Pearls And Other Issues
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Localization Of Accessory Pathways
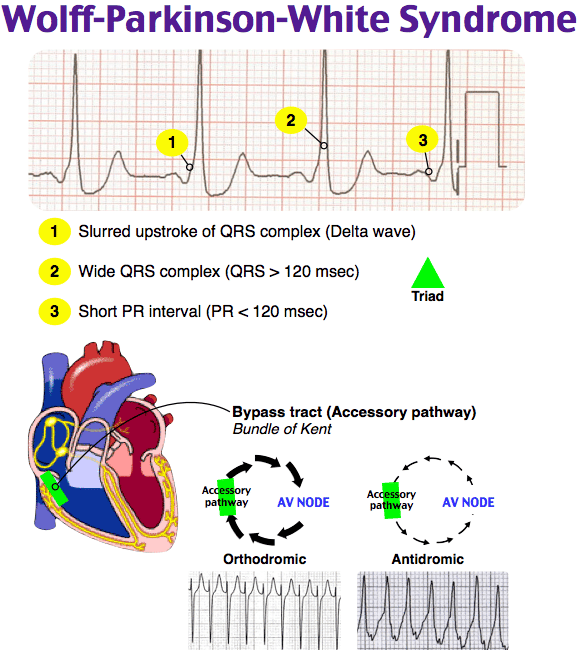
The location of the AP can often be determined through analysis of the spatial direction of the delta wave in the 12-lead ECG by reviewing the maximally preexcited QRS complexes. A general rule is that Q waves point away from the earliest site of ventricular activation, which is typically the insertion point of the bypass tract. The most common locations for APs, in decreasing order of frequency, are the left free wall, the posteroseptal and right free wall, and finally the midseptal and anteroseptal regions of the heart.
Several algorithms are available to predict the location of the AP. These algorithms may not be totally accurate because maximal preexcitation is needed, and usually the QRS in WPW pattern is a fusion between AV node and AP depolarization , precordial lead placement may vary, as well as chest shape and size and heart shape, size, and location.
A practical concept is that a negative delta wave usually signals the location of the AP, as follows:
- A negative delta wave in a left-side lead such as I and aVL indicates a left-side AP
- A negative delta in a right-side lead such as V1 predicts a right-side AP
- An isoelectric delta in V1 predicts an anteroseptal AP
- A negative delta in the inferior leads indicates a posteroseptal AP
- A positive delta in the inferior leads predicts an anteroseptal AP
A more specific algorithm for location of the AP, based on the polarity of the delta wave or first 40 ms of the QRS, predicts the following AP locations:
Home Remedies: Vagal Maneuvers
Sometimes, a persons rapid heartbeat corrects itself. Alternatively, some simple physical movements may help to correct the heartbeat.
These exercises include:
- bearing down as if having a bowel movement
- massaging the sides of the neck over the carotid artery
- holding an ice pack on the face
- gagging or forceful coughing
Therapists call these exercises vagal maneuvers because they affect the vagus nerve that runs from the abdomen to the brain. A branch of it runs to the heart.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can cause a variety of results, depending on what organ it affects. If the heart is beating too fast, it acts as a brake and slows the heart rate down.
If vagal maneuvers do not normalize the heart rhythm, a doctor may inject an antiarrhythmic drug to bring the heartbeat back to normal.
Another option is a procedure known as cardioversion. This intervention is when a doctor places paddles or patches on the persons chest and applies an electric shock to the heart, to restore normal heart rhythm.
Doctors usually use cardioversion for people who have not responded to vagal maneuvers or medication.
Recommended Reading: Is Rls A Sign Of Parkinson’s
Wpw Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for Wolff Parkinson White syndrome is broad and includes acute events such as myocardial infarction, structural disease such as congenital abnormality or hypertrophy, and other conduction abnormalities such as regular narrow complex tachycardia, irregular narrow complex tachycardia, and regular wide complex tachycardia.1
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you keep getting a fast or noticeable heartbeat . It’s important to get it checked out in case it could be something serious.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if:
- your heartbeat doesn’t go back to normal in a few minutes
- you have chest pain that lasts more than 15 minutes you may also have pain in your arms, back or jaw
- you have chest pain and other symptoms like feeling sick, being sick , shortness of breath or sweating
- someone passes out and doesn’t regain consciousness
If you’ve been diagnosed with WPW syndrome and you experience an episode, first try the techniques you’ve been taught or take any medication you’ve been given.
