Treatment Options For Alzheimers Dementia And Parkinsons
There are many different types of dementia, but Alzheimers is the most common and serious. The symptoms of Alzheimers include decreased memory, communication problems, and confusion. There is no cure for Alzheimers, but there are treatments available that can help improve the patients quality of life.
Parkinsons is a progressive disorder that causes difficulty with movement and coordination. Early signs may include difficulty walking, slowness, unsteadiness, and poor balance. Parkinsons can lead to disability if left untreated. There is no cure for Parkinsons, but there are treatments available that can help improve the patients quality of life.
Dementia affects people in different ways, but usually it causes problems with memory and thinking skills. Other symptoms can include changes in mood, behavior, and activity level. There is no one-size-fits-all solution for treating dementia, but various treatments can help improve the patients quality of life.
The Effects Of Alzheimers On The Brain
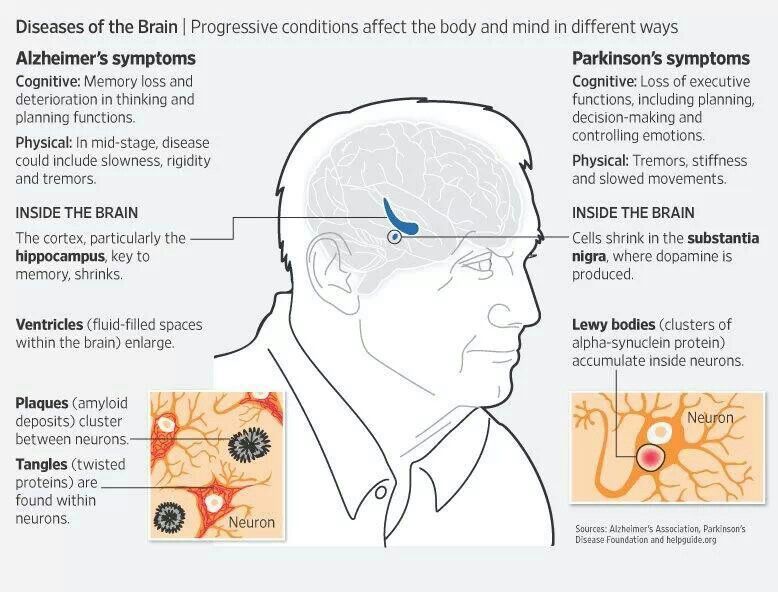
In people with Alzheimers disease, brain cells die and connections between brain cells may break down. One of the hallmark symptoms is abnormal protein deposits in the brain called plaques and tangles.
Plaques are dense clusters of protein that can block communication between neurons. Tangles are proteins that twist together that lead to the death of healthy brain cells.
In advanced Alzheimers, the brain shows significant shrinkage. Changes in the brain may occur a or more before symptoms start.
Its impossible to diagnose Alzheimers with complete accuracy while a person is alive. The diagnosis can only be confirmed when the brain is examined under a microscope during an autopsy. However, specialists can make the correct diagnosis up to 90 percent of the time.
The symptoms of Alzheimers and dementia can overlap, but there can be some differences.
Both conditions can cause:
- behavioral changes
- difficulty speaking, swallowing, or walking in advanced stages of the disease
Some types of dementia will share some of these symptoms, but they include or exclude other symptoms that can help make a differential diagnosis.
Lewy body dementia , for example, has many of the same later symptoms as Alzheimers. However, people with LBD but are more likely to experience initial symptoms such as visual hallucinations, difficulties with balance, and sleep disturbances.
Key Brain Changes Are Different
The key brain changes linked to Parkinsons disease and Parkinsons-related dementia are abnormal deposits of common brain proteins, called alpha-synuclein. These deposits are known as Lewy bodies, named after the doctor who discovered them. As more of these proteins clump in the brain, normal brain cells begin to die off.1
In Alzheimers disease, the key brain changes include the buildup of different brain proteins, called amyloid and tau. When amyloid proteins clump together, they form abnormal structures known as plaques. Abnormal groups of tau proteins form tangles.3 Over time, the buildup of these proteins causes normal brain cells to die, and affected parts of the brain may shrink.5
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Face
Do You Die From Pd Dementia
People with Parkinsons-related dementia often want to know how the disease can impact their lifespan. While people with Parkinsons can expect a similar lifespan to the general population, studies show both Parkinsons disease dementia and Lewy body dementia can shorten lifespan, generally due to medical complications from the disease, rather than the disease itself.
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
Read Also: Can Parkinsons Be Treated If Caught Early
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease, and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Because Lewy bodies occur in dementia with Lewy bodies and in Parkinson disease dementia, some experts think that the two disorders may be part of a more generalized synucleinopathy affecting the central and peripheral nervous systems. Lewy bodies sometimes occur in patients with Alzheimer disease, and patients with dementia with Lewy bodies may have neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease overlap considerably. Further research is needed to clarify the relationships among them.
