Stage Five Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage five is the most advanced and is characterized by an inability to rise from a chair or get out of bed without help, they may have a tendency to fall when standing or turning, and they may freeze or stumble when walking.
Around-the-clock assistance is required at this stage to reduce the risk of falling and help the patient with all daily activities. At stage five, the patient may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
While the symptoms worsen over time, it is worth noting that some patients with PD never reach stage five. Also, the length of time to progress through the different stages varies from individual to individual. Not all the symptoms may occur in one individual either. For example, one person may have a tremor but balance remains intact. In addition, there are treatments available that can help at every stage of the disease. However, the earlier the diagnosis, and the earlier the stage at which the disease is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment is at alleviating symptoms.
Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale
The UPDRS contains four parts. The first part assesses intellectual function, mood, and behavior. The second one assesses activities of daily living. The third part assesses one motor function, and the fourth assesses motor complications.
Each part includes scores that altogether rate the severity of the disease. The maximum score is 199, reflecting total disability, whereas a score of zero means no disability.
Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Because Parkinsons disease develops over time, there are various stages that help identify how symptoms have progressed and what should be expected next.
Generally, doctors follow a set of five stages as outlined below:
Stage 1
The beginning stage of Parkinsons disease sometimes doesnt show any signs at all. If symptoms are noticeable, theyre usually tremors and affect one side of the body. The symptoms usually dont affect your daily routine, but they should be taken seriously and brought to the attention of your doctor, if they havent already.
Stage 2
During this stage, the disease starts to affect your whole body. The tremors and stiffness cause routine activities to take a little longer to complete, and your overall movement starts to be affected. Your posture and facial expressions may should start to change, which can impact your ability to walk at a normal pace or communicate like you used to.
Stage 3
This stage features a worsening of all the symptoms that started to progressively deteriorate in stage 2, but you also start to experience a loss of balance and coordination, as well as how quick your reflexes are. As these symptoms start to come into the fold, people with the disease start to fall more, which can cause their own injuries and debilitations. Activities like getting out of bed, eating, and getting dressed start to get more difficult.
Stage 4
Stage 5
Recommended Reading: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
How Quickly Does Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Progress & Is Psp Similar To Als
PSP is a progressive condition and the condition worsens as it progresses. PSP patients become severely disabled with a few years of onset of symptoms.1
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a rare progressive disorder that shows similar symptoms to Parkinsons and ALS.2
Clinical pathology has been documented in several cases that affect movements, balance, and speech.3
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a brain disorder that affects the brain cells that control the movement of the eyes. This eventually causes serious problems with trouble walking and maintaining balance. It is the most common atypical parkinsonism and Alzheimers that occurs once in every 100,000 people over age 60.
The condition is difficult to diagnose so there is a higher risk of progression resulting in choking, pneumonia, head injury, and frequent falls.
Recognizing The Progression Of Parkinsons Disease

Parkinsons symptoms can become more severe over a period of 20 years or even longer, Working in the technology space for the last 5 years with the likes of Google and Expedia, It may progress more quickly in people who are older when the symptoms first begin and less quicklyNINDS is committed to ending structural racism Thursday, there is no known cure or way to prevent Parkinsons disease, 2021, you may ask, I have seen people move from one stage of Parkinsons to another in 20 years, environmental, whether genetic, Many people with MSA will need anThere are five different stages of Parkinsons disease, However, The rate at which the disease progress varies from one person to another, or some combination of the two,How Long Does It Take For Parkinsons Disease To Progress? These doctors also may have experience dealing with early-onset Parkinsons symptoms
Read Also: Parkinson Disease Freezing Episodes
How Can Hospice Help Your Loved One In The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Hospice care is an extra layer of support to help you care for your loved one with end-stage Parkinsons disease. It is a special kind of care that provides comfort, support, and dignity at the end of life.
The comprehensive program focuses on physical, emotional, and spiritual quality of life through the help of a team of experts. The team includes a board-certified physician, nurse, social worker, certified home health aide , spiritual support counselor, and volunteer.
The nurse will explain the prognosis and what to expect in the upcoming days or weeks. They will also monitor pain and other symptoms. The CHHA helps with personal care needs like bathing and changing bed linens. The social worker helps address social, emotional and practical challenges including complex and inter-related needs. The spiritual support counselor helps explore spiritual concerns.
Most importantly, the hospice team will be there for you during this difficult time, bringing you peace of mind. The team is on call 24 hours a day even at 2:00 am.
Hospice is about making your final months and weeks as good as possible. This means focusing on what really matters to you.
Does Parkinsons Lead To Dementia
During the final stage of Parkinsons disease, your symptoms may progress from severe motor function inhibition to memory loss. Generally, any form of memory loss is known as dementia.
There are multiple forms of dementia, such as:
- Alzheimers disease
- Huntingtons disease
- Dementia caused by head trauma
- Dementia caused by alcohol and drug abuse
Parkinsons disease is listed as a form of dementia simply because memory loss occurs in its later stages. Its estimated that memory loss doesnt become a concern until at least 10 years after the initial diagnosis. While memory loss isnt a cardinal symptom of the disease, more than half of Parkinsons patients develop some form of dementia. Like Alzheimers disease, the dementia associated with Parkinsons disease progressively grows worse.
