Parkinson’s Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
The key pathological hallmark found in brains of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia patients are abnormal microscopic deposits composed of alpha-synuclein. This protein is found widely in the brain but its normal function is not yet well understood. The deposits are called “Lewy bodies”. Lewy bodies are also found in several other neurodegenerative brain disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies . Evidence suggests that Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, may be linked to the same underlying abnormalities in brain processing of alpha-synuclein.
Whats The Outlook For People With Parkinsons Plus
Although there currently isnt a treatment to halt the progression of Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
The exact outlook for Parkinsons plus syndrome depends on the person and the specific condition they have. Someone who is otherwise healthy when theyre diagnosed will typically have a longer life expectancy than someone who is already facing other health conditions when theyre diagnosed. Your doctor will monitor your condition over time and can let you know how its progressing.
Clinical Presentation And Diagnosis
Onset of PSP typically begins in the sixth or seventh decade of life. The patient develops bradykinesia, rigidity, dysarthria, dysphagia, and dementia, as in patients with idiopathic PD. However, tremor is rare, and the patient has severe postural instability. Axial rigidity appears to be more prominent than limb rigidity. Consistently, patients have downgaze ophthalmoparesis and pseduobulbar palsy. Eyelid problems are present including eyelid freezing and difficult with either opening or closing the eyes. The association of dementia in PSP is contentious. Dystonia is present in about 13% of patients with pathologically proven PSP.
The supranuclear component of the disorder is ocular paresis, which can be overcome by vertical doll’s-eyes maneuvers. The combination of vertical paresis and a history of frequent falls due postural instability is central to the diagnosis of PSP. Some patients develop severe palilalia, emotional incontinence, and other evidence of bilateral frontal lobe dysfunction. Occasionally, patients present with akinesia of gait, speech, and handwriting, without rigidity, tremor, dementia, or gaze paresis. Blepharospasm and dry eyes have been reported. Dubois et al noted that the applause sign was useful in the clinical diagnosis of PSP.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Plus Syndrome
Parkinsons plus syndrome is the name for a group of neurological conditions that are very similar to Parkinsons disease. Because these conditions cause symptoms that are very similar to Parkinsons, they are often incorrectly diagnosed. However, these conditions can even be treated using many of the same medications and therapies as Parkinsons.
Conditions that are considered Parkinsons plus syndromes include:
What Are Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Lewy Body Dementia

Parkinsons disease is a progressive, degenerative neurological movement disorder that affects approximately 7 million people worldwide. It is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease.
Up to 80% of Parkinsons disease patients will develop Parkinsons disease dementia that is characterized by a progressive loss of memory and decline in intellectual abilities.
About 15% of Parkinsons disease diagnoses include so-called Parkinsons plus syndromes. One of these syndromes is Lewy body dementia , also known as dementia with Lewy bodies , a form of progressive dementia accounting for 20% of dementias in people over the age of 65.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Ask The Doctor Webinar
On 6 April, the US-based CureforPSP, hosted a webinar with Lawrence I. Golbe MD, one of the worlds leading clinical experts in PSP and related neurodegenerative conditions.
Dr. Golbe is the author of A Clinicians Guide to Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. In the webinar, Dr. Golbe answered questions submitted by patients and families about PSP, MSA, and CBS.
Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease
It may be helpful for people with Parkinson’s disease and their families to be familiar with some of the ways the disease is described. Experts describe symptoms and stages of the disease differently.
Parkinson’s disease sometimes is described as early, moderate, or advanced.
- Early disease describes the stage when a person has a mild tremor or stiffness but is able to continue work or other normal daily activities. This often refers to a person who has been newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
- Moderate disease describes the stage when a person begins to experience limited movement. A person with moderate Parkinson’s disease may have a mild to moderate tremor with slow movement.
- Advanced disease describes the stage when a person is significantly limited in his or her activity, despite treatment. Daily changes in symptoms, medicine side effects that limit treatment, and loss of independence in activities of daily living are common. A person with advanced Parkinson’s disease may have significant problems with posture, movement, and speech.
Parkinson’s disease may also be described by five stages:
Medical professionals may refer to this scale when discussing the disease and decisions about treatment.
Also Check: When Was Parkinson\’s Discovered
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Treatment Of Atypical Parkinsonism
While no current therapy can slow or stop progression, treatment can ease symptoms of atypical parkinsonisms. Because symptoms overlap across these conditions, treatments overlap, too.
