How Do You Diagnose Wolff
Diagnosing WPW patients is based on the presence of tachyarrhythmias and pre-excitation. Men are more frequently diagnosed compared to women. The gender distinction is not observed in children.
Electrocardiogram or a continuous- or person-triggered ambulatory ECG monitoring e.g. a Holter monitor may help diagnose and distinguish between WPW alone and WPW with AF.
A normal heart rate for an adult ranges between 60 to100 beats per minute while in infants and children it is less than 150 beats per minute. During an episode of tachycardia, the heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute.
Electrophysiologic study that uses catheters to assess the heart can help to detect the accessory pathway. A negative EPS indicates low risk of getting future ventricular fibrillation , atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia , or pre-excited atrial fibrillation
If You Develop Any Symptoms Of Wpw
You should see your physician right away or consider going to the emergency room if you develop symptoms such as a fluttering sensation in the chest, chest pain, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or dizziness. Your physician can order testing to see if you have WPW or another abnormal heart rhythm and can offer the appropriate treatment.
Prognosis Of Patients With Wpw Syndrome
In only 1% of cases, WPW syndrome can lead to life-threatening ventricular fibrillation.
Recommended Reading: Support Groups For Parkinson’s
Risk Factors For Developing Wpw
Risk factors for developing WPW include:
- Having a family member with pre-excitation or WPW: This is because mutations in certain genes can cause WPW.
- Congenital heart defect: Some people who are born with a specific heart defect known as “Ebstein’s anomaly” can develop WPW. This can occur if their mother was taking certain medications while she was pregnant.
Wondering if you have wolff-parkinson-white syndrome?
Free, secure, and powered by Buoy advanced AI to get you the best way to better. Learn about our technology.
Pearls And Other Issues

Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Recommended Reading: Does Green Tea Help Parkinson’s
When Will I Feel Better After Treatment For Wolff
At-home remedies like the Valsalva maneuver or coughing may slow your rapid heartbeat right away. Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect if youre taking medications for WPW.
Your provider can tell you when symptoms should improve after ablation or surgery for WPW. They can also tell you what to expect during recovery and when you can return to daily activities.
How Is It Diagnosed
Your doctor may ask you to get tested for WPW syndrome if you have atrial fibrillation or a family history of WPW syndrome. You may need to be screened for WPW syndrome if you are going to play competitive sports.
Your doctor will use your medical history, family history, physical exam, and heart tests to diagnose WPW syndrome. Sometimes WPW syndrome is diagnosed during a routine heart test. Common heart tests to diagnose WPW include an EKG and a Holter monitor. You may also need a stress test to measure your heart rhythm while your heart is working hard and beating fast.
You may also need an electrophysiology study to see whether you are at risk of more serious health problems.
You May Like: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause
How Is It Treated And Managed
Catheter ablation is the most common treatment for people who have WPW syndrome and symptoms of an arrhythmia. This procedure can cure WPW syndrome in most people. If this treatment works for you, you can go back to your normal activities.
You may need one of more of the following treatments for an irregular heartbeat:
- Medicines that can control or prevent a fast heartbeat
- Cardioversion, which uses an electrical shock to your heart to restore its rhythm
If you have no symptoms of arrhythmias, you may not need any treatment. You may need regular checkups to check for a rapid or irregular heartbeat. Tell your doctor right away if you have any symptoms.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare but dangerous condition. A high index of clinical suspicion and close attention to concerning symptoms may be crucial in making a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis or sufficient concern is established, an interprofessional approach will be necessary for further evaluation and management. This approach, paired with education and shared decision making with patients and their families, will help guide treatment plans.
It is often difficult to develop and carry out well structured and rigorous studies in rare medical conditions. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is no exception, and most of the evidence is drawn from case series and population studies. The pathophysiologic basis is well understood, and surgical or catheter ablation has been shown to be successful and low risk. In high-risk patients, ablation is the most definitive treatment, but more future studies would help delineate medical management and ablation thresholds in some low-risk patients.
You May Like: What Prevents Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Causes Of Wolff
Not much is known on how the extra electrical connection develops in the heart. In hereditary WPW, scientists have attributed a region on chromosome 7 as responsible for the syndrome, and they have also identified a gene responsible for the syndrome. However, the association between the gene and the pathophysiology of the condition is still not clear.
