The Role Of Dementia And Age
Dementia also plays an important role in survival with Parkinson’s. By the end of the above study, nearly 70% of the population with Parkinson’s had been diagnosed with dementia, and those with dementia had a lower survival rate as compared to those without.
This means that those with dementia were more likely to die during the six-year period than those without dementia. In addition, scientific studies have shown that increasing age is linked to an increased risk of death.
It’s important to remember that how a person’s Parkinson’s disease manifests and progresses is variable, and a person’s neurologist cannot accurately predict individual life expectancy.
There are simply no key signs or symptoms that allow a healthcare provider to perfectly predict longevity. An older age and the presence of dementia are simply associated with an increased risk of dying.
Survival In Incident Idiopathic Parkinsonism
Clinical characteristics at baseline for the patients with idiopathic parkinsonism are shown in . Survival data from first evaluation to death or end of the study were obtained for all participants . Of the 178 patients with idiopathic parkinsonism, 109 died during follow-up. Seventy-seven of the deaths occurred in the PD group, 12 in the MSA group, and 16 in the PSP group. The 4 patients with unclassifiable parkinsonism likely represent cases of late-onset PD but were excluded from further analyses, as they did not fulfill specific diagnostic criteria. The overall mean age at death was 82.0 years. Deep brain stimulation or pumps for intestinal delivery of levodopa were used or had been used by 12 of the 143 patients with PD.
Kaplan-Meier plots of survival in patients with Parkinson disease in relation to clinical and neurobiological phenotype at baseline . Severe hyposmia is defined by a B-SIT score < 4. All variables were significantly related to survival at the p< 0.001 level except the tremor or PIGD/intermediate variable , which was significant at the p = 0.004 level . B-SIT = Brief Smell Identification Test PIGD = postural imbalance and gait disorder.
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
Don’t Miss: Medical Supplies For Parkinson’s Patients
Searches And Data Extraction
A PubMed search was conducted in April 2006 for articles published in English using the following search terms: AND NOT WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome .
Of the retrieved articles, 54 containing original LE, mortality or survival data were selected for further review. Articles were excluded if they did not provide LE or SMR estimates, or did not use PD diagnosis as the outcome. Studies beginning after 1984 were preferred so that the use of levodopa medication was widespread, as it is now. All articles were evaluated by one of the authors and data on SMRs, stratified by age or sex, collected. For the analysis of LE compared with the 2003 actuary data, only articles from the UK and, as the number of UK studies reporting age specific data was limited, Western Europe were included.
Eat Healthy Meals Throughout The Day
- Consuming a variety of foods from all five food groups provides consistent energy and keeps your immune system healthy. Focus on eating a minimum of five fruits and vegetables each day, eating a variety of high fiber foods, and staying hydrated, all of which help prevent constipation, which is often an issue for people diagnosed with YOPD.
- Watch this to learn how to use nutrition to help you live well with Parkinsons.
You May Like: What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
Reported Standardised Mortality Ratios From 1935 To 2001
The SMRs or mortality ratios comparing PD cases and controls from 39 studies from 1935 to 2006 are reported in table 11.. The SMRs ranged from 1, indicating no differences compared with the general population, to 3.4, indicating more than threefold higher mortality in PD. The time trend of estimates is inconsistent, although there appears to be a decrease in the 1970s, corresponding to the introduction of levodopa trials during that time period .). A geographical trend is not apparent, as the SMRs within each geographical region are as variable as between regions .
Table 1Summary of studies that have reported a standardised mortality ratio, comparing Parkinson’s disease patients with a general population
| Reference/date |
|---|
Figure 1Standardised mortality ratios for Parkinson’s disease from 39 studies by publication date.
How Early Can Parkinsons Disease Be Treated
Every day, researchers around the world are working to find treatments and trying to slow down the progression and harmful effects of early-onset Parkinsons and Parkinsons disease. While no cure presently exists, there are certain medications that may reduce the symptoms and help a person to maintain their mobility.
The treatment approach to early-onset Parkinsons has been to lay down medications until a persons symptoms start to affect their daily life considerably.
Conversely, the Parkinsons medication levodopa and its alternative, including Carbidopa-levodopa, are likely to cause increased symptoms in a younger person with Parkinsons disease. Accordingly, healthcare professionals may recommend different medications, such as:
- MAO-B inhibitors, such as selegiline
- dopamine agonists, such as ropinirole
These drugs are associated with fewer side effects in young people as compared to levodopa.
