Asceneurons Innovation In Pdd And Dlb
Several symptomatic treatments addressing motoric disturbances in PD are currently available. In contrast, there is a very high unmet medical need for novel symptomatic medications to mitigate the cognitive decline in Parkinsons disease dementia patients since available options have limited efficacy and considerable side effects. As the disease progresses, balancing the benefits of medications with their side effects becomes challenging for caregivers.
Given the high unmet medical need in PDD, a symptomatic treatment for one of the more debilitating facets of PD would bring significant benefit to PD patients and their caregivers.
In May 2022, Asceneuron has initiated a preclinical proof-of-concept study to assess the disease-modifying properties of Asceneurons OGA inhibitor ASN51 in a preclinical model of inherited PD. The genetic model is characterized by the overexpression of -synuclein harbouring the A53T mutation known to cause early-onset, familial PD in humans. Aggregated forms of -synuclein are the main component of the characteristic Lewy body pathology and thus thought to be causative of the loss of dopaminergic neurons in PD. The aim of this study is to extend previously published findings demonstrating a reduction of motor impairment with Asceneurons OGA inhibitors to this alternative genetic disease model.
How To Take Care Of Myself Or Manage Symptoms
Parkinsonism refers to a wide range of conditions and diseases with similar effects and symptoms. Most of these diseases and conditions are severe and have a high risk of complications when theres a delay in diagnosing and treating them.
Because many of these conditions are so severe and need diagnosing and treating sooner rather than later, you shouldn’t try to self-diagnose or treat parkinsonism. If you think you have a form of parkinsonism, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider as soon as possible. They can help you by determining if you have one of these conditions, or they can refer you to a specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
Corticobasal Degeneration And Corticobasal Syndrome
Corticobasal degeneration and corticobasal syndrome are caused by degeneration in the cerebral cortex and the basal ganglia .
Corticobasal Degeneration is a degenerative brain disease affecting people from the age of 40 onwards. There are neurological similarities to PSP, but the classical clinical picture is often distinct. Patients diagnosed with CBD may also develop features of PSP and vice versa.
Cognitive problems are common in CBD and are often one of the first symptoms, such as apathy, impulsive behaviour, changes in empathy, and language symptoms. Other signs are progressive numbness and loss of use of one hand. There may also be jerking of the fingers, slowness and awkwardness and the feeling of having an alien limb with complex unintentional movements of one limb causing problems with normal motor tasks. Gradually the arm and/or leg on one side is affected and then the arm and/or leg on the other.
You May Like: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Typically Progress
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
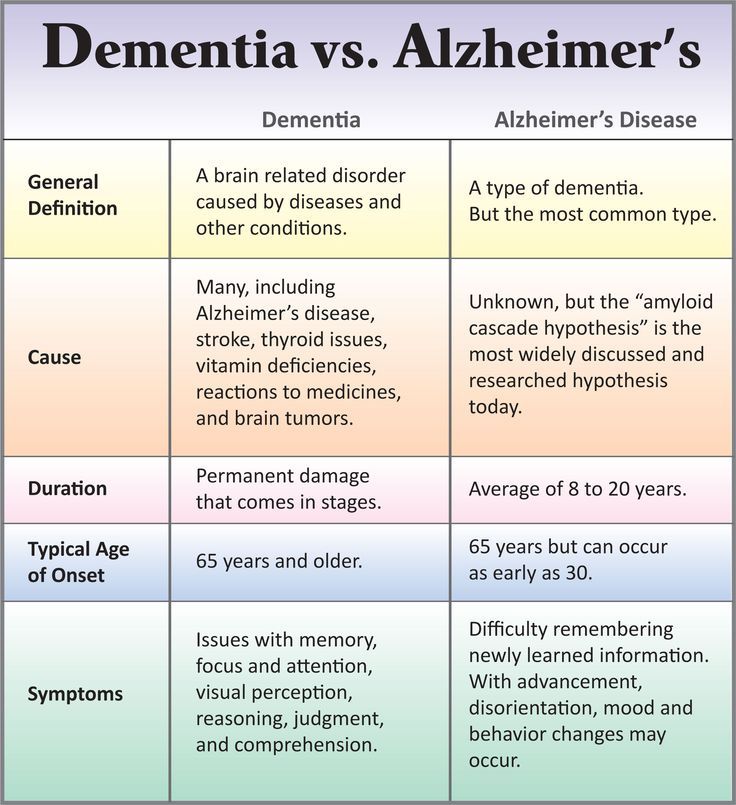
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
What Causes The Condition
The causes of parkinsonism depend on the specific subtype of the condition.