Dial 999 or go to your nearest accident and emergency department if these measures don’t stop the episode within a few minutes, or if someone you know has WPW syndrome and collapses or faints.
Also Check: Can You Test For Parkinson’s Disease
Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
James, TN. Morphology of the human atrioventricular node, with remarks pertinent to its electrophysiology. Am Heart J. vol. 62. 1961. pp. 756-71.
Lev, M, Leffler, WB, Langendorf, R. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular preexcitation terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. vol. 34. 1966. pp. 718-33.
Murdock, CJ, Leitch, JW, Teo, WS. Characteristics of accessory pathways exhibiting decremental conduction. Am J Cardiol. vol. 67. 1991. pp. 506-10.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Anderson, RH, Becker, AE, Brechenmacher, C. Ventricular pre-excitation: a proposed nomenclature for its substrates. Eur J Cardiol. vol. 3. 1975. pp. 27-36.
Mahaim, I, Benatt, A. Nouvelles recherches sur les connections superieures de la branche du faisceau de His-Tawara avec cloison interventriculaire. Cardiologia. vol. 1. 1937. pp. 61
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinsons Disease Be Treated
Symptmes Du Syndrome De Wpw
Le syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White est une cause fréquente de tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire Tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire La tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire est un rythme cardiaque rapide et régulier qui débute et sarrête brutalement et qui a son origine au niveau en apprendre davantage . Très rarement, ce syndrome provoque un rythme cardiaque extrêmement rapide et potentiellement mortel pendant la fibrillation auriculaire Fibrillation auriculaire et flutter auriculaire La fibrillation et le flutter auriculaires sont des formes de décharges électriques très rapides qui entraînent une contraction très rapide des oreillettes quelques-unes en apprendre davantage .
Si les nourrissons développent des arythmies dues à ce syndrome, ils peuvent devenir essoufflés ou léthargiques, perdre leur appétit, ou présenter des pulsations de thorax rapides et visibles. Une insuffisance cardiaque peut se développer.
Lorsque des épisodes de tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire due à un syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White surviennent chez des personnes plus âgées, ils provoquent en général plus de symptômes, comme un évanouissement, un essoufflement et une douleur thoracique.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Nightmares
Serotonin Syndrome : Symptoms Causes &
Serotonin syndrome, also known as serotonin toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from having too much serotonin in your body. Learn about serotonin syndrome symptoms, the medications that can cause the condition, and how it can beWebMDWebMD Better information. Better health.Treatment of atrial flutter · After atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is the most important and most common atrial tachyarrhythmia. Although it was first described 80 years ago, techniques for its diagnosis and management have changed little for decades. The diagnosis rested almost entirely with the 12 lead ECG, and treatment options included only the use of a digitalis compound to slow and control the ventricular
-
Symptoms suggestive of recurrent tachycardias in addition to the following ECG characteristics
-
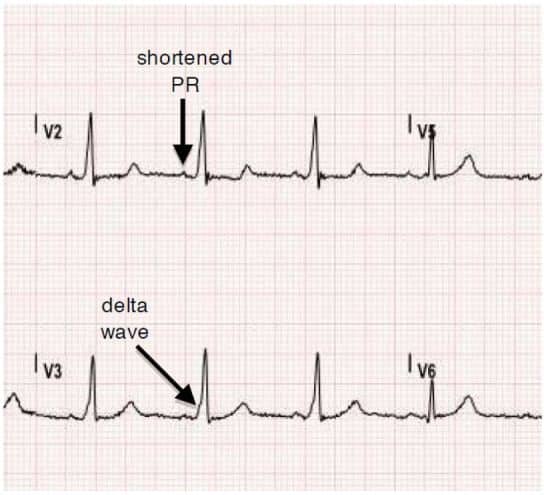
Shortened P-R interval of < 0.12 s
-
Slurred slow rising onset to QRS known as the delta wave
-
A prolonged QRS complex > 0.11 s
Figure 6
BCT with delta wave.
Tachycardias Generated Outside The Circuit:
Tachyarrhythmias generated in the atria with no relation with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome , transmitted to the ventricles through the accessory pathway. As the pathway lacks the slow conductions properties of the AV node, this can cause critically elevated ventricular frequencies and ensue ventricular fibrillation.
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Also Check: Johns Hopkins Parkinson’s Disease And Movement Disorders Center
When Will I Feel Better After Treatment For Wolff
At-home remedies like the Valsalva maneuver or coughing may slow your rapid heartbeat right away. Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect if youre taking medications for WPW.