Read Also: What Medications Can Cause Parkinson’s
Is There A Test To Diagnose Pd Dementia
There is no single test for PDD. The diagnosis is made clinically. If you or someone you spend time with notices cognitive changes, it is important to discuss them with your care team. If you dont have a care team in place, its important to find a specialist or physician familiar with dementia or geriatric medicine. Call the Parkinson’s Foundation Helpline 1-800-4PD-INFO for a referral.
Symptoms Related To Brain Function Are Different
There is some overlap, but in general, the overall cognitive symptoms that people experience with Parkinsons disease dementia and Alzheimers are different. Alzheimers mainly affects language and memory at the outset, whereas Parkinsons affects problem-solving, speed of thinking, memory, and mood.6
Unlike in Alzheimers disease, people with Parkinsons-related dementia often experience hallucinations, delusions, and paranoid thoughts. Both conditions can lead to depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.4,6
You May Like: How To Control Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
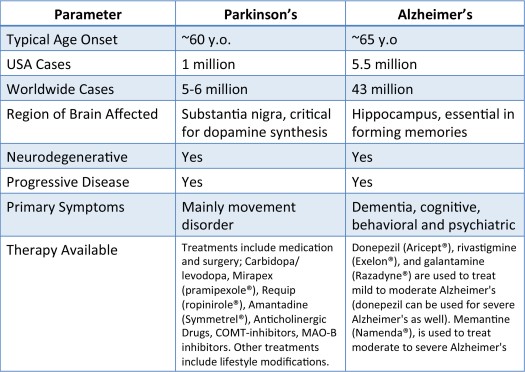
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease , the most common form of dementia among older adults, is an irreversible degeneration of the brain that causes disruptions in memory, cognition, personality, and other functions that eventually lead to death from complete brain failure. Genetic and environmental factors including diet, activity, smoking, traumatic brain injury, diabetes, and other medical diseases contribute to the risk of developing this form of the disease. The hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease are the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques between nerve cells in the brain and neurofibrillary tangles, which are twisted fibers found inside the brain’s cells). These tangles consist primarily of a protein called tau.
Recommended Reading: What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Parkinson’s Disease
The Differences Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s
16 October, 2020
Do you know the differences between Alzheimers and Parkinsons? First of all, we must say that both diseases constitute two of the causes of dementia. Now, lets be a bit more specific. According to data from the WHO , dementia due to Alzheimers disease represents 60-70% of all cases of dementia in the world.
However, its important to keep in mind that theyre very different diseases. Additionally, we must make clear that having either condition doesnt always lead to the development of dementia . In this sense, we know that between 20-60% of people with Parkinsons disease end up developing dementia.
Buter et al. conducted a study that was published in the journal Neurology. It was conducted with 233 patients with Parkinsons disease. The researchers were able to observe that about 60% of them developed Parkinsons dementia in a period of 12 years.
So whats dementia? It refers to the set of symptoms that arise as a consequence of neurological damage or disease. These symptoms involve the loss or weakening of the mental faculties and mainly affect three different areas: cognitive , behavioral , and personality .
Alzheimers And Parkinsons Disease: Similarities And Differences
James M. Ellison, MD, MPH
Swank Center for Memory Care and Geriatric Consultation, ChristianaCare Configure
- Expert Advice
Explore the similarities and differences between two common degenerative brain disorders.
Ron brings his 78-year-old wife, Sara, to the Memory Clinic, with a pressing concern. Sara is forgetting things more often even though her Parkinsons disease symptoms appear to be under good control with standard medications, healthy diet, and plenty of physical activity. She is losing her train of thought mid-sentence and she became very confused about where she was while driving the well-traveled route to her daughters home. Is she developing dementia? Is that a part of Parkinsons disease? Or is she developing Alzheimers disease? And what are the differences between Alzheimers and Parkinsons?
Recommended Reading: Gait Training Exercises For Parkinson’s
Coping With Alzheimers And Parkinsons Disease
Living with both Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease is extremely challenging. The dementia of Alzheimers combined with the movement effects of Parkinsons can make self-care especially difficult.
Rivastigmine is the only medication that is specifically approved for the treatment of Parkinsons dementia. Additionally, you may need medication for the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease and medication to help with other symptoms, such as dry skin.
Data Extraction And Literature Quality Evaluation
The authors N.-N. Hou and X. Zuo completed literature retrieval and selection independently. When there was a disagreement, L. Cui and H.-M. Wu participated to reach a consensus. Extracted from the studies were author name, publication year, gender, age range, study design, response rate, diagnostic criteria, case number, study location, urban/rural, education, and sample size. All eligible studies were systematically evaluated for quality based on their sample size, study design, response rate and diagnostic assessment. The detailed scoring criteria were performed as previously described by Prince et al. .
