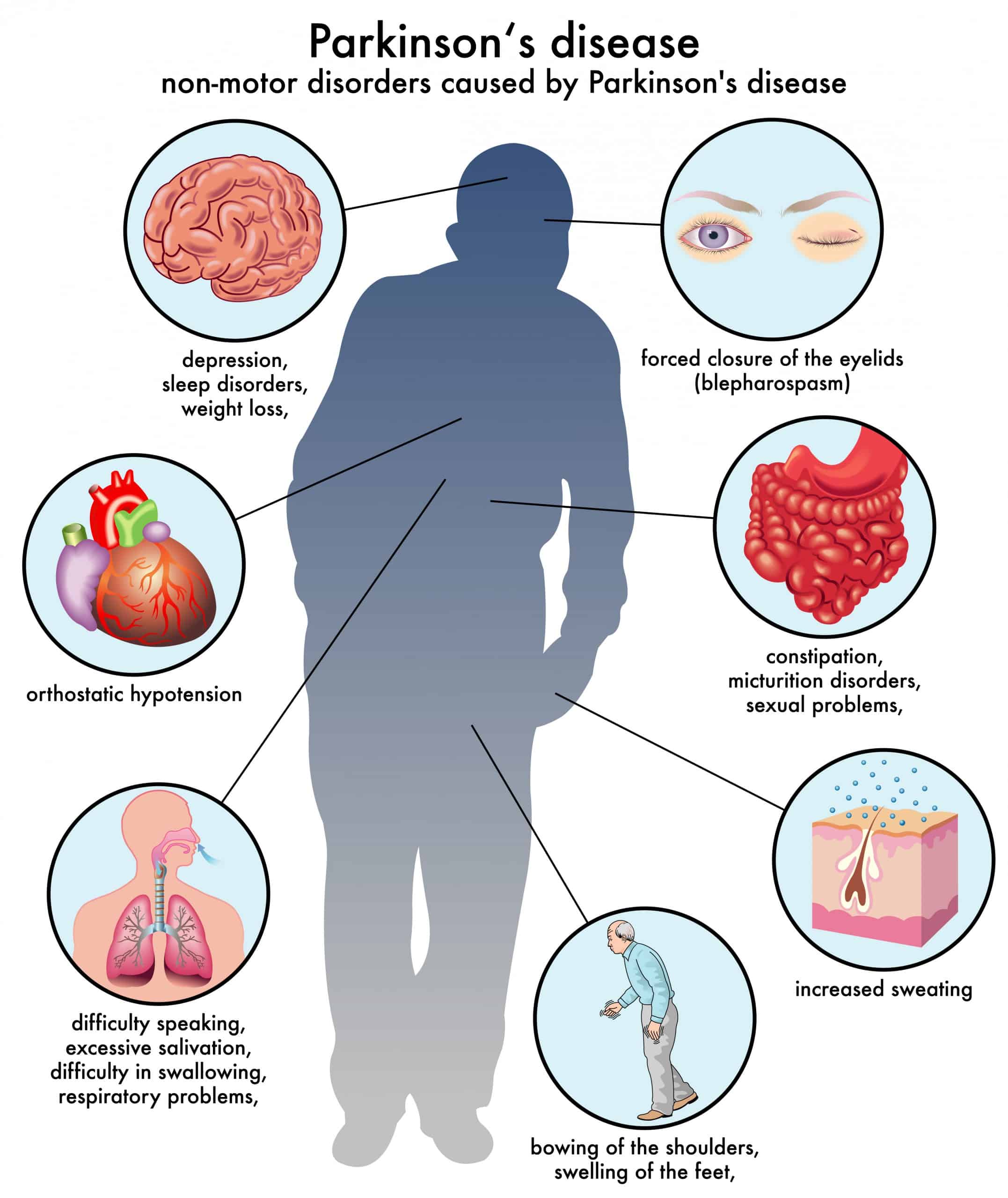
Fecal Incontinence In Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Fecal incontinence is a very debilitating symptom that can occur in advanced PD and refers to the involuntary release of fecal matter.
