How Can Botox Help Essential Tremor
Now that were familiar with what Botox is, well discuss how Botox is used for essential tremor treatment. Since Botox works by weakening the muscle it is injected into, it can be helpful to alleviate symptoms of essential tremor. When Botox is injected into the body part with tremor, the toxin paralyzes the muscle and the nerve, thus temporarily stopping the tremor. Botox can be used for head, voice, hand and facial tremors. If its done properly, using Botox for essential tremor can be safe, but there are still a few important facts to keep in mind, which will be covered later in the post.
What Does Botulinum Toxin Treatment For Parkinsons Look Like
The effects of Botulinum toxin take hold about 3-10 days after the injections and last approximately three to four months, so the treatments typically need to be repeated on a regular basis. Although this means routine injections, it also means that Botulinum toxin injections do not have any permanent side effects. Some side effects may still occur with Botulinum toxin injections and the doctor who performs the procedure will review these with you. An advantage of using Botulinum toxin for the treatment of the conditions noted above, is that the toxin typically only impacts the areas into which it is injected, as opposed to oral medications which have a more widespread effect, and therefore more potential for side effects.
Preparation Of Botulinum Toxin For Injection
The toxin is produced by the gram-negative anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is harvested from a culture medium after fermentation of a toxin-producing strain of C botulinum, which lyses and liberates the toxin into the culture. The toxin is then extracted, precipitated, purified, and finally crystallized with ammonium sulfate. BTX-A should be diluted with preservative-free saline and the preparation used within 4 hours of reconstitution. Conditions for the stability of the toxin in solution include pH 4.26.8 and temperature less than 20 degrees Celsius. Crystallized toxin is inactivated quickly in solution by shaking.
Biological activity of the BTX-A distributed by Allergan Inc. onabotulinumtoxin A is different from that of the BTX-A produced by Speywood Pharmaceuticals in England abobotulinumtoxinA or Japan. The potency of BTX is expressed as mouse units, with 1 mouse unit equivalent to the median lethal dose for mice. BOTOX® is dispensed in small vials containing 100 units , while a vial of Dysport contains 500 U. The relative potency of BOTOX® units to Dysport units is approximately 1:3. BOTOX® units are used throughout this article. Most physicians dilute the vial of BOTOX® with 1-4 mL of saline, for a concentration of 2.5-10 U/0.1 mL.
Don’t Miss: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Progress
Nationally Recognized Quality Of Care
- U.S. News & World Report ranks Northwestern Memorial Hospital in the top 10 for neurology and neurosurgery.
- Northwestern Memorial Hospital is the only hospital to offer three designated Centers of Excellence for movement disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Wilson disease.
Conditions Treated Using Botulinum Toxin In Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Personality Changes
Specialized Customized Care For Your Needs
Our goal is the same as yours to rid you of the symptoms of your condition. We accomplish this through the latest targeted medication to enhance your natural neurochemistry, combined with disease-specific physical, occupational and speech therapy. If medications are not effective, the specialists at Inova are uniquely trained to use deep brain stimulation , intestinal gel and targeted botulinum injections to improve your quality of life.
Our multidisciplinary team of neurologists, neurosurgeons, neuropsychiatrists, neurophysiologists, and physical, occupational and speech therapists have dedicated their careers to understanding and treating:
Botulinum Toxin Calms Muscles Restoring Natural Body Position
The mainstay of treatment of dystonia is with injection of botulinum toxin, such as Botox or Xeomin.
Botulinum toxin injections work by causing a disruption between the nerve and the muscle, thereby weakening the muscle into which it is injected.
Conditions treated with botulinum toxin injection:
- Blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm: facial muscles are injected to reduce involuntary blinking or grimacing movements.
- Spasticity due to stroke or multiple sclerosis or other conditions: upper or lower limb muscles are injected to relax abnormal muscle posture and stiffness.
- Migraine: muscles of the face and neck are injected to reduce muscle tension that contributes to headache. There may also be a reduction in the release of substance P, which contributes to the pain pathway.
- Sialorrhea : salivary glands are injected to reduce release of saliva.
- Cervical dystonia: muscles that are pulling or twisting the neck to one side are overactive, Botox works to calm those specific muscles down and allows for a more natural and neutral head position.
Depending on the muscle injected, EMG guidance may be used during Botox injection to verify muscle activity and ensure the most active part of the muscle is being injected.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Symptoms Be Something Else
Restoring The Quality Of Life You Deserveinova Parkinson’s And Movement Disorders Center
Be it Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia or other movement disorders, the Inova Parkinson’s and Movement Disorders Center provides comprehensive care designed to get you moving again.