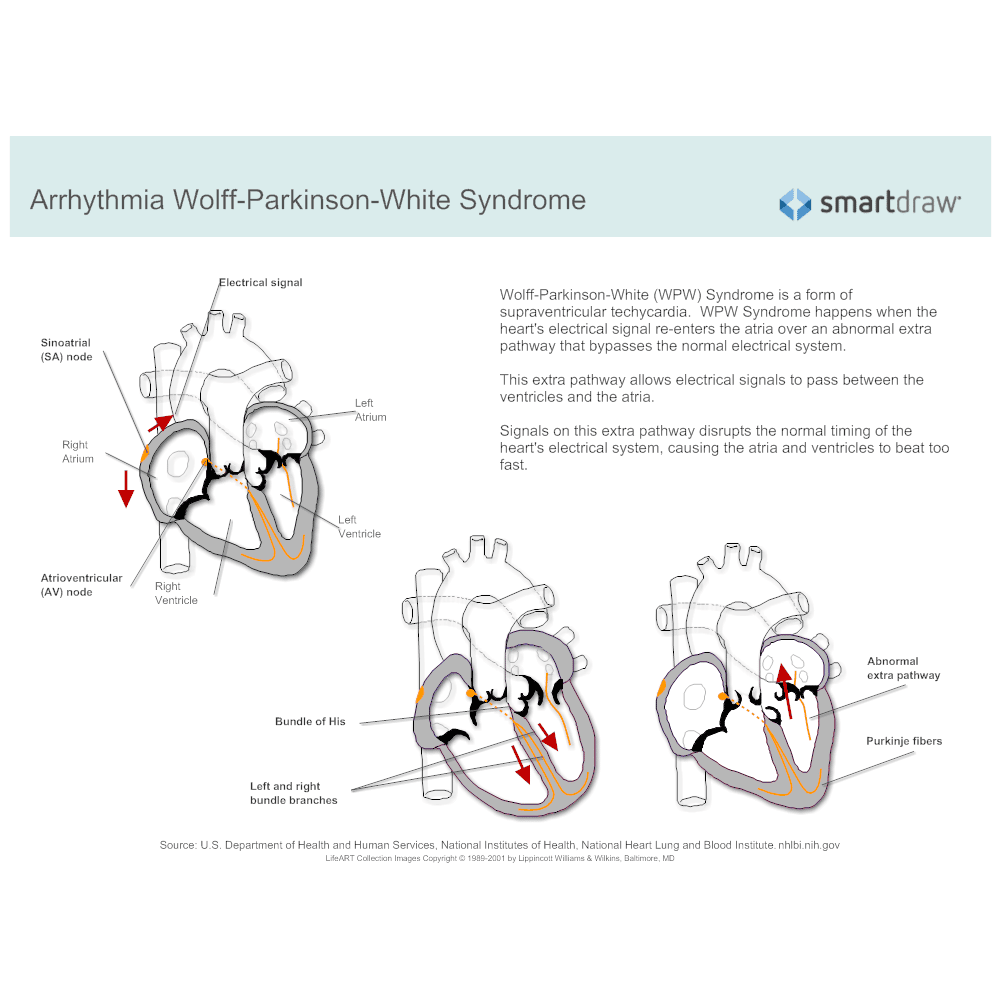
The accessory pathway bypasses the standard AVN that is the standard route for electrical conduction of the heart rate. There are 5 types of accessory pathways between the atrium and ventricle.
There are risk factors for sudden death associated with WPW syndrome. They are:
- Ebstein anomaly
- History of tachycardia
The WPW syndrome is also associated with other congenital conditions, such as Ebstein anomaly. It is also observed as part of other genetic conditions, such as Pompe disease, tuberous sclerosis complex, Danon disease, and hypokalemic periodic paralysis.
Are There Complications Of Wolff
Some people may experience low blood pressure during episodes of rapid heartbeat. A rare complication of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is sudden cardiac death.
If you have any symptoms of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, see your provider. Getting timely care for this condition can help avoid complications.