Once again, fecal incontinence, especially if it is a new symptom, should be fully evaluated to determine if there is a cause unrelated to PD. Diseases of the gut such as inflammatory bowel disease or compression of the lower spine cord can be the reason.
If related to PD, there are typically two situations to consider. One possibility is that severe constipation with impacted bowel movement allows loose stool from higher up in the gastrointestinal tract to escape around the edges of the obstruction. In this situation, fecal incontinence could be a harbinger of bowel obstruction. Aggressive and continuous treatment of constipation can help avoid this potential scenario.
As with urinary incontinence, frequent and rapid exchange of dirtied incontinence products can keep skin intact and prevent infection.
Tips and Takeaways
Read Also: Exercise Class For Parkinsons Disease
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinsons disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
Dont Miss: On And Off Phenomenon
Recommended Reading: What Medication Is Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Read Also: Jefferson Health’s Comprehensive Parkinson’s Disease & Movement Disorder Center
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Parkinsons disease causes a specific area of your brain, the basal ganglia, to deteriorate. As this area deteriorates, you lose the abilities those areas once controlled. Researchers have uncovered that Parkinsons disease causes a major shift in your brain chemistry.
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements using cells that require dopamine. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
As Parkinson’s disease progresses, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
Read Also: On-off Phenomenon
Don’t Miss: Does Michael Bolton Have Parkinson’s
Emergencies And Complications Of Device
Device-aided therapies include deep-brain stimulation, levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel, and apomorphine subcutaneous injections and infusion. These are indicated to treat response fluctuations, such as recurrent disabling offs and dyskinesias refractory to standard therapy. Deep-brain stimulation is also used for drug-refractory tremor. Emergencies and complications related to device-aided therapies are not uncommon, and require prompt medical attention since they are generally associated with significant aggravation of Parkinsons disease symptoms .
An algorithm approach for DBS efficacy loss. DBS, deep-brain stimulation LD, levodopa.
Gut Microbiome Of Patients Favors Inflammation Study Suggests
Here, an international team of scientists conducted analyses of data collected from 55 Parkinsons patients and 55 people without the disease . The collected data included evaluations of stool and blood samples, as well as clinical data.
In line with prior findings, this analysis found that Parkinsons patients had reduced levels of fecal butyrate, and lower abundances of butyrate-producing bacteria in their guts.
Statistical analyses also showed that, among those with Parkinsons, lower levels of butyrate were associated significantly with more severe depression, as measured by the Geriatric Depression Scale .
The scientists then conducted a series of analyses to look for epigenetic changes associated with altered butyrate levels. Epigenetics refers to chemical alterations made to DNA molecules that do not alter the genetic sequence, but can change how the DNA is read for instance, increasing or decreasing the activity of individual genes.
This study is the first to examine the possible role of epigenetic changes as a link between gut microbiota, its metabolites, and the pathophysiology of neural and immune cells in Parkinsons, the researchers wrote.
Our results suggest that butyrate may impact through epigenetic effects on innate immune cells, the researchers wrote.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Chronic
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Dont Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
Also Check: How Long Do You Live After Being Diagnosed With Parkinson’s
Apomorphine Subcutaneous Injections And Infusion
Apomorphine is an alternative therapy for patients with disabling motor and non-motor fluctuations poorly controlled with conventional treatment. It is a potent dopamine agonist with a short-acting effect that makes it effective in complicated situations such as off dystonia episodes or unpredictable disabling off. Subcutaneous injections are used as a rescue therapy when a rapid on is needed. The effect is quick and lasts 4590min. Patients needing more than three to six injections per day are best treated with a continuous infusion therapy.
Overall, studies report improvement of off time of 50%80%. Its effect on dyskinesias is more controversial. Reductions may occur after a few weeks or months of continuous therapy and mostly if large reduction in levodopa dose can be achieved.
