Trouble Moving Or Walking
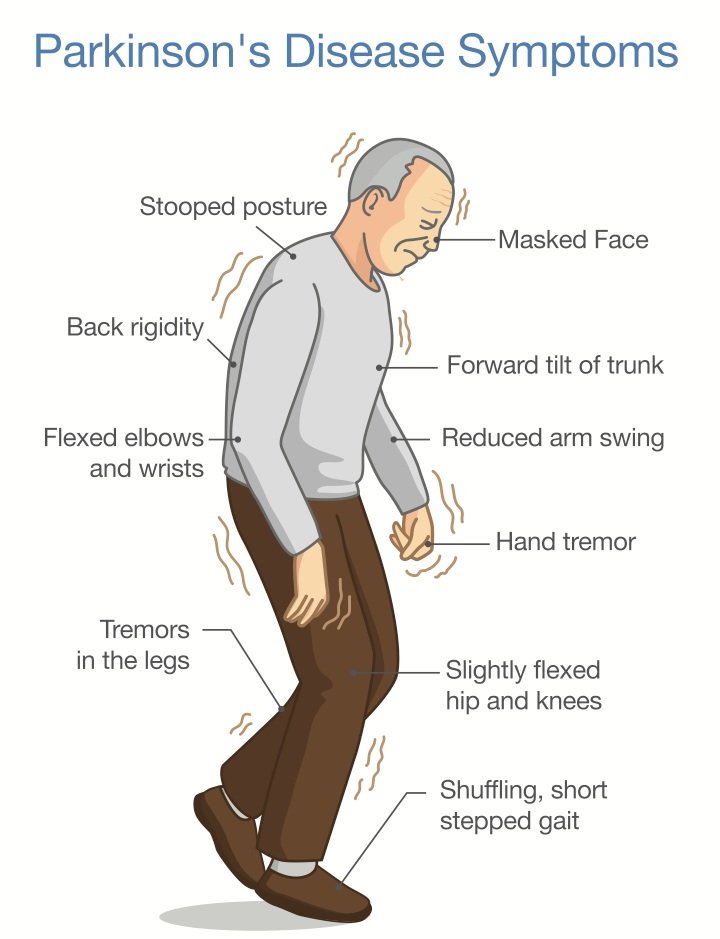
Do you feel stiff in your body, arms or legs? Have others noticed that your arms dont swing like they used to when you walk? Sometimes stiffness goes away as you move. If it does not, it can be a sign of Parkinson’s disease. An early sign might be stiffness or pain in your shoulder or hips. People sometimes say their feet seem stuck to the floor.
What is normal?If you have injured your arm or shoulder, you may not be able to use it as well until it is healed, or another illness like arthritis might cause the same symptom.
The Plus Side Of An Early Diagnosis
The news is not nearly all bad for those with young-onset Parkinsons. For one thing, patients with YOPD are better candidates for surgical procedures and medical innovations being used or developed to treat Parkinsons disease. For another, younger patients are less likely to be coping with other health problems at the same time.
Targeting Parkinsons-Linked Protein Could Neutralize 2 of the Diseases Causes
Researchers report they have discovered how two problem proteins known to cause Parkinsons disease are chemically linked, suggesting that someday, both could be neutralized by a single drug designed to target the link.
Spatial Analysis Of Parkinson Disease: Bayesian Modeling And Mapping Of Parkinson Disease Incidence And Prevalence
To produce smoothed disease maps, we applied a conditionally autoregressive model to predict county level incidence and prevalence rates of Parkinson disease. This model is derived from a traditional multilevel design, but takes into account spatial adjacency relationships between counties by assuming that neighboring areas had similar spatial variation.
To capture the random effects between counties, we computed the median relative risk and interquartile relative risk . The median relative risk is always greater than or equal to 1 and higher values suggest greater spatial variance. The interquartile relative risk reflects a difference of relative risks between the highest and lowest quartiles of incidence or prevalence. We also performed a high/low Getis-Ord General G cluster analysis to determine the probability of nonrandom grouping of either high or low county prevalence or incidence.
Read Also: Life Expectancy Of Parkinson’s Patients
What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is often divided into two parts: early stage and advanced stage disease.
- Early stage: when symptoms appear and start to affect everyday activities, such as washing, getting dressed and walking.
- Advanced stage: when motor complications occur from the long term use of one of the main treatments for Parkinsons disease, levodopa.
