What Genes Are Linked To Parkinsons Disease
Several genes have been definitively linked to PD:
- SNCA. This gene, which makes the protein alpha-synuclein, was the first gene identified to be associated with Parkinsons. Research findings by the National Institutes of Health and other institutions prompted studies of the role of alpha-synuclein in PD, which led to the discovery that Lewy bodies seen in all cases of PD contain clumps of alpha-synuclein. This discovery revealed the link between hereditary and sporadic forms of the disease.
- LRRK2. Mutations in LRRK2 were originally identified in several English and Basque families as a cause of a late-onset PD. Subsequent studies have identified mutations of this gene in other families with PD as well as in a small percentage of people with apparently sporadic PD. LRRK2 mutations are a major cause of PD in North Africa and the Middle East.
- DJ-1. This gene normally helps regulate gene activity and protect cells from oxidative stress and can cause rare, early forms of PD.
- PRKN . The parkin gene is translated into a protein that normally helps cells break down and recycle proteins.
- PINK1. PINK1 codes for a protein active in mitochondria. Mutations in this gene appear to increase susceptibility to cellular stress. PINK1 has been linked to early forms of PD.
- GBA . Mutations in GBA cause Gaucher disease , but different changes in this gene are associated with an increased risk for Parkinsons disease as well.
Quest To Develop Better Treatment Therapies
In addition to their unique morphology, the A9 DA neurons are pacemakers they fire action potentials continuously regardless of synaptic input.
They depend on Ca2+ channels to maintain the pacemaking activities. Thus, the cells need to deal with a lot of stress from handling Ca2+ and dopamine, Feng says. These unique features of A9 DA neurons make them vulnerable. Lots of efforts are being directed at understanding these vulnerabilities, with the hope of finding a way to arrest or prevent their loss in Parkinsons disease.
Pacemaking is an important feature and vulnerability of A9 DA neurons. Now that we can generate A9 DA pacemakers from any patient, it is possible to use these neurons to screen for compounds that may protect their loss in PD, Feng notes. It is also possible to test whether these cells are a better candidate for transplantation therapy of PD.
To differentiate human iPSCs to A9 DA neurons, the researchers tried to mimic what happens in embryonic development, in which the cells secrete proteins called morphogens to signal to each other their correct position and destiny in the embryo.
Feng notes the A9 DA neurons are in the ventral part of the midbrain in development.
Thus, we differentiate the human iPSCs in three stages, each with different chemicals to mimic the developmental process, he says. The challenge is to identify the correct concentration, duration, and treatment window of each chemical.
The Concept Of Pd Without Parkinsonism
It is now widely accepted that the classic PD course actually represents a relatively late stage of a broader process of disease . The extended PD course acknowledges a considerable pre-diagnostic phase, during which the underlying pathology has commenced, but symptomatology is either absent, non-specific or too subtle to meet current diagnostic criteria . The pre-diagnostic phase is commonly further subdivided into an at risk phase, a preclinical or premotor phase and a prodromal phase, depending on clinicopathologic manifestations .
If we are to move forward clinically and scientifically, we first need to come to grips that PD can be present in the absence of Parkinsonism. We then need objective and reliable measures to accurately identify those at risk of developing PD or those in the earliest developmental stages when traditional motor symptomatology has not emerged.
Read Also: How Many People In The Us Have Parkinson’s Disease
The Future Of Parkinson Disease Therapies And The Challenges With Stem Cell Therapies
In a presentation at the 2022 ATMRD Congress, Rajesh Pahwa, MD, FANA, FAAN, spoke about the hope held for stem cell approaches and the potential to improve care with several therapies with possible approvals on the horizon.
The future of therapeutics for Parkinson disease appears to be bright, with the pipeline of clinical development featuring a vast number of investigational and varied approaches to treating the condition. This is notable because although levodopaa gold standard therapyhas provided many patients with relief from PD symptoms, there are still limitations to its abilities, and there are several needs that remain unaddressed.
If I were to predict, I would say the next four of them would definitely be in the market in the next 3 to 4 years, Pahwa said. We have had levodopa which is the gold standard for the treatment of Parkinson disease. We have had different extended forms of levodopawe had the sustained release carbidopa-levodopa that came out 30 years ago. We had the extended-release capsules that came out, about 4 to 5 years ago now. The next generation, so to speak, is IPX-203.
READ MORE: The Importance of Treatment Nuance and Novel Options in Treating Parkinson Disease
REFERENCES1. Pahwa R. Emerging Parkinsons disease therapies. Presented at: ATMRD Congress June 17-19, 2022 Washington, DC.
Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
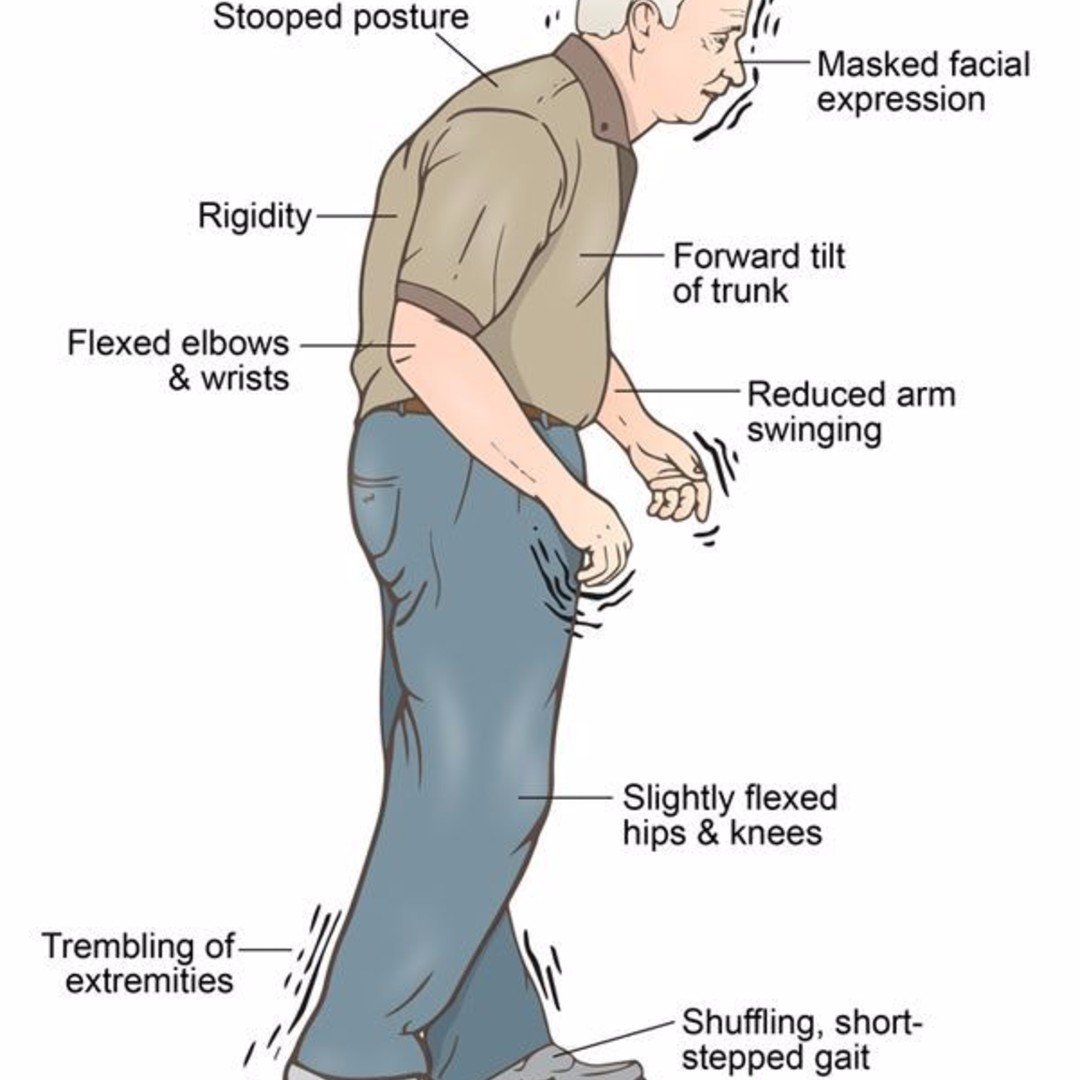
At present, no treatment cures or stops PD progression however, various therapeutic options are limited to partially alleviating the signs and symptoms, allowing patients to improve their QoL by less for a time, which depends on the diseases progression. Treatment options include surgical and pharmacological therapies.
Surgical treatment: Deep brain stimulation Focused ultrasound Cell replacement therapies. Many patients with moderate to advanced disease resort to this type of treatment in conditions where they do not respond to pharmacological medication. However, in this type of treatment, essential aspects such as cost and risk must be considered, which are generally high. Its success depends on the appropriate selection of patients and the surgeons experience and skill to optimize results and minimize complications . In this respect, it is preferable to use less invasive, cheaper, and less risky therapies, so pharmacological therapies are used as first-choice treatments.
Pharmacological treatment: Most of these drugs have focused on restoring neuronal dopaminergic transmission . However, drugs targeting the glutamatergic, noradrenergic, serotonergic, and cholinergic systems are also being used, playing a fundamental role in the basal ganglia circuits. Nevertheless, these do not stop the progression of the disease if they have managed to improve the characteristic symptoms.
