Lewy Bodies: More Than Lbd
LBD is characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the nerve cells of the brain, meaning that LBD patients have Lewy bodies in the brain.2 However, Lewy bodies are also common with other conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons disease. In fact, most people with PD also have Lewy bodies in their brain. However, even if they have Lewy bodies, not all Parkinsons patients will also develop LBD.2
Causes Of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease is thought to be caused by the abnormal build-up of 2 proteins called amyloid and tau.
Deposits of amyloid, called plaques, build up around brain cells. Deposits of tau form “tangles” within brain cells.
Researchers do not fully understand how amyloid and tau are involved in the loss of brain cells, but research into this is continuing.
As brain cells become affected in Alzheimer’s, there’s also a decrease in chemical messengers involved in sending messages, or signals, between brain cells.
Levels of 1 neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, are particularly low in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Medicines like donepezil increase levels of acetylcholine, and improve brain function and symptoms.
These treatments are not a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but they do help improve symptoms.
Read more about treatments for dementia.
The symptoms that people develop depend on the areas of the brain that have been damaged by the disease.
The hippocampus is often affected early on in Alzheimer’s disease. This area of the brain is responsible for laying down new memories. That’s why memory problems are one of the earliest symptoms in Alzheimer’s.
Unusual forms of Alzheimer’s disease can start with problems with vision or with language.
Read more about Alzheimer’s disease.
Conceptualization Of The Diseases Needs And Interventions
Both dementia and PD are incurable and progressive diseases with often complex problems and needs, for which tailored interventions are available . For dementia, experts agree that recognizing its eventual terminal nature is the basis for anticipating future problems and an impetus to the provision of adequate palliative care . Some advocate advanced dementia to be a terminal disease to support eligibility for palliative care. However, as about half of dementia patients never reach an advanced stage , it may be a late trigger to initiate palliative care. There is no consensus, however, at which stage palliative care in dementia should start .
Table 2. Conceptualization of the disease, needs of patients and family caregivers, and interventions.
For PD there are no curative treatments either, but the success of dopaminergic replacement therapy and deep brain stimulation has enabled the majority of patients to live independently with a relatively low symptom burden for the first 10 years after diagnosis-when they live up to a decade . This may contribute to PD generally not being recognized as an illness for which a palliative approach may be helpful . A US patient and caregivers council recommends palliative care to be available from diagnosis of PD . This is also the ideal of the European Parkinson’s Disease Association although they emphasize that when to start palliative care is an individual decision.
Recommended Reading: What Essential Oils Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
Cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease may range from a single isolated symptom to severe dementia.
- The appearance of a single cognitive symptom does not mean that dementia will develop.
- Cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease usually appear years after physical symptoms are noted.
- Cognitive symptoms early in the disease suggest dementia with Parkinsonian features, a somewhat different condition.
Cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease include the following:
- Loss of decision-making ability
- Loss of short- and long-term memory
- Difficulty putting a sequence of events in correct order
- Problems using complex language and comprehending others’ complex language
Persons with Parkinson’s disease, with or without dementia, may often respond slowly to questions and requests. They may become dependent, fearful, indecisive, and passive. As the disease progresses, many people with Parkinson’s disease may become increasingly dependent on spouses or caregivers.
Major mental disorders are common in Parkinson’s disease. Two or more of these may appear together in the same person.
The combination of depression, dementia, and Parkinson’s disease usually means a faster cognitive decline and more severe disability. Hallucinations, delusions, agitation, and manic states can occur as adverse effects of drug treatment of Parkinson’s disease, this might complicate the diagnosis of Parkinson’s dementia.
