Suicidal Behavior In Parkinson’s Disease
Suicidal behavior includes suicidal ideations, suicidal gestures, attempted suicide and completed suicide. Compared to other aspects, little information is available about suicidal behavior in patients with PD. A longitudinal follow-up study of 8 years duration reported the risk of death in patients with PD due to suicide to be 5.3 times higher than expected. Studies that have evaluated suicidal behaviors have reported rates of suicidal ideations/death in patients with PD to vary from 22.7% to 30%. The risk factors for suicidal ideations/death include depression, anxiety, hopelessness, level of education level, age of onset of PD, duration of illness, and history of impulse-control disorder . The odds ratio for suicidal ideation/death in patients with PD for different risk factors are 4.6 to 5.9 , 2.45 to 19.2 , 1.2 , 2.92 and 4.97 to 6.08 in various studies. Other studies have reported increased risk for suicidal ideations with increasing severity of depression with odds ratio of 2.92.
European Parkinsons Disease Association
The European Parkinsonâs Disease Association is a European Parkinson’s umbrella organisation. They represent 45 member organisations and advocate for the rights and needs of more than 1.2 million people with Parkinsonâs and their families.
The EPDA vision is to enable all people with Parkinson’s in Europe to live a full life while supporting the search for a cure.
The group launched the European Parkinsonâs Disease Standards of care Consensus Statement in the European Parliament in November 2011. The document defines what the optimal management of Parkinsonâs should be and what good-quality care should consist of. The document is not only developed by experts in the field of Parkinsonâs but includes the voice of people with Parkinsonâs. In addition to this, they have produced some amazing resources to introduce people to the condition.
Motor Circuit In Parkinson Disease
The basal ganglia motor circuit modulates the cortical output necessary for normal movement .
Signals from the cerebral cortex are processed through the basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit and return to the same area via a feedback pathway. Output from the motor circuit is directed through the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata . This inhibitory output is directed to the thalamocortical pathway and suppresses movement.
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways, as follows:
-
In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
-
The indirect pathway contains inhibitory connections between the striatum and the external segment of the globus pallidus and between the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus striatal neurons with D2 receptors are part of the indirect pathway and project to the GPe
The STN exerts an excitatory influence on the GPi and SNr. The GPi/SNr sends inhibitory output to the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus. Dopamine is released from nigrostriatal neurons to activate the direct pathway and inhibit the indirect pathway. In Parkinson disease, decreased striatal dopamine causes increased inhibitory output from the GPi/SNr via both the direct and indirect pathways .
Dont Miss: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinsons
Read Also: How Long Does Parkinson’s Disease Last
Nursing Education To Improve Hospital Care For Parkinsons
A new educational program for nurses prepares them to improve hospital care for people with Parkinsons disease . The program, developed by and with nurses and tools affiliated with the Parkinsons Foundation, is described in the online March 3 edition of the Journal of Gerontological Nursing.
People with PD visit the hospital for a host of reasons, such as a disease-related fall or a urinary tract infection or for reasons unrelated to PD, such as heart problems or back surgery. Unfortunately, many people with Parkinsons find that during hospital stays, their symptoms worsen. Not only that, they tend to be hospitalized more often than their peers without PD, and hospital stay is often longer.
One reason is that hospital staff may have little experience with PD. Staff may be unaware of the complexities of Parkinsons and its symptoms. For example, its essential for people with PD to get their medications on time at the hospital. But studies have shown that, during a hospital stay, people with PD often receive their medications late, or even skip doses, and may be given other medications for pain, nausea, depression or psychosis that interfere with PD medications.
Results:
The program included the following:
What Does It Mean?
