Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease: Motor Symptoms
The clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is based on the presence of characteristic motor symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and resting tremor but neuropathology is still considered the gold standard for definite diagnosis. Differentiating PD from other movement disorders can be challenging throughout the disease course, because signs and symptoms often overlap. Indeed, neuropathology studies reveal that clinical diagnosis of PD can be confirmed with an accuracy of about 75%. Good response to levodopa is often used to support the diagnosis of PD. However, cases of pathologically proven PD with poor response to levodopa have also been reported.
Misdiagnosis of PD can occur for several reasons. In a community-based study of patients taking antiparkinsonian medication, the most common misdiagnosis were essential tremor, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular parkinsonism. In addition, many of the prominent features of PD may also occur as a result of normal aging or from comorbid and multifactorial medical conditions .
R. Savica, … G. Logroscino, in, 2016
Definition And Differential Diagnosis
There are many manifestations of but the classical diagnostic symptoms are:
- slowness and poverty of movement
- stiffness
The physical signs of include:
- slowness of movement
- rest tremor.
At diagnosis, these signs are usually unilateral, but they become bilateral as the disease progresses. Later in the disease additional signs may be present including postural instability , cognitive impairment and orthostatic hypotension .
There is no single way to define Parkinsons disease or what is often called idiopathic Parkinsons disease in order to differentiate it from other causes of parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy .
is traditionally defined, pathologically, by the finding of Lewy bodies and degeneration of catecholaminergic neurones at post-mortem. Using a pathological definition of PD is problematic for a number of reasons:
- A pathological diagnosis is not practical in life.
- Lewy body inclusions in catecholaminergic neurones are seen in individuals without clinical evidence of it is presumed that these are pre-clinical cases.
- Lewy bodies have not been found in otherwise typical individuals with with Parkin mutations, although such rare young-onset genetic cases of PD might be said not to have idiopathic PD.
In recent years, attempts to define genetically have become possible with the discovery of monogenic forms of the disease. However, such families account for a very small proportion of cases.
Common causes of tremor.
Looking For Signs Of Parkinsons
Your specialist will examine you to look for common signs of Parkinsons. You may be asked to:
- write or draw to see if your writing is small or gradually fades
- walk to see whether theres a reduction in the natural swing of your arm or in your stride length and speed
- speak to see if your voice is soft or lacks volume
The specialist will also look at and ask you about your:
- face to see if there is a masked look or if you have difficulty with facial expressions
- limbs to see if you have a tremor, any stiffness or slowness of movement
As well as examining you for any of the typical signs of Parkinsons, the specialist will also look for signs that may suggest a different diagnosis.
It may be helpful to take someone with you for support when seeing a specialist. Taking a list of questions you want to ask can also be useful so you dont forget to mention something you want to know about. If a healthcare professional says something you dont understand, dont be afraid to ask them to explain what they mean.
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Tests Might I Have
Your doctor may want to start by testing your blood or doing a brain scan to rule out other conditions.
People who have Parkinsonâs disease donât make enough of a brain chemical called dopamine, which helps you move. If those first tests donât show a reason for your symptoms, your doctor may ask you to try a medication called carbidopa-levodopa, which your brain can turn into dopamine. If your symptoms get much better after you start the drug, your doctor probably will tell you that you have Parkinsonâs disease.
If the medication doesnât work for you and thereâs no other explanation for your issues, your doctor might suggest an imaging test called a DaTscan. This uses a small amount of a radioactive drug and a special scanner, called a single photon emission computed tomography scanner, to see how much dopamine is in your brain. This test cant tell you for sure that you have Parkinsons disease, but it can give your doctor more information to work with.
It can take a long time for some people to get a diagnosis. You may need to see your neurologist regularly so they can keep an eye on your symptoms and eventually figure out whatâs behind them.
