Parkinsons Disease And Your Bladder
Many diagnosed with Parkinsons disease experience urinary tract issues. A Michigan Medicine urologist discusses treatment options for patients to consider.
Anne Pelletier-Cameron, M.D., often jokes to her patients that shes a female plumber of the lower urinary tract. On a more professional note, however, shes a urologist in the Michigan Medicine Department of Urology.
In this role, Pelletier-Cameron treats patients with a variety of lower urinary tract symptoms. Some of her patients have been diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, a progressive nervous system disorder that impacts movement. But the breakdown of nerve cells that characterize Parkinsons disease can also cause non-movement symptoms, including bladder issues.
Half of all women and 17% of men will experience urinary incontinence, or the inability to hold urine, she says, noting that for Parkinsons disease patients, those numbers escalate.
Many of my PD patients end up having other bladder problems, including issues with urgency and frequency, says Pelletier-Cameron. Nocturia, or the need to urinate many times during the night, is also common, along with difficulty in emptying the bladder.
Pelletier-Cameron says the impact of bladder symptoms cant be ignored.
Bladder And Constipation Problems
Parkinsons commonly leads to problems with constipation and bladder control, including urinary urgency, frequency, retention and nocturia.
These problems add to the challenge of living with Parkinsons and can have a negative effect on a persons quality of life. It is important to seek help in managing these problems, as both issues can be effectively managed.
Management Of Incontinence In Patients With Parkinsons Disease
It is estimated that two-thirds of all patients with PD have some degree of bladder problems ranging from complete inability to empty the bladder to the more common problem of urinating too often and to the ability to make it to the bathroom in time . Common dysfunctions are bladder overactivity, causing urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence . Getting up at night to use the bathroom is the most prevalently reported non-motor symptom with PD, reported by more than 60%. Weak voiding is also a common dysfunction. Patients may feel like they must go frequently, but when they go it may take longer than average to void. Constipation is another common issue that may arise and being constipated can affect medication absorption. Some studies suggest that 80% of people who have Parkinsons Disease report constipation.
Patients with Parkinsons Disease may also have difficulty eliminating urine. This can be caused by a sphincter that wants to close when the bladder is ready to empty or by a bladder muscle that is too weak to expel urine. This is a concern because incomplete bladder emptying can cause accumulation of urine and the growth of bacteria. The latter can result in an infection. The symptoms of difficulty eliminating urine include weak urinary stream, dribbling or leaking, and feeling that the bladder has not completely emptied.
Patient should be educated to alert their health care provider is they have any of the following signs:
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Cause Double Vision
What Examinations May I Need To Have
Your GP or specialist will probably ask a series of questions to find out what the problem is. These may include:
- When did the trouble start?
- How often does it happen?
- Can you feel when your bladder or bowel is full?
- Are you having difficulty emptying your bladder or bowel?
- How often are you using the toilet?
Parkinson’s symptoms, such as slowness of movement and rigid muscles, affect the muscles in the bowel wall. This can make it harder to push stools out of the body. You may be asked to keep a chart for several days of how often you use the toilet and how much you drink.
You may also be asked for a urine sample to test for infection and they will normally carry out a physical examination.
Bladder or bowel problems can be complex in Parkinson’s, so sometimes specialist tests or X-rays may be needed. All of these can usually be done in an outpatient department or clinic.
Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
This condition is known for its three hallmarksymptoms:
- Muscle stiffness
But youll find a host of other symptoms that can appeardepending on the stage of illness and what area of the brain is currentlyaffected. This is why symptoms can varywidely between patients, but the progression of the disease is inevitable.
A Parkinsons diagnosis is far from simple. It often takesyears to arrive at a certain conclusion, because there is no single diagnostictest. Its a matter of assessing progressive symptoms and ruling out similarillnesses.
Recommended Reading: Does Lack Of Sleep Cause Parkinson’s
Risk Of Specific Cancers
Subgroup analysis revealed that PD is associated with a decrease in smoking-related cancers, including colon, rectal, and colorectal cancer , lung cancer , and oral cancers , even though statistical significance was not reached for oral cancer.
