Motor Fluctuations And Dyskinesia
For the treatment of motor features of tremor, bradykinesia, and rigidity associated with Parkinsons disease, dopaminergic therapies are initially effective however, motor fluctuations eventually complicate therapy and can cause significant disability and impair quality of life. Sustained-release carbidopa/levodopa and bromocriptine have not been found to reduce off time.
Risk factors for motor complications include disease severity, younger age at onset of Parkinsons disease, high levodopa dosage, and longer disease duration. The motor fluctuations usually are addressed with levodopa adjustments as well as adjunctive medications or surgery as discussed below.
You May Like: Parkinsons Disease And Cbd
Medication Guidelines For Parkinsons Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Recommended Reading: Young Onset Parkinsons Symptoms
Box 9 Biomarkers And Neuroprotective Strategies In Pd
Current antiparkinsonian therapies do not have any significant effect on the progressive loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and thus do not influence the course of this disease.
Despite promising preclinical results, neuroprotective trials have failed in PD patients.
The combination of early nonmotor symptoms, most particularly anosmia, with imaging techniques to assess changes in striatal dopamine transporter may be a suitable approach to identify at-risk PD patients prior to the appearance of motor symptoms, thus allowing early start of neuroprotective therapy.
Proteomics and related omics methods represent other interesting avenues to identify PD biomarkers.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Surgery For Parkinson’s
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
Choosing The Best Treatment Plan For You
As you may know, medications are the backbone of the Parkinsons treatment plan. But because the disease affects everyone differently, and each persons response to therapy will vary, there is no hard-and-fast rule about when you should begin taking medication and what to take first. Some doctors prescribe medication upon diagnosis. Others believe that drugs, especially levodopa, should be delayed as long as possible to avoid earlier onset of medication-related side effects.
Your involvement from the very start is important because you want to be sure your doctor is addressing your individual needs. When your doctor writes a new prescription, or makes a change to an existing one, take the opportunity to ask for an explanation. If her response goes something like, I always start my Parkinsons patients on X dosage of Y, a dopamine agonist, you might want to consider switching to a movement disorders specialist, a neurologist who has had special training in Parkinsons disease and other movement disorders.
You May Like: What Is Bradykinesia In Parkinsonâs
Read Also: Do You Feel Unwell With Parkinson’s
Pharmacological Advances: Charcot And Gowers
Early treatment of Parkinsonâs disease. Prescription dated 1877 from the College of Physicians of Philadelphia Library. In treating Parkinsonâs disease, Charcot used belladonna alkaloids as well as rye-based products that had ergot activity, a feature of some currently available dopamine agonists. Charcots advice was empiric and preceded the recognition of the well-known dopaminergic/cholinergic balance that is implicit to normal striatal neurochemical activity .
Everything, or almost everything, has been tried against this disease. Among the medicinal substances that have been extolled and which I have myself administered to no avail, I need only enumerate a few .
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests arent necessary unless you dont respond to treatment for Parkinsons disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
You May Like: Psychotherapy For Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: When To Start Parkinson’s Medication
Dbs Vs Ablative Surgeries For Pd
A specific challenge for neurosurgical treatments is that, as for any treatment for lifelong progressive diseases, they must be affordable in order to be practical for large numbers of patients. In the United States and other developed countries, DBS procedures have been embraced by both physicians and the public despite their high up-front costs, the substantial costs arising from the need to test and adjust stimulation parameters in the postoperative period, replacement of batteries, and the need for a high level of medical expertise throughout the pre-, peri-, and postoperative phases of the treatment. Similar conditions do not exist in developing countries, amounting to a continued need to optimize and develop less-costly alternatives, including ablative procedures. An important advancement in this field has been the demonstration that STN lesions are effective in the treatment of PD . A significant complication is, however, the development of persistent hemi-chorea in a small percentage of patients, requiring subsequent pallidotomy. The need for future long-term studies that explore the clinical effectiveness of refined and more selective methods of subthalamotomy, and the development of surgical techniques to reduce the occurrence of dyskinesias, is warranted. A summary of the main findings related surgical therapies for PD is presented in .