Englewood Hospital Will Host Panel Discussion; Jewish Home Family Initiating New Support Group
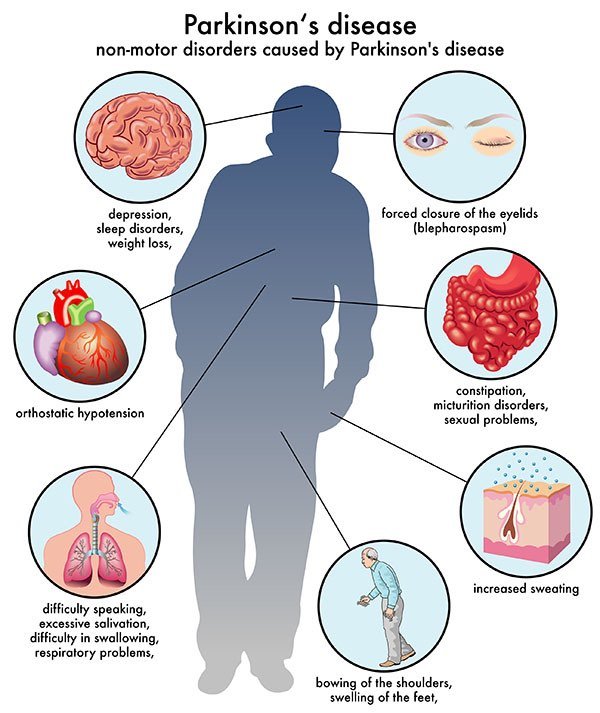
My father and both of his sisters were afflicted with Parkinsons disease, a neurological disorder that affects movement by hindering walking and affecting motor control of the hands and head. So the question Is Parkinsons a Jewish genetic disorder? has personal meaning to me.
On December 12, a program addressing that question and other topics related to Parkinsons disease will take place at Englewood Hospital and Medical Center. Dr. Lana Chahine, a neurologist and Parkinsons researcher, will speak, and a panel of experts will answer questions on the topic.
Co-sponsored by the Jewish Home Family, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and Englewood Hospital and Medical Center, the free program is open to physicians, medical and elder care professionals, and members of the community. Parkinsons patients and their families are particularly encouraged to attend.
The December 12 program also marks the launch of a new community resource, the Center of Excellence in the Care of Parkinsons. The center has been developed by the Jewish Home Family, a multifaceted eldercare organization serving Bergen, Hudson, and Rockland counties.
Inheriting the LRKK2 mutation raises the risk of Parkinsons to about 30 percent, Dr. Alweiss said. While that figure is much higher than the risk the general public faces, If you have the gene there is still a good chance that you wont get the disease, he said.
Also Check: Sleep And Parkinson’s
Geographic Distribution Of Parkinson Disease In The Us
The incidence and prevalence of Parkinson disease varied significantly across the United States. Disease rates were highest in the Midwest and Northeast regions, where the incidence and prevalence of Parkinson disease were 210 times greater than the rates of many Western and Southern US counties. The median relative risk and interquartile relative risk indicated that the spatial variations of the incidence and prevalence were considerable .
County level age- and race-standardized incidence of Parkinson disease among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States .
Common Misdiagnosis: Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord are damaged. Muscle contractions are a common physical symptom. In contrast, PD has a variety of physical, mental, and emotional symptoms.
My husband started tremors 14 years ago but was only diagnosed last year. The doctor had previously said it was peripheral neuropathy.
My old neurologist for 11 years said peripheral neuropathy! VA then said 50/50 Parkinsons and sent me to the CU Movement Disorder Center. My new neurologist watched me walk along with other tests and said Parkinsons.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Whats Different About Young
The age of diagnosis matters for a variety of reasons, from probable causes of early cases to symptoms and treatment:
- Genetics.;As with any case of Parkinsons disease, the exact cause is usually unknown. That said, The young-onset cases of Parkinsons disease are, on average, a bit more likely to be familial or genetic, says Gregory Pontone, M.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Movement Disorders Psychiatry Clinic.
- Symptoms.;In many patients with YOPD, dystonia is an early symptom. People with YOPD also report more dyskinesia . They also tend to exhibit cognitive problems, such as dementia and memory issues, less frequently.
- Progression.;Patients with young-onset Parkinsons appear to have a slower progression of the disease over time, says Pontone. They tend to have a milder course, staying functional and cognitively intact for much longer.
- Treatment.;Most patients with Parkinsons take the medication levodopa. However, other drugs, such as MAO-B inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine, and dopamine receptor agonists, may be used before levodopa.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder and the most common movement disorder. Characteristics of Parkinsons disease are progressive loss of muscle control, which leads to trembling of the limbs and head while at rest, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. As symptoms worsen, it may become difficult to walk, talk, and complete simple tasks.
The progression of Parkinson’s disease and the degree of impairment vary from person to person. Many people with Parkinson’s disease live long productive lives, whereas others become disabled much more quickly. Complications of Parkinsons such as falling-related injuries or pneumonia. However, studies of patent populations with and without Parkinsons Disease suggest the life expectancy for people with the disease is about the same as the general population.
Most people who develop Parkinson’s disease are 60 years of age or older. Since overall life expectancy is rising, the number of individuals with Parkinson’s disease will increase in the future. Adult-onset Parkinson’s disease is most common, but early-onset Parkinson’s disease , and juvenile-onset Parkinson’s disease can occur.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Parkinson’s Dementia
Prevalence Of Parkinsons State
Western and Southern states appear to have lower rates of Parkinsons disease, while Northeastern and many Midwestern states have higher rates . Mississippi and Montana have the lowest rates of Parkinsons, at 5.1 per 10,000. Vermont has the highest rate of Parkinsons at 9.9 per 10,000.