Both apomorphine subcutaneous injections and infusion are safe in terms of procedure but can cause adverse events related to the drug itself. These include nausea, hypotension, excessive somnolence and neuropsychiatric problems, such as confusional state, impulse control disorder and dopamine dysregulation syndrome. Subcutaneous nodules develop in 37% of cases treated with infusions although these are usually not severe and can be managed with non-pharmacological measures, the treatment may need to be stopped.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
![Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinsons Disease [PD]](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/neural-stem-cell-therapy-for-parkinsons-disease-pd.jpeg)
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
APDAUncategorizedDeath in Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: 7 Helpful Hand Exercises For Parkinson’s
Carbidopa And Levodopa Extended Release Capsules
Carbidopa and levodopa extended release is an oral formulation of levodopa designed to combine both immediate release and extended release pharmacokinetics, allowing for less frequent dosing and more stable and longer lasting plasma concentrations of levodopa compared to other formulations of oral levodopa. CD-LD ER capsules contain 4 varieties of beads: one with immediate release carbidopa-levodopa, two with different extended release carbidopa-levodopa formulations, and a fourth with an active excipient containing tartaric acid to facilitate enteral absorption .
Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that CD-LD ER provides a rapid rise in plasma levodopa concentration with prolonged duration relative to other oral levodopa formulations . In an open-label, randomized crossover study of CD-LD ER and CD-LD IR, the time to Cmax was similar for both drugs , but the duration of levodopa concentration above 50% of Cmax was 2.6 h longer for CD-LD ER versus CD-LD IR. Following a single dose, improvements in UPDRS part III scores were similar for both medications up to 2 h post-dosing, but for hours 3 through 6 UPDRS part III scores were significantly more improved with CD-LD ER than CD-LD IR. According to clinicians ratings, at 6 h, 68% of subjects were rated as ON without troublesome dyskinesia after taking CD-LD ER compared to 4% after taking CD-LD IR .
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson’s Disease That Cause Death
Many people wonder if you can die from Parkinsons disease. The answer is no. Parkinsons disease itself is not fatal. However, people with Parkinsons disease can experience progressively worsening symptoms before passing away.
Two major causes of death in people with Parkinsons disease are falls and pneumonia. Serious falls may require surgery and other treatments, which puts a person at risk of other complications like blood clots, infections, anesthesia-related complications, and heart failure, any of which can lead to death.
References:
Also Check: Parkinson Disease Produces Dementia As Well As
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Don’t Miss: Dbs And Parkinson’s Disease
Greater Than The Sum Of Its Parts
The study also shows that different forms of specialized allied health therapy reinforce each other. For example, patients with Parkinson’s disease who receive both physical and occupational therapy from specifically trained therapists have far fewer complications than patients who receive specialist occupational therapy but regular physical therapy. ‘For the first time, we are able to show a team effect,’ Darweesh says. ‘The combination of the different forms of specialized allied health therapy is greater than the sum of its parts. We therefore call on allied healthcare professionals from different disciplines: work together! People with Parkinson’s disease really benefit from a jointly developed treatment plan.’
Key Measures For The Prevention Of Complications
-
Parkinsons disease nurse specialists should support patients and caregivers by clarifying concerns and implementing a treatment plan.
-
Patients, caregivers and medical staff are responsible for bringing all the medication updated, and paying attention to medication timings.
-
If at all possible, avoid changing abruptly or changing more than one antiparkinsonian medication at a time.
-
Patients and caregivers should be provided with a list of drugs capable of worsening parkinsonism.
-
Patients taking dopamine agonists should be informed about sleep attacks and risk of impulse-control disorders before starting treatment and regularly during follow-up.
-
Periodically, at least annually, review falls, sleepiness, cognition, autonomic disturbances and psychiatric symptoms.
-
Disease rehabilitative therapy should be proposed to minimise complications such as falls and swallowing problems.
-
In case of elective admission, it is important to plan in advance how to make medication changes. If oral medication intake is limited, consider transdermal agonists, enteral administration of usual medication, and levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel infusion.
You May Like: What Cold Medicine Can You Take With Parkinson’s
Does Parkinsons Affect Your Lifespan
Parkinsons research and treatments have come a long way, so much so that the average life span of a person with Parkinsons is the same or near the same as someone without Parkinsons disease. However, the lifespan of a person can vary widely based upon that persons health choices, such as their diet, exercise routine, if they have a history of smoking and many other factors. So, for most people with Parkinsons, as long as you focus on managing your Parkinsons disease and make healthy choices your lifespan should not be shortened.