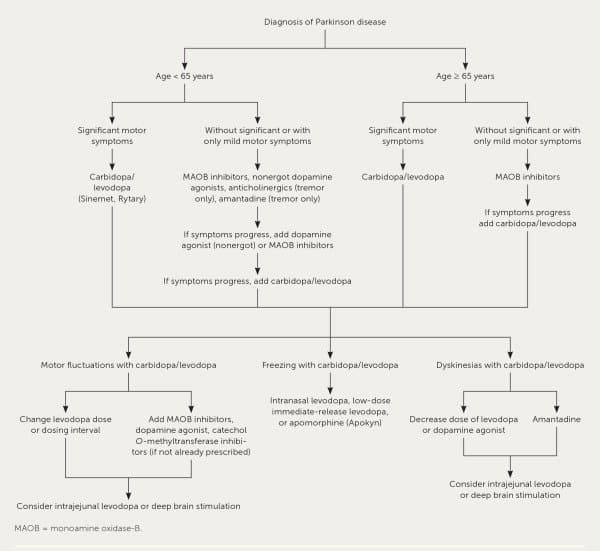
Treatment Of Motor Fluctuations
A number of strategies can reduce motor fluctuations in patients with PD. Optimising the amount of levodopa delivered to the brain is the main approach and can be achieved by increasing the levodopa dose, adjusting the timing of administration and/or adding adjunctive agents., Administering levodopa with a low protein meal or empty stomach, if tolerated, can improve absorption. Smaller, more frequent dosing may also help. Changing to a controlled-release formulation could theoretically improve fluctuations however, studies have shown no difference in symptoms compared to immediate-release preparations.
Adjunctive agents such as dopamine agonists, catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibitors and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors have been shown to improve fluctuations. Direct head-to-head studies comparing these medications are lacking however, a Cochrane review involving 44 randomised controlled trials suggested dopamine agonists were most effective in reducing âoffâ time . In older people, choice of adjunctive agent should be based on factors including comorbidities, adverse effects and patient preference.
Dopamine Agonists
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Articles 2020
Treatment Of Late Stage Complications Of Parkinsons Disease
Postural hypotension
Levodopa and dopamine agonists worsen postural hypotension and it may be necessary to lower the dose of levodopa or withdraw the agonist. Treatment is difficult, but patients should be advised to sleep with the head of the bed raised by one or two bricks and to add salt to their diet. Fludrocortisone can then be added at a dose of 0.1 mg in the morning, increasing if necessary up to 0.5 mg in the morning. If these measures are ineffective, the alpha agonist midodrine 10-20 mg four hourly can be useful but it is experimental and only available via the Special Access Scheme. Patients treated for postural hypotension need to have electrolytes, renal function and supine blood pressures closely monitored.
Parkinsonian psychosis, depression and dementia
Psychotic symptoms such as visual hallucinations and persecutory delusions occur most commonly in the setting of dementia, which may be mild and therefore easily missed. Most drugs for Parkinsons disease make these symptoms worse. Depression is also common and requires treatment in its own right.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a condition where a part of your brain deteriorates, causing more severe symptoms over time. While this condition is best known for how it affects muscle control, balance and movement, it can also cause a wide range of other effects on your senses, thinking ability, mental health and more.
You May Like: How To Reduce Hand Tremors In Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
Read Also: Parkinsons Disease And Essential Tremor
The Palliative Care Offered Can Be Improved
Region Skåne is participating in the study and funding it, which is expected to be completed in the spring and be evaluated next year.
Many of these patients are not receiving adequate treatment. There is a whole lot that needs to be improved and we are also building in the palliative concept. It may sound sad, but it is positively meant that in the final phase of the disease, the focus is no longer on maximum mobility but on the patients quality of life, which includes medication, provision of nutrition, where the patient should reside and additional related matters. The treatment of the non-motor symptoms becomes even more important in these stages, stresses Per Odin.