Exhibit 2: Prevalence of Parkinsons Disease, by geography
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease .
What is normal?If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Also Check: Lrrk2 Parkinson
Rural Versus Urban Analysis
The United States Department of Agriculture’s rural-urban continuum classification system defines rurality by absolute population and classifies each county in the US by degree of rurality in a rank order fashion using a nine-tier scale from a population of less than 2,500 to a population of greater than 1 million. This system separately classifies less populated areas which are adjacent to large urban areas, such as suburbs.
To determine the relationship between rurality and Parkinson disease, we applied the rural-urban continuum classification system to county level age and race standardization for Parkinson disease prevalence and incidence from the year 2002. We compared the mean prevalence and incidence across these categories of rurality using a Kruskal-Wallis test. The prevalence and incidence for the most rural counties were also compared to those of the most urban counties with a two-tailed t test.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
Its estimated that approximately four people per 1,000 in Australia have Parkinsons disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 80,000 people living with Parkinsons disease, with one in five of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50. In Victoria, more than 2,225 people are newly diagnosed with Parkinsons every year.
Common Treatments For Multiple Sclerosis
Overview Multiple sclerosis is an immune-related disease that causes inflammation by attacking myelinated axons in the central nervous system. They damage the myelin and axon in different degrees and cause significant physical disabilities between the ages of 20-25 years in every 30% of patients. The most distinguishing factor of …
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy Dementia
Genetics Coffee Consumption And Parkinson’s Disease
This web page is archived for historical purposes and is no longer being maintained or updated.
Office of Public Health GenomicsCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
SMART way to learn the Common Signs of Parkinson’s Disease… Nursing Mnemonics
Double vision is common in people with Parkinsons affecting up to an estimated 30% of patients and is linked to both motor and nonmotor disease symptoms, a new large-scale, longitudinal study has found.
Parkinsons patients with double vision were more likely to be older, non-white, female, have had the disease for a longer time, and experience greater motor, nonmotor, and daily activity limitations.
The positive news for patients is that the condition is easily treatable, researchers noted.
The study, Prevalence and risk factors for double vision in Parkinson disease, was published in the journal Movement Disorders Clinical Practice.
Visual impairment is reported by some Parkinsons patients, with one of the most common complaints being double vision. However, the investigators noted that clinical study groups are prone to under-ascertainment, as neurologists may;not be comfortable addressing visual symptoms, and patients frequently do not disclose non-motor symptoms such as double vision unless specifically asked.
Thus, the conditions prevalence and risk factors remain unknown.
To fill this knowledge gap, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania examined the prevalence and risk factors for double vision in a large-scale electronic survey conducted between March 2015 and June 2020.
patients should be screened for visual symptoms in addition to other non-motor symptoms, the researchers concluded.
Don’t Miss: Gabapentin And Parkinson’s
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
You May Like: Parkinson\’s Life Expectancy
General Approach To Management
The primary goal in the management of PD is to treat the symptomatic motor and nonmotor features of the disorder, with the objective of improving the patients overall quality of life. Appropriate management requires an initial evaluation and diagnosis by a multidisciplinary team consisting of neurologists, primary care practitioners, nurses, physical therapists, social workers, and pharmacists., It is also important that the patient and his or her family have input into management decisions.
Effective management should include a combination of nonpharmacological and pharmacological strategies to maximize clinical outcomes. To date, therapies that slow the progression of PD or provide a neuroprotective effect have not been identified., Current research has focused on identifying biomarkers that may be useful in the diagnosis of early disease and on developing future disease-modifying interventions.,
Treatment For Parkinsons Disease

Today there is no treatment to cure the disease.;Several therapies are available to delay the onset of motor symptoms and improve them somewhat.;All of these therapies are designed to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain, either by replacing dopamine, mimicking it, or prolonging the effect by inhibiting its breakdown.;Studies have shown and observed that early therapy in the non-motor stage can somehow delay the onset of motor symptoms, thus extending peoples quality of life.
Treatments for Parkinsons include:
Read Also: Essential Oils And Parkinson’s
Medications For People With Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain and other organs such as the gut, which produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This causes a deficiency in the availability of dopamine, which is necessary for smooth and controlled movements.;Medication therapy focuses on maximising the availability of dopamine in the brain. Medication regimes are individually tailored to your specific need. Parkinsons medications fit into one of the following broad categories:;
- levodopa dopamine replacement therapy
- dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine
- COMT inhibitors used along with levodopa. This medication blocks an enzyme known as COMT to prevent levodopa breaking down in the intestine, allowing more of it to reach the brain
- anticholinergics block the effect of another brain chemical to rebalance its levels with dopamine
- amantadine has anticholinergic properties and improves dopamine transmission
- MAO type B inhibitors prevent the metabolism of dopamine within the brain.
