How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Imaginggenetic Feature Selection From Os
Due to a limited number of samples, we adopted a nested five-fold cross-validation. For the outer loop, we separated the data into training and test sets using a fivefold split. For the inner loop, the training data were subject to another fivefold cross-validation where the inner training set was used to train the model and the remaining set was used as the validation set to tune the hyperparameters of the model. The value of w was set using the formula given in a previous study adjusted for the dimensions of Z. Optimal value of regularization parameters , \) was determined within each training set via internal fivefold cross-validation .
where \,.\, and \ denoted the i-th subset of the validation set and u-I and v-i, denoted the estimated loading vectors from the datasets except for the i-th subset in the inner loop. We calculated the average metric score over the five folds in and chose the average as the hyperparameters. Coming back to the outer loop, we used data from four folds to train the regression model and applied the learned model to the left-out test fold. We repeated this process five times with a different fold left-out each time. The software code used in this study is available at code-sharing website .
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Don’t Miss: Are Weighted Blankets Good For Parkinson’s
Csf And Serum Biomarkers
Table e-2 shows characteristics of CSF and serum biomarkers. Across the whole population, the levels of CSF -syn, total tau , and tau phosphorylated at Thr181 were reduced in the patients compared with HCs, while levels of CSF -amyloid 142 and serum urate were not different between groups . In HCs, all biomarkers increased with the age except for A142 . In patients with PD, only -syn and t-tau increased with the age but not p-tau181 , A142 , or serum urate . In older age subgroups, the reduction of -syn and t-tau were greater compared with younger age subgroups .
Unique Characteristics Of Young
Although Parkinson’s is similar among people of all ages, those with young-onset PD generally have slower disease progression. They also tend to experience more side effects from dopaminergic medications and are more likely to have dyskinesias in response to the drug levodopa. Dyskinesias are abnormal, involuntary movements. They appear like a dance with wiggling movements of arms, legs, body or face.
Other problems associated with PD, such as memory loss, confusion, and problems with balance tend to occur less often in people with young-onset Parkinson’s. However, as with PD in older patients, the disease severity and symptoms vary from person to person.1,2
Don’t Miss: Wehaveparkinsons
How Many People Does Parkinsons Disease Affect
Parkinsons disease affects 1 in every 500 people in Canada. Over 100,000 Canadians are living with Parkinsons today and approximately 6,600 new cases of PD are diagnosed each year in Canada . Most are diagnosed over the age of 60 however, at least 10% of the Parkinsons population develops symptoms before the age of 50. Approximately four million people worldwide are living with the condition.
Seven Signs Of Early Onset Of Parkinsons
There are a number of symptoms that can warn us about early onset of Parkinsons. There are several characters, but we will focus on these seven:
- Sleep disorders. The most common sleep disorders are insomnia , restless legs syndrome and REM sleep behavior syndrome.
- Depression. It is one of the first symptoms that occurs and it is actually considered as an early indicator of this disease.
- Other mood swings. In addition to depressive symptoms, anxiety and apathy are very common. These symptoms can affect the desire to seek help and a solution in a negative way.
- Cognitive changes. Many people with early-onset Parkinsons usually find it difficult to do more than one thing at a time. Poor performance of tasks, slow thinking, difficulty focusing and concentrating, memory problems and dementia are all symptoms of early onset of Parkinsons.
- Tremors. Although they usually begin in the hands, they start in other patients in the jaw or in the feet. The most characteristic of these tremors is that they occur when resting.
- Bradykinesi. This is a gradual loss of spontaneous movement. In general, movements simply become slower. This is one of the most debilitating and frustrating symptoms for the people affected.
- Exhaustion. With early onset of Parkinsons, the patient feels tired all the time without having exhausted himself.