The subgroup analysis also showed that PD was associated with an increased risk of brain cancers and melanoma . These conclusions are consistent with earlier findings .
Establishment Of Weighted Co
Genes co-expressed with SNCA from LinkedOmics database were selected based on a common threshold . All selected genes were used to construct a weighted correlation network using the R package WGCNA . The R function pick SoftThreshold was used to decide the soft thresholding power . The hierarchical clustering and the dynamic tree cut function embedded in WGCNA were used to detect the functional modules. Then, the relationships between all detected modules and clinical traits were evaluated based on the correlation score of the eigengene for each module and the measured clinical traits. The hub genes for each module were chosen according to the module membership and the difference between intramodular and intermodular connectivity . The corresponding top five hub genes for each module as well as the eigengene for each module were extracted for survival analysis. The p values were calculated using log-rank test. Finally, the brown module in the WGCNA analysis significantly related to BLCA OS and DFS was further analyzed for GO and KEGG enrichment.
Read Also: What Is Parkinson’s Plus
Common Elements To Both Designs
We assessed associations stratified by sex, race/ethnicity and age at time of selection , and separately for specific cancer sites and smoking-related and other cancers. Associations by age strata for selected cancer sites are also presented. We limited cancer-site specific analyses to sites with at least 20 PD cases.
All models were adjusted for: sex, race/ethnicity, age , cancer registry and frequency of physician visits. For cohort models, the baseline hazard was also stratified on birth year , and case-control analyses were adjusted for year of selection .
The first PD claim date was treated as the diagnosis date. PD risks were analysed across time intervals: < 1 year 1< 5 years 5< 10 years and 0< 10 years after cancer and < 1 year 1< 5 years and 0< 5 years before cancer because some claims were limited to 5 years. Also, because patients with serious disease often receive heightened medical surveillance, we adjusted for physician visit frequency. In the cohort analyses, physician visits were counted during 6-month intervals between the selection and censor dates and, in the case-control analyses, we adjusted for the average number of visits across all intervals Claims by physicians with limited responsibility for direct patient care were excluded.
Increasing Your Fibre Intake
Eating the right amount of fibre and drinking enough fluids can help if you have constipation.
To get more fibre in your diet:
- choose a breakfast cereal containing wheat, wheat bran or oats, such as Weetabix, porridge or bran flakes.
- eat more vegetables, especially peas, beans and lentils.
- eat more fruit fresh, stewed, tinned or dried. High fibre fruits include prunes or oranges.
- drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration. Lots of fluids are suitable, including water, fruit juice,
- milk, tea and squashes. Cut out caffeine to avoid overstimulation of your bladder.
If you find it difficult chewing high-fibre food, you can get some types which dissolve in water. You can also get drinks which are high in fibre.
Try to increase how much fibre you get gradually to avoid bloating or flatulence .
A dietitian can give you further advice. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Parkinson’s Disease
Way Of Producing Adult Nerve Cells Aids Memory Eases Anxiety In Mice
In a 2019 article for the University of Michigans health blog, author Jane Racey Gleeson noted that For PD patients, bladder issues are often due to fluctuations in dopamine levels affecting the bladder muscles and nerves, which are critical to how it functions. PD is also thought to impact the nerve pathway between the bladder and the area of the brain that controls bladder function.
My sister says that her bladder medication helps with her urgency issues most of the time, but not always. She wears incontinence pads, especially at nighttime.
All of this is so embarrassing, Bev said. I never thought this would be such a problem for me.
In addition to medication, other treatments for bladder control include deep brain stimulation and kegel exercises, which help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles that surround the bladder. Implants and percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation are also options.
Managing bladder problems can pose additional challenges for people with PD. Complicating the urgency issue are Bevs mobility problems. She cant always move quickly enough to get to the bathroom in time. I know that this is very frustrating for her.