Read Also: Does Agent Orange Cause Parkinson’s
Types Of Lewy Body Dementia And Diagnosis
LBD refers to either of two related diagnoses dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. Both diagnoses have the same underlying changes in the brain and, over time, people with either diagnosis develop similar symptoms. The difference lies largely in the timing of cognitive and movement symptoms.
In DLB, cognitive symptoms develop within a year of movement symptoms. People with DLB have a decline in thinking ability that may look somewhat like Alzheimers disease. But over time, they also develop movement and other distinctive symptoms of LBD.
In Parkinsons disease dementia, cognitive symptoms develop more than a year after the onset of movement symptoms . Parkinsons disease dementia starts as a movement disorder, with symptoms such as slowed movement, muscle stiffness, tremor, and a shuffling walk. These symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Later on, cognitive symptoms of dementia and changes in mood and behavior may arise.
Not all people with Parkinsons disease develop dementia, and it is difficult to predict who will. Many older people with Parkinsons develop some degree of dementia.
Caregivers may be reluctant to talk about a persons symptoms when that person is present. Ask to speak with the doctor privately if necessary. The more information a doctor has, the more accurate a diagnosis can be.
Can You Have Both Parkinsons And Alzheimers
People who already have Parkinsons disease and later develop signs of dementia are diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia.6 However, if you first have Alzheimers disease and develop signs of movement difficulties, you can also have a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
Tell us about your experience in the comments below, or with the community.
You May Like: Does Jesse Jackson Have Parkinsons
What Is Lewy Body Dementia Causes Symptoms And Treatments
On this page:
Lewy body dementia is a disease associated with abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. Lewy body dementia is one of the most common causes of dementia.
LBD affects more than 1 million individuals in the United States. People typically show symptoms at age 50 or older, although sometimes younger people have LBD. LBD appears to affect slightly more men than women.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with similar symptoms found in other brain diseases or in psychiatric disorders. Lewy body dementia can occur alone or along with other brain disorders.
It is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms start slowly and worsen over time. The disease lasts an average of five to eight years from the time of diagnosis to death, but can range from two to 20 years for some people. How quickly symptoms develop and change varies greatly from person to person, depending on overall health, age, and severity of symptoms.
In the early stages of LBD, symptoms can be mild, and people can function fairly normally. As the disease advances, people with LBD require more help due to a decline in thinking and movement abilities. In the later stages of the disease, they often depend entirely on others for assistance and care.
What Is Alzheimers Disease
Alzheimers disease is a progressive brain illness that wreaks havoc on memory and concentration capabilities, as well as the capability to transport out some of the most basic routine work like thinking, reacting, and even standing straight.
Symptoms develop in the mid-sixties in the majority of persons with the illness . Early-onset Alzheimers disease is exceedingly rare and develops between the ages of 30 to 60.
The far more frequent cause of cognition diminution in elderly people is Alzheimers disease.
Alzheimers disease affects around 4 million people in the United States aged 65 and up. Eighty percent of them are 75 years of age or older.
It is expected to affect 60 percent to 70 percent of the approximately 50 million individuals globally who have demented memory.
Everyone experiences memory issues now and again, but Alzheimers disease causes cognitive problems that continue and increases exponentially along with the onset of first symptoms, impairing ones ability to perform at home or in the workplace.
Alzheimers disease impairs concentration and reasoning, particularly when it comes to complex notions like numbers, letters, creativity, and imagination.
Multitasking is particularly tough, and managing finances, balancing checkbooks, and paying payments on time can be difficult. A person with this disorder may end up losing the ability to identify and cope with arithmetic and symbols.
You May Like: Is Neuropathy A Sign Of Parkinson’s
Lewy Body Dementia: A Common Yet Underdiagnosed Dementia
While its not a household word yet, Lewy body dementia is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known disorders like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons, it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In fact, many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD.
Tips For Communicating With A Person With Pdd
PD-related mood and motor changes can impact communication cognitive changes and Parkinsons disease dementia can further these difficulties.
- Stay calm and be patient. It is not usually helpful to try to reason or argue with someone experiencing a hallucination or delusion. If the person is frightened by the hallucination or delusion, try to redirect their attention to something else.
- Acknowledging what the person is seeing, even if you do not see it, can reduce stress.
- Speak slowly and at eye level. Communicate in simple sentences.
- Ask one question at a time and wait for an answer.
- Limit distractions. Turn off the TV or radio before asking a person with PDD to do something.
- Consider causes behind disruptive behavior. Can your loved one be hungry, thirsty, tired, in pain, frustrated, lonely or bored?
- If the person is stuck on an idea, try agreeing with them, then changing the subject.
- Its okay to use humor to diffuse stressful situations but avoid negative humor or sarcasm these can be misunderstood.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Sydney M. Spagna, Clinical Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Recommended Reading: Entacapone Side Effects Parkinson’s