Read Also: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Dont Miss: Wearable Technology For Parkinson Disease
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Don’t Miss: Levodopa Toxicity Signs And Symptoms
Genetics In Yopd And Its Implications For Management
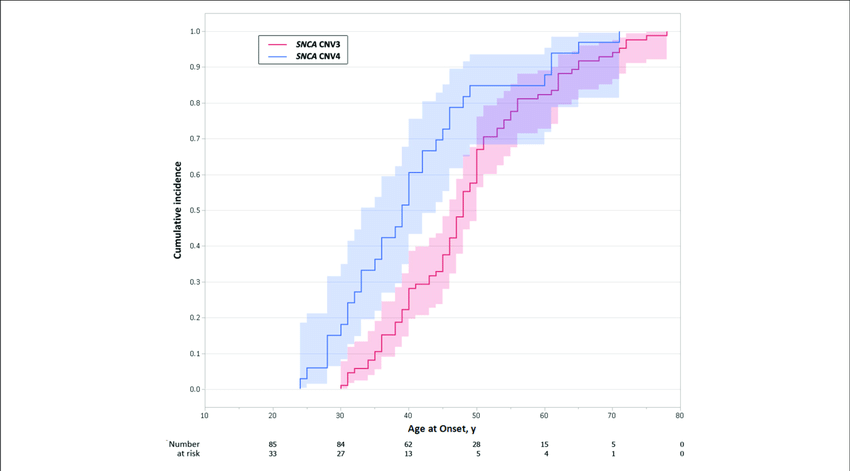
The genetic background of PD is gradually being revealed and consists of the spectrum from common variants that have small contributions to an increased vulnerability, to true monogenic forms . Some of the genes that previously received a PARK locus symbol are in fact unconfirmed, are risk alleles, or if mutated give rise to a more complex phenotype. A new nomenclature of genetic movement disorders, including PD, was recently proposed and has tried to deal with these complexities . Here, we focus on the confirmed genes that can be considered monogenic forms of PD. These mainly include the dominant genes SNCA, LRRK2, GBA, and VPS35, and the recessive genes Parkin, PINK1, DJ1. The common picture from the literature is that PD patients with a mutation in one of these genes present at an earlier age, particularly for the recessive genes and SNCA . So, vice versa, if a PD patient presents at a young age, the option of a genetic etiology is often considered. While next generation sequencing platforms have simplified screening the relevant genes, we have to critically address the question: what is the actual benefit of genetic testing in YOPD?
You May Like: Prayers For Parkinsons Disease
Reported Standardised Mortality Ratios From 1935 To 2001
The SMRs or mortality ratios comparing PD cases and controls from 39 studies from 1935 to 2006 are reported in table 1. The SMRs ranged from 1, indicating no differences compared with the general population, to 3.4, indicating more than threefold higher mortality in PD. The time trend of estimates is inconsistent, although there appears to be a decrease in the 1970s, corresponding to the introduction of levodopa trials during that time period .). A geographical trend is not apparent, as the SMRs within each geographical region are as variable as between regions .
Table 1Summary of studies that have reported a standardised mortality ratio, comparing Parkinson’s disease patients with a general population
| Reference/date |
|---|
Figure 1Standardised mortality ratios for Parkinson’s disease from 39 studies by publication date.
Read Also: What Essential Oils Help Parkinson’s
Searches And Data Extraction
A PubMed search was conducted in April 2006 for articles published in English using the following search terms: AND NOT WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome .
Of the retrieved articles, 54 containing original LE, mortality or survival data were selected for further review. Articles were excluded if they did not provide LE or SMR estimates, or did not use PD diagnosis as the outcome. Studies beginning after 1984 were preferred so that the use of levodopa medication was widespread, as it is now. All articles were evaluated by one of the authors and data on SMRs, stratified by age or sex, collected. For the analysis of LE compared with the 2003 actuary data, only articles from the UK and, as the number of UK studies reporting age specific data was limited, Western Europe were included.
What Is Parkinsonism Is It Different From Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is the most common cause of parkinsonism, a category of neurological diseases that cause slowed movement.
No quick or easy diagnostic tests exist for Parkinsons disease, so a patient may receive an initial diagnosis of parkinsonism without a more specific condition being confirmed.
Classic Parkinsons disease referred to as idiopathic because it has no known cause is the most common and most treatable parkinsonism.
