Recognition And Localization Of Accessory Pathways
When retrograde atrial activation during tachycardia occurs over an AP that connects the left atrium to the left ventricle, the earliest retrograde activity is recorded from a left atrial electrode . This is a left lateral pathway.
When retrograde atrial activation during tachycardia occurs over an AP that connects the right ventricle to the right atrium, the earliest retrograde atrial activity is generally recorded from a lateral right atrial electrode. This is a right ventricular free wall pathway.
Participation of a septal accessory pathway creates earliest retrograde atrial activation in the low-right atrium situated near the septum, anteriorly or posteriorly .
Retrograde atrial activation over the AP can be confirmed by inducing premature ventricular complexes during tachycardia to determine whether retrograde atrial excitation can occur from the ventricle at a time when the His bundle is refractory . Failure to advance the atrium when the His is refractory does not exclude an AP, particularly if far from the pacing site .
With entrainment pacing from the right ventricular apex, orthodromic reentrant tachycardia will return with a V-A-V response, typically with a short postpacing interval tachycardia cycle length difference if septal in origin. VA intervals remain fixed during SVT, and AV block cannot occur if the AV AP is critical to the circuit.
Atrial Fibrillation And Wolff
Atrial fibrillation may be particularly dangerous for people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. The extra pathway can conduct the rapid impulses to the ventricles at a much faster rate than the normal pathway can. The result is an extremely fast ventricular rate that may be life threatening. Not only is the heart very inefficient when it beats so rapidly, but this extremely fast heart rate may also progress to ventricular fibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation is a potentially fatal, uncoordinated series of very rapid, ineffective contractions of the ventricles caused by many chaotic electrical… read more , which is fatal unless treated immediately.
Symptoms Of Wpw Syndrome
Typically, when teenagers or people in their early 20s first experience an arrhythmia due to this syndrome, it is an episode of palpitations Palpitations Palpitations are the awareness of heartbeats. The sensation may feel like pounding, fluttering, racing, or skipping beats. Other symptomsfor example, chest discomfort or shortness of breathmay… read more that begins suddenly, often during exercise. The episode may last for only a few seconds or may persist for several hours. For most people, the very fast heart rate is uncomfortable and distressing. A few people faint.
In older people, episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia due to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome tend to cause more symptoms, such as fainting, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease Common
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Diagnosis
If your doctor thinks you might have Wolff Parkinson White syndrome after assessing your symptoms, theyll probably recommend having an electrocardiogram and will refer you to a cardiologist .
An ECG is a test that records your hearts rhythm and electrical activity. Small discs called electrodes are stuck onto your arms, legs and chest and connected by wires to an ECG machine. The machine records the tiny electrical signals produced by your heart each time it beats.
If you have Wolff Parkinson White syndrome, the ECG will record an unusual pattern that isnt usually present in people who dont have the condition.
To confirm the diagnosis, you may be asked to wear a small portable ECG recorder so your heart rhythm can be recorded during an episode. A Holter monitor records your heart activity for 24 hours. An event recorder monitors heart activity when you experience symptoms of a fast heart rate. The recorder will trace your heart rate continuously over a few days, or when you switch it on at the start of an episode.
Electrophysiological testing. Thin, flexible tubes tipped with electrodes are threaded through your blood vessels to various spots in your heart. The electrodes can precisely map the spread of electrical impulses during each heartbeat and identify an extra electrical pathway.
Also Check: Parkinsons Disease And Vision Problems
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment depends on the type and frequency of arrhythmias, associated symptoms such as syncope, and presence of structural heart disease. Typically a physician will recommend an ablation procedure to further define the characteristics of the accessory pathway, and ultimately, to eliminate the pathway entirely.
- Observation – If you have no symptoms, you may not require treatment. Your doctor may choose to have regular follow-up without treatment.
- Medications – A variety of drugs are available to treat arrhythmias. Because everyone is different, it may take trials of several medications and doses to find the one that works best for you. It is important to know:
- The names of your medications
- What they are for
- How often and at what times to take them
Recommended Reading: How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed And Treated
What Are The Long
Overall, the outlook for children with WPW is excellent. The problem resolves in the majority of infants by 12 months of age although SVT may recur later in childhood.
When the problem persists, radiofrequency ablation has proven to be safe and effective.
