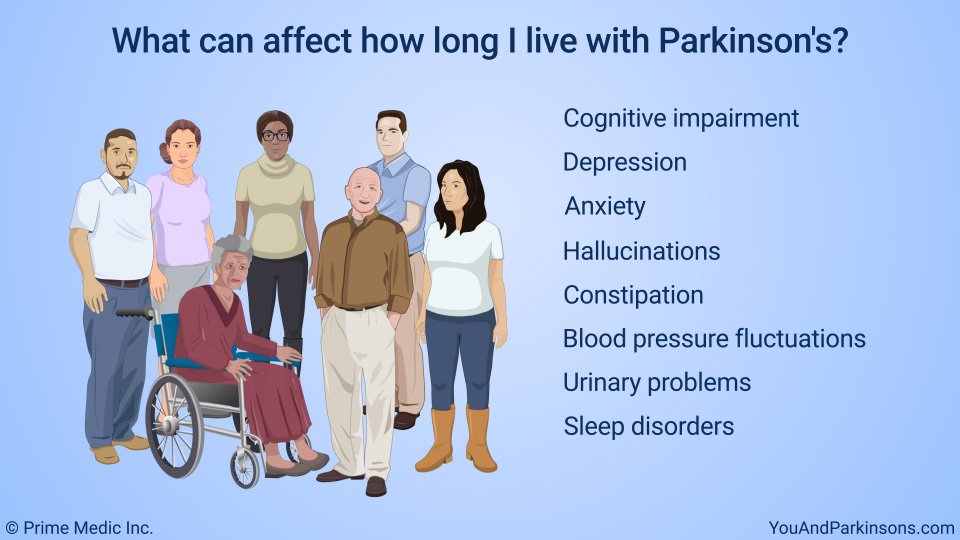
Specialist Support For Life After A Parkinsons Diagnosis
If you have been diagnosed with Parkinsons and would like a little extra support at home, our dedicated team of carers are on hand to support in any way you need. If youd like to speak to one of our experts about receiving Parkinsons care at home, simply call our customer care specialists on or request a callback and we will call you.
For support or information on an integrative medical plan following a Parkinsons diagnosis, please click here to visit Parkinsons Care and Support UK.
Page reviewed by Raj Senniappan, Occupational Therapist on March 15, 2021
Physical And Neurological Examination
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
- head trauma.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Genetically Inherited
Other Challenges Of Diagnosing Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease progresses slowly, often with non-motor symptoms appearing months or years before motor symptoms. This can make it challenging for doctors to diagnose you in the early stages, especially since the diagnostic criteria is based mostly on motor symptoms. You may have to wait until your symptoms progress for you and your doctor to confirm your diagnosis.14
Age and gender can be another issue. Since Parkinsons is associated more with older men, doctors may not think their younger or female patients have Parkinsons.5 On the other hand, since the disease is associated with aging, your symptoms may be blamed on getting older.
Remember that movement disorder specialists are extremely knowledgeable about Parkinsons disease and can help put the pieces together where other more generalized doctors may not. Never hesitate to fight for the care you deserve.
Related: Heres whats important to remember if you were just diagnosed with Parkinsons disease.
If You Notice Oily Skin On Your Scalp You May Want To Get Checked For Parkinson’s
Many people with Parkinson’s experience a surprising symptom with no obvious connection to the condition: having oily skin on their scalp. This occurs thanks to an increase in sebum, an oily substance produced by the body’s sebaceous glands. This can cause the scalp and hair to appear greasy and shiny. “Some people may only have minor issues, while others may have more severe problems that can affect daily life and cause them discomfort or embarrassment,” explains health organization Parkinson’s UK.
This increase in sebum can also cause a distinct smell associated with PD, according to the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and researchers say this symptom may someday prove diagnostically useful. “If we can define what is behind this Parkinson’s scent, perhaps we can develop objective tests to diagnose the disease earlier,” said Perdita Barran, BSc, PhD, a researcher studying sebum characteristics in PD patients. “Measuring Parkinson’s disease with such an easy-to-obtain sample, a swab of skin secretions, would also allow for more widespread screening,” she said.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Imaging Can Help With Diagnosis
Doctors use two tests that take detailed pictures of your brain. Each one may help your doctor make a diagnosis. These tests are:
- PET scan: This shows how your brain functions. It shows how the brain uses sugar. This scan can help tell the difference between Parkinson’s and .
- DaTscan: This shows problems with brain cells that make dopamine. Healthy brain cells light up during the test. Cells without enough dopamine appear dark. This scan can help your doctor tell the difference between Parkinson’s and a brain disease called .
Imaging studies are a newer way to diagnose Parkinson’s. However, not every healthcare facility can do them. It takes an experienced doctor to interpret the scans accurately. These scans also can be very expensive. Be sure to check with your insurance company ahead of time to see whether you are covered and what your out-of-pocket costs will be.
How Common Is Parkinsons Disease
- Nearlyone million people in the U.S. are living with PD and this number is expected to rise to 1.2 million by 2030.