Your provider can tell you when symptoms should improve after ablation or surgery for WPW. They can also tell you what to expect during recovery and when you can return to daily activities.
How Is The Problem Treated
See supraventricular tachycardia. Patients may be treated with heart medicines to prevent episodes of SVT. In general, infants are treated until their first birthday and then the medicines can be stopped. In older children, radiofrequency ablation has become first line treatment as it is safe with high success rates.
Recommended Reading: What Is Parkinson’s Syndrome
What Are The Two Forms Of Robinow Syndrome
Robinow syndrome is a rare disorder that affects the bones as well as other parts of the body. Two forms of Robinow syndrome have been described: autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome, and the milder autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome. They are distinguished based on their modes of inheritance, symptoms, and severity.
How To Know If Unborn Baby Has Down Syndrome
An ultrasound can detect fluid at the back of a fetuss neck, which sometimes indicates Down syndrome. The ultrasound test is called measurement of nuchal translucency. During the first trimester, this combined method results in more effective or comparable detection rates than methods used during the second trimester.
Don’t Miss: Is Ashwagandha Good For Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome symptoms vary. You might not have any symptoms at all. Or you may experience:
These tests give your healthcare provider information about your heart rate, rhythm and presence of any conduction abnormalities. Your provider can see visible heartbeat differences in a Wolff-Parkinson-White EKG versus a normal EKG.
Deterrence And Patient Education
The dysrhythmias causing electrical abnormalities associated with WPW syndrome are a result of a congenital abnormality forming an accessory pathway. There is nothing that can be done to prevent WPW pattern. After WPW syndrome has manifested with the presentation of a tachyarrhythmia, an electrophysiologic study can be performed to map and assess risks of the accessory pathway, and catheter radiofrequency ablation of the pathway can be curative. For patients that this is not an option or preference, antiarrhythmic medications can be a reasonable alternative option.
You May Like: What Can Parkinson’s Disease Lead To
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare but dangerous condition. A high index of clinical suspicion and close attention to concerning symptoms may be crucial in making a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis or sufficient concern is established, an interprofessional approach will be necessary for further evaluation and management. This approach, paired with education and shared decision making with patients and their families, will help guide treatment plans.
It is often difficult to develop and carry out well structured and rigorous studies in rare medical conditions. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is no exception, and most of the evidence is drawn from case series and population studies. The pathophysiologic basis is well understood, and surgical or catheter ablation has been shown to be successful and low risk. In high-risk patients, ablation is the most definitive treatment, but more future studies would help delineate medical management and ablation thresholds in some low-risk patients.
Prevalence Symptoms And Prognosis Of Wpw Syndrome
An electrocardiographic pattern of preexcitation occurs in the general population at a frequency of around 1.5 per 1000. Of these, 50% to 60% of patients become symptomatic. Approximately one-third of all patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia are diagnosed as having an AP-mediated tachycardia. Patients with AP-mediated tachycardias most commonly present with the syndrome of PSVT.
Population-based studies have demonstrated a bimodal distribution of symptoms for patients with preexcitation, with a peak in early childhood followed by a second peak in young adulthood. Nearly 25% of infants who demonstrate preexcitation and/or have AP-mediated arrhythmias will lose evidence of preexcitation and/or become asymptomatic over time as the conduction property of the AP can degenerate with time.
Pappone et al reported that during a mean follow-up of 37.7 months, 18.2% and 30% of noninducible patients have lost the anterograde and retrograde conduction, respectively. The mean age of these patients was 33.6 ± 14.3. Compared to others who had persistent conductibility through the AP, these patients were asymptomatic, noninducible, and had longer minimal 1:1 conduction cycle length through the AP during the baseline EPS.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease Funding Opportunities
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Parkinson’s Naturally
Treatments For Wpw Syndrome
In many cases, episodes of abnormal heart activity associated with WPW syndrome are harmless, don’t last long, and settle down on their own without treatment.
You may therefore not need any treatment if your symptoms are mild or occur very occasionally, although you should still have regular check-ups so your heart can be monitored.
If your cardiologist recommends treatment, there are a number of options available. You can have treatment to either stop episodes when they occur, or prevent them occurring in the future.
What Are The Typical Electrophysiologic Findings Of Wpw Syndrome
Electrophysiology study in patients with WPW syndrome can help to confirm the presence of an AP, differentiate this condition from other forms of SVT, and to localize the pathway participating in the tachycardia for ablative therapy.
Figure 8.