Read Also: What Is The Test For Parkinson’s Disease
Risk Of Sudden Death And Risk Stratification
The incidence of ventricular fibrillation in patients with preexcitation is variously estimated to be between 0.32 and 1.4% . The risk of sudden cardiac death is estimated to be less than .015 per patient year , . Cardiac arrest may be the initial presenting symptom, particularly among young patients, where almost 50% had no prior cardiac symptoms , , . In several studies, cardiac arrest due to WPW is more common in the first 3 decades of life and is more common among
Orthodromic Tachycardia With Concealed Accessory Pathway
Some APs are unable to conduct in an antegrade fashion. These are called concealed APs, because “manifest” preexcitation is a delta wave that is visible on a surface 12-lead ECG. They account for about 30% of all SVTs induced on EPS.
Although no evidence of the pathway is present during sinus rhythm , orthodromic tachycardias can occur. Orthodromic tachycardia may also occur when there are two or more accessory connections, and in that case, the retrograde conduction may occur through the AV node, through one of the accessory connections, or through both.
This type of SVT may be difficult to distinguish from the usual AV nodal reentrant tachycardia on a standard surface ECG. In adults, if the heart rate is higher than 200 bpm or a retrograde P wave is visible in the ST segment , a concealed AP-mediated orthodromic reentrant tachycardia may be the diagnosis. However, this determination is most accurately made with electrophysiologic studies , or if SVT terminates with a single PVC. Other differentiating factors include the following :
Recommended Reading: Who Is Most Likely To Have Parkinson’s Disease
How To Manage Or Live With Wpw
There is no way to prevent WPW, but you can prevent complications by learning as much as you can about the disease and working closely with your cardiologist to find the best treatment. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do a Valsalva maneuver.
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions:
-
Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control.
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet.
Supraventricular Tachycardia: Incidence Mechanisms And Symptoms
Among patients with preexcitation, approximately 20 to 30% will develop episodes of supraventricular tachycardia , , , , with peaks in infancy and the second decade of life , . The most common mechanism of supraventricular tachycardia associated with an accessory connection is atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia using the atrioventricular node in the antegrade direction and the accessory connection as the retrograde limb from ventricle to atrium, referred to as
Recommended Reading: Does Senator Susan Collins Have Parkinson’s
The Risks Of Wpw Syndrome
The main consequences are:
Key Points About Wpw Syndrome
- WPW syndrome is a rapid heartbeat due to an extra electrical pathway connecting the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
- While some people might not experience WPW syndrome, those who do can experience fainting, tiredness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can disappear over time but can be treated by your doctor through medication or surgery.
- WPW is caused by a gene mutation or is present at birth.
Read Also: How To Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome include the sense of feeling the heart beat rapidly , lightheadedness, fainting, chest pain, and dizziness.
Some people do not have symptoms.
Episodes of WPW can trigger a life-threatening heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation, although this is extremely rare. Your doctor may recommend that you wear medical alert jewelry to alert medical professionals of your condition if you are at risk for ventricular fibrillation.
Home Remedies: Vagal Maneuvers
Sometimes, a persons rapid heartbeat corrects itself. Alternatively, some simple physical movements may help to correct the heartbeat.
These exercises include:
- bearing down as if having a bowel movement
- massaging the sides of the neck over the carotid artery
- holding an ice pack on the face
- gagging or forceful coughing
Therapists call these exercises vagal maneuvers because they affect the vagus nerve that runs from the abdomen to the brain. A branch of it runs to the heart.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can cause a variety of results, depending on what organ it affects. If the heart is beating too fast, it acts as a brake and slows the heart rate down.
If vagal maneuvers do not normalize the heart rhythm, a doctor may inject an antiarrhythmic drug to bring the heartbeat back to normal.
Another option is a procedure known as cardioversion. This intervention is when a doctor places paddles or patches on the persons chest and applies an electric shock to the heart, to restore normal heart rhythm.
Doctors usually use cardioversion for people who have not responded to vagal maneuvers or medication.
Also Check: Vcu Parkinson’s And Movement Disorders Center
How Do You Treat Wolff
Combined diagnosis and treatment is a good strategy to manage the condition. The goal in treating WPW syndrome is to extend the refractory period of the accessory pathway compared with that of the traditional AVN. This gives the ventricle more time to transmit the next electrical impulse through the AP. In this way, the heart rate is stabilized.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is used to treat Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome combined with AF. This procedure helps to destroy the tissue that is causing the rapid heartbeat. The procedure has an 85% to 95% success rate. However, RF ablation leads to complications, such as sudden death, stroke, cardiac surgery, and myocardial infarction.