- We do not yet have an accurate estimate of the number of Black and African Americans living with PD in the U.S. Studying health disparities, conducting more targeted and inclusive research, promoting more awareness and disclosure of symptoms, and more accurately diagnosing PD in the Black community will help us learn more.
Read Also: Hand Tremors And Memory Loss
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
What Parkinsons Diagnosis Criteria Do Doctors Use
Until the 1980s, there was no formal diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons disease. Beginning with James Parkinsons 1817 article, An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, and Margaret Hoehn and Melvin Yahrs description of the five stages of motor progression in 1967, scientists focused on the unique ways Parkinsons disease affects movement. A few scientists also noted non-motor symptoms like issues with automatic body functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
With the discovery in the 1950s of levodopa, a drug that gets turned into dopamine in your brain and thus replaces some of the dopamine that is lost due to PD, and the discovery of how dramatically levodopa improves motor symptoms, the medical community continued to focus more of their efforts on defining and treating Parkinsons as a motor condition.7
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Symptoms
The underlying cause of Parkinsons symptoms relates to a decline in the production of a brain chemical called dopamine. Many of the cells which produce dopamine are in the Basal Ganglia located in the middle of the brain. This lack of dopamine means people can have difficulty controlling their movements and moving freely.
Parkinsons Tremors: Causes Types And Treatments
Tremors are one of the major symptoms of Parkinsons disease for many people living with the condition. They can affect either side of the body, impacting arms and hands as well as the head and torso. Tremors can be frustrating to live with, especially when accompanied by other symptoms of PD like slowness, freezing, and loss of balance.
If you have PD, its important to understand the different types of tremors and treatments, as well as how tremors caused by Parkinsons are different from tremors caused by other conditions.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Change Your Personality
Further Testing In Parkinson’s
In other situations, where perhaps the diagnosis is not as clear, younger individuals are affected, or there are atypical symptoms such as tremor affecting both hands or perhaps no tremor at all, further testing may help. For example, imaging can play a role in differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsons. It can also be important to confirm what is initially a clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons prior to an invasive treatment procedure such as surgical DBS
Testing For Parkinson’s Disease
There are no blood tests or brain scans that can make the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Right now, the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease is still made based on the history and the examination.
In some cases, a doctor may order medical imaging such as a or an to make sure nothing else is happening, but these scans will not show any changes relating to Parkinsons disease.
In 2012, the FDA approved a special kind of brain scan called a DaT scan. In this scan, people receive an injection of a dye and then pictures show if there is a brain problem relating to the chemical dopamine. However, this scan was approved only to help figure out if someone with tremor has a disease in the Parkinson family or if their tremor might be related to a different disease called familial essential tremor.
Most of the time, a neurologist especially a movement disorders specialist can know if someone has a disease in the Parkinson family or familial essential tremor without doing this scan. It is also important to know that this scan cannot help a doctor know if a person has Parkinsons disease or one of the other parkinsonisms. Thus, this scan is only used in a few situations. It is not for everyone who might have Parkinsons disease.
In This Section:
You May Like: Is Parkinsons Fatal
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic neurological condition. It is progressive and symptoms worsen over time. It is named after Dr James Parkinson who first described the condition in 1817.
People with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of nerve cells in the part of their brains responsible for controlling voluntary movements. This part of the brain is called the substantia nigra . The nerve cells in the substantia nigra usually produce a chemical called dopamine which helps transmit messages from the brain to the rest of the body via the central nervous system . As these cells are lost, people with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of dopamine and the messages controlling movement stop being transmitted efficiently.
Parkinsons disease is more common as people get older but it can affect younger adults. Men tend to be affected in slightly higher numbers than women.
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
You May Like: Hemp Oil For Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Managed
Your doctors will tailor your treatment based on your individual circumstances. You will manage your condition best if you have the support of a team, which may include a general practitioner, neurologist, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, psychologist, specialist nurse and dietitian.
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, symptoms can be treated with a combination of the following.
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease .
What is normal?If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Memory Issues
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
You May Like: What To Expect With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
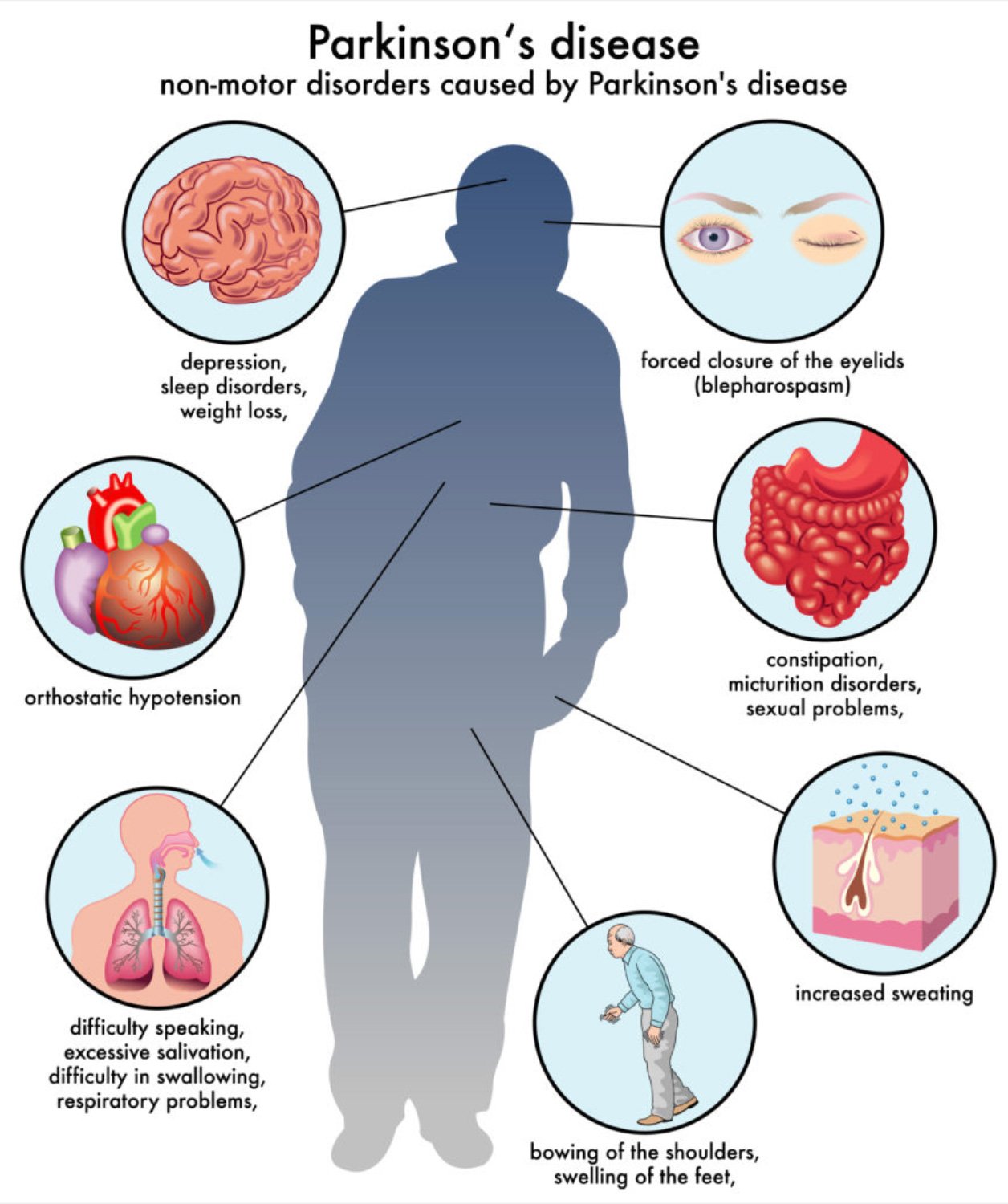
Parkinsons disease occurs when brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Parkinsons affects nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
Tests To Rule Out Other Conditions

Blood tests can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
An MRI or CT scan can check for signs of a stroke or brain tumor, which may cause similar symptoms.
Hydrocephalus due to atrophy can occur with some types of dementia and would be visible with one of these imaging tests. If the person has neurologic symptoms but a normal scan result, Parkinsons disease may be present.
The doctor a lumbar puncture to rule out inflammation or a brain infection.
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Is An Early Diagnosis Possible
In the early stages, it would be difficult for your GP to say whether you have Parkinsons or not, as there are so many conditions that have similar symptoms.
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of Parkinsons and are concerned, have a chat with your GP and they will guide you through the process. Without the formal tests and input from your doctor, its hard to accurately understand the root cause of your symptoms, so take it one step at a time and try not to worry.
Ological Limitations Of The Diagnostic Studies
When interpreting the literature about diagnosis, the following methodological issues should be considered:
- lack of long-term prospective clinical and pathological as a reference standard
- lack of operational definitions such as defining specialists or clinical diagnostic criteria
- unclear whether investigators were blinded to initial diagnosis
- sample sizes necessarily limited by the number of cases available with neuropathological outcomes
- trial age groups are often young as studies were performed by neurologists who see a younger population of people with PD
- most studies included people with established disease lasting some years
- varying geographical locations
- some studies are in specialised units and may not reflect the diagnostic accuracy of other units in the UK
- exclusion of some studies using magnetic resonance volumetry and magnetic resonance spectroscopy as they lacked appropriate population, intervention and outcome criteria
- lack of statistical details of diagnostic accuracy such as sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive values
- lack of economic evaluations of SPECT.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Taking Sinemet
How Can I Try To Get An Early Diagnosis
By the time Parkinsons causes noticeable motor symptoms, usually about 50 percent of the cells that produce dopamine in your substantia nigra have already died off. Non-motor symptoms, such as constipation, loss of smell, or restless sleep, often appear before motor symptoms.
Theres still debate among medical professionals on how long non-motor symptoms may appear before an individual has noticeable changes in their movement. Its thought that they could appear years to decades beforehand.
But a formal Parkinsons diagnosis requires the symptom slowness of movement. In the time before this symptom appears, your doctor cant make a Parkinsons diagnosis, but they may alert you that youre at a high risk of developing Parkinsons in the future if these or other symptoms appear at any point.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