Region Skåne has shown significant interest in the concept and sees it partly as a pilot project and then later a model for the university hospitals to reach out to patients to a greater degree than has occurred so far. A model that can also be used with other diseases and disorders with similar problems.
These disease groups, perhaps eventually all people, should have the right to palliative therapies at the end of life. If people knew they would be well cared for, I think much of the anxiety for the latter parts of life and finally death would diminish a bit. We are focusing on Parkinsons disease, however I believe that our palliative work can serve as a model in the work with many other diseases.
Recommended Reading: What Vitamins Should Not Be Taken With Parkinson’s
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications arent as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Parkinsons Treatment For Motor Symptoms
The majority of medications developed specifically to treat Parkinsons disease target common motor symptoms. Many of these treatments are designed to increase the level of the dopamine, a neurotransmitter that transfers signals between nerve cells. Dopamine is involved in regulating signals for movement, which is reduced in the brains of Parkinsons disease patients.
Read Also: A Cure For Parkinson’s Disease
Beyond Symptomatic Therapy: Neuroprotection Studies In Pd
Neuroprotective therapies are interventions that produce enduring benefits by favorably influencing the underlying etiology or pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders . Although there is currently no definitive methodology to assess neuroprotection in PD patients , multiple attempts have been made to assess the effects of medications on disease progression.
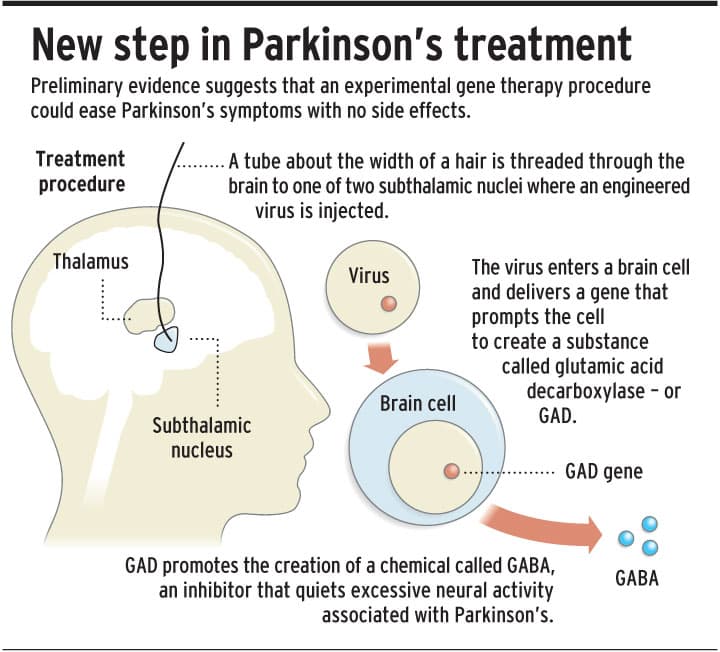
Surgical Therapies With Transplantation And Gene Therapy
Cell transplantation is regarded as a potential future PD treatment. There have been trials using autologous and non-autologous cells. Human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells are few of the cells that have been included in these transplantation studies. One of the concerns with cell transplantation using stem cells is the ethical bounds that must be considered.
Since the first clinical trial in 1987 involving the transplantation of dopaminergic- neuron-rich human fetal mesencephalic tissue into PD patients striatums, more research has aimed to explore whether the grafted dopaminergic neurons will live and form connections in the brain, if the patients brain can harmonize and make use of the grafted neurons, and if the grafts can generate significant clinical improvement. Clinical trials with cell therapy intend to discover if there are long-lasting improvements following restoration of striatal DA transmission by grafted dopaminergic neurons. Experimental data from rodents and nonhuman primates show that fetal ventral mesencephalon intrastriatal grafted DA neurons demonstrate many morphological and functional characteristics of normal DA neurons. Significant improvements of PD-like symptoms in animal models have been demonstrated after successful reinnervation by the grafts. Dopaminergic grafts can reinnervate the striatum in the brain, restore regulated release of DA in the striatum, and can become functionally integrated into neural circuitries.