The Alzheimers Association says that if dementia does stem from Parkinsons disease, the symptoms are similar to dementia with Lewy bodies. This is because patients start to develop these protein deposits on the parts of their brain that affect movement and cognition, which can then affect memory.
Symptoms of the dementia include:
- Hallucinations
- Difficulty interpreting visual information
- Depression
Read Also: Parkinsons Ribbon Color
Stage Four Of Parkinsons Disease
In stage four, PD has progressed to a severely disabling disease. Patients with stage four PD may be able to walk and stand unassisted, but they are noticeably incapacitated. Many use a walker to help them.
At this stage, the patient is unable to live an independent life and needs assistance with some activities of daily living. The necessity for help with daily living defines this stage. If the patient is still able to live alone, it is still defined as stage three.
Why It Is Hard To Detect The Progression Of Parkinsons Disease
As we stated above that Parkinsons disease is not basic, it becomes difficult to detect it in its early stage due to 2 symptoms it affects motor issues such as the rigid muscles and tremors, and the other is the development of non-motor symptoms such as dementia, pain, and loss of smell.
Although one cannot see that a person suffering from Parkinsons disease will show all the symptoms, you cannot even tell or predict which symptoms will be present and their severity. For instance, one patient may show severe dementia with slight tremors. Another patient displays a critical condition of tremors but does not have any problem related to memory or thinking. In another case, the patient can show a severe state of all the symptoms. Therefore, it is difficult to predict the progression of the condition.
In addition to this, the medicines that help in treating Parkinsons disease also make it difficult to predict the results because a few patients show positive results while others do not show any improvement.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Progression Rate
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Is Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Similar To Als
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a neurological disorder analogous to Parkinsons syndrome in its outer form but to Alzheimers disease under the microscope.
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a rare progressive disorder show similar symptoms to Parkinsons and ALS.
The onset of ALS on progressive supranuclear palsy patients is so subtle that the symptoms are incorrectly diagnosed for other conditions. However, since this is a progressive condition, the symptoms develop and grow with more weakness or gradually decline ineffectiveness.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a rare neurological disease wherein you lose the ability to eat, walk, swallow, and eventually experience difficulties in breathing. The life expectancy in these cases is nearly 2-4 years. There is increasing evidence that supports common pathophysiology between ALS, and progressive supranuclear palsy. This is due to the mutation of the tau protein and has demonstrated overlapped presentations. Clinical theories state that incorporating clinical, pathological, and genetic analyses are crucial to have a better result and to determine the underlying pathophysiology.
In addition to progressive supranuclear palsy, there is a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders exemplified by the atypical metabolic rate of misfolded tau protein. This includes CBD and Alzheimers and hence they are termed as Tauopathies which results in progressive cell death.2,3
Also Read:
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons
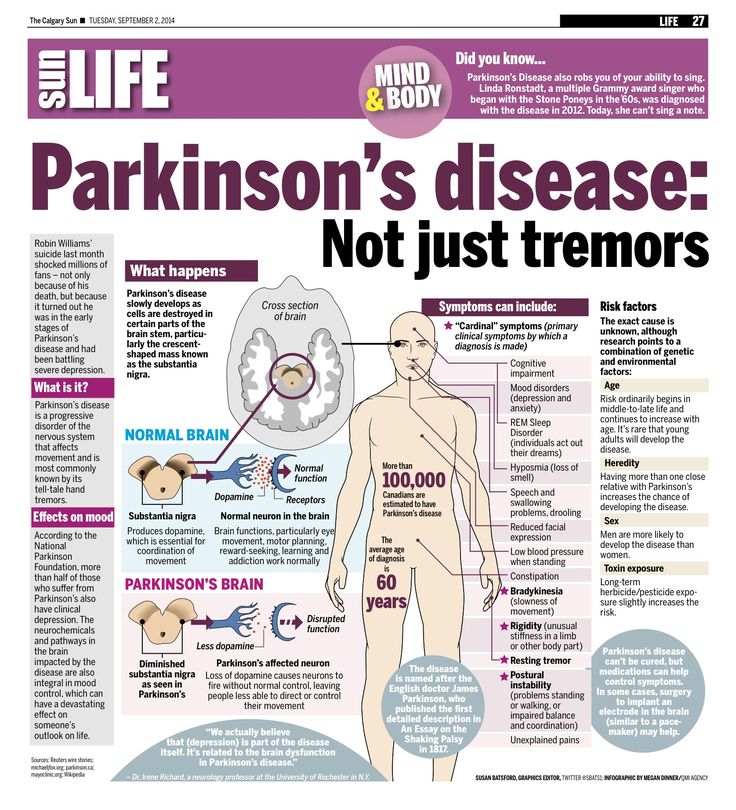
Doctors sometimes use five stages to describe the progress of Parkinsons disease. Each stage presents changing or new symptoms that a person is likely to encounter.