Parkinsons disease
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements. The neurons that fine-tune your movements need dopamine. Without it, they can’t do their job correctly. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
With lack of dopamine, the basal ganglia start to deteriorate. As they do, you lose the abilities they once controlled. As Parkinson’s disease gets worse, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
Genetic Parkinsons disease
The only confirmed causes of Parkinson’s disease are genetic mutations that you inherit from your parents. Genetic Parkinson’s disease accounts for about 10% of all cases.
Idiopathic Parkinsons disease
When Parkinsons disease isnt genetic, experts classify it as idiopathic . That means they dont know exactly why it happens.
Secondary parkinsonism
Secondary parkinsonism means this condition is happening because of another medical condition. Examples of secondary parkinsonism include:
Also Check: Patron Saint For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that is most commonly known for affecting function and movement, though it also affects cognition, particularly as the disease progresses. Parkinsons disease primarily impacts dopaminergic, or dopamine-producing, neurons in a specific area of the brain known as the substantia nigra. Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter that transmits signals between neurons and plays a crucial role in movement and motor control.
The lack of dopamine makes it challenging for the brain to coordinate muscle movements and can also contribute to mood and cognitive issues later in the disease course. Patients with Parkinsons disease also lose nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, a chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system responsible for controlling a wide range of functions in the body, such as blood pressure and heart rate.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect a condition that falls under parkinsonism, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests forthcoming
There are also new lab tests that, while still experimental or waiting for approval, might be able to help with diagnosing Parkinson’s disease or other conditions like it. These tests look for misfolded or malfunctioning alpha-synuclein proteins in your cerebrospinal fluid or nerves. But more research and testing are necessary before these tests are widely available.
You May Like: Why Do People Get Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
The key pathological hallmark found in brains of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia patients are abnormal microscopic deposits composed of -synuclein. This protein is found widely in the brain and its normal function is not yet well understood. The deposits are called “Lewy bodies”. Lewy bodies are also found in several other neurodegenerative brain disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies . Evidence suggests that Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, may be linked to the same underlying abnormalities in caused by the deposition of -synuclein.
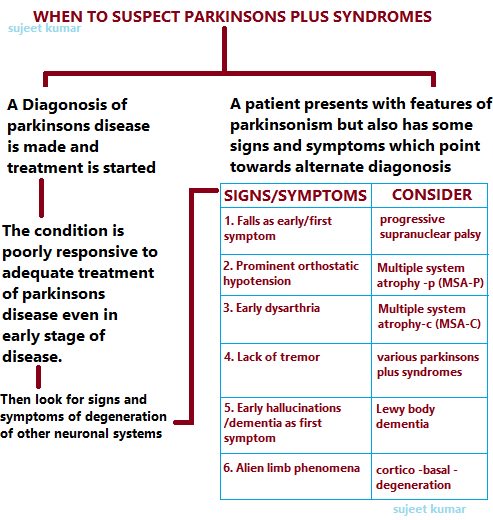
Whats The Outlook For People With Parkinsons Plus
Although there currently isnt a treatment to halt the progression of Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
The exact outlook for Parkinsons plus syndrome depends on the person and the specific condition they have. Someone who is otherwise healthy when theyre diagnosed will typically have a longer life expectancy than someone who is already facing other health conditions when theyre diagnosed. Your doctor will monitor your condition over time and can let you know how its progressing.