Read Also: What Is Vascular Parkinson’s Disease
Bryans Early Onset Parkinsons Diagnosis
Bryan is a 35-year-old nurse, rock climber, husband, and new father to a four-month-old baby boy. He is also someone who is living with YOPD. YOPD is defined as Parkinsons that is diagnosed before the age of 50 and includes about 10% of people living with PD. Younger people will experience the disease differently than those who are diagnosed older, in part due to their different life circumstances. Employment, new relationships, and parenthood add particular challenges that those who are diagnosed older may not have to navigate. When and how to disclose the diagnosis is also of particular concern.
Young Onset Parkinsons : An Introduction
Although the average age to develop Parkinsons is around 60, young onset Parkinsons occurs in 5-10% of people diagnosed. 20% are under the age of 50. Some challenges in Parkinsons are universal, regardless of age, but there are a number of issues specific to younger people.
Generally, Parkinsons proceeds more slowly in younger people. While no two people are the same, someone whose onset age is 40 can expect to work for another 15-20 years on average. For someone with an onset age of 60, the average figure would be half that. These figures are based on the kinds of treatment available today. Future treatment will be even more effective in prolonging the productive life of people with Parkinsons.
Larry Gifford hosts a panel discussion on Living Well with Young Onset Parkinsons in May of 2020.
The following characteristics tend to be present in young onset Parkinsons:
- Young onset Parkinsons is less likely to lead to dementia and balance problems
- It is more likely to include focal dystonia, which is cramping or abnormal posturing of one part of the body.
- Younger people are more sensitive to the benefits of Parkinson medications, but they tend to experience the dyskinetic side effects of levodopa sooner than older people.
- They also tend to experience dose-related fluctuations at an earlier stage of the disease, including wearing off* and the on-off effect. See Parkinson Canada Information Sheet, Parkinsons Medications: What you need to know!
Medication
You May Like: When Was Parkinson’s Disease Discovered
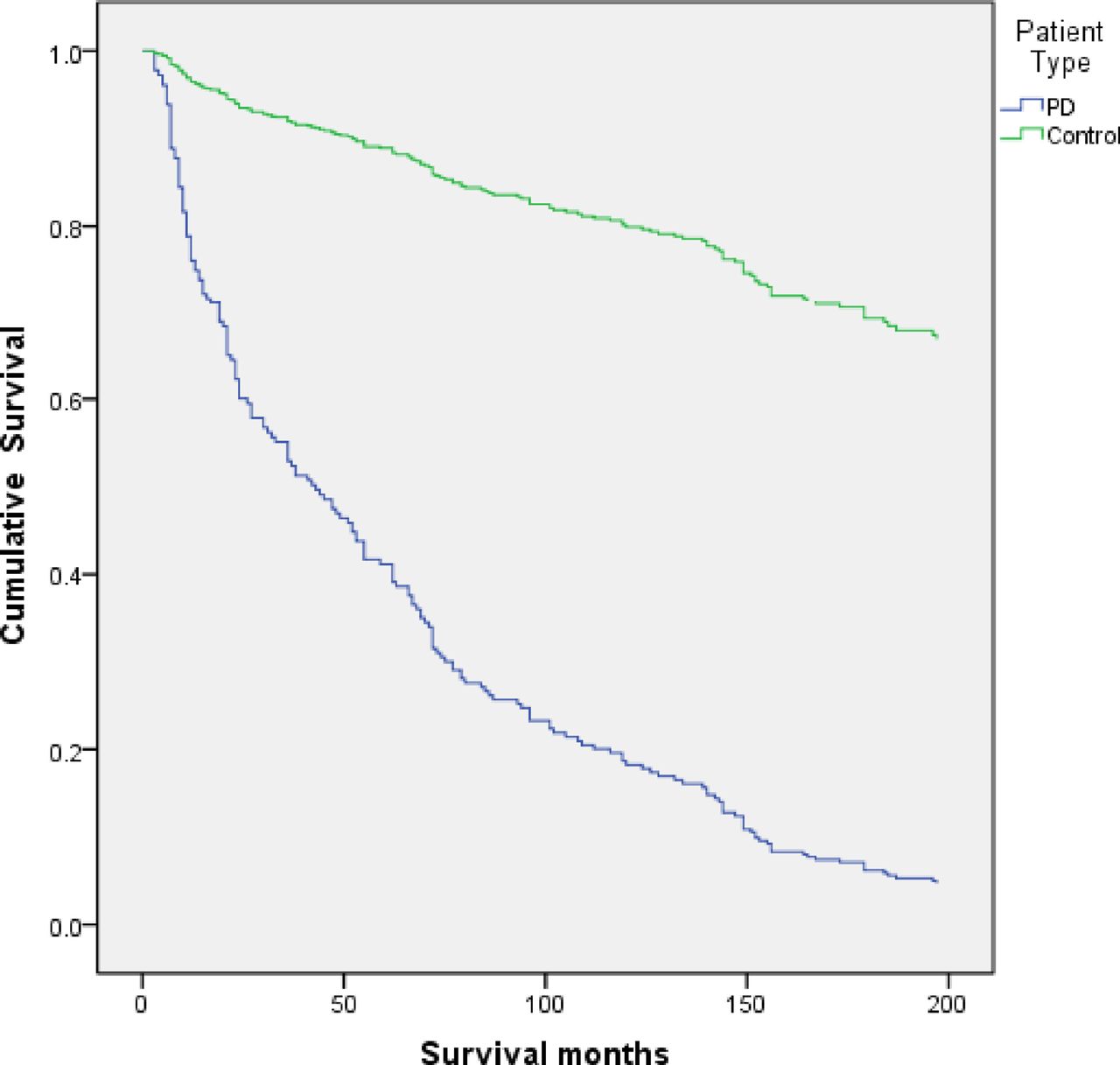
Complications Related To Parkinson’s Can Affect Survival
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology.
