What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Ways To Decrease The Risk Of Parkinsons And Alzheimers
There is currently no cure for either disease. Parkinsons is considered a more treatable condition, however, especially in the early stages of the disease. Treatments include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes. Research continues to suggest that a brain-healthy lifestyle can help prevent both Alzheimers and Parkinson’s. Here are some basic guidelines:
Are There 2 Types Of Parkinson’s Disease
TwoParkinson’s diseaseParkinson’s diseasetwotypes
Similarly one may ask, what are the two types of Parkinson’s disease?
Types of Parkinson’s and parkinsonism
- Corticobasal Degeneration
- Dementia with Lewy Bodies
- Drug-induced parkinsonism.
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
- Vascular parkinsonism.
Similarly, what are the two most common secondary parkinsonism? Secondary parkinsonism may be caused by health problems, including:
- Brain injury.
- Diffuse Lewy body disease
- Encephalitis.
- Stroke.
Additionally, what kind of Parkinson’s are there?
Secondary parkinsonism includes drug-induced parkinsonism, vascular parkinsonism, normal pressure hydrocephalus , corticobasal degeneration , progressive supranuclear palsy , and multiple system atrophy .
What is the difference between Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism?
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative brain disorder that progresses slowly in most people. Parkinsonism is a general term that refers to a group of neurological disorders that cause movement problems similar to those seen in Parkinson’s disease such as tremors, slow movement and stiffness.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Ribbon
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Whats The Difference Between Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
In dementia with Lewy bodies, dementia always appears first. There can also be changes in alertness as well as visual hallucinations. However, because of the presence of Lewy bodies throughout the entire brain, characteristics of this disease not only include cognitive characteristics, but also physical, sleep, and behavioral changes. As the disease progresses, the motor symptoms common to Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems will appear.
For more information on dementia with Lewy bodies, visit www.lbda.org.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Are There Types Of Parkinsons
Over the last decade, it has become apparent that the way we currently diagnose Parkinsons as a single condition is an oversimplification. This is likely impacting both the quality of care people with Parkinsons receive, as well as research into new and better treatments.
When we consider how Parkinsons affects people so differently, the idea that there might be many subtypes of the condition shouldnt come as a shock. Its clear that not everyone has the same symptoms, as Martin writes about in his blog:
Parkinsons itself is likely an umbrella term for several subtypes of the condition. We could consider the future of Parkinsons diagnosis to follow a similar path to say breast cancer, which is no longer seen as a single condition but a collection of conditions that happen to occur in the same area of the body but have different causes and respond differently to treatments.
So researchers are now investing time and energy in trying to unpick these different subtypes in Parkinsons research that will hopefully give people answers to some really important questions, such as:
- Whats the best type of therapy for me?
- What symptoms will I develop? and,
- How fast will my Parkinsons progress?
Practical Management Of Sleep Disorders In Parkinsonism
Some patients with parkinsonism and sleep disturbance require a polysomnogram for diagnosis of the cause of the sleep disorder. Patients who complain about daytime sleepiness with sudden onsets of sleep during the day should be screened for sleep apnea syndrome, and may then require respiratory polysomnography. Patients who present with probable RBD and hallucinations may need a polysomnogram to evaluate better whether both syndromes are relevant, because the treatment options are different. Simultaneous closed-circuit television monitoring and surface electromyographic monitoring of all four extremities often is helpful if nocturnal myoclonic movements or the RBD is contributing to the sleep disturbance.
If daytime sleepiness is a prominent complaint, a multiple sleep latency test helps to determine its severity and circadian variation. It is usually best to record the patient while he or she is on the usual medication schedule, but if medications appear to be a major factor in the sleep disturbance, definite diagnosis may require 2 or more nights of recording under different treatment regimens.
Federico Eduardo Micheli, María Graciela Cersósimo, in, 2007
Don’t Miss: Parkinsons And Genetics
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Stage Three Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage three is considered mid-stage and is characterized by loss of balance and slowness of movement.
Balance is compromised by the inability to make the rapid, automatic and involuntary adjustments necessary to prevent falling, and falls are common at this stage. All other symptoms of PD are also present at this stage, and generally diagnosis is not in doubt at stage three.