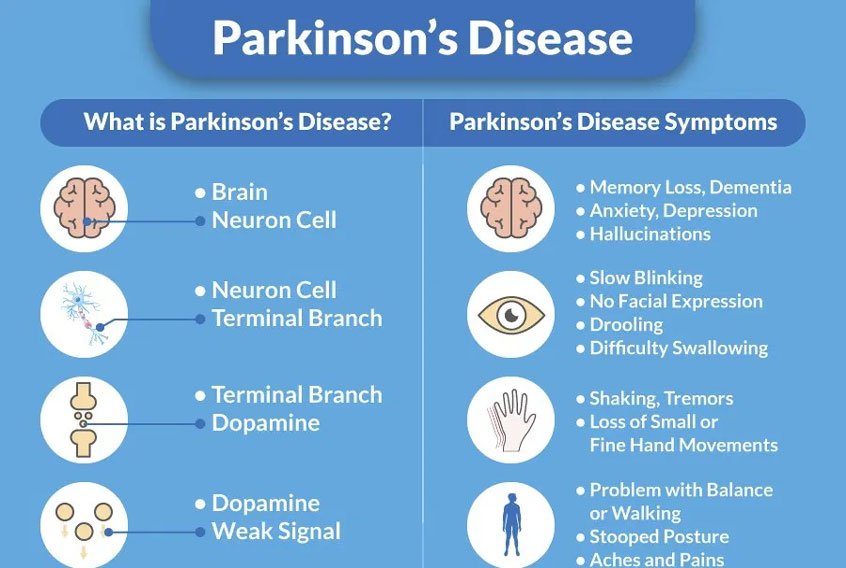
What Is Parkinson Disease

Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Sleep Problems In Parkinson\’s Disease
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Treatments for DLB are similar to PDD and are aimed at symptom control. The motor symptoms of slowness, stiffness and walking difficulties can be treated with Levodopa. However, Levodopa can cause or exacerbate hallucinations, making it difficult to use it as a treatment for patients who have or are at risk of having hallucinations. Sometimes, clinicians will need to treat the hallucinations more aggressively in order for a patient to tolerate Levodopa given to help the motor symptoms. On the flipside, anti-psychotic medications to control hallucinations can worsen motor symptoms, so treating all the symptoms of LBD simultaneously can be a tricky balancing act.
Can You Have Both Parkinsons And Alzheimers
People who already have Parkinsons disease and later develop signs of dementia are diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia.6 However, if you first have Alzheimers disease and develop signs of movement difficulties, you can also have a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
Tell us about your experience in the comments below, or with the community.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Parkinson
Signs And Symptoms Of Pdd
Common signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia include:
- Poor memory and concentration
- Depression
- Visual hallucinations
If youve noticed some of the above signs and symptoms in yourself or a loved one, its important to get them checked out. But dont jump to conclusions. People with Parkinsons often experience cognitive changes such as anxiety, lack of motivation, and slowed thinking. These symptoms do not automatically mean dementia.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Lewy Body Dementia
Unfortunately, LBD is usually the most frequently misdiagnosed type of dementia. LBDA estimates that it often takes about three doctors and over a year and a half to diagnose LBD. Their survey of nearly 1,000 participants with LBD discovered that about 80 percent of them were misdiagnosed. In an article published in nature, Susan Schneider Williams, Robin Williams wife, writes about their struggle to get an accurate diagnosis and determine what was happening to his brain. My hope is that it will help you understand your patients along with their spouses and caregivers a little more. And as for the research you do, perhaps this will add a few more faces behind the why you do what you do, she writes.
People can either be diagnosed with dementia with Lewy bodies or Parkinsons disease dementia. If someone is experiencing symptoms that could be LBD, they should try visiting a neurologist, rather than a general physician, to try and get an accurate diagnosis. While LBD can still only be officially diagnosed by an autopsy, doctors use the following methods to determine if someone may have LBD:
They can look for biomarkers of Lewy Body Dementia, including abnormal proteins, with the following:
- A SPECT or PET scan
- cardiac scintigraphy, which looks at how nerves are functioning in the hearts blood vessels
- Sleep tests that monitor brain waves
In addition, doctors may do the following:
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Initial cognitive deterioration in dementia with Lewy bodies resembles that in other dementias. However, dementia with Lewy bodies often manifests with early and prominent deficits in attention, executive function, and visuoperceptual ability prominent or persistent memory impairment tends to occur as the dementia progresses.
Extrapyramidal symptoms occur. However, in dementia with Lewy bodies , cognitive and extrapyramidal symptoms usually begin within 1 year of each other. Also, the extrapyramidal symptoms differ from those of Parkinson disease in dementia with Lewy bodies, tremor does not occur early, rigidity of axial muscles with gait instability occurs early, and deficits tend to be symmetric. Repeated falls are common.
Fluctuating cognitive function is a relatively specific feature of dementia with Lewy bodies. Periods of being alert, coherent, and oriented may alternate with periods of being confused and unresponsive to questions, usually over a period of days to weeks but sometimes during the same interview.
Memory is impaired, but the impairment appears to result more from deficits in alertness and attention than in memory acquisition thus, short-term recall is affected less than digit span memory .
Patients may stare into space for long periods. Excessive daytime drowsiness is common.
Visuospatial and visuoconstructional abilities are affected more than other cognitive deficits.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia Diagnosed
No single test can diagnose Parkinsons disease dementia. Instead, doctors rely on a series or combination of tests and indicators.
Your neurologist will likely diagnose you with Parkinsons and then track your progression. They may monitor you for signs of dementia. As you get older, your risk for Parkinsons dementia increases.
Your doctor is more likely to conduct regular testing to monitor your cognitive functions, memory recall, and mental health.