Contact Our Information And Referral Helpline
The Parkinson Canada Information and Referral Helpline is a toll-free Canada-wide number for people living with Parkinsons, their caregivers and health care professionals. We provide free and confidential non-medical information and referral services. When you have questions or need assistance, our information and referral staff help connect you with resources and community programs and services that can help you. We provide help by phone or email, Monday to Friday, 9:00 a.m. 5:00 p.m. ET.
Don’t Miss: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
How Can I Try To Get An Early Diagnosis
By the time Parkinsons causes noticeable motor symptoms, usually about 50 percent of the cells that produce dopamine in your substantia nigra have already died off. Non-motor symptoms, such as constipation, loss of smell, or restless sleep, often appear before motor symptoms.
Theres still debate among medical professionals on how long non-motor symptoms may appear before an individual has noticeable changes in their movement. Its thought that they could appear years to decades beforehand.
But a formal Parkinsons diagnosis requires the symptom slowness of movement. In the time before this symptom appears, your doctor cant make a Parkinsons diagnosis, but they may alert you that youre at a high risk of developing Parkinsons in the future if these or other symptoms appear at any point.
Read Also: Medicinal Plants For Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Parkinson’s Last
Early Signs Of Parkinson’s
Early physical signs include the common motor symptoms: tremor, muscle rigidity and slowness. They may also include the following:
- Symptoms starting on one side of the body
- Change in facial expression
- Failure to swing one arm when walking
- Stooped posture
- Loss of sense of smell
- Depression or anxiety
Some of these symptoms are quite common and by no means exclusive to Parkinsons, so if you have some of them, it does not mean you have Parkinsons.
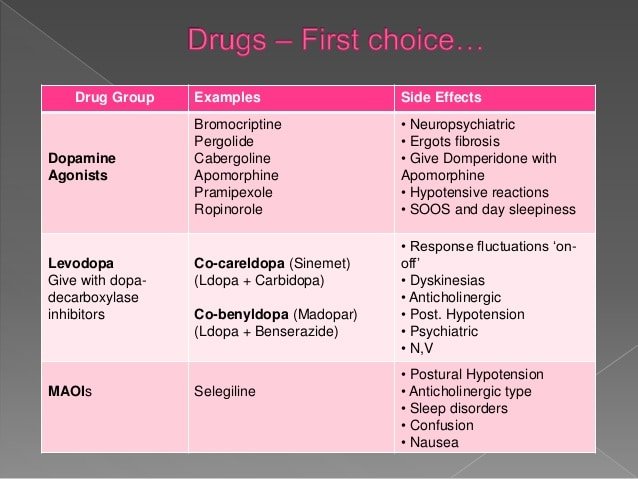
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Go Away
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Read Also: Parkinsons Disease Mental Health
Read Also: Journal Of Parkinson’s Disease Impact Factor
Obtaining A Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis
During the exam, the neurologist will look for cardinal symptoms of the disease. Facial expressions and features will be assessed. The doctor will look for signs of tremor while the patient is at rest. The doctor may watch how easily the patient stands up from sitting in a chair. The doctor may also stand behind the patient and gently pull back on the patients shoulders and look for how easily the patient can regain balance. Good responsiveness to levodopa also helps support the diagnosis of PD. However, taking levodopa may exclude patients from clinical studies that need to recruit recently diagnosed patients who have not yet had treatment . Participation in a clinical trial should be discussed with the doctor.
PD can be challenging to accurately diagnose, particularly in early stages of the disease, which is why a neurologist trained in movement disorders is critical. Approximately 5-10% of patients with PD are misdiagnosed, as many of the symptoms of PD are similar to other diseases. If the patient thinks that he or she has been misdiagnosed, a second opinion may help.1,2
Blood Tests And Spinal Fluid Tests
A blood test or spinal fluid test cant be used to diagnose Parkinsons. But they can be used to search for certain proteins that indicate you may have another neurodegenerative condition with similar symptoms.
