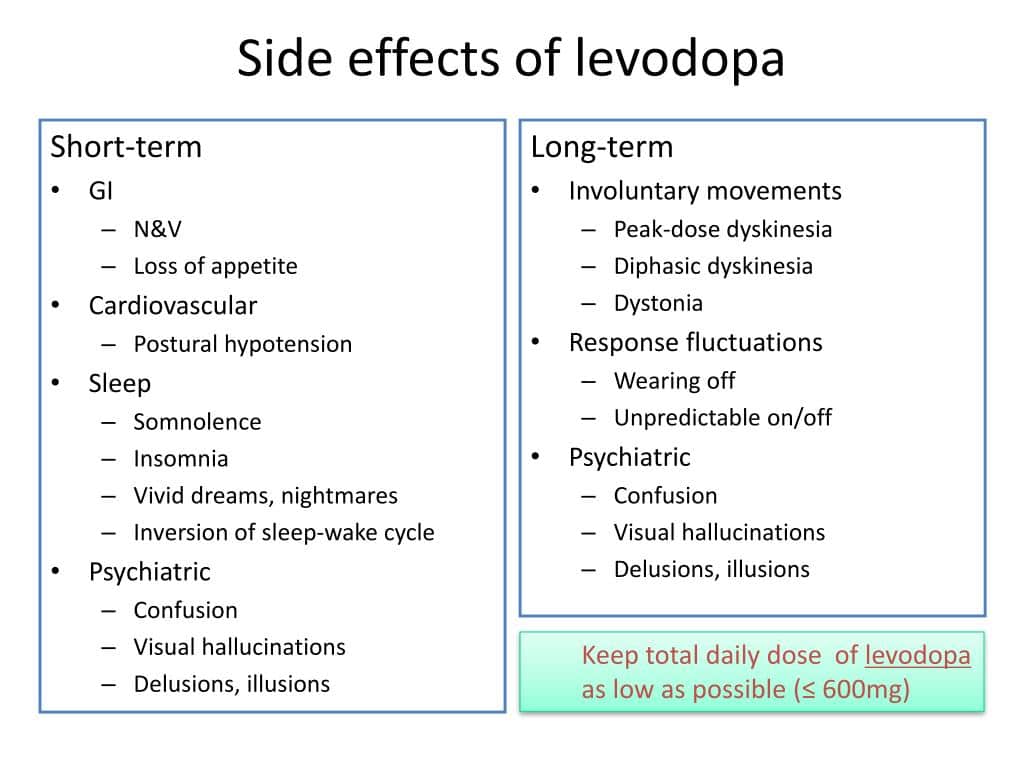
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinson’s disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
Recommended Reading: Does Stress Cause Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Drugs
The most common reactions include nausea, vomiting, dizziness , sleepiness and visual hallucinations.
In the last few years, levodopa and dopamine agonists in particular have been associated with the emergence of behavioral changes such as impulse control disorders. These are characterized by failure to resist an impulse to perform certain actions.
Impulse control disorders include a range of behaviors such as compulsive gambling or shopping, hypersexuality, binge eating, addiction to the Internet or to other recreational activities. These activities are often pleasant in the moment, but over time may become harmful to you or to others. If you are experiencing these behaviours, tell your neurologist/doctor. Often the medication can be adjusted which can reduce or control the behaviour.
Care partners can play an important role in helping to identify when these behaviours occur. If you are a care partner, tell the person if you have noticed a change in his/her behaviour or personality and encourage him/him/her to speak with the doctor immediately so medication can be adjusted.
Mechanism Of Action Of Available Drugs
The major classes of drugs currently available for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease are shown in Table 1. Many aim to increase dopamine in the brain, by increasing its production or altering its metabolism .
|
Table 1 |
Drugs with alter metabolism in boxed red italics
Levodopa
Levodopa is absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the brain where it is converted to dopamine. Levodopa has a short plasma half-life of about one hour. Early in Parkinson’s disease, levodopa has a long duration of action which is independent of plasma concentration, but as the disease progresses, the duration of the effect reduces. The short-duration effect is strongly linked to plasma concentration and lasts, at most, hours.
Slow-release preparations are gradually absorbed, resulting in more sustained plasma concentrations. They have reduced bioavailability higher doses are required to match the benefit of an equivalent strength of a standard preparation. Rapid release preparations are taken in liquid form to enhance passage through the stomach and absorption from the small intestine.