Treatment of motor symptoms:
Treatment of non-motor symptoms:
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Guidelines
How Can People Cope With Parkinson’s Disease
While PD usually progresses slowly, eventually daily routines may be affectedfrom socializing with friends to earning a living and taking care of a home. These changes can be difficult to accept. Support groups can help people cope with the diseases emotional impact. These groups also can provide valuable information, advice, and experience to help people with PD, their families, and their caregivers deal with a wide range of issues, including locating doctors familiar with the disease and coping with physical limitations. A list of national organizations that can help people locate support groups in their communities appears at the end of this information. Individual or family counseling may also help people find ways to cope with PD.
People with PD may also benefit from being proactive and finding out as much as possible about the disease in order to alleviate fear of the unknown and to take a positive role in maintaining their health. Many people with PD continue to work either full- or part-time, although they may need to adjust their schedule and working environment to accommodate their symptoms.
Advanced And Future Treatments For Parkinsons
While theres no cure for Parkinsons disease, recent research has led to improved treatments.
Scientists and doctors are working together to find a treatment or prevention technique. Research is also seeking to understand who is more likely to develop the disease. In addition, scientists are studying the genetic and environmental factors that increase the chance of a diagnosis.
Here are the latest treatments for this progressive neurological disorder.
In 2002, the FDA approved deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinsons disease. But advances in DBS were limited because only one company was approved to make the device used for the treatment.
In June 2015, the FDA approved the
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s More Common In Males
What Will A Cure For Parkinson’s Look Like
Parkinson’s varies so much from person to person. There are over 40 symptoms of Parkinsons. Tremor. Pain. Hallucinations. Everyones experience is different.
Because of this, there may not be a single ‘cure’.
Instead, we may need a range of different therapies to meet the needs of the individual and their specific form of the condition.
This mix may include treatments, therapies and strategies that can:
- slow or stop the progression of the condition
- replace or repair lost or damaged brain cells
- control and manage particular symptoms
- diagnose Parkinson’s at the earliest possible stage.
And this could involve medical treatments, such as drugs and surgical approaches, as well as lifestyle changes, for example to diet and exercise.
Is It Time To Redefine Pd
Not only do these pathological findings provide an explanation for the wide range of non-motor symptomatology, indicating a more complex and systemic nature of PD, they also hint toward possible extranigral origins and earlier disease onset. To that effect, Braak et al. proposed a six-point staging system, based on post-mortem histopathological evidence of abnormal -synuclein accumulation throughout the nervous system of individuals with differing disease durations. They describe a rather systematic propagation of -synuclein aggregates along interconnected neural networks, starting in the lower brainstem and anterior olfactory system and progressing to cortical areas with advancing disease. The pathology only reaches dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra toward stages three and four, relating to the classic motor symptomatology.
As it stands, the traditional concept of PD as just a movement disorder is gradually making way for a more comprehensive and encompassing definition that recognizes the innate complexity of PD as a syndrome and the multiple affected neuroanatomical structures that lie at the foundation of the broad symptomatic range. Redefining PD as a multi-system neurodegenerative disorder not only acknowledges the widespread spatial organization of neurodegeneration and possibly a peripheral origin, but also implies earlier temporal progression along a much more extended disease continuum.
Recommended Reading: How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Help Parkinson’s
Advances In Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is another established treatment for PD that is useful in treating dopamine-dependent motor symptoms when levodopa-induced side effects become particularly problematic. DBS involves the surgical implantation of electrodes that stimulate subcortical structures including the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus9194. DBS offers significant improvements in motor symptoms and fluctuations in comparison to best medical therapy in some advanced PD patients, but dopamine-resistant symptoms other than tremor respond poorly95. It has also been suggested in an open-label trial that DBS is beneficial in early PD patients, with improved tremor scores and reduced development ofde novo tremor96. In addition to surgical complications, DBS strategies may cause cognitive and neuropsychiatric adverse effects as well as speech dysfunction. Novel DBS approaches, including adaptive DBS, targeting different regions, and refined intra-operative imaging techniques promise to offer improved clinical applicability and reduce the impact of adverse effects97.
A Review On Parkinsons Disease Treatment
Tori K. Lee Eva L. Yankee
Department of Biology, Angwin, CA 94508, USA .
Correspondence Address: Tori K. Lee, Department of Biology, Pacific Union College, 1 Angwin Ave, Angwin, CA 94508, USA. E-mail: tolee@puc.edu
Received:First Decision:Revised:Accepted:Available online:Academic Editors:Copy Editor:Production Editor:
© The Author 2021. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Don’t Miss: Can Lyrica Cause Parkinson’s
What Is The Prognosis
The average life expectancy of a person with PD is generally the same as for people who do not have the disease. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available for people with PD. However, in the late stages, PD may no longer respond to medications and can become associated with serious complications such as choking, pneumonia, and falls.