Eccentric retrograde conduction through the accessory pathway located in left free wall. Note the eccentric activation of the atrium with pacing from the ventricle, with earliest atrial depolarization at the distal CS lead . The panel shows right ventricular apical pacing at 200 beats/min . His p, proximal His His d, distal His V, ventricular electrogram A, atrial electrogram CS, coronary sinus CS 9-10, the most proximal electrode in the CS catheter RVa, right ventricular apex RVa d, distal right ventricular apex.
Retrograde conduction over most APs is nondecremental. Hence, in the absence of intraventricular conduction delay or the presence of multiple bypass tracts, the VA conduction time is the same over a range of pace cycle lengths. The exception to this is the slowly conducting decremental posteroseptal pathway found in the permanent form of junctional reciprocating tachycardia, in which the VA conduction time increases with increasing ventricular pacing rate.
It is important and often challenging to differentiate retrograde conduction over septal pathway from conduction over the normal AV system. One maneuver that can make this differentiation is differential pacing and measuring the VA conduction time.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Urinary Incontinence
Risk Assessment And Need For Ablation
If AF is induced during either an intraesophageal or an EPS, the shortest RR interval between two consecutive preexcited QRSs is measured. If the interval is less than 220 ms, then the risk of sudden death due to VF is believed to be high. Specifically, according to one study, the most discriminating predictor of VF in patients with WPW syndrome was the shortest RR interval during AF of 172 ± 23 ms . Those patients were considered to be at high risk for developing VF and sudden death should AF occur.
A study of asymptomatic children with WPW pattern who underwent EPS for risk stratification reported that a high proportion of subjects experienced sustained AVRT, AF, or both, with the shortest RR between two consecutive preexcited QRSs being 230-250 ms . The authors concluded that those results may be indicative of the necessity of RF ablation in all asymptomatic individuals with WPW pattern.
Asymptomatic Ventricular Preexcitation : When To Be Concerned
- A
Quick Takes
- A significant proportion of patients with ventricular preexcitation remain asymptomatic yet at the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Intermittent ventricular preexcitation during ambulatory monitoring or abrupt and complete termination of accessory pathway conduction during stress testing suggests a low-risk pathway.
- Shortest preexcited RR interval during atrial fibrillation < 250 ms, or accessory pathway effective refractory period < 240 ms suggest a high-risk pathway.
BackgroundIncomplete embryological atrioventricular annuli development and fibrous separation failure between the atria and ventricles can result in remnants of functional myocardial cells that form accessory pathways . APs can bypass the atrioventricular node-His-Purkinje system , resulting in rapid anterograde ventricular preexcitation and potentially fatal arrhythmias.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome affects 0.1-0.3% of the general population.1 The characteristic electrocardiogram features are shortened PR interval , slurred QRS upstroke , and prolonged QRS duration . The degree of VPE is determined by the relative conduction properties of the AVN and AP. In the absence of a documented tachyarrhythmia or related symptoms, the ECG findings alone are referred to as WPW pattern. The chief fear of both WPW syndrome and pattern is the risk for sudden cardiac death presumed to result from rapid VPE precipitating ventricular fibrillation .
Figure 1
You May Like: How To Control Drooling With Parkinson’s
Fibrillation Auriculaire Et Syndrome De Wolff
La fibrillation auriculaire peut être particulièrement dangereuse en cas de syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White. La voie accessoire peut conduire les impulsions rapides vers les ventricules à un rythme beaucoup plus rapide que celui de la voie normale . Il en résulte une fréquence ventriculaire extrêmement rapide et potentiellement mortelle. Le cur est non seulement très peu efficace lorsquil bat aussi rapidement, mais ce rythme cardiaque extrêmement élevé peut également évoluer en une fibrillation ventriculaire Fibrillation ventriculaire La fibrillation ventriculaire est une série non coordonnée, potentiellement mortelle, de contractions très rapides et inefficaces des ventricules , provoquée par en apprendre davantage , qui est mortelle si elle nest pas rapidement traitée.
Read Also: Can Parkinsons Be Reversed With Exercise
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment will depend on how severe your symptoms are, and how often you have them. You may only need to be observed by your healthcare provider if you are not having symptoms. You may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to slow or regulate your heartbeat.
- Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure used to send energy to the area of your heart that has an electrical problem. The energy causes an area of the heart muscle to scar. This stops the electrical problem and allows your heart to beat normally.
- Cardioversion is a procedure used to give your heart an electrical shock. The shock may help put your heartbeat back into a normal rhythm. Cardioversion may be needed if other treatments do not work.
Read Also: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Do To You