From the first moments you meet with one of our specialists, you will understand our team’s dedication to individualized care. Each person has his or her own unique brand of Parkinson’s, essential tremor, dystonia, Huntington’s disease or tic disorder and deserves a personalized treatment plan to address specific needs. Our experienced movement disorders team will work with you to chart a path to better health.
What Causes Speech And Swallowing Difficulties Associated With Parkinsons
There are multiple reasons why Parkinsons can lead to speech and swallowing difficulties. For example:
- Parkinsons affects the muscles and nerves in your face, throat, mouth, tongue, respiratory system, and larynx. As these muscles and nerves weaken, you might have more speaking and swallowing difficulties.
- Parkinsons makes it difficult for your muscles to activate. This includes the muscles you need to speak and swallow, such as your throat, tongue, and larynx.
- Parkinsons affects the areas of your brain that control the speech process.
- Parkinsons changes the way your brain processes information. This can make it difficult to be part of conversations and communicate your thoughts.
- Parkinsons can cause your movements to become smaller and less powerful. This includes the movements you make with your mouth and throat that affect speech and swallowing.
- Parkinsons can reduce your sensory awareness. You might not realize that the volume, speed, or pitch of your voice has changed. You might feel that you are shouting even when you are speaking at a normal volume.
- Parkinsons can reduce your ability to prompt your own outward speech and begin conversations. Often, people with Parkinsons who are able to answer questions or respond to others have difficulty voicing thoughts without being asked.
Speech therapy can benefit people with Parkinsons.
Speech and language therapists are healthcare professionals who can work with patients to help improve:
Don’t Miss: How Does Parkinson’s Affect Speech
Research And Clinical Trials
The Parkinson’s and Movement Disorders Center brings together the advanced resources of Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, one of the nation’s premier institutions for research into movement disorders. The school was recently named by the National Institutes of Health as one of only 12 centers in the country to receive the prestigious Morris K. Udall Center grant for Parkinson’s research.
Through our center, patients have access to many ongoing clinical trials for all types of movement disorders.
Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Botox For Parkinsons Patients
Botulinum toxin is a highly successful treatment for movement disorders in adults such as dystonia, spasticity, blepharospasm or hemifacial spasm. Patients with abnormal postures or tightness in their head, face, eyes, arm or leg may benefit greatly from Botox. Its also proven effective in treating drooling in Parkinsons disease and related disorders.
Botulinum toxin works by reducing the transmission of nerve signaling to muscles. The nerves take up the toxin and then lose the ability to release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. When strategically injected into problematic muscles, it can temporarily reduce their overactive contraction, which lets the normal muscles in that body part work better to maintain a more neutral and functional posture.
Your physician will educate you fully on the procedure, on the different toxins available that can be used for your condition, and what benefits they hope to achieve for your individual care management. Its important to understand that you will not see an immediate effect from the medication improvement generally begins within a two-day two-week range.
Keep in mind that Botulinum toxin is not a cure for your disorder. Its a symptomatic treatment option to help you with your activities of daily living.
Talk to your Mercy neurologist about Botox as a treatment for Parkinsons Disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Affect Your Eyes
Does Botox Work For Hand Tremors
Botox injections have been useful in the treatment of hand tremors for some patients. The toxin must be placed directly into the target muscles and repeated every three months in order for the effects to last. If youre not sure how many units of botox for hands is needed, it varies on the person and severity of the case. Majority of patients receive between 25-75 units of Botox per hand.
Side Effects Of Using Botox
In general, side effects of Botulinum toxin can be due to over-weakening of the injected muscle, which, if done on leg and foot muscles, for example, could interfere with walking.
Uncommonly, Botulinum toxin can diffuse to neighboring muscles and cause more widespread side effects. For example, injections of neck muscles could result in toxin diffusing locally to muscles used for swallowing and cause difficulty swallowing. Even less common, are side effects due to travel of the toxin to more distant parts of the body via the bloodstream. For example, injections of any body part could theoretically result in difficulty swallowing or breathing if the toxin travels to these muscles. This is very rare however and Botulinum toxin injections are typically very safe. The full risk profile for your particular situation however, needs to be discussed with the physician performing the injections.
There are typically no limitations after the injections and you can return immediately to your normal activities.
Although dermatologists often use Botulinum toxin for cosmetic purposes, only a neurologist is qualified to determine whether the injections can help with certain PD symptoms. If you are interested to investigate whether Botulinum toxin injections may help you, discuss this with your neurologist. If he/she feels that they may be helpful, but does not perform them, he/she can refer you to a neurologist who does.