Read Also: Is There A Test For Parkinson’s
Initial Drug Treatment In Parkinsons Disease
The bottom line
-
First line treatments for Parkinsons disease include levodopa, non-ergot dopamine agonists, and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors
-
Consider starting levodopa treatment in all patients, especially those with serious motor impairment or cognitive impairment
-
Monitor for motor complications and impulsivity and adjust doses accordingly
-
Do not stop treatment abruptly because this may cause malignant hyperthermia
A 69 year old retired bus driver with no medical history of note presented to the outpatients department with a three year history of progressive tremor of the right hand slowness of movement and difficulty turning in bed at night, buttoning shirts, and using cutlery. He is keen to know what is wrong and whether it can be treated.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinsonâs Doctors
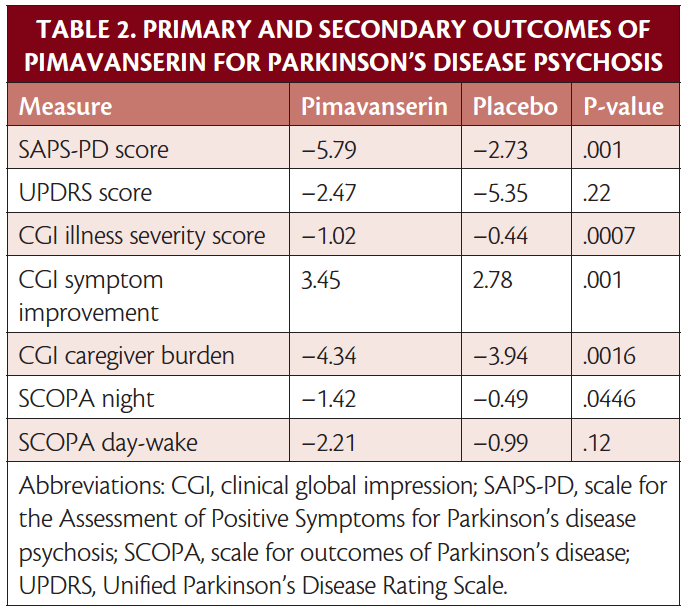
Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Andrew Schleisman, PharmD Candidate 2017
Mikayla Spangler, PharmD, BCPSAssociate Professor of Pharmacy Practice
Emily Knezevich, PharmD, BCPS, CDEAssociate Professor of Pharmacy PracticeCreighton University School of Pharmacy and Health ProfessionsOmaha, Nebraska
US Pharm. 2016 41:HS20-HS26.
ABSTRACT: Delusions and hallucinations in patients with Parkinsons disease, a condition known as Parkinsons disease psychosis , have historically been treated with clozapine and quetiapine because of their relatively low likelihood of worsening motor symptoms. Although clozapine is considered the drug of choice, it is underused in this population because of the need for frequent monitoring. Quetiapine, on the other hand, is generally first-line treatment despite its questionable efficacy. Consequently, in 2006, the American Academy of Neurology identified a need for the development of a novel antipsychotic with evidence of both safety and efficacy in patients with PDP. Pimavanserin, which has shown promise in clinical trials, recently became the first agent to receive FDA approval for the treatment of PDP.
You May Like: What Are The Signs Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Farm Chemicals
Common Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Box 1 Cardinal Motor Features Of Parkinson’s Disease
Bradykinesia/akinesia
Slowness of movement, fatiguing with decreased amplitude of movement, arrests in ongoing movement
Decreased spontaneous movements such as eye blinking, swallowing, and arm swing
Early feature
Tremor
Rhythmic sinusoidal movement of a body part due to regular contractions of reciprocally innervated muscles
Occurs at rest
Increase in resistance to passive movement
Cogwheel
Patients may complain of stiffness but not a major source of disability
Early feature
Postural instabilityretropulsion, propulsion, falls
Late feature
Shuffling, lack of arm swing
Festination: going from walking to running
Freezing: Feet sticking to the floor like glue, occurs with turning, gait initiation, enclosures like doorways
Late feature
Read Also: The Economic Burden Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinsons disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