Often a physician will diagnose impairments in reflexes at this stage by standing behind the patient and gently pulling the shoulders to determine if the patient has trouble maintaining balance and falls backward . An important clarifying factor of stage three is that the patient is still fully independent in their daily living activities, such as dressing, hygiene, and eating.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
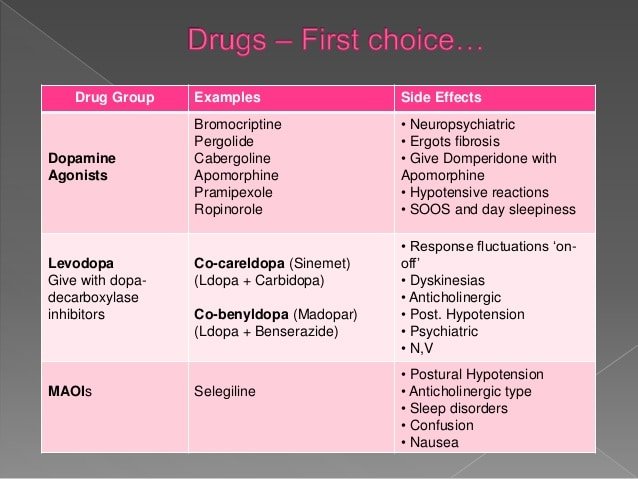
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease
Perhaps expression analysis of genes in brains of patients with various neurodegenerative and recognizing disease-specific patterns will in the future assist in differentiating PD from other parkinsonian disorders. For example, using microarray technology in SN samples from six patients with PD, two with PSP, one with FTDP, and five controls, Hauser and colleagues found 142 genes that were differentially expressed in PD cases and controls, 96 in the combination of PSP-FTDP, and 12 that were common to all three disorders. Further studies are needed to confirm this intriguing finding.
Claudia Trenkwalder, in, 2005
You May Like: Parkinson Awareness Color
The Purpose Of Clinical Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the parkinsonian syndromes is entirely clinical, as at the present time no imaging, biochemical, or genetic tests definitively diagnose or separate the different diseases. Diagnosis relies on taking a complete medical history that includes timeline of symptoms, recognition of the important clinical signs, and consideration of the differential diagnoses. Individuals diagnostic acumen is substantially influenced by clinical experience, and even among movement disorder specialists, the clinical diagnosis can change over time because of emerging clinical signs.
Motor Circuit In Parkinson Disease
The basal ganglia motor circuit modulates the cortical output necessary for normal movement .
Signals from the cerebral cortex are processed through the basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit and return to the same area via a feedback pathway. Output from the motor circuit is directed through the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata . This inhibitory output is directed to the thalamocortical pathway and suppresses movement.
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways, as follows:
-
In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
-
The indirect pathway contains inhibitory connections between the striatum and the external segment of the globus pallidus and between the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus striatal neurons with D2 receptors are part of the indirect pathway and project to the GPe
The STN exerts an excitatory influence on the GPi and SNr. The GPi/SNr sends inhibitory output to the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus. Dopamine is released from nigrostriatal neurons to activate the direct pathway and inhibit the indirect pathway. In Parkinson disease, decreased striatal dopamine causes increased inhibitory output from the GPi/SNr via both the direct and indirect pathways .
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
What Are The Different Forms Of Parkinsonism
There are three main forms of parkinsonism, as well as other related conditions.
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinsons are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
Vascular parkinsonism affects people with restricted blood supply to the brain. Sometimes people who have had a mild stroke may develop this form of parkinsonism.
Common symptoms include problems with memory, sleep, mood and movement.
Some drugs can cause parkinsonism.
Neuroleptic drugs , which block the action of the chemical dopamine in the brain, are thought to be the biggest cause of drug-induced parkinsonism.
The symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism tend to stay the same only in rare cases do they progress in the way that Parkinsons symptoms do.
Drug-induced parkinsonism only affects a small number of people, and most will recover within months and often within days or weeks of stopping the drug thats causing it.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
A doctor who suspects that a patient might have Parkinsons disease will ask for a medical history and perform a few movement tests to check for tremors and muscle stiffness. Since Parkinsons can also be confused with other parkinsonisms, which are conditions that look like Parkinson’s disease , it’s beneficial for patients to receive a diagnosis from a specialized clinic like the Yale Medicine Movement Disorders Program.