For movement symptoms, such as stiffness and slowness, doctors may prescribe levodopa. Unfortunately, if this medication does ease symptoms, its benefit may not be significant or long-lasting. In people who have dementia with Lewy bodies, levodopa may worsen hallucinations, so doctors prescribe it cautiously. For dystonia in CBD, botulinum toxin injections such as Botox or Myobloc into the muscles may be an option. For walking and balance problems, as well as falls, occupational and physical therapy are helpful. Canes and walkers may provide extra stability, though in some cases wheelchairs may be necessary.
Memory and thinking problems may be treated with medications such as Exelon , Aricept , Razadyne or Namenda . In DLB, these drugs also may help with behavioral changes and hallucinations.
Speech therapy treats speech and swallowing problems. Therapists may recommend exercises to strengthen speech and swallowing muscles, as well as diet adjustments and behavioral strategies to improve swallowing. If swallowing problems lead to weight loss or recurrent pneumonia , doctors may consider a feeding tube.
Doctors can use a variety of medications to ease mood, behavioral and sleep problems.
Don’t Miss: Tardive Dyskinesia Prognosis
Living With Psp Msa Or Cbs
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy , Multiple System Atrophy and Cortico Basal Syndrome are conditions that initially present like Parkinsons but progress and affect people differently.
They are commonly referred to as Atypical Parkinsons.
It is not yet known what causes PSP, MSA or CBS and there are currently no treatments to cure or slow their progression.
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is a rare condition affecting parts of the brain that control walking, eye movements, balance, speech and swallowing.
Progressive – means symptoms get worse over timeSupranuclear – refers to the part of the brain thats affectedPalsy – means a weakness or paralysis in part of the body
Other terms sometimes used to describe PSP are Steele-Richardson-Olszewski Syndrome, Richardsons Disease, Parkinsons Plus, PSP-Parkinsonism and Pure Akinesia with Gait Freezing.
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Current Treatment Options
While there is no specific cure for Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can control your symptoms. A doctor can develop a plan for your overall health and to treat your specific symptoms. Medications that treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease often do not work as well for Parkinsons plus syndrome.
Treatment options might include:
- Walking and balance assistance. You might receive physical and occupational therapy to help keep you moving. Therapists can help you build strength and prevent falls. They can also help you learn to use canes, walkers, and other mobility aids, if needed.
- Swallowing and speech assistance. A speech therapist can help you adjust to changes that might make it hard to swallow and speak. They can help you communicate and can recommend foods and beverages that are easier to swallow.
- Medications for cognitive issues. Your doctor might prescribe a variety of medications that can help with your focus and memory. Many of these medications are also used for conditions such as Alzheimers or dementia.
- Medications for trouble with movement. You might be prescribed medications that can help you control your muscles and movement. These medications might also address stiffness and balance problems.
- Medications to help with mood symptoms. If youre experiencing depression, anxiety, or other mood-related concerns, your doctor might prescribe medications that can help with these symptoms.
Asceneurons Innovation In Pdd And Dlb
Several symptomatic treatments addressing motoric disturbances in PD are currently available. In contrast, there is a very high unmet medical need for novel symptomatic medications to mitigate the cognitive decline in Parkinsons disease dementia patients, since available options have limited efficacy and considerable side effects. As the disease progresses, balancing the benefits of medications with their side effects becomes challenging for caregivers.
Asceneuron has generated small molecules of novel chemical classes that have the potential to deliver novel, well-tolerated and efficacious drugs to treat learning and memory deficits in dementia. Our positive allosteric modulators of the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor have the potential to bring the first approved treatment for PDD to patients and a new class of molecules for the treatment of dementia in general. M1 PAMs induce a change in the shape of the receptor, enhancing binding to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. As a result, receptor activity is potentiated so that it can still fulfill its signaling functions, critical for cognition, even in situations where acetylcholine levels are reduced as observed in Parkinsons disease dementia and other dementia in general.
Given the high unmet medical need in PDD, a symptomatic treatment for one of the more debilitating facets of PD would bring significant benefit to PD patients and their caregivers.
You May Like: Parkinson Hereditary Risk
Parkinson’s Disease And Parkinsonism
Parkinson’s disease is named for Dr. James Parkinson, who in 1817 first described the features of this illness. Features of Parkinson’s disease include tremor, slow movement , and rigid muscles . People with parkinsonism may have Parkinson’s disease or another illness with similar symptoms.