Tips and takeaways
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Die From Parkinson’s Disease
Different Types Of Botulinum Toxin
There are eight different botulinum toxin species that occur in nature. There are only two however, that are produced commercially Botulinum toxin A and B.
The commercially available products are:
Each of the above agents are FDA approved for a slightly different list of clinical indications.
Botulinum Toxin Type A
BTX proteins have been studied since the early 1900s, initially to gain an understanding of botulism, a form of food poisoning. Later, they were studied because of the unique and specific muscle paralysis induced by minute amounts of the toxins. During the past 30 years of work on the use of the toxin for human treatment, selective procedures for the production, purification, and dispensing of the toxin have been developed to make it suitable for injection. Today BTX-A is employed and considered safe and effective for the treatment of movement disorders and spasticity. One of the more common movement disorders treated with BTX-A is focal dystonia. The most common types are cervical dystonia, blepharospasm, hand dystonia, oromandibular dystonia, occupational dystonia, and laryngeal dystonia.
The administration of BTX therapy for focal dystonia requires a thorough understanding of the toxin itself and practical knowledge of typical dosages and anatomy, along with basic electromyographic skills. The optimal dose of BTX is the least amount needed to achieve a predetermined outcome without causing an adverse effect such as weakness.
Many factors affect the dose of BTX including severity and chronicity of the disease, number of muscles involved, previous response to BTX, concurrent other medical therapy used, and the experience of the person performing the injection. Smaller doses are used in children, proportionate to the body mass.
Also Check: How To Overcome Freezing In Parkinson’s
Uses Of Botulinum Toxin In Parkinsons Disease
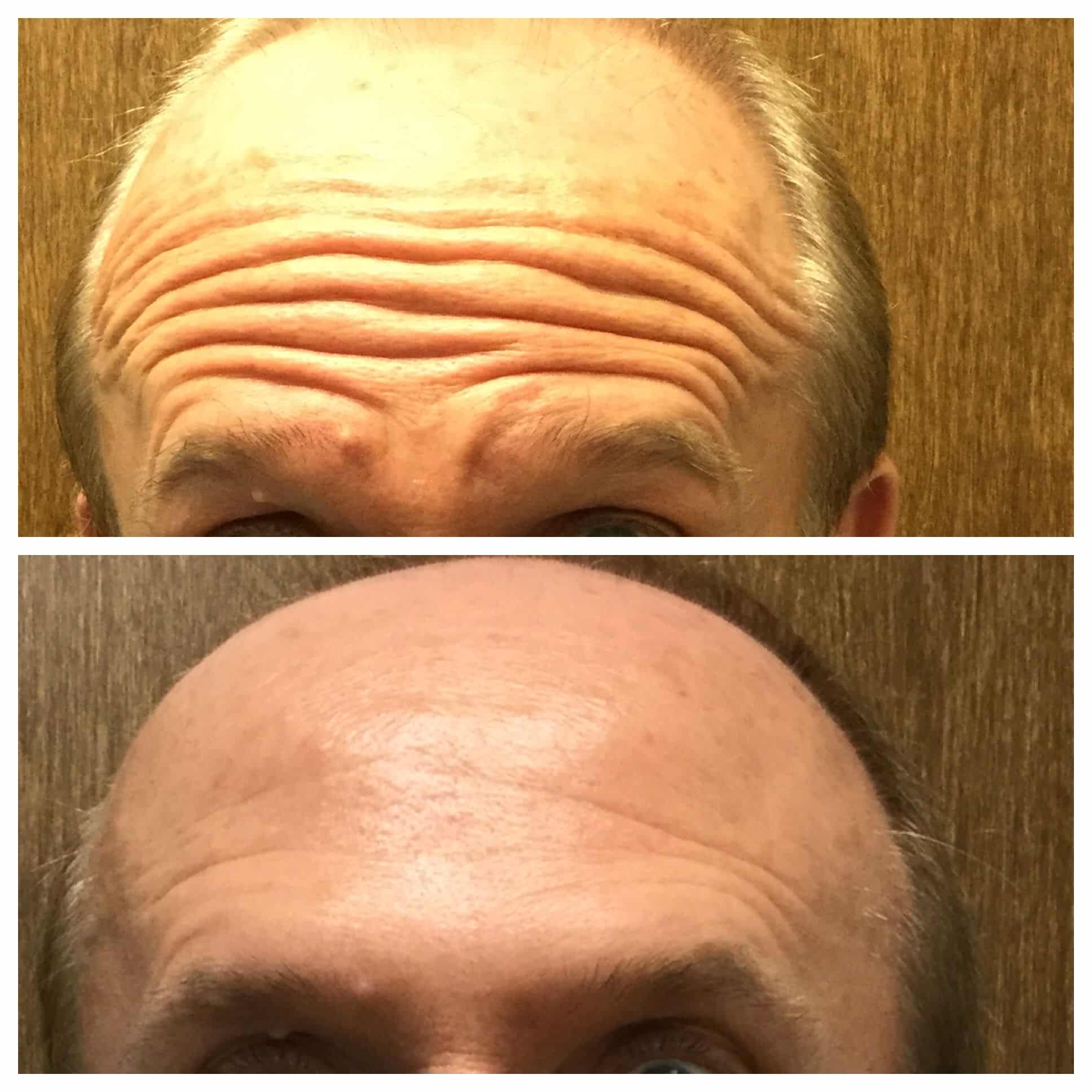
You most likely know that Botulinum toxin is used for cosmetic purposes to decrease wrinkles. Prior to being used in this way, Botulinum toxin was used for medical purposes to control abnormal movements. In the right hands, it can be a very effective measure to control a variety of problems related to PD.
