Stage Two Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage two is still considered early disease in PD, and it is characterized by symptoms on both sides of the body or at the midline without impairment to balance. Stage two may develop months or years after stage one.
Symptoms of PD in stage two may include the loss of facial expression on both sides of the face, decreased blinking, speech abnormalities, soft voice, monotone voice, fading volume after starting to speak loudly, slurring speech, stiffness or rigidity of the muscles in the trunk that may result in neck or back pain, stooped posture, and general slowness in all activities of daily living. However, at this stage the individual is still able to perform tasks of daily living.
Diagnosis may be easy at this stage if the patient has a tremor however, if stage one was missed and the only symptoms of stage two are slowness or lack of spontaneous movement, PD could be misinterpreted as only advancing age.
Parkinson’s Disease And Movement Disorders Center
Our center provides compassionate and timely treatment to patients with movement disorders, such as dystonia, ataxia, essential tremor and similar conditions. But our mission goes beyond patient care excellence. By offering educational events and support groups, we empower patients and caregivers to become better partners in their health.
Fluids For Constipation In Parkinsons Disease
Be guided by your doctor, but general suggestions include:
- Try to drink six to eight glasses of fluid every day. Water is best, but you can also include fluid in the form of soup, juice, tea and coffee.
- Limit drinks that cause dehydration such as alcohol, tea and coffee.
- Spread your drinks throughout the day.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Hallucinations
What Can You Do If You Have Pd
- Work with your doctor to create a plan to stay healthy. This might include the following:
- A referral to a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain
- Care from an occupational therapist, physical therapist or speech therapist
- Meeting with a medical social worker to talk about how Parkinson’s will affect your life
For more information, visit our Treatment page.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Could Rdp Phenotype Be Broader Similar To Atp1a2 Mutations
While RDP is the first human disease to be associated with mutations of ATP1A3, three neurological diseases have been associated with mutations in the ATP1A2 subunit: infantile seizures, familial hemiplegic migraine and more recently familial common migraine . The dominant characteristics of patients presenting with diseases caused by mutations in ATP1A3 and ATP1A2 are consistent with what is known about the major cell-type distribution of 3 and 2 in the brain . The Na,K-ATPase converts metabolic energy by moving Na out of the cell and K into the cell, restoring the ion gradients of the cell reduced by the activity of ion channels and Na+-dependent carriers . The Na,K-ATPase has three subunits, , , with the representing the catalytic component of the enzyme. The 3 isoform is expressed exclusively in neurons in the CNS and given the highly regulated structure of 3 is reasonable to postulate that defects in ATP1A3 would cause neurological disease beyond dystonia. The phenotype of ATP1A2 mutations continues to broaden with the recent report of Todt et al., implicating mutations in the ATP1A2 gene in familial common migraine . The broad and varied phenotype of ATP1A2 mutations is important to consider when evaluating the non-motor findings in patients with ATP1A3 mutations.
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
Cognitive And Psychiatric Symptoms
- depression and anxiety
- mild cognitive impairment slight memory problems and problems with activities that require planning and organisation
- dementia a group of symptoms, including more severe memory problems, personality changes, seeing things that are not there and believing things that are not true
My Parkinsons Story: Advanced Parkinsons
This 10-minute video alternates between an interview with a man and his wife and his palliative care team, including a doctor, nurse, clerg and social worker. The man and his wife shares his experience with late stage Parkinsons. The palliative care team explains that their job is to support the best physical, emotional and spiritual wellbeing of the immediate family as well as help the family make end of life decisions.
Read Also: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Someone Has Parkinson’s
When To Seek Hospice Care
When you or your loved one have a life expectancy of six months or less, you become eligible for hospice care a type of comfort care provided at the end of life for someone living with end-stage Parkinsons disease. Hospice provides extra support so your loved one can live as comfortably as possible.
If you have experienced a significant decline in your ability to move, speak, or participate in activities of daily living without caregiver assistance, its time to speak with a hospice professional.
Read more: What is hospice care?
Some of the things that determine whether your loved one with end-stage Parkinsons is eligible for hospice include: difficulty breathing, bed bound, unintelligible speech, inability to eat or drink sufficiently, and/or complications including pneumonia or sepsis.
If you live in South Jersey, our nurse care coordinator can answer your questions and decide if your loved one is ready for hospice care. Call us 24/7 at 229-8183.
Possible Second Rdp Locus
A kindred with eight individuals affected by RDP was recently reported in whom no mutations of ATP1A3 were found . The proband presented at 6 years with overnight onset of dysphonia, dysphagia, orofacial dystonia and dystonia of all four limbs, which meets our RDP diagnostic criteria. Five of the affected individuals in this family had concurrent renal disease consisting of hypoplasia, cysts or fatal renal failure with no details available, which were never observed in RDP patients with ATP1A3 mutations. The most likely explanation for lack of a mutation in ATP1A3 is a second RDP locus. A non-coding mutation of ATP1A3 is presumably possible, although we view this as less likely given that all mutations found to date in ATP1A3 are missense changes in specific regions of the protein.
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s Disease Terminal
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Parkinsons disease causes a specific area of your brain, the basal ganglia, to deteriorate. As this area deteriorates, you lose the abilities those areas once controlled. Researchers have uncovered that Parkinsons disease causes a major shift in your brain chemistry.
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements using cells that require dopamine. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
As Parkinson’s disease progresses, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
Also Check: How Is Parkinson’s Inherited
Complications In Advanced Pd
While worsening of motor function and drug-induced motor complications represents a major challenge in patients with mid-stage to advanced disease, in the advanced stage of PD the most troublesome and distressful complications are usually nonmotor symptoms, including psychiatric and cognitive disorders, autonomic disturbances, and sleep disorders that significantly increase the need for supportive care. Unfortunately, these symptoms are frequently neglected in clinical practice due to limited consultation time, perception of the patient and caregivers that their symptoms are unrelated to the disease, or insufficient awareness of the clinicians, who generally focus on motor symptoms .