Other conditions and diseases that cause parkinsonism may also cause symptoms that are not seen with Parkinson’s disease. These conditions may be treated differently than Parkinson’s disease. Unlike Parkinson’s, some conditions that cause parkinsonism are reversible.
- Parkinson’s-plus syndromes are a group of disorders characterized by the degeneration of nerve cells in different parts of the brain. They include progressive supranuclear palsy , corticobasal degeneration , and multiple system atrophy , among others. Parkinson’s-plus syndromes have parkinsonian features as well as features that are not associated with Parkinson’s disease. These syndromes usually respond poorly to levodopa or dopamine agonists.
- Secondary or symptomatic parkinsonism describes the syndrome of parkinsonism when it occurs as the result of an identifiable cause. For example, certain medicines, brain tumors, strokes, infections , and toxins can cause secondary parkinsonism.
Abnormality Of Tau Protein
PSP has been considered to be a tau protein disorder. Cortical fibrillary tangles of PSP are similar to those observed in Alzheimer disease with regard to the presence of an abnormally phosphorylated tau protein. Tau is a component of a microtubule-associated protein that is responsible for axonal transport of vesicles. The mechanism whereby this is involved in PSP has yet to be determined. PSP overlaps with corticobasal degeneration in this regard, and the latter may have a stronger association with tau protein abnormalities than does PSP.
Tau proteins exist in 6 isoforms encoded by a single gene. Different electrophoretic patterns have been identified in the various disorders associated with tau abnormalities. Thirty-two mutations have been identified in more than 100 families. About half of the known mutations have their primary effect at the protein level. They reduce the ability of tau protein to interact with microtubules and increase its propensity to assemble into abnormal filaments. The other mutations have their primary effect at the RNA level and perturb the normal ratio of 3-repeat to 4-repeat tau isoforms. When studied, this change resulted in a relative overproduction of tau protein with 4 microtubule-binding domains in the brain.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Language Disorders In Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Together with DAT and VaD, DLB is another common form of progressive dementia. However, this entity is a relatively recent one, and as such, there is debate on its classification. DLB is commonly regarded as a Parkinson-plus syndrome that bears the clinical features of both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Pathologically, the cortical neurons of individuals presenting with DLB contain, as the name implies, Lewy bodies or intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies. Clinically, the disease presents with a grouping of distinctive symptoms. According to McKeith et al. , the clinical presentation must include a dementia plus two of the following: a fluctuating cognition with pronounced variations in attention and alertness, recurrent visual hallucinations, and spontaneous motor features of parkinsonism .
Treatments And Professional Support
Current treatments for PSA, MSA and CBS are symptom driven, so therapies and strategies are required to help people with Atypical Parkinsons and carers to make the most of living with the condition.
The best practice approach requires a neurologist specialising in movement disorders, an understanding GP and a multi-disciplinary team. This is optimally through a Movement Disorder Clinic, however for many people this is not possible due to geographical location.
Specialist support beneficial for people with Atypical Parkinsons can include a:
- physiotherapist to assess mobility, provide appropriate walking aids and help maintain safe mobility as long as possible
- speech pathologist to assess and manage saliva, swallowing and communication changes
- occupational therapist to assess and provide equipment and strategies to maintain independence
- social worker to help organise support systems and respite
- psychologist and neuropsychologist to assist with emotional needs and mood changes and adapting to thinking difficulties and changes in behaviour
- Parkinsons Nurse who specialise in Atypical Parkinsons.
Recommended Reading: End Stage Parkinson Disease Life Expectancy
What Are The Symptoms Of These Diseases
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve motor control, such as tremor , slowness of movement, stiffness of the limbs and trunk as well as postural instability. Many patients develop a decline in thinking and reasoning known as Parkinsons disease dementia if it occurs more than one year after the initial diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Common symptoms for PDD include decline in memory, concentration and judgment, visual hallucinations, depression, irritability and anxiety.
The central feature of Lewy body dementia is progressive cognitive decline, combined with pronounced fluctuations in alertness and attention, complex visual hallucinations and motor symptoms such as rigidity and the loss of spontaneous movement. It can easily be mistaken for Alzheimers disease or for Parkinsons disease dementia .