In cases where a diagnosis is difficulta test called DaTscan can be used to confirm a diagnosis. has been proven to diagnose parkinsonism. DaTscan is an injection composed of small amounts of radioactive dye to mark dopamine receptors in the brain. Once administered, doctors can use an imaging device called a single-photon emission computed tomography , to identify reduced dopamine levels in the braina clear sign of parkinsonism.
Also Check: Parkinsons Fatal
Treatment For Atypical Parkinsonism Symptoms
Because PD medication response is poor in these syndromes, treatment focuses on symptom management e.g. physical therapy for fall prevention, speech therapy to maximize communication, swallow therapy to prevent aspiration.
Other symptoms that can be addressed include dystonia, myoclonus, blood pressure dysfunction and urinary dysfunction.
Tips and takeaways:
- Atypical parkinsonism is a very complicated group of diseases that are hard to diagnose. Sometimes a neurologist will change the diagnosis as new symptoms develop or become more apparent.
- Despite the fact that these conditions typically do not respond well to medications for PD, many of the presenting symptoms can be addressed, so make sure to raise all of your concerns with your neurologist.
Do you have a question or issue that you would like Dr. Gilbert to explore? Suggest a Topic
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert
APDA Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer
From Subtypes To Better Treatments
With the identification of different subtypes of Parkinsons progressing, researchers at UCL wanted to find out if they could use donated tissue from the Parkinsons UK Brian Bank to retrospectively subtype Parkinsons. They wanted to look at the early symptoms of Parkinson’s to see if it could predict how Parkinsons would progress.
The team analysed the medical records from 111 patients whose brains arrived at the Brain Bank between 2009 and 2017. They discovered that separating people into three subtypes could predict how the condition progressed.
The subtypes they used were:
Talking about the study to Neurology Today, Thomas T. Warner, MD, PhD, director of the Reta Lila Weston Institute at UCL Institute of Neurology, said:
This analysis suggests that we may be able to use this type of classification to help guide treatment, as well as help patients better understand their disease course.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Parkinsons affects nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsonism And Pd
Parkinsonism is a clinical phenotype consisting of bradykinesia and rigidity. Resting tremor can be part of parkinsonism but is not necessarily present. Postural instability may also be present. Bradykinesia refers not just to a slowness of movements but to difficulty initiating movements with a characteristic diminishing amplitude to repetitive movements. Parkinsonian rigidity worsens when the patient is distracted. Parkinsonism can be caused by neuroleptic exposure , cerebrovascular disease, and other neurodegenerative conditions. PD is an idiopathic neurodegenerative disorder producing parkinsonism as its cardinal manifestation.
Don’t Miss: Rapid Onset Parkinsonism
Multiple System Atrophy Formerly Called Shy
As predicted by the name of this parkinsonism, multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems of the body. It affects both the motor skills movement system and the involuntary system of the body. Though the symptoms can often be treated with medications, there is no cure. In addition, there are no drugs that are able to slow the progress of MSA.
The Oxford Parkinsons Disease Centre
We started writing about this topic in 2015, at the time there were a few papers detailing small scale studies about how Parkinsons affects people differently, but it was clear that more data was needed.
Fortunately, Parkinsons UK had recently renewed a grant from the Oxford Parkinsons Disease Centre to support the world-leading Discovery project. This included a study led by Dr Michele Hu with over 1,400 participants with and without Parkinsons that might shed more light on the subtyping situation.
We interviewed Dr Michele Hu, as well as two participants taking part in this pioneering project, in the Winter 2015 edition of our research magazine.
Weve discovered that there are differences between men and women who have Parkinsons. Men are more likely to experience problems with memory, postural hypotension and sleep problems. While women tend to experience more problems with posture and balance.
Even more excitingly, we think that we are beginning to be able to separate the people with Parkinsons in our study into distinct groups based on their symptoms and how the condition is progressing.
Dr Michele Hu, University of Oxford
It was a study that might open the door to separating Parkinsons out into groups. Something that, if it were made possible, could improve not only how we treat Parkinsons today but would also play a vital role in developing and testing new treatments that may slow or stop the condition.
Read Also: How Quickly Does Parkinson’s Disease Progress