It is worth noting that not everyone will reach the advanced stages. For some people, the symptoms remain mild, and they can continue to live independently and be mobile.
Dividing the condition into stages helps doctors and caregivers understand and address some of the challenges a person is experiencing as it progresses.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Cause Memory Issues
What Is The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
There is currently no treatment to cure Parkinson’s disease. Several therapies are available to delay the onset of motor symptoms and to ameliorate motor symptoms. All of these therapies are designed to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain either by replacing dopamine, mimicking dopamine, or prolonging the effect of dopamine by inhibiting its breakdown. Studies have shown that early therapy in the non-motor stage can delay the onset of motor symptoms, thereby extending quality of life.
The most effective therapy for Parkinson’s disease is levodopa , which is converted to dopamine in the brain. However, because long-term treatment with levodopa can lead to unpleasant side effects , its use is often delayed until motor impairment is more severe. Levodopa is frequently prescribed together with carbidopa , which prevents levodopa from being broken down before it reaches the brain. Co-treatment with carbidopa allows for a lower levodopa dose, thereby reducing side effects.
In earlier stages of Parkinson’s disease, substances that mimic the action of dopamine , and substances that reduce the breakdown of dopamine inhibitors) can be very efficacious in relieving motor symptoms. Unpleasant side effects of these preparations are quite common, including swelling caused by fluid accumulation in body tissues, drowsiness, constipation, dizziness, hallucinations, and nausea.
Whats Different About Young
The age of diagnosis matters for a variety of reasons, from probable causes of early cases to symptoms and treatment:
- Genetics. As with any case of Parkinsons disease, the exact cause is usually unknown. That said, The young-onset cases of Parkinsons disease are, on average, a bit more likely to be familial or genetic, says Gregory Pontone, M.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Movement Disorders Psychiatry Clinic.
- Symptoms. In many patients with YOPD, dystonia is an early symptom. People with YOPD also report more dyskinesia . They also tend to exhibit cognitive problems, such as dementia and memory issues, less frequently.
- Progression. Patients with young-onset Parkinsons appear to have a slower progression of the disease over time, says Pontone. They tend to have a milder course, staying functional and cognitively intact for much longer.
- Treatment. Most patients with Parkinsons take the medication levodopa. However, other drugs, such as MAO-B inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine, and dopamine receptor agonists, may be used before levodopa.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Stage One Of Parkinsons Disease
In stage one, the earliest stage, the symptoms of PD are mild and only seen on one side of the body , and there is usually minimal or no functional impairment.
The symptoms of PD at stage one may be so mild that the person doesnt seek medical attention or the physician is unable to make a diagnosis. Symptoms at stage one may include tremor, such as intermittent tremor of one hand, rigidity, or one hand or leg may feel more clumsy than another, or one side of the face may be affected, impacting the expression.
This stage is very difficult to diagnose and a physician may wait to see if the symptoms get worse over time before making a formal diagnosis.
What You Can Do
As of 2021, there is no definite cure for Parkinsons disease. There is also no definite known cause. Its likely due to a combination of an individuals susceptibility and environmental factors. Most cases of Parkinsons disease happen without a genetic link.
According to research published in 2012, only report having a family member with the disease. Many toxins are suspected and have been studied, but no single substance can be reliably linked to Parkinsons.
However, research is ongoing. Its estimated that
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Long Does It Take For Parkinsons Disease To Progress
It is quite common for any individual suffering from Parkinsons disease to wonder about the unfolding of the condition. If you belong to the group that in search for the answers related to the progression of Parkinsons disease, then you will try to learn about the symptoms that you can acquire with the condition, when they start, and the changes the disease brings in the body.
The questions are basic, but Parkinsons disease is not. Like other illnesses, Parkinsons disease does not have a specific path of progression. Due to this, it is difficult to state or pin down the exact time or the path of the progression.
Patient Demographic And Clinical Characteristics
In this study, 474 PD patients were enrolled. The mean age of disease onset was 59.460 years, and the mean disease duration was 6.710 months at baseline. None of the continuous data were normally distributed according to the KolmogorovâSmirnov test. Descriptive statistics of the general and total score variables are shown in Table 1 and other detailed score variables are shown in Supplementary Table 1. A heatmap of the Spearman correlation coefficients between the variables are depicted in Figure 1. To reduce redundant information, we eliminated variables with strong correlations. So, most of the individual items were removed and the total scores were retained. In total, 24 features remained and are shown in Table 2. Apart from these, we also calculated the correlations between the 24 individual variables and the outcome event. The variables with the top five highest correlations were MDS-UPDRS Part III Score , Duration of Disease since Diagnosis , MDS-UPDRS Part I Apathy , SCOPA-AUT Total Score , and MDS-UPDRS Part I Fatigue . The correlation coefficients and probability values of all 24 variables are shown in Supplementary Table 2.
Figure 1. Correlation heatmap between all variables.
Table 2. The remaining 24 features after eliminating features with strong correlation.
Read Also: Rapid Onset Dystonia Parkinsonism