Open heart surgery is an effective treatment for WPW but is performed only in the case of a heart surgery for an associated condition.
Medications:
There are 4 drugs that are used to treat WPW:
Electrical cardioversion can be used to immediately treat patients with WPW and AF, who are unstable.
Vagal maneuvers are postures that slow the heart rate by affecting the vagus nerve, such as putting an ice pack on the face or bending down while coughing.
Treatments For Wpw Syndrome
In many cases, episodes of abnormal heart activity associated with WPW syndrome are harmless, don’t last long, and settle down on their own without treatment.
You may therefore not need any treatment if your symptoms are mild or occur very occasionally, although you should still have regular check-ups so your heart can be monitored.
If your cardiologist recommends treatment, there are a number of options available. You can have treatment to either stop episodes when they occur, or prevent them occurring in the future.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Doctor Do You See For Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Wpw Syndrome
Doctors arent sure what causes WPW syndrome. The extra electrical pathway in the heart is present at birth, so its likely caused by some abnormality that occurs during fetal development. A small percentage of people with WPW syndrome have been found to have a gene mutation that is thought to be responsible for the disorder.
In a normal heart, the heartbeat is initiated by the sinus node in the upper right section of the heart muscle. This is where the electrical impulses that start each heartbeat begin. Those impulses then travel to the atria, or upper heart chambers, where the initiation of contraction occurs. Another node called the atrioventricular node, or AV node, then sends the impulse to the lower heart chambers called the ventricles where ventricular contraction occurs and the blood is pumped out of your heart. Ventricular contraction is much stronger than atrial contraction. The coordination of these events is essential for maintaining a normal, regular heartbeat and rhythm.
In a heart affected by WPW syndrome, however, an extra electrical pathway can interfere with the normal heartbeat. This extra pathway creates a shortcut for the electrical impulses. As a result, these impulses may activate the heartbeats too early or at the wrong time.
If its left untreated, the abnormal heartbeat, arrhythmia, or tachycardia, can cause blood pressure, heart failure, and even death.
Acute Therapy For Svt
Based on severity of symptoms, termination of acute episodes of SVT may be achieved with vagal maneuvers, drug administration, or cardioversion. Once congestive heart failure is present, vagal maneuvers are less likely to be effective . As the majority of episodes of SVT represent orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia, drugs acting at the atrioventricular node are first-line pharmacologic agents. Intravenous administration of adenosine is highly effective, but rarely may be associated with
Read Also: What Is The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s In Early Stages
What Is Characteristic Of Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a specific type of abnormality of the electrical system of the heart. This syndrome causes a specific pattern on an electrocardiogram and is linked to an episode of rapid heart rates, such as supraventricular tachycardia or atrial fibrillation. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a treatable medical condition. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is also referred to as WPW syndrome and pre-excitation syndrome.
What Can I Expect If I Have Wolff
You will work with your healthcare provider to manage any symptoms of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Youll have regular appointments to make sure your symptoms are under control or havent gotten worse. Make sure to attend all your appointments and follow your providers instructions. Let your provider know right away if you experience new or worsening symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Is Shortness Of Breath A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Wpw Syndrome Diagnosed
People experiencing a fluttering or racing heartbeat usually tell their doctors. The same applies to those experiencing chest pain of difficulty breathing. However, if you dont have symptoms, the condition may go unnoticed for years.
If you have a racing heartbeat, your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and conduct tests that measure your heart rate over time to check for tachycardia and diagnose WPW syndrome. These heart tests may include:
Deterrence And Patient Education
The dysrhythmias causing electrical abnormalities associated with WPW syndrome are a result of a congenital abnormality forming an accessory pathway. There is nothing that can be done to prevent WPW pattern. After WPW syndrome has manifested with the presentation of a tachyarrhythmia, an electrophysiologic study can be performed to map and assess risks of the accessory pathway, and catheter radiofrequency ablation of the pathway can be curative. For patients that this is not an option or preference, antiarrhythmic medications can be a reasonable alternative option.
You May Like: Why Do Boxers Get Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome symptoms vary. You might not have any symptoms at all. Or you may experience:
These tests give your healthcare provider information about your heart rate, rhythm and presence of any conduction abnormalities. Your provider can see visible heartbeat differences in a Wolff-Parkinson-White EKG versus a normal EKG.