Recommended Reading: How Close Is A Cure For Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
In dementia with Lewy bodies, dementia always appears first. There can also be changes in alertness as well as visual hallucinations. However, because of the presence of Lewy bodies throughout the entire brain, characteristics of this disease not only include cognitive characteristics, but also physical, sleep, and behavioral changes. As the disease progresses, the motor symptoms common to Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems will appear.
For more information on dementia with Lewy bodies, visit www.lbda.org.
Abnormality Of Tau Protein
PSP has been considered to be a tau protein disorder. Cortical fibrillary tangles of PSP are similar to those observed in Alzheimer disease with regard to the presence of an abnormally phosphorylated tau protein. Tau is a component of a microtubule-associated protein that is responsible for axonal transport of vesicles. The mechanism whereby this is involved in PSP has yet to be determined. PSP overlaps with corticobasal degeneration in this regard, and the latter may have a stronger association with tau protein abnormalities than does PSP.
Tau proteins exist in 6 isoforms encoded by a single gene. Different electrophoretic patterns have been identified in the various disorders associated with tau abnormalities. Thirty-two mutations have been identified in more than 100 families. About half of the known mutations have their primary effect at the protein level. They reduce the ability of tau protein to interact with microtubules and increase its propensity to assemble into abnormal filaments. The other mutations have their primary effect at the RNA level and perturb the normal ratio of 3-repeat to 4-repeat tau isoforms. When studied, this change resulted in a relative overproduction of tau protein with 4 microtubule-binding domains in the brain.
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Ms And Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of These Diseases
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve motor control, such as tremor , slowness of movement, stiffness of the limbs and trunk as well as postural instability. Many patients develop a decline in thinking and reasoning known as Parkinsons disease dementia if it occurs more than one year after the initial diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Common symptoms for PDD include decline in memory, concentration and judgment, visual hallucinations, depression, irritability, and anxiety.
The central feature of Lewy body dementia is progressive cognitive decline, combined with pronounced fluctuations in alertness and attention, complex visual hallucinations, and motor symptoms such as rigidity and the loss of spontaneous movement. It can easily be mistaken for Alzheimers disease or for Parkinsons disease dementia .
What Are The Current Treatment Options
While there is no specific cure for Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can control your symptoms. A doctor can develop a plan for your overall health and to treat your specific symptoms. Medications that treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease often do not work as well for Parkinsons plus syndrome.
Treatment options might include:
- Walking and balance assistance. You might receive physical and occupational therapy to help keep you moving. Therapists can help you build strength and prevent falls. They can also help you learn to use canes, walkers, and other mobility aids, if needed.
- Swallowing and speech assistance. A speech therapist can help you adjust to changes that might make it hard to swallow and speak. They can help you communicate and can recommend foods and beverages that are easier to swallow.
- Medications for cognitive issues. Your doctor might prescribe a variety of medications that can help with your focus and memory. Many of these medications are also used for conditions such as Alzheimers or dementia.
- Medications for trouble with movement. You might be prescribed medications that can help you control your muscles and movement. These medications might also address stiffness and balance problems.
- Medications to help with mood symptoms. If youre experiencing depression, anxiety, or other mood-related concerns, your doctor might prescribe medications that can help with these symptoms.
Also Check: Do I Have Parkinson’s Disease Test
How Do Treatments Differ
MS treatments can ease your symptoms during an attack or slow down the diseaseâs effects on your body.
Steroids like prednisone calm the inflammation that damages your nerves.
Plasma exchange is another therapy if steroids donât work. Your doctor will use a machine to remove the plasma portion of your blood. The plasma gets mixed with a protein solution and put back into your body.
Some people with both diseases who take anti-inflammatory medicines like steroids see their Parkinsonâs symptoms get better.
Disease-modifying treatments slow down MS nerve damage and disability. They include:
Medications to treat Parkinsonâs either raise your dopamine levels or offer a substitute. They can ease Parkinsonâs symptoms like tremors. Over time, they may become less effective.
Medicines used to treat Parkinsonâs include:
Deep-brain stimulation is another treatment for Parkinsonâs. A doctor places electrodes into your brain. They send out electric pulses that ease symptoms in your body.