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
Degeneration Of Neurotransmitter Systems
More widespread dopaminergic deficits in the brain
By definition, all patients with PD have a moderate-to-severe loss of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal projection pathway. More widespread degeneration of dopaminergic terminals in the striatum particularly denervation of dopaminergic terminals in the associative dorsal caudate nucleus occurs in those with PD-MCI than in those with PD without cognitive impairment . However, in patients with PD-MCI, there is relative preservation of other dopaminergic systems in the brain, whilst those with PDD have a considerable loss of the lateral dopaminergic system to frontal, parietal and temporal cortical regions . In healthy individuals, cortical dopamine modulation can boost working memory as well as visuospatial and attentional processing, and promotes cognitive effort,, suggesting a key role for dopamine in cognitive function.
Fig. 2: Neurotransmitter deficits associated with cognitive decline in PD and DLB.
Noradrenergic locus coeruleus and sympathetic systems
Basal forebrain cholinergic systems
Serotonergic dysfunction is not directly related to cognitive decline
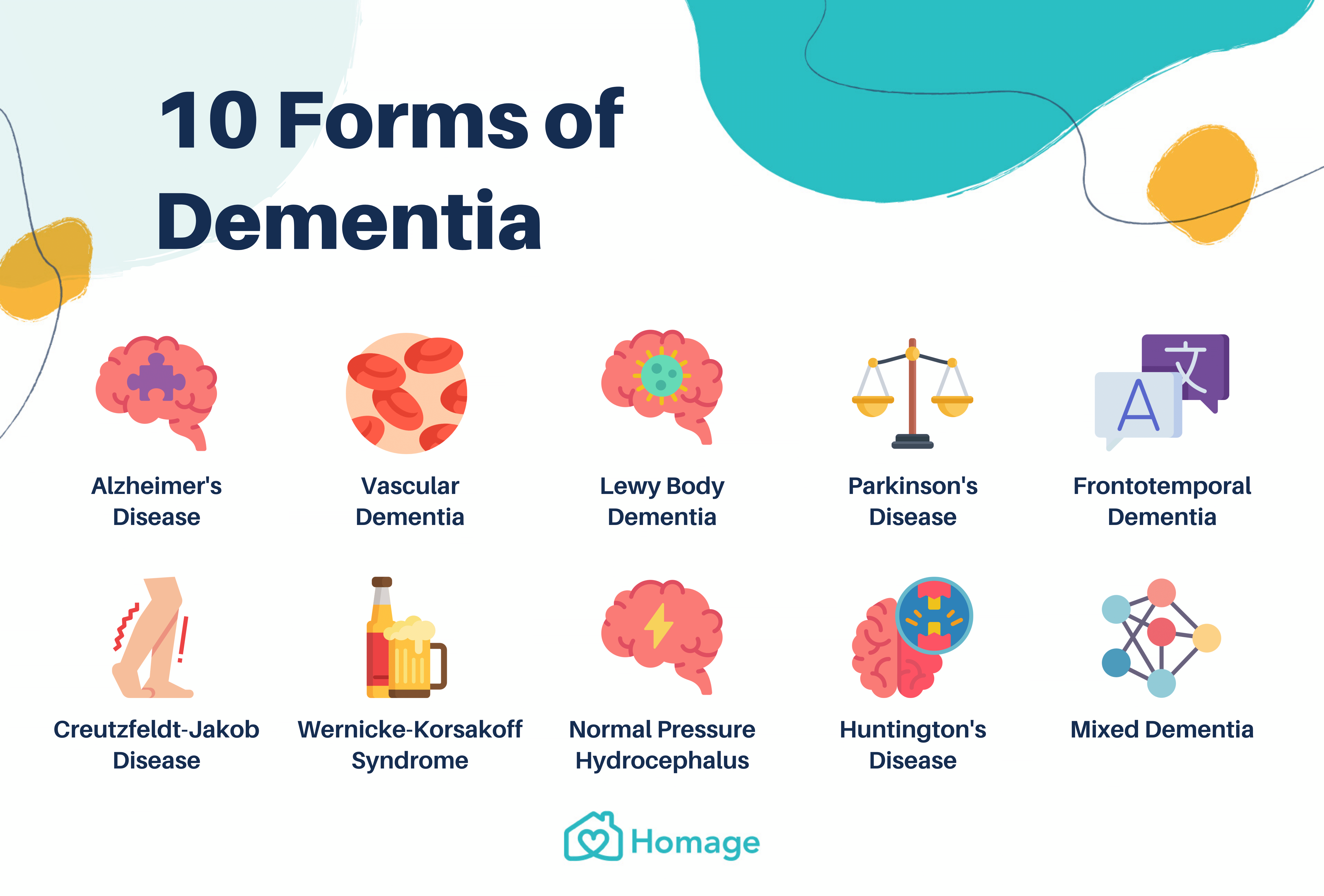
Rarer Causes Of Dementia
There are many rarer diseases and conditions that can lead to dementia, or dementia-like symptoms.