Although this was a sensitive topic to write about, both Bev and I wanted others who may be experiencing the same issues to know theyre not alone.
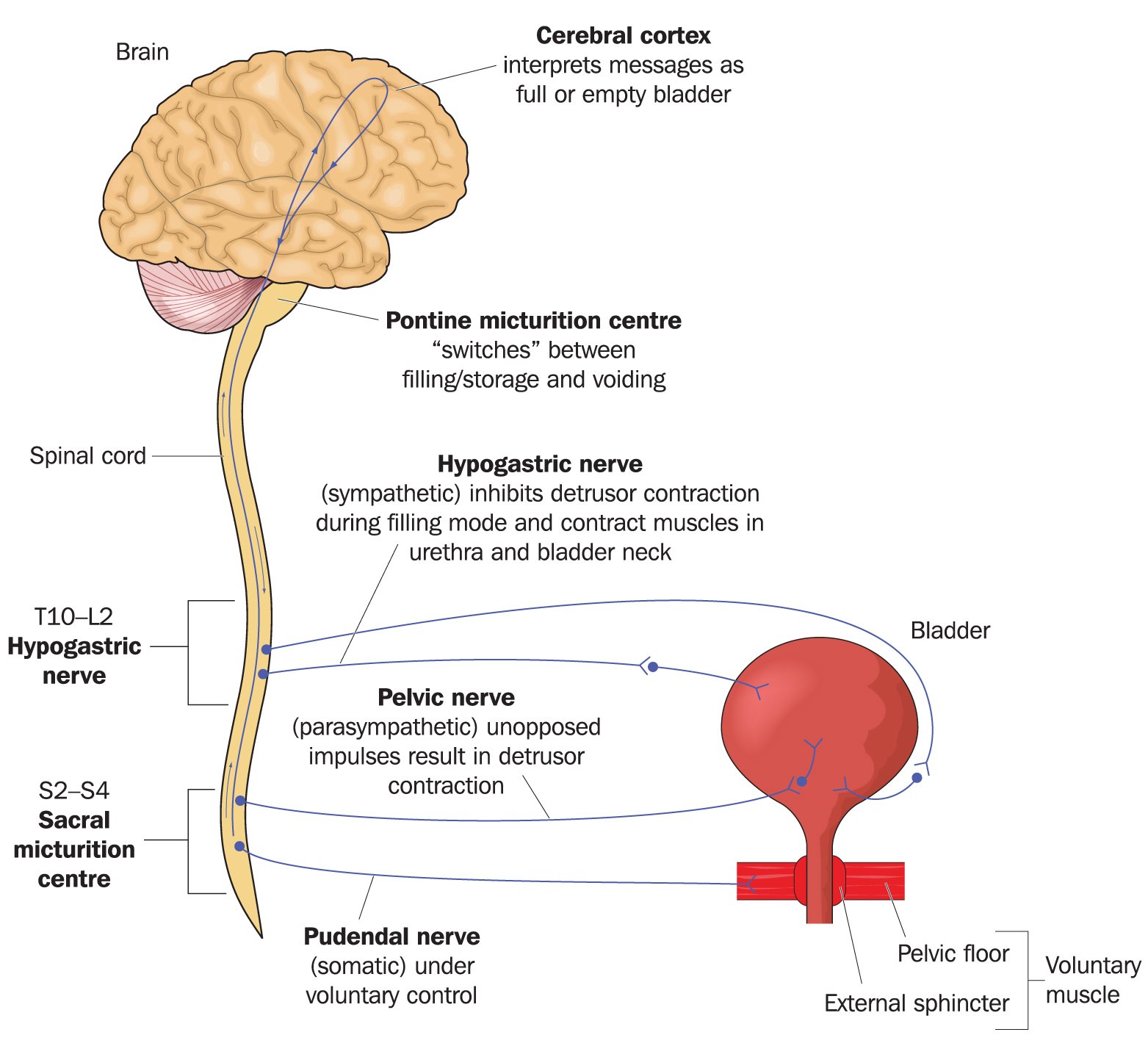
Why Do Urgency And Frequency Occur
Bladder difficulties in Parkinsons are related to changes in the level of dopamine affecting the function of the bladder muscle. Parkinsons is also thought to affect the nerve pathway between the bladder and the part of the brain controlling bladder function. Some of the symptoms that affect bladder control are related to the level of dopamine in your body which will rise and fall depending on your medication level.