Reference
DiBartolo MC. . Enhancing Care for Hospitalized Patients With Parkinsons Disease: Development of a Formal Educational Program for Nursing Staff. Journal of Gerontological Nursing doi:10.3928/00989134-20170223-02
Surgical Therapies With Transplantation And Gene Therapy
Cell transplantation is regarded as a potential future PD treatment. There have been trials using autologous and non-autologous cells. Human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells are few of the cells that have been included in these transplantation studies. One of the concerns with cell transplantation using stem cells is the ethical bounds that must be considered.
Since the first clinical trial in 1987 involving the transplantation of dopaminergic- neuron-rich human fetal mesencephalic tissue into PD patients striatums, more research has aimed to explore whether the grafted dopaminergic neurons will live and form connections in the brain, if the patients brain can harmonize and make use of the grafted neurons, and if the grafts can generate significant clinical improvement. Clinical trials with cell therapy intend to discover if there are long-lasting improvements following restoration of striatal DA transmission by grafted dopaminergic neurons. Experimental data from rodents and nonhuman primates show that fetal ventral mesencephalon intrastriatal grafted DA neurons demonstrate many morphological and functional characteristics of normal DA neurons. Significant improvements of PD-like symptoms in animal models have been demonstrated after successful reinnervation by the grafts. Dopaminergic grafts can reinnervate the striatum in the brain, restore regulated release of DA in the striatum, and can become functionally integrated into neural circuitries.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s A Genetic Disorder
How Is Parkinsonism Diagnosed
You should be referred to a Parkinsons specialist for the diagnosis of any parkinsonism. They may wish to explore different things before giving you a diagnosis.
Your specialist will look at your medical history, ask you about your symptoms and do a medical examination.
Telling the difference between types of parkinsonism isnt always easy, for the following reasons:
- The first symptoms of the different forms of parkinsonism are so similar.
- In many cases, parkinsonism develops gradually. Symptoms that allow your doctor to make a specific diagnosis may only appear as your condition progresses.
- Everyone with parkinsonism is different and has different symptoms.
One of the most useful tests to find out what sort of parkinsonism you may have is to see how you respond to treatment.
If your specialist thinks you have idiopathic Parkinsons, theyll expect you to have a good response to Parkinsons drugs such as levodopa . A good response means that your symptoms will improve. Sometimes, it will only be clear that youve responded to medication when the drug is reduced or stopped, and your symptoms become more obvious again.
If you dont have any response to Parkinsons medication, your specialist will have to look again at your diagnosis.
If you have both unusual symptoms and no response to Parkinsons drugs, this doesnt automatically mean you have another form of parkinsonism. But it will make your specialist want to reconsider your diagnosis.
Current tests available include:
Nursing Care Plan For Parkinsons Disease 5
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Verbal Communication related to the rigidity of facial muscles, lack of stimuli, decreased circulation to the brain, and psychological barriers secondary to Parkinsons disease as evidenced by stuttering, inability to name words, inability to identify objects, inappropriate verbalization, and facial muscle rigidity.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to use other methods to communicate and make his or her needs known.
- The patient will be able to use techniques and other assistive devices that will help him or her to improve the patients ability to communicate.
- The patient will be capable of speaking in an understandable way as much as possible.
- The patient will be able to comprehend communication and will be able to exhibit minimal frustration and anxiety with speech attempts.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Parkinson’s Cause Tremors
Nursing Care Plan For Parkinsons Disease 2
Impaired physical mobility related to disease process of Parkinsons disease as evidenced by bradykinesia, cognitive impairment, inability to bear weight, rigidity, tremors, generalized weakness, inability to do activities of daily living as normal, and verbalization of overwhelming tiredness
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to perform activities of daily living within the limits of the disease.