Exercise guidelines: Guidelines are best made by a patients doctor so that all relevant factors can be included. Participation in vigorous competitive sports may be restricted until the problem is treated by radiofrequency ablation. If the pathway does not conduct rapidly , usually no activity restrictions are needed .
If an episode of SVT occurs during sports, the child should remove herself/himself from participation until the arrhythmia is converted. Also, activities that involve climbing heights should be avoided since an episode may cause dizziness leading to a fall.
References
Bolling S, Morady F, Caukins H, Kadish A, de Buitleir M, Langberg J, Dick M, Lupinetti F, Bove E. Current treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results and surgical implications. Ann Thor Surg. 52:461-468,1991.
Deal B, Dick M, Beerman L et al. Cardiac arrest in young patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. PACE 1995 18:815.
Dick M, OConnor B, Serwer G, LeRoy S, Armstrong B. Use of radiofrequency energy to ablate accessory connections in children. Circulation 84:2318-24, 1991.
Reviewed September, 2012
Also Check: Parkinsons And Bad Taste In Mouth
Termination Of Acute Episodes
Narrow-complex atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
Narrow-complex reentrant tachycardia manifests with normal QRS complexes, a ventricular rate higher than 200 bpm, regular RR intervals, and a retrograde P wave well beyond the end of QRS.
It should be treated in the same way as AV nodal reentrant tachycardia , by blocking AV node conduction with vagal maneuvers , IV adenosine 6-12 mg via a large-bore line in adults, or IV verapamil 5-10 mg or diltiazem 10 mg in adults. In pediatric patients, adenosine and verapamil or diltiazem dosing regimens are weight-based.
Both adenosine and calcium channel blockers have been reported to result in atrial fibrillation with rapid, preexcited atrial fibrillation eventuating in ventricular fibrillation therefore, close monitoring during administration of these agents is essential, and cardioversion equipment and medications must be immediately available. Use of adenosine is preferred due to its short duration of action.
Atrial flutter/fibrillation or wide-complex tachycardia
AF or atrial flutter can be recognized by the presence of abnormal aberrant QRS complexes and irregular RR intervals. In this setting, drugs that prolong the refractory period of the bypass tract should be used, including procainamide .
Hemodynamically unstable tachycardia and electrical cardioversion
Further measures
Transfer
Read Also: How Many People Have Parkinson’s Disease
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Causes
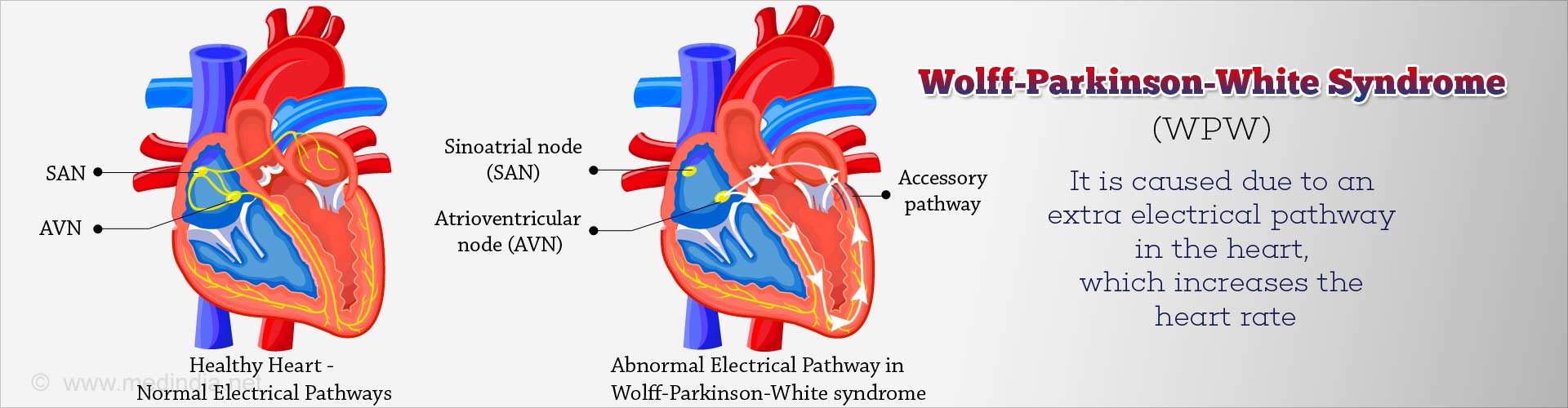
When the heart beats, its muscular walls contract to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, allowing the heart to fill with blood again. This is controlled by electrical signals.