Show Sources
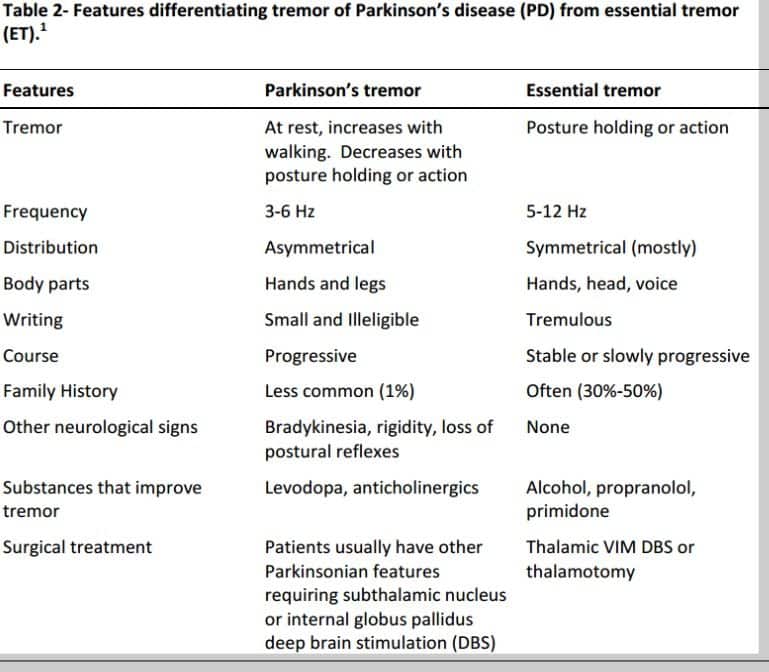
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
Also Check: How To Live With Parkinson’s
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Some symptoms of Parkinsons affect a persons ability to move. These symptoms are often called motor symptoms, and they include:
- Stiffness of muscles
- Tremor of an arm or leg while at rest
- Unstable posture
Other symptoms of Parkinsons dont affect a persons movement. These nonmotor symptoms may include:
- Digestive problems, such as constipation
- Cognitive changes, such as loss of attention, difficulty solving problems, memory loss, and trouble with language
Parkinsons symptoms may take several years to appear. A majority of people with Parkinsons live for many years with the condition.
How Is Parkinsonism Treated
The treatments for parkinsonism depend on the condition itself and what caused it. Most forms of parkinsonism are treatable, and some can stop entirely .
Some examples of treatable conditions include:
In general, your healthcare provider is the best person to provide more information about whether or not your condition is treatable or curable. That’s because so many different conditions fall under parkinsonism, many of which are very different from person to person. Your provider can tell you more about if your condition is treatable and what your treatment options are with your specific case and circumstances.
Read Also: What’s The Difference Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
Read Also: How Can Someone Get Parkinson’s Disease
Other Types Of Parkinsonism
Like Parkinsons, MSA can cause stiffness and slowness of movement in the early stages. However, people with MSA can also develop symptoms that are unusual in early Parkinsons, such as unsteadiness, falls, bladder problems and dizziness.
PSP affects eye movement, balance, mobility, speech and swallowing. Its sometimes called Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus mainly affects the lower half of the body. The common symptoms are walking difficulties, urinary incontinence and memory problems. Removing some cerebrospinal fluid through a needle in the lower back can help with these symptoms in the short term. If there is improvement after this procedure, an operation to divert the spinal fluid permanently can help in the long term.
While these are not parkinsonian disorders, you may be diagnosed with one of these conditions if tremor is your only symptom.
There are several other, much rarer, possible causes of parkinsonism. These include rare conditions like Wilsons disease, an inherited disorder where theres too much copper in your bodys skin and muscles.
Multiple System Atrophy Formerly Called Shy
As predicted by the name of this parkinsonism, multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems of the body. It affects both the motor skills movement system and the involuntary system of the body. Though the symptoms can often be treated with medications, there is no cure. In addition, there are no drugs that are able to slow the progress of MSA.
You May Like: What Not To Eat If You Have Parkinson’s