These conditions account for only 5% of dementia cases in the UK.
They include:
- problems with planning and reasoning
These symptoms are not severe enough to cause problems in everyday life.
MCI can be caused by an underlying illness, such as depression, anxiety or thyroid problems.
If the underlying illness is treated or managed, symptoms of MCI often disappear and cause no further problems.
But in some cases, people with MCI are at increased risk of going on to develop dementia, which is usually caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
Read more about how to prevent dementia.
Don’t Miss: Can Gabapentin Cause Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts don’t know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
Box 2 Diagnostic Procedure Movement Disorder Society Pdd Criteria8144
Level I Parkinson disease dementia
-
A diagnosis of Parkinson disease based on the UK Brain Bank criteria for PD
-
PD developed prior to the onset of dementia
-
Mini-Mental State Examination below 26
-
Cognitive deficits severe enough to impact daily living independent of motor symptoms
-
Impairment in more than one cognitive domain, that is, at least two of the following aspects:
-
Months Reversed or Seven Backward
-
Lexical Fluency or Clock Drawing
-
MMSE Pentagons
-
Absence of other abnormalities that obscure diagnosis
Level II Comprehensive assessment for characterizing PDD
The level II evaluation assesses four domains:
-
Psychosis
Computerized cognitive testing
Digital computerized cognitive testing, which can be carried out remotely from patients homes, has become an interesting alternative to traditional pen-and-paper testing. Benefits of computerized testing include the opportunity for frequent testing with less learning effects, which increases the sensitivity to detect decline, cost-efficiency and the availability of large normative databases. Opportunities for conducting both remote functional assessments and digital interventions on the same online platform are being studied,.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Dementia
The mechanisms of dementia are not yet fully understood, although we know that the process involves neurodegeneration . It is not possible to predict who will be affected. The most notable risk factors are:
- advancing age there is a much lower incidence of dementia in people under 50 years of age. Usually a number of years pass from being diagnosed with Parkinsons to the onset of dementia, maybe up to 15 years in some cases
- poor motor response to levodopa treatment
- falls
- changes in the structure and chemistry of the brain – the process that causes of the loss of dopamine cells in the brain is thought to be responsible for cognitive changes
- microscopic deposits, or Lewy bodies, in the nerve cells of the brain stem
- hallucinations or delusions early on in the condition increases the risk of developing dementia
- non-motor symptoms: hyposmia , dysautonomias , REM-sleep disorder
- a higher risk of dementia in people who were diagnosed with Parkinsons late in life and have had the condition for a long time, or who have relatives with dementia.
What Is Needed For A Parkinson’s Disease Dementia Diagnosis
There is no definitive medical test that confirms cognitive decline or dementia in Parkinson’s disease. The most accurate way to measure cognitive decline is through neuropsychological testing.
- The testing involves answering questions and performing tasks that have been carefully designed for this purpose. It is carried out by a specialist in this kind of testing.
- Neuropsychological testing addresses the individual’s appearance, mood, anxiety level, and experience of delusions or hallucinations.
- It assesses cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, orientation to time and place, use of language, and abilities to carry out various tasks and follow instructions.
- Reasoning, abstract thinking, and problem solving are tested.
- Neuropsychological testing gives a more accurate diagnosis of the problems and thus can help in treatment planning.
- The tests are repeated periodically to see how well treatment is working and check for new problems.
Imaging studies: Generally, brain scans such as CT scan and MRI are of little use in diagnosing dementia in people with Parkinson’s disease. Positron emission tomographic scan may help distinguish dementia from depression and similar conditions in Parkinson’s disease.
Also Check: Parkinsons Disease Hereditory
Lewy Body Dementia: A Common Yet Underdiagnosed Dementia
While its not a household word yet, Lewy body dementia is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known disorders like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons, it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In fact, many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD.
Are There Medicines To Treat Pdd
Though there is no cure for PDD yet, there are medications that help manage the symptoms. These medications are called cholinesterase inhibitors, and they can help if a person with PDD is having memory problems. Some examples of these medicines are donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine. Sleep problems may be managed by sleep medications such as melatonin.
Because people with PDD are usually very sensitive to medications, any new medication, even one that is not being used for the brain, needs to be reviewed with the persons provider to avoid potential contraindication.
Don’t Miss: Is Pd Hereditary
Causes Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Lewy bodies are tiny clumps of a protein called alpha-synuclein that can develop inside brain cells.
These clumps damage the way the cells work and communicate with each other, and the brain cells eventually die.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is closely related to Parkinson’s disease and often has some of the same symptoms, including difficulty with movement and a higher risk of falls.
Read more about dementia with Lewy bodies.
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