Complications With Particular Clinical Applications
See the list below:
-
Ten percent of patients develop ptosis, which improves spontaneously in less than 2 weeks.
-
Other complications include blurring of vision, tearing, and local hemorrhage.
Cervical dystonia
The most common adverse effects include neck weakness , dysphagia , and local pain. The occurrence of dysphagia appears to be related to the dose and the muscles injected.
Adverse effects are transient and usually resolve spontaneously within 2-3 weeks.
Oromandibular dystonia
Adverse effects are uncommon and include dysphagia and pain at the injection site.
Allam et al support the view that executive dysfunction in primary cranial dystonia is secondary to the disrupting effects of the symptoms. Treatment with BTX alleviates the symptoms and, consequently, improves sustained attention.
Laryngeal dystonia
Swallowing difficulties, which can last for 3-7 days, occur in 60% of patients.
Transient hypophonia and stridor also have been reported.
Hemifacial spasm
Adverse effects depend on location of injection.
Lower face injections may result in facial weakness and asymmetry, face and mouth droop, drooling, and loss of facial expression. Forehead injections can result in brow ptosis or loss of eyebrow elevation.
References
Albanese A, Bhatia K, Bressman SB, Delong MR, Fahn S, Fung VS, et al. Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov Disord. 2013 Jun 15. 28 :863-73. .
Recommended Reading: Cure For Parkinson’s Disease 2022
What Is Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin is a substance produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. Botulism is caused by the harmful effects of this toxin. If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can spread throughout the body, causing widespread muscle weakness. In its full-blown form, botulism can cause difficulty with swallowing and breathing by causing weakness of the muscles that control these functions.
The good news is that decades ago, scientists learned how to isolate the toxin and harness its power for medical use, and it can be safely injected into particular muscles in order to decrease unwanted movements of those muscles.
How Do Bladder Botox Injections Work
Topics in this Post
Botox injections are not just for wrinkles on your face. They also can be used to help if you have ongoing bladder continence issues. Botox is one option to treat urge incontinence or overactive bladder in people who have not had success with other treatment options.
Urinary incontinence is common and can impair your social, physical or mental well-being. Approximately 17% of women and 3% to 11% of men suffer from urge incontinence at some point in their lives.
Urge incontinence is the unintentional loss of urine caused by your bladder contracting.
Also Check: What Causes Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Applications Of Botulinum Toxin Injections
See the list below:
Spasticity, upper and lower limb spasticity
Migraine headache
Overactive bladder, urinary incontinence
Treatment of focal dystonia with BTX is designed to improve the patient’s posture and function and to relieve associated pain.
In a study of 123 subjects with a history of 28 moderate-to-severe migraine attacks per month with or without aura, Silberstein et al found that BTX-A was found to be safe and significantly reduced migraine frequency, migraine severity, acute medication usage, and occurrence of migraine-associated symptoms.
Moffat et al studied BTX treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis and found that axillary botulinum toxin treatment is durable. Patients experience gradual return of symptoms between 6 and 24 months. A minority of cases do not require retreatment at this time.
Lin et al report that corticosteroid is superior to BTX-A in relieving pain in tennis elbow at 4 weeks after injection. Because BTX injection did not reduce pain significantly but is associated with weakness, the muscle weakness caused by BTX is unlikely to be the sole mechanism of the pain relief observed in previous studies.
Toffola et al found that BTX-A injection treatment effectively reduced facial synkinesis, thus improving facial expression symmetry both at rest and in voluntary movements.