In Wolff Parkinson White syndrome, theres an extra electrical connection in the heart, which allows electrical signals to bypass the usual route and form a short circuit. This means the signals travel round and round in a loop, causing episodes where the heart beats very fast.
The extra electrical connection is caused by a strand of heart muscle that grows while the unborn baby is developing in the womb.
Its not clear exactly why this happens. It just seems to occur randomly in some babies, although rare cases have been found to run in families.
Wolff Parkinson White is more common in males than in females.
How To Manage Or Live With Wpw
There is no way to prevent WPW, but you can prevent complications by learning as much as you can about the disease and working closely with your cardiologist to find the best treatment. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do a Valsalva maneuver.
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions:
-
Dont smoke.
-
Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control.
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet.
Recommended Reading: Can Someone Die From Parkinson’s Disease
Home Remedies: Vagal Maneuvers
Sometimes, a persons rapid heartbeat corrects itself. Alternatively, some simple physical movements may help to correct the heartbeat.
These exercises include:
- bearing down as if having a bowel movement
- massaging the sides of the neck over the carotid artery
- holding an ice pack on the face
- gagging or forceful coughing
Therapists call these exercises vagal maneuvers because they affect the vagus nerve that runs from the abdomen to the brain. A branch of it runs to the heart.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can cause a variety of results, depending on what organ it affects. If the heart is beating too fast, it acts as a brake and slows the heart rate down.
If vagal maneuvers do not normalize the heart rhythm, a doctor may inject an antiarrhythmic drug to bring the heartbeat back to normal.
Another option is a procedure known as cardioversion. This intervention is when a doctor places paddles or patches on the persons chest and applies an electric shock to the heart, to restore normal heart rhythm.
Doctors usually use cardioversion for people who have not responded to vagal maneuvers or medication.
Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute Cardiologists And Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to treat your abnormal heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices – Call Cardiology Appointments at toll-free 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or request an appointment online.
- Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more information, please contact us.
- You may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Internet.
The Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute has specialized centers to treat certain populations of patients:
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Develop
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyHeartDiseaseTeam is the social network for people with heart disease and their loved ones. On MyHeartDiseaseTeam, more than 47,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with heart disease.
Are you or is someone you care for living with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome? How do you manage symptoms such as shortness of breath or a racing heartbeat? Share your experience in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on your Activities page.
Further Information And Support

You can get in touch with the Arrhythmia Service on extension 5298, email them on or contact them via MyGOSH once you have registered. More information about MyGOSH is at www.gosh.nhs.uk/your-hospital-visit/mygosh
There are various organisations in the UK that support people with heart problems.
The biggest is the British Heart Federation their helpline is on or you could visit their website at www.bhf.org.uk
SADS UK can also offer help and support call them on or visit their website at www.sadsuk.org.
Also Check: What Causes Parkinson Disease And Alzheimer
What Are Possible Complications Of Wolff
WPW usually is not a major problem for most people. You can manage or correct the condition with treatment. Worrisome symptoms include fainting with very rapid heart rates. There is a very small risk of cardiac arrest if the heart rate becomes extremely rapid. This may be seen in people who also have atrial fibrillation .
What Are The Typical Electrophysiologic Findings Of Wpw Syndrome
Electrophysiology study in patients with WPW syndrome can help to confirm the presence of an AP, differentiate this condition from other forms of SVT, and to localize the pathway participating in the tachycardia for ablative therapy.
Figure 8.
Eccentric retrograde conduction through the accessory pathway located in left free wall. Note the eccentric activation of the atrium with pacing from the ventricle, with earliest atrial depolarization at the distal CS lead . The panel shows right ventricular apical pacing at 200 beats/min . His p, proximal His His d, distal His V, ventricular electrogram A, atrial electrogram CS, coronary sinus CS 9-10, the most proximal electrode in the CS catheter RVa, right ventricular apex RVa d, distal right ventricular apex.