About 15 percent of people with parkinsonism have atypical variants, which are also known as Parkinsons plus syndromes.
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Research And Statistics: Who Has Parkinsons Disease
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, nearly 1 million people in the United States are living with the disease. More than 10 million people worldwide have Parkinsons.
About 4 percent of people with Parkinsons are diagnosed before age 50.
Men are 1.5 times more likely to develop the disease than women.
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Ribbon
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Tips For Caring For Someone With Parkinsons Disease
Caring for a loved one with early onset Parkinsons can be difficult. If youre a caregiver for someone with this condition, its important that you remember your own emotional and physical health.
Not only are you dealing with a difficult diagnosis, youre also managing an increased number of responsibilities. Burnout is common in caregivers, so make sure youre checking in with your own needs.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation Center for Parkinsons Research recommends these tips for caregivers:
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson Disease Genetic
The Plus Side Of An Early Diagnosis
The news is not nearly all bad for those with young-onset Parkinsons. For one thing, patients with YOPD are better candidates for surgical procedures and medical innovations being used or developed to treat Parkinsons disease. For another, younger patients are less likely to be coping with other health problems at the same time.
Targeting Parkinsons-Linked Protein Could Neutralize 2 of the Diseases Causes
Researchers report they have discovered how two problem proteins known to cause Parkinsons disease are chemically linked, suggesting that someday, both could be neutralized by a single drug designed to target the link.
Caring For Your Health With Parkinson’s Disease
In addition to caring for your Parkinson’s health, it is also important to care for your overall health. This means visiting your primary care physician periodically for preventive care like the annual flu shot and cancer screeningsfor example, a mammogram for breast cancer screening and a colonoscopy for colon cancer screening.
A primary care physician can also evaluate for risk factors related to heart attacks and strokes, and provide counseling on exercise, smoking, alcohol use, depression, or other mental health concerns. Regular visits to your primary care physician or neurologist will also allow them to catch bacterial infections like urinary tract infections before they get serious.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Fatal
Complications Related To Parkinson’s Can Affect Survival
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology. She is an associate professor of neurology at Tufts Medical School and medical director of the Lahey Clinic Multiple Sclerosis Center in Lexington, Massachusetts.
Parkinson’s is a common neurodegenerative disease, and although it is not fatal, research suggests it may influence life expectancy.
A 2012 study in Archives of Neurology examined the six-year survival of nearly 140,000 Medicare beneficiaries with Parkinson’s disease in the United States. During the six-year period, 64% of the participants with Parkinson’s disease passed away.
The risk of death of those with Parkinson’s was then compared to Medicare beneficiaries who did not have Parkinson’s or any other common diseases, including:
When controlling for variables like age, race, and gender, the six-year risk of death among people with Parkinson’s was found to be nearly four times greater than those Medicare beneficiaries without the disease or other common diseases.
At the same time, the rate of death among those with Parkinson’s disease was similar to those with hip fracture, Alzheimer’s dementia, or a recent heart attackalthough it was higher than those who had been newly diagnosed with either colorectal cancer, stroke, ischemic heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Read Also: Parkinson Disease Stages Life Expectancy
Signs Of Early Onset Of Parkinsons Disease
Early onset of Parkinsons disease begins before the age of 50. It is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects the nervous system. It causes damage and subsequent deterioration of the neurons located in the black matter. The average age for onset of Parkinsons is 60, and the cases increase significantly with age. However, about 5 to 10 percent of people with Parkinsons disease experience early onset of Parkinsons before they turn 50.
Mutations of certain genes, such as the Parkin gene, can contribute to its early onset. People with one or more close family members with Parkinsons are at greater risk of developing the disease.
Overall, the risk of developing the disease is only 2 to 5 percent, unless the disease is part of family history. It is estimated that between 15 and 25 percent of people with Parkinsons know that they have a family member with the disease.
In very rare cases, the symptoms of Parkinsons may occur in people under the age of 20. This is known as youthful Parkinsons. It usually begins with the symptoms of dystonia and bradykinesia. The drug, levodopa, can often improve these symptoms.