Proper supporting care becomes increasingly important in advanced PD. Rehabilitative and support services for patients and family become key interventions as the disease reaches its more debilitating stages and pharmacologic or surgical treatment becomes less relevant. Management of motor and nonmotor complications in advanced PD requires careful and ongoing assessment of whether symptoms are a side effect of medication or related to the progression of the disease .
Medication Issues
Also Check: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Recommended Reading: Are There Prenatal Tests For Parkinson Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Read Also: What Drugs Are Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease:
- tremor
- bradykinesia
- postural instability
Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinsons.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinsons disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinsons. If you suspect Parkinsons, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Introducing an easier way to track your symptoms and manage care.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
You May Like: Voice Amplification Devices For Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson Disease Treated
Parkinson disease can’t be cured. But there are different therapies that can help control symptoms. Many of the medicines used to treat Parkinson disease help to offset the loss of the chemical dopamine in the brain. Most of these medicines help manage symptoms quite successfully.
A procedure called deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat Parkinson disease. It sends electrical impulses into the brain to help control tremors and twitching movements. Some people may need surgery to manage Parkinson disease symptoms. Surgery may involve destroying small areas of brain tissue responsible for the symptoms. However, these surgeries are rarely done since deep brain stimulation is now available.
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Diagnose Parkinson’s
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
- Dementia with Lewy bodies is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder in which abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein build up in multiple areas of the brain.
- DLB first causes progressive problems with memory and fluctuations in thinking, as well as hallucinations. These symptoms are joined later in the course of the disease by parkinsonism with slowness, stiffness and other symptoms similar to PD.
- While the same abnormal protein is found in the brains of those with PD, when individuals with PD develop memory and thinking problems it tends to occur later in the course of their disease.
- There are no specific treatments for DLB. Treatment focuses on symptoms.
Who Does It Affect
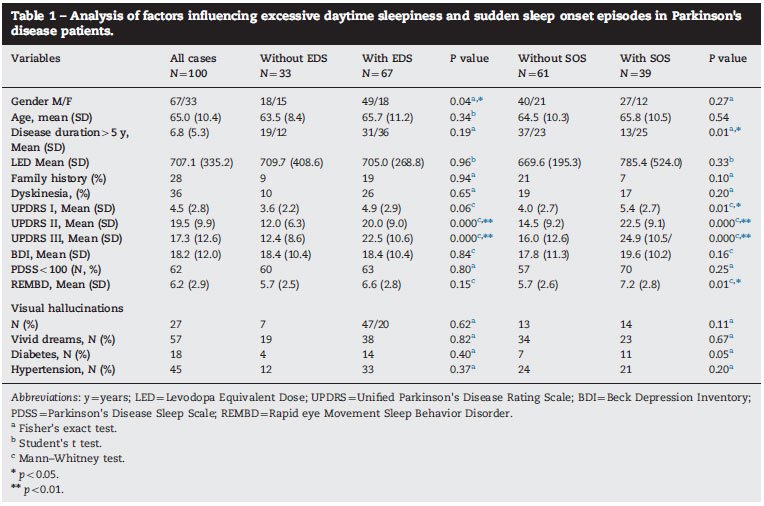
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Weight Loss
Aspect : Weight/malnutrition Status In Pd
Weight loss and malnutrition are not benign phenomena during the course of PD. PD patients in low BMI group showed lower scores of the K-MMSE and 3MS compared to stable BMI group, implying the potential relation between weight loss and cognitive decline in PD patients . Low BMI and malnutrition is one such risk factor for osteoporosis in PD patients, which deserves more attention for the concomitant risk of fractures . In addition, a growing body of evidence suggested weight loss and malnutrition in PD was associated with worsening life qualities . With respect to survival, only one study explored the association between changes in BMI and survival among persons with PD . According to this study, changes in BMI was not associated with survival after adjusting for covariates although there was inverse correlation between BMI changes and UPDRS score variations. One thing to note is the low number of death in the study limits the results. Moreover, low body weight patients tend to receive significantly higher daily dose of levodopa per kilogram body weight, which may contribute to developing dyskinesias .
Table 1. Summary of literature on weight change in PD patients.
You May Like: Medications For Parkinsons Disease And Side Effects
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Ms And Parkinson’s Disease
Response To Treatment And Surgery
Oral treatment in the form of anticonvulsants, antihistamines, anticholinergics, antiparkinsonian drugs, and antipsychotic drugs has shown no consistent beneficial effects.2 The use of botolinum toxin has been beneficial only for focal dystonia and provided temporary relief of focally impaired areas such as lingual or oromandibular dystonia in generalised cases.
Surgical treatment provided partial relief, but one patient had residual hemiparesis. The patient with implantation became infected and developed an abscess, which caused his death.1
Two patients with XDP had undergone pallidotomy in the USA with unsuccessful results.9 One of these patients died 48 hours after surgery.
Tips For Caring For Someone With Parkinsons Disease
Caring for a loved one with early onset Parkinsons can be difficult. If youre a caregiver for someone with this condition, its important that you remember your own emotional and physical health.
Not only are you dealing with a difficult diagnosis, youre also managing an increased number of responsibilities. Burnout is common in caregivers, so make sure youre checking in with your own needs.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation Center for Parkinsons Research recommends these tips for caregivers:
Also Check: How To Fight Parkinson’s