PD is a slowly progressive disorder. It is not possible to predict what course the disease will take for an individual person.
One commonly used scale neurologists use for describing how the symptoms of PD have progressed in a patient is the Hoehn and Yahr scale.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinsons disease is movement disorder of the nervous system that worsens over time. As nerve cells in parts of the brain weaken or are damaged or die, people may begin to notice problems with movement, tremor, stiffness in the limbs or the trunk of the body, or impaired balance. As these symptoms become more obvious, people may have difficulty walking, talking, or completing other simple tasks. Not everyone with one or more of these symptoms has PD, as the symptoms appear in other diseases as well.
No cure for PD exists today, but research is ongoing and medications or surgery can often provide substantial improvement with motor symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Cause Nightmares
Link Could Play Role In Pd Development
To investigate the mechanism of Syn-induced immune responses to viral infections in the brain, the researchers challenged Syn knock-out mice and human Syn KO dopaminergic neurons with RNA virus infection. They discovered that Syn is required for neuronal expression of interferon-stimulated genes . They then found that following any stimulus that triggers interferon signals, a type of immune response, Syn interacts with signaling proteins in neurons to trigger expression of ISGs.
This work provides the first clear mechanism that links inflammation and aSyn, a protein that is closely associated with the development of Parkinsons disease.
The authors mention that this data confirms that Syn responds to infection and inflammatory pathways and suggests that this interaction may play an important role in the development of Parkinsons disease. The next important step is to determine if the interactions between interferon and Syn trigger the formation of the toxic forms of misfolded Syn, called fibrils, that have been found in Parkinsons disease.
The researchers suggest future studies are needed to look into the interactions between type 1 interferon signals in neurons and misfolded Syn to determine if drugs that inhibit these interactions can prevent the formation of misfolded Syn. This would result in a potential disease-modifying therapeutic approach that is needed for patients.
Scientists Take The Next Step In Unraveling The Relationship The Protein Plays In The Disease
minute read.
An international team of scientists is advancing research in Parkinson’s disease. Today, the team released a new study outlining research that could potentially change the future of treating patients.
Currently, there are no disease-modifying therapies for Parkinsons disease that can change the progression of the disease. An international team of scientists led by faculty at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is hoping to change that.
Today, the team published new research in the journal Brain that takes scientists one step closer to understanding -synuclein , a key protein that they found links inflammation and Parkinsons disease.
The protein Syn is predominantly expressed in neurons and is associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinsons disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. This new study identifies the novel mechanism that links interferon activation and Syn function in neurons as a potential trigger for developing Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Hallucinate
Current And Future Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Despite the fact that, in terms of prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinsons Disease is only surpassed by Alzheimers Disease, there remains no cure. Treatments are purely palliative, seeking to manage symptoms and make day-to-day life easier for sufferers. Care options range from physical therapy to surgery, though some drugs have been developed that appear to alleviate the physical symptoms. However, none of these options slow the progression of the disease.
Dopaminergic neurons such as those of the substantia nigra are more susceptible to the neurotoxic Lewy body aggregates than other neurons in the brain. This causes an overall reduction in the amount of dopamine, the brains motivational chemical, which in turn affects the initiation and execution of movement. Consequently, L-DOPA injections remain the most common treatment for those suffering with PD. L-DOPA is then converted to dopamine by dopamine decarboxylase. Whilst effective at treating early-stage Parkinsons, patients need progressively stronger doses as the decarboxylase enzymes become insensitive to the dose. There are other side effects, such as unintentional movement and nausea.
References:
Lehmann, S., Jardine, J., Garrido-Maraver, J., Loh, S.H. and Martins, L.M. . Folinic acid is neuroprotective in a fly model of Parkinsons disease associated with pink1 mutations. Science Matters doi: 10.19185/matters.201702000009
Direct Infusion Of Glial Cell Line Derived Neurotrophic Factor Into The Brain
The strategy of infusion GDNF directly into the brain has been studied in a number of clinical trials since the early 2000s. The most recent study was published in 2019 and presented the results of a trial that surgically implanted a specially designed delivery system into the brains of 35 people with PD. The study lasted 40 weeks and was placebo controlled which means half the participants received the medication and half underwent all the steps of the infusion but did not receive medication. The two groups were compared and these results were published in the journal Brain. Although there was a trend toward improvement in the treatment groups as compared to the placebo group when evaluated off of medication, the trend was not statistically significant and therefore the trial did not ultimately prove that GDNF infusion was helpful for symptoms of PD.
Recommended Reading: Rem Sleep Disorder Parkinson’s Risk