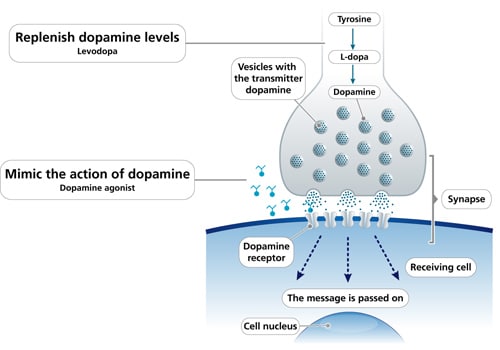
Dopamine agonists
Apomorphine is a potent emetic so patients must be pre-treated with domperidone 20 mg three times daily orally for at least 48 hours before the first injection. Domperidone should be continued for at least a few weeks once regular intermittent treatment has commenced. The dose can then be tapered slowly as tolerance to the emetic effects of apomorphine usually develops.
Also Check: What Chemicals Can Cause Parkinson
Electrode Location And Stimulation
All patients underwent a postoperative brain MRI within 1 week after surgery. We generated patient-specific anatomical models of the STN using an academic DBS research software tool., A 3D visualization of both the implanted DBS electrodes and the volumes of the STN in the left and right hemispheres was constructed for each patient using pre- and postoperative T1-weighted MRIs. The distance between the active electrode contact and the center of the STN was then calculated for the left and right electrodes along the x-axis , y-axis , and z-axis .
Strengths And Comparisons With Other Studies
Although traditional meta-analyses have been previously published, and network meta-analyses have compared drugs, little attention has been paid to the treatment of motor fluctuation that occurs in PD patients with a focus on comparing a limited group of classes or individual therapies . In contrast to previous meta-analyses, the current analysis is the first network meta-analysis, and it integrates the broad basis of published evidence regarding randomized controlled trials to determine the efficacy and safety of drugs being used as adjuvant treatments with L-dopa for motor fluctuations in PD patients and allows a comprehensive evaluation of several categories of drugs under one overall analysis. Furthermore, this network meta-analysis also integrates evidence that is directly and indirectly compared. It has previously been reported that monoamine oxidase -B inhibitors appear to have weaker anti-Parkinsonian effects than levodopa .
NMA is a method that combines direct and indirect evidence for analysis, which breaks through the limitations of only two direct comparisons, and supports the complexity of comparison of multiple interventions. In fact, our network meta-analysis of head-to-head comparisons is relatively small. Consequently, the validity of the results after merging the direct and indirect evidence decreases.
Read Also: How Effective Is Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsonâs disease is an illness in the brain that affects many different parts of the body.
Your brain has different areas that deal with separate body parts. Cells in these brain areas are called neurons.
Neurons send electrical signals to each other to direct your body. Signals between neurons tell your body to move, make you feel pain and other sensations, manage your breathing, and perform many more needed functions.
Chemicals called neurotransmitters help these electrical signals travel between neurons throughout the brain. For example, dopamine is a chemical that plays a role in movement, motivation, and other behaviors.
The part of the brain that helps with movement and produces dopamine is called the basal ganglia. In cases of Parkinsonâs disease, cells in this area of the brain become damaged and produce less dopamine and other important neurotransmitters. This can cause problems with moving, thinking, and other functions.
Parkinsonâs disease isnât contagious. It usually appears in people around age 60 and older. People as young as their early twenties can get diagnosed with Parkinsonâs disease, though.
How Anticholinergics Are Used
These medications are older and are not used very often for Parkinsons today. Sometimes they are prescribed for reducing tremor and muscle stiffness. They can be used on their own, especially in the early stages of your Parkinsons when symptoms are mild, before levodopa is prescribed.
Anticholinergics can also be used with levodopa or a glutamate antagonist. They are taken as tablets or as a liquid.
You May Like: Is There A Genetic Test For Parkinson’s
Side Effects And Problems With Dopamine Agonists
Common side effects of dopamine agonists include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hallucinations or delusions and confusion
- Existing dyskinesias becoming more troublesome initially
If you are taking Cabergoline , Pergolide or Bromocriptine your neurologist or GP will have to arrange a chest CT scan or ultrasound of your heart yearly as over time these medications may affect heart or lung tissue.
This precaution does not apply to the other dopamine agonists available in Australia.
Levodopa Versus Dopamine Agonist After Subthalamic Stimulation In Parkinson’s Disease
Onanong Phokaewvarangkul MD, PhD
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn Centre of Excellence for Parkinson’s Disease & Related Disorders, Chulalongkorn University and King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Thai Red Cross Society, Bangkok, Thailand
Yu-Yan Poon RN
Edmond J. Safra Program in Parkinson’s Disease, Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders Clinic, Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Renato P. Munhoz MD, PhD
Edmond J. Safra Program in Parkinson’s Disease, Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders Clinic, Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Suneil K. Kalia MD, PhD
Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurosurgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurosurgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurosurgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Edmond J. Safra Program in Parkinson’s Disease, Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders Clinic, Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Correspondence to:
Onanong Phokaewvarangkul MD, PhD
Yu-Yan Poon RN
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s Disease