Other conditions such as weak pelvic floor muscles or an enlarged prostate will contribute to bladder symptoms. Constipation can also worsen bladder symptoms by putting pressure on the bladder.
Don’t Miss: How To Detect Early Signs Of Parkinson’s
What Happens To Someone Who Has Urinary Incontinence
The pelvic floor consists of a hammock of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue, which covers the bottom of the pelvic cavity and assists in supporting the abdominal and pelvic organs. The pelvic floor maintains continence of bowel and bladder and plays an important role in sexual function.
The pelvic floor muscle consists of three layers and has fast and slow-twitch fibers to assist with support and sphincter properties. The muscle is the same in women and men and both sexes benefit from maintaining good strength and tone of the pelvic floor muscle.
As we age and with certain diseases such as PD our muscles become weak and the signals do not always tell the muscles to tighten up when they need too. Add a few pounds to the belly region also and you have the perfect storm for Peezing, Peelaughing, as well as a host of other words for embarrassing moments due to urinary incontinence or urgency!
Recommended Reading: Hard To Urinate When Bladder Full
Botulinum A Toxin As Second Line Treatment For Refractory Detrusor Over Activity And Over Active Bladder Symptoms
To date when urinary incontinence persists and patients become severely disabled a long-term indwelling catheter remains the only option for avoiding urinary incontinence. Botulinum A toxin has been successfully introduced for the treatment of intractable detrusor overactivity and it is now widely used for a number of neurological conditions characterized by muscle hyperactivity . Intravesical injections of BoNT/A provide satisfactory long-term results, and are now considered as second line-therapy in neurogenic patients who do not respond to standard anticholinergics.The use of botulinum neurotoxins in the lower urinary tract was pioneered as early as 20 yr ago with injections into the urethral sphincter reducing bladder-voiding pressures, urethral pressures, and post void residual urine.
BoNT/A consists of a light chain attached to a heavy chain via a disulfide bond with an associated zinc atom. It is synthesised as a single-chain polypeptide with a molecular weight of 150 kDa, which is then cleft into its active dichain polypeptide form. The heavy chain allows for binding to the neuron and internalisation of the toxin, whereas the light chain actively cleaves SNAP25 on the protein complex that is responsible for docking and releasing vesicles containing neurotransmitters .
Recommended Reading: Does Bactrim Treat Bladder Infection
Read Also: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Keep Their Eyes Closed
Bowel Incontinence: Another Embarrassing Casualty Of Pd
Fecal Incontinence is where you lose control of your bowels. This blog post explains the primary cause of this in Parkinsons disease. Problems reaching the toilet in time because of mobility, abdominal bloating or cramping compound the problem. Dr. De León has included a check list of things to help minimize occurrences and embarrassment, even to the point of surgery, if necessary.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Include:
1. Tremors: The shaking usually starts from the fingers or a limb. You may experience a pill-rolling tremor, which is when the hand is shaking in such a way that the tip of the thumb and forefinger rub together in a circular motion.
2. Slow movements: Parkinsonâs will eventually begin to slow down the movements and functions of the body, making simple tasks more challenging and time-consuming.
3. Rigid muscles: You can experience pain or stiffness in the muscles, which can limit your range of motion.
4. Speech changes: Speech can change in several different ways you may become very soft spoken, slur your words, or even talk at an unusually rapid pace.