Parkinson’s is a common neurodegenerative disease, and although it is not fatal, research suggests it may influence life expectancy.
A 2012 study in Archives of Neurology examined the six-year survival of nearly 140,000 Medicare beneficiaries with Parkinson’s disease in the United States. During the six-year period, 64% of the participants with Parkinson’s disease passed away.
The risk of death of those with Parkinson’s was then compared to Medicare beneficiaries who did not have Parkinson’s or any other common diseases, including:
When controlling for variables like age, race, and gender, the six-year risk of death among people with Parkinson’s was found to be nearly four times greater than those Medicare beneficiaries without the disease or other common diseases.
At the same time, the rate of death among those with Parkinson’s disease was similar to those with hip fracture, Alzheimer’s dementia, or a recent heart attackalthough it was higher than those who had been newly diagnosed with either colorectal cancer, stroke, ischemic heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Circumstances And Societal Engagement In Yopd And Implications For Management
In general, people with YOPD tend to have different family and societal engagements to those with late-onset PD. For example, most people diagnosed with YOPD will have a job, whereas some people with late-onset PD have already retired. Additionaly, it is not unusual that people with YOPD have young children , or may want to start a family.
Recommended Reading: How Is Lewy Body Dementia Different From Parkinson’s
Parkinsons Disease: Is Death Inevitable
Death is inevitable for us all, but Parkinson’s disease in itself is not a death sentence. Your prognosis will depend on your age, general health, and how your Parkinson’s has progressed. However, there is no reason to assume that you won’t continue to live a full and productive life with the condition.
Scientists are performing new medical trials and research all the time to look for a cure for Parkinsons disease, while our understanding of medications and treatments is better than it has ever been. Therefore, there are plenty of ways you can control the symptoms of Parkinsons disease and make changes to your lifestyle as necessary. Many Parkinsons patients take up yoga, gardening, swimming and walking to improve their strength, flexibility and mental health. Others use physical therapy, massage and meditation to help keep symptoms at bay. These are great ways to extend your life expectancy with or without Parkinsons disease.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal? Life Expectancy for Parkinsons, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2022, September 21 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/information/is-parkinsons-disease-fatal-life-expectancy-for-parkinsons
Parkinsons Disease Is A Progressive Disorder
Parkinsons Disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement and, in some cases, cognition. Individuals with PD may have a slightly shorter life span compared to healthy individuals of the same age group. According to the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research, patients usually begin developing Parkinsons symptoms around age 60 and many live between 10 and 20 years after being diagnosed. However, a patients age and general health status at onset factor into the accuracy of this estimate. Age is the greatest risk factor for this condition, but young-onset Parkinsons disease, which affects people before age 50, accounts for between 10 and 20 percent of PD cases.
While there is no cure for Parkinsons disease, many patients are only mildly affected and need no treatment for several years after their initial diagnosis. However, PD is both chronic, meaning it persists over a long period of time, and progressive, meaning its symptoms grow worse over time. This progression occurs more quickly in some people than in others.
Pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions can help manage some of the symptoms, like bradykinesia , rigidity or tremor , but not much can be done to slow the overall progression of the disease. Over time, shaking, which affects most PD patients, may begin to interfere with activities of daily living and ones quality of life.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Clinical Trials
Mean Life Expectancy In Patients With Pd Compared With The General Population
The estimated changes in LE compared with the general population for a range of possible SMR values, stratified by age and sex, using the Gompertz function and the 2003 UK mortality rates, are presented in table 2. Calculated LEs ) and AAD ) were compared between patients with PD and the UK general population. The graphical comparisons show that LE and AAD are considerably shorter or earlier in patients with age at onset before 50years compared with the general UK population. This difference decreases with increasing age in females and males. The mean LE of patients with PD with onset between 25 and 39years was 38 years, corresponding to an AAD of 71 years compared with an LE of 49 and AAD of 82 years in the general population. The mean LE of patients with PD with onset between 40 and 64years was 21 years, resulting in an AAD of 73 years compared with an LE of 31 and an AAD of 83 years in the general population. The mean LE for older individuals with PD was 5 years, resulting in an AAD of 88 years compared with an LE of 9 years and an AAD of 91 years in the general population. The SMR calculations were the same for both sexes, and therefore changes in LE were the same, but the actual LE and AAD estimates were higher in women because they live longer, on average, than males in the general population.
| Age |
|---|
How Long Can A Person Live With Parkinsons Disease
The first thing to understand when seeking an estimate regarding life expectancy for any patient is that the answer is never definite. Each person is different and there is no formula for determining exactly how quickly a chronic disease will progress, how seriously it will affect the body, or whether additional complications may develop along the way.
Don’t Miss: Can A Person Die From Parkinson’s Disease
What Is The Main Cause Of Death In Parkinsons Disease Patients
Parkinson’s is often referred to as a “bespoke” disease because it affects each patient differently. Another factor worth considering is that Parkinson’s disease generally affects people in their 60s, most of whom die of unrelated conditions such as cancer, heart disease or stroke. However, the most common cause of death in those with Parkinson’s disease is pneumonia. This is because the disease can impair your ability to swallow in the later stages, putting you at risk for aspirating food or liquid into the lungs.
The Last Year Of Life In Parkinsons Disease
The study also examined nearly 45,000 hospitalizations in people with terminal Parkinsons, meaning their end-of-life period.
Of those with terminal PD, the most common reasons for being in the hospital were:
- Lung disease that was not from an infection
Less common causes for hospitalization were problems related to the stomach or intestines, muscles, nervous system, or endocrine system .
It is not surprising that infection was the most common hospitalization before death, as people with Parkinsons are vulnerable to developing a number of infections as a result of their disease. For example, bladder dysfunction in Parkinsons increases a persons risk of developing urinary tract infections, which can become life-threatening if not detected and treated promptly.
In addition, research suggests that aspiration pneumonia is 3.8 times more common in people with Parkinsons as compared to the general population. It has also been consistently reported to be the main cause of death in people with Parkinsons.
Aspiration pneumonia results from underlying swallowing difficulties, which leads to stomach contents being inhaled into the lungs. Immobilization and rigidity, which can impair phlegm removal, also contribute to the development of pneumonia in people with Parkinsons.
Read Also: How Does Amantadine Work For Parkinson’s
How Can Parkinsons Affect My Career
Parkinsons disease does not necessarily lead to early retirement. Depending on your particular situation, you may be able to continue working several years after your diagnosis. However, adjustments will be necessary to continue performing your job well while limiting stress:
- Review key responsibilities
- Divide each area into specific tasks
- Determine if your symptoms will interfere with your ability to perform each task
- Look for new ways of doing things
- Set a schedule that allows you to tackle difficult or demanding tasks when you are at your best
- Set times for time-consuming tasks
You are not required by law to disclose your medical condition to your employer, provided you are able to perform your duties appropriately. However, informing your employer will allow you to request accommodations at work to meet your particular needs.
If you are reluctant to inform your employer out of fear of being discriminated against due to your illness, know that you have rights. Inform yourself of labour rights of people with disorders to know your rights and the resources available.
Common Signs Of Young Onset Parkinsons
Symptoms of Young Onset Parkinsons are often different from Parkinsons that develops later in life. In young onset Parkinsons the first symptom is often dystonia: involuntary muscle contractions that may cause stiffness, twisting and repetitive motions in the limbs. Leg or foot dystonia is particularly common affecting up to 50 percent of diagnosed young people.
Many of the more common signs of Parkinsons in the elderly are less common early on in young onset Parkinsons disease, such as tremors, cognitive problems including memory loss and dementia, and loss of balance and coordination.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Medicine Side Effects