Retrograde conduction over most APs is nondecremental. Hence, in the absence of intraventricular conduction delay or the presence of multiple bypass tracts, the VA conduction time is the same over a range of pace cycle lengths. The exception to this is the slowly conducting decremental posteroseptal pathway found in the permanent form of junctional reciprocating tachycardia, in which the VA conduction time increases with increasing ventricular pacing rate.
It is important and often challenging to differentiate retrograde conduction over septal pathway from conduction over the normal AV system. One maneuver that can make this differentiation is differential pacing and measuring the VA conduction time.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Disease Make You Tired
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
Synonyms of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
- Accessory Atrioventricular Pathways
- WPW Syndrome
General Discussion
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare congenital heart disorder involving irregularities in the electrical system of the heart. In individuals with WPW syndrome, an abnormal alternate electrical pathway , exists between the atrium and the ventricle, resulting in abnormal heartbeat rhythms and faster than normal heartbeats .
The normal heart has four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria and the two lower chambers are the ventricles. Within the right atrium of a normal heart is a natural pacemaker that initiates and controls the heartbeat. The electrical stimulus travels from the pacemaker to the ventricles along a specific pathway consisting of conducting tissue and known as the AV node. The extra electrical pathway in individuals with WPW syndrome bypasses the normal route and causes the ventricles to beat earlier than normal and can allow electrical impulses to be conducted in both directions .
Signs & Symptoms
The symptoms associated with WPW syndrome vary greatly from case to case. Some individuals may not have any abnormal heartbeats or associated symptoms . Although the disorder is present at birth , symptoms may not become apparent until adolescent or early adulthood.
Causes
Affected Populations
Related Disorders
Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of WPW syndrome. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis.
Causes Of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
WPW syndrome is a form of tachycardia that results from an extra electrical bundle, which is called an accessory pathway or bypass tract that runs from the atrium to the ventricles. As a result the conduction runs quickly than in a slower rate because it did not go through the normal pathway, which is the AV node which impedes the flow to facilitate a normal cardiac rate.
You May Like: Vascular Parkinsonism And Cognitive Impairment
Don’t Miss: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Do To The Body
Characteristic Features Of Wpw Syndrome
The classic ECG morphology of WPW syndrome is described as a shortened PR interval and a slurring and slow rise of the initial upstroke of the QRS complex , a widened QRS complex with a total duration greater than 0.12 seconds, and secondary repolarization changes reflected as ST segmentT wave changes that are generally directed opposite the major delta wave and QRS complex. In reality, the ECG morphology varies widely.
Depending on the location of the AP in relation to the sinus node and the relative transmission characteristics of the AP and the AV node, the morphology of the ECG may vary from a classic presentation, termed manifest preexcitation, to near normal.
In some cases, the electrical impulses arrival at the ventricles occurs slightly earlier through the AP , creating preexcitation.
The QRS interval is widened because the ventricles are initially activated via the AP, which lies outside the normal conducting system, producing an early, albeit relatively slow, initial propagation of depolarization forces through the ventricular tissue. This produces the delta wave. The delta wave makes the QRS appear wider than expected and the PR interval somewhat shortened. This is known as a manifest AP because it is easily identifiable on ECG.
An AP that does not manifest on ECG is revealed when the rate exceeds the refractory period of the AV node. This has been described as a latent AP. A latent AP can conduct both antegrade and retrograde transmissions.
Risk Assessment And Need For Ablation
If AF is induced during either an intraesophageal or an EPS, the shortest RR interval between two consecutive preexcited QRSs is measured. If the interval is less than 220 ms, then the risk of sudden death due to VF is believed to be high. Specifically, according to one study, the most discriminating predictor of VF in patients with WPW syndrome was the shortest RR interval during AF of 172 ± 23 ms . Those patients were considered to be at high risk for developing VF and sudden death should AF occur.
A study of asymptomatic children with WPW pattern who underwent EPS for risk stratification reported that a high proportion of subjects experienced sustained AVRT, AF, or both, with the shortest RR between two consecutive preexcited QRSs being 230-250 ms . The authors concluded that those results may be indicative of the necessity of RF ablation in all asymptomatic individuals with WPW pattern.
Also Check: Is Dropping Things A Sign Of Parkinson’s