Right At Homes Trained Care Experts Can Help
If you are one of the 1 million Americans with this chronic condition, you know that symptoms generally develop slowly over the years. Our goal is to be there for you as the disease progresses, providing as much or as little care as needed. Right at Homes specialized home care teams know just how to work with the muscle stiffness and tremors to help prevent frustration and falls. We also help individuals with Parkinsons disease stand strong with these beneficial caregiving services:
Recommended Reading: What Is The Test For Parkinson’s
Psychosis In Parkinson’s Disease
Psychosis is generally not considered as a primary symptom of idiopathic PD, although there are case reports of psychosis in patients with PD from the pre-levodopa era. The inability to reliably discriminate post-encephalitic Parkinsonism from idiopathic PD and the lack of recognition of the numerous parkinsonian disorders that are not idiopathic PD make these reports suspect. In fact some authors suggest that the occurrence of psychotic symptoms in an untreated PD patient constitutes an atypical feature and cast doubt on the diagnosis.
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
You May Like: How To Get Tested For Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There is no specific diagnostic procedure to diagnose PD. However, the following are helpful to come up with the diagnosis:
- Medical History Taking
- Physical Examination
- Single Photon Emission CT scan -this form of imaging shows the blood flow to tissues and organs
- Dopamine transporter scan this imaging is often used to confirm the diagnosis of PD. It is not typically requested as medical history and physical examination are often conclusive.
Dont Miss: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
You Are Reading A Preview
Activate your 30 day free trial to continue reading.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Parkinson’s Disease
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinsons. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
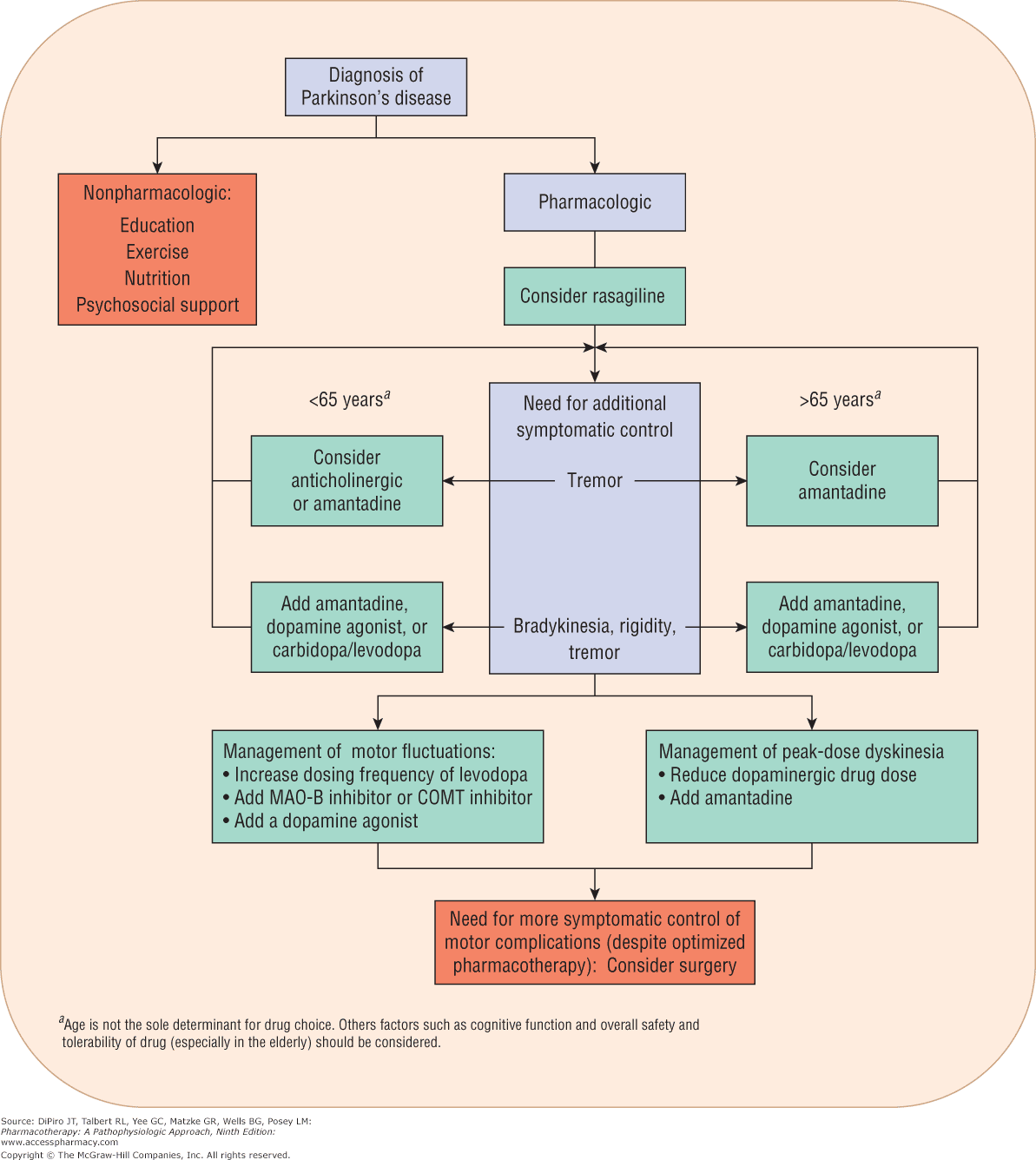
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Read Also: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Fatigue
Remaining Issues In The Pharmacotherapy Of Early Parkinsons Disease
In spite of the plethora of recent work addressing dopamine agonist monotherapy, many questions still remain. A change in practice to using agonist monotherapy for every new case of Parkinsons disease would double or treble the cost of treatment immediately. Is this worth it from the National Health Services perspective in terms of cost effectiveness, and from the patients perspective in terms of quality of life? Is agonist monotherapy neuroprotective and/or is levodopa toxic? It has been suggested that agonist monotherapy delays motor complications until levodopa is introduced, then complications accelerate until they