5. Reduced balance or posture: You may have difficulty walking at a fast pace or maintaining your balance.
You May Like: Is Red Wine Good For Parkinson’s
The Expression Of Snca And Key Genes Detected In Patients With Blca
To verify SNCA expression in BLCA, we performed IHC staining on the tissue microarray containing samples from 63 cases of BLCA and paired adjacent nontumor tissues purchased from Outdo Biotech . The results showed that the protein level of -Syn was significantly downregulated in primary BLCA tissues compared with adjacent non-tumor samples . The prognostic value of SNCA was further investigated in these patients. As shown in Fig. C, the BLCA patients with high SNCA expression exhibited significantly shorter OS than those with low SNCA expression . We then performed qRT-PCR analysis on 20 pairs of BLCA and para-cancer tissue samples of our cohort at the transcription level. SNCA expression was significantly lower in BLCA tissues than in para-cancer tissues . These data confirmed the downregulated expression of SNCA in BLCA, which was consistent with the results from TCGA and GEO cohorts.
Fig. 6
Total of 20 genes among the hub genes were significantly correlated with OS and DFS , of which the six key genes screened by univariate Cox analysis, which were significant risk factors for OS in BLCA, were CNTN1, DACT3, MYLK1, PDE2A, RBM24, and ST6GALNAC3 . These six genes expression of 404 BCLA tissues and 28 normal bladder specimens from TCGA were analyzed with GEPIA2. We found the all the six genes were significantly downregulated in BLCA . The results were confirmed by qRT-PCR for the 20 pairs of BLCA and para-cancer tissue samples of our cohort .
Opposing Molecular Pathways Of Pd And Cancer
PD involves degeneration of the dopamine producing cells of the substantia nigra, while cancer, with its proliferative nature , lies on the opposite end of the spectrum. Several PD-related genes have been found to possibly mediate the relationship between PD and subsequent cancer. These genes include LRRK2, PARK2, a tumor suppressor gene, PARK5, coding for the ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase-L1 enzyme involved in ubiquitin-recycling, PARK7 , a strong anti-oxidant, and PARK6 , a cell death and cell cycle regulator . Oxidative damage, alterations in protein ubiquitination, and cell cycle dysregulation have been implicated in cancer pathogenesis . Therefore, the PARK family proteins involved both in PD and regulation of replication stress can possibly mediate both pathologies.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Care Of Parkinson Patient
Balance Impairment And Falls In Parkinsons Disease
One of the most challenging symptoms of Parkinsons disease that fundamentally affects quality of life is balance impairment that can lead to falls.
Falls are one of the major causes of emergency room visits and hospitalizations for people with PD, so finding ways to prevent as many falls as possible is a high priority for people with PD. Thankfully there are things you can do to improve your stability and decrease the likelihood of falling, and well share some helpful tips and advice below.
Also Check: Interstitial Cystitis Or Bladder Cancer
Urinary Problems In Parkinsons Disease
This 1-hour webinar is an interview with Dr. Janis Miyasaki, Dr. Jorges Juncos, and retired movement disorder specialist and young onset Parkinsons patient, Dr. Maria De Leon. They discuss the effect of Parkinsons disease on the autonomic nervous system, which regulates many body functions, including bladder control. Urinary problem diagnosis, symptom management and ongoing research on the topic wrap up the hour.
Read Also: Different Types Of Bladder Cancer
You May Like: Average Life Expectancy Parkinson’s
How Parkinsons Disease Affects Your Bladder Control
If you have Parkinsons disease, its notuncommon for you to develop bladder control problems at some point. This canfurther complicate your life by disrupting your sleep and affecting your sociallife. Its important to be aware of this common Parkinsons symptom andunderstand how to recognize and manage it with appropriate treatments anduseful products.
Parkinsons disease carries a long list ofpossible symptoms often categorized as either motor or nonmotor. This isbecause its a disease of the nervous system and is considered a degenerativebrain disorder originating from the basal ganglia. This part of your brainslowly loses proper function and decreases dopamine output. The end result isthe impairment of many physical movements, mood, thinking, sleep, and automaticfunctions.
In short, Parkinsons can affect almost everyarea of your life including your bladder control, which means understanding andpreparation are critical.