The presence of elevated levels of a nerve protein called neurofilament light chain protein may indicate that you have another movement disorder, such as:
- multiple system atrophy
- corticobasal degeneration
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Molecular Imaging In Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD relies on the clinical manifestation of cardinal motor symptoms, bradykinesia, and tremor at rest or rigidity . A positive response to dopaminergic drugs is supportive of the diagnosis. Single photon emission computed tomography or PET ligands that are specific for dopamine transporters indirectly enable the quantification of the deficit of dopaminergic nigrostriatal projections and can provide further support of diagnosis . Deficiencies of monoamine synthesis can be measured with dihydroxyphenylalanine which is a substrate for the enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in all monoaminergic neurons including noradrenergic neurons .
The role of deficits of noradrenaline in motor and non-motor symptoms is not clear and research on the noradrenergic system in PD patients has been hindered by lack of specific methods to visualize the noradrenergic neurons and projections in vivo. We have recently carried out PET studies to investigate the role of noradrenaline in non-motor symptoms in PD patients and these studies will form the basis of discussions in the paragraphs below.
Paul Johns BSc BM MSc FRCPath, in, 2014
How Common Is Parkinsons Disease
- Nearlyone million people in the U.S. are living with PD and this number is expected to rise to 1.2 million by 2030.
- We do not yet have an accurate estimate of the number of Black and African Americans living with PD in the U.S. Studying health disparities, conducting more targeted and inclusive research, promoting more awareness and disclosure of symptoms, and more accurately diagnosing PD in the Black community will help us learn more.
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Medical History And Physical Exam
The process of diagnosing Parkinsons usually begins with the neurologist evaluating your medical history and performing a physical exam. For a formal diagnosis to be made, you need to have a general slowness of movement with either a resting tremor or rigidity.
During the physical exam, your doctor will have you perform a series of tests to monitor your movement. An example of a test they might use is a finger tap, where they measure how many times you can tap your finger in 10 to 15 seconds.
They will also look for signs that you may have another condition. A group of movement disorders collectively called parkinsonisms can produce symptoms that are indistinguishable from those of Parkinsons but are not the same. Usually, additional tests are needed to rule out these conditions as well.
Why Is Distinguishing Young
Socially, people who are affected by PD at a younger age experience the disease differently they may be at a different stage of their career and often have less time to engage in their own care. They may also have children or are planning to have children and have questions regarding passing on PD genes.
Medically, doctors tailor treatment when it is a younger person with PD. The younger you are, the more likely the disease is genetic. Your care team may offer genetic testing or counseling. Younger brains also have a higher neuroplasticity potential which allows the brain to handle and respond to disease and therapy differently.
Don’t Miss: When Was Muhammad Ali Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
If Its Not Parkinsons Disease What Could It Be
Here are some possibilities:
Side effects of medication: Certain drugs used for mental illnesses like psychosis or major depression can bring on symptoms like the ones caused by Parkinsonâs disease. Anti-nausea drugs can, too, but they typically happen on both sides of your body at the same time. They usually go away a few weeks after you stop taking the medication.
Essential tremor: This is a common movement disorder that causes shaking, most often in your hands or arms. Itâs more noticeable when youâre using them, like when you eat or write. Tremors caused by Parkinsonâs disease usually happen when youâre not moving.
Progressive supranuclear palsy: People with this rare disease can have problems with balance, which may cause them to fall a lot. They donât tend to have tremors, but they do have blurry vision and issues with eye movement. These symptoms usually get worse faster than with Parkinson’s disease.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus : This happens when a certain kind of fluid builds up in your brain and causes pressure. People with NPH usually have trouble walking, a loss of bladder control, and dementia.
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
A diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is likely if you have at least 2 of the 3 following symptoms:
- shaking or tremor in a part of your body that usually only occurs at rest
- slowness of movement
- muscle stiffness
If your symptoms improve after taking a medication called levodopa, it’s more likely you have Parkinson’s disease.
Special brain scans, such as a single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases to try to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