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is named for the presence of abnormal protein deposits of alpha-synuclein that are also seen in people with PD. DLB is the second most common type of dementia after Alzheimers disease, and it is a progressive disorder. In people with DLB, the Lewy bodies are found throughout the brain. DLB is characterized by cognitive impairments, visual hallucinations, inability to focus, inflexible thinking and paranoia. DLB patients initially have these cognitive symptoms but also develop motor symptoms similar to PD such as bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and shuffling walk. Similar to PD, DLB patients also have REM sleep behavior disorder in which they act out their dreams. DLB is treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and atypical antipychotics. However, there is no cure for DLB.
Recommended Reading: Essential Oils For Parkinson’s
Atypical Parkinsonism Is A Group Of Conditions Which May Appear Similar To Parkinsons Disease But Have Other Clinical Signs And Symptoms
The term parkinsonism refers to the appearance on exam similar to Parkinsons disease, but Parkinsons disease is not the only cause of parkinsonism.
Atypical parkinsonism is often referred to as Parkinsons-plus because the conditions have parkinsonism plus another symptom.
Causes of Parkinsonism Other than Parkinsons Disease Include:
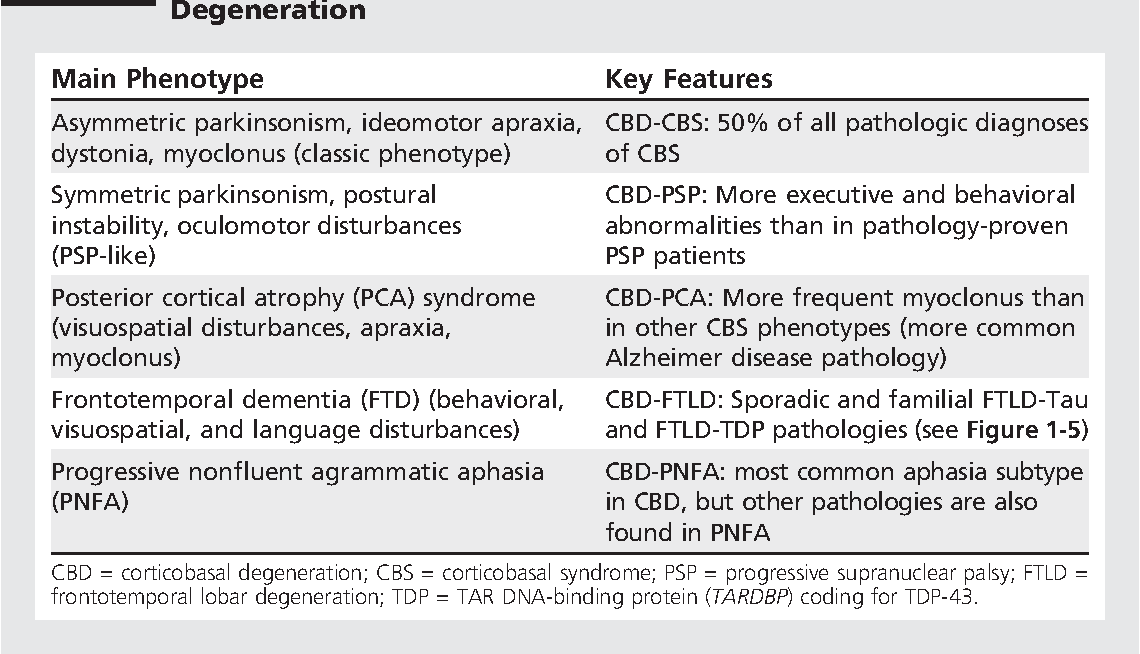
CBD is a rare cause of atypical parkinsonism, and is manifested by dementia, unilateral parkinsonism, unilateral abnormal involuntary movements, and apraxia .
VASCULAR PARKINSONISM:This refers to shuffling gait, imbalance, and stooped posture due to multiple small strokes. These strokes may not have been apparent to the patient but as they accumulate the gait, balance and often memory are affected.
DRUG-INDUCED PARKINSONISM:Drug-induced parkinsonism refers to the appearance of parkinsonism in patients who are taking certain psychiatric or nausea medications such as Haldol , Abilify and Reglan . These patients do not have Parkinsons disease or a neurodegenerative condition. Treatment for drug-induced parkinsonism is slowly tapering off the offending medications. However, sometimes the medications cannot be stopped DaTscan can be useful to differentiate between drug-induced and degenerative parkinsonism.