are as severe as they would have been if an agonist had never been given. No data on this are available from the existing trials so this possibility remains. The recent agonist monotherapy trials included predominantly younger patients with Parkinsons disease: ropinirolemean age 63 years pramipexolemean age 61 years pergolidemean age 59 years. So the results of these trials should not be generalised to the elderly population in whom further data are required before recommendations can be made. Similar questions are outstanding regarding selegiline monotherapy in terms of its effects on quality of life, cost effectiveness, and neuroprotection.
Figure 3
Summary of the design of the PD MED trial . COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase MAOB, monoamine oxidase B.
Encouragingthe Use Of Assistive Devices
An electric warming tray keeps food hot and permits thepatient to rest during the prolonged time that it takes to eat. Specialuten-sils also assist at mealtime. A plate that is stabilized, a nonspill cup,and eating utensils with built-up handles are useful self-help devices. Theoccupational therapist can assist in identifying appropriate adaptive devices.
Read Also: Do I Have Parkinson’s Disease Test
Pathogenesis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of mechanisms have been implicated in PD pathogenesis, with -synuclein aggregation central to the development of the disease. Multiple other processes are thought to be involved, with several studies suggesting that abnormal protein clearance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation play a role in the onset and progression of PD. However, the relationship between these pathways remains unclear.
Recommended Reading: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinsons
The Role Of Nurses In Parkinson’s Disease
Research has shown increasing specialization among nurses who care for patients with PD thus, knowledge of the pathophysiology of this disease is arguably an important starting point for vocational training . Based on this, we sought to hierarchically organize the major motor and nonmotor symptoms of PD using evidence gathered from the literature .
Figure 1.
Classification of the main motor and nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease.
The symptoms of PD are divided into motor and nonmotor each of these classifications contains various other signs and symptoms related to both the neurodegenerative disease process itself as well as multifactorial causes. Thus, hierarchical organization of symptoms is not an easy task, and various descriptions have been proposed to facilitate understanding of the pathophysiology of the disease however, none of them have structured the symptoms into an organizational chart.
Our research on nursing diagnoses, outcomes, and interventions was based on this chart.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dat Scan For Parkinson’s Disease
