Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons.
When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator.
Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
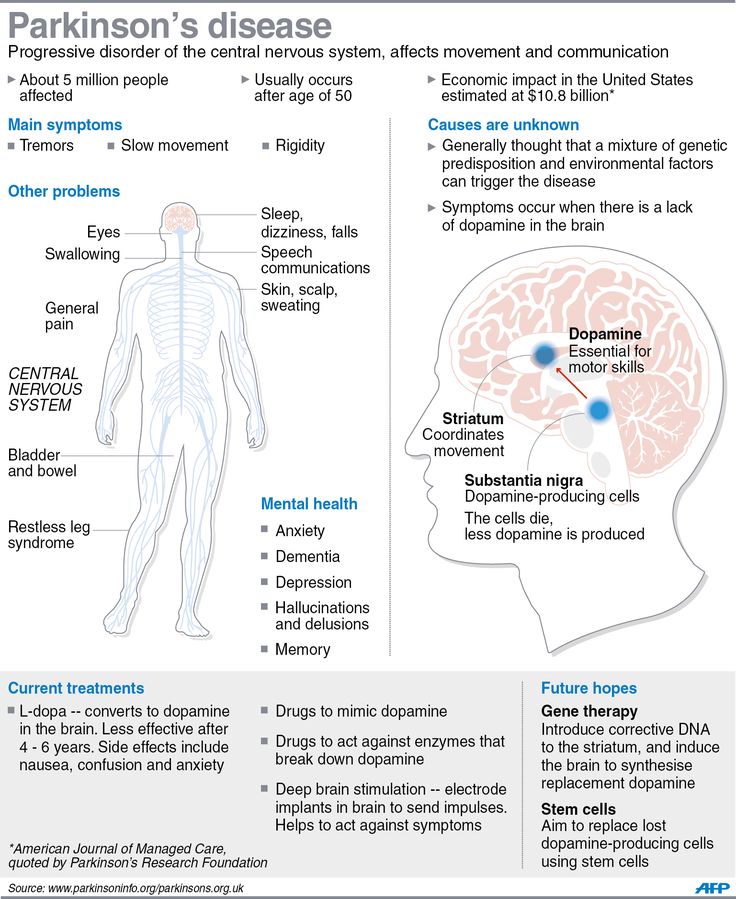
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinsons. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinsons also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
Its estimated that approximately four people per 1,000 in Australia have Parkinsons disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 219,000 people living with Parkinsons disease, with one in five of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50. In Victoria, there are more than 80,000 people living with Parkinsons.
Don’t Miss: What Is Lewy Body Parkinson
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
Locating The Basal Ganglia
|
The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located deep within the brain. They include the following:
The basal ganglia help initiate and smooth out muscle movements, suppress involuntary movements, and coordinate changes in posture. |
Read Also: Are Weighted Blankets Good For Parkinson’s
Selected Major Accomplishments In Va Research
- 2001: six VA Parkinsons Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Centers
- 2003:Initiated a landmark clinical trial to assess the effectiveness of deep brain stimulation for PD
- 2009:Determined that DBS may hold significant benefits for people with PD who no longer respond to medication
- 2014:Found that walking is a safe and accessible way to improve PD symptoms
- 2015:Developed a procedureto convert fibroblasts into dopamine neurons
- 2017:Found that DBS in PD patients gives a slight survival advantage
- 2019: Found that fatigue in PD patients may be a result of lower diastolic blood pressure
- 2020: Teamed up with the Parkinsons Foundation to support Veterans living with PD
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Someone with the symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be sent to see a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain, nerves, and muscles. The neurologist may do some tests, including a brain scan and blood tests. These tests will not make the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, but the doctor will want to make sure that there is no other problem causing the symptoms. To diagnose Parkinsons disease, the doctor relies on a persons medical history, symptoms, and a physical exam.
You May Like: Are There Any New Drugs For Parkinson’s
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Body
Life with Parkinsons is challenging, to say the least. This progressive disease starts slowly, and because theres currently no cure, it gradually worsens how you think and feel.
Giving up may seem like the only solution, but it certainly isnt. Thanks to advanced treatments, many people are able to continue living healthy, productive lives with Parkinsons.
Take a glance at this infographic to get a visual picture of how Parkinsons can affect everything from your memory to your movement.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Affect Your Eyes
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Parkinsons disease causes a specific area of your brain, the basal ganglia, to deteriorate. As this area deteriorates, you lose the abilities those areas once controlled. Researchers have uncovered that Parkinsons disease causes a major shift in your brain chemistry.
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements using cells that require dopamine. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
As Parkinson’s disease progresses, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
How Fast Does Parkinsons Disease Progress
Lorene Lowe |
6 Signs Your Parkinsons Disease Is Progressing
- Medication not working.
Edith Gutierrez | Answered December 1, 2020
In most cases, symptoms change slowly, with substantive progression taking place over the space of many months or years. Many people with PD have symptoms for at least a year or two before a diagnosis is actually made.Nov 24, 2015
Also Check: Clinical Course Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Body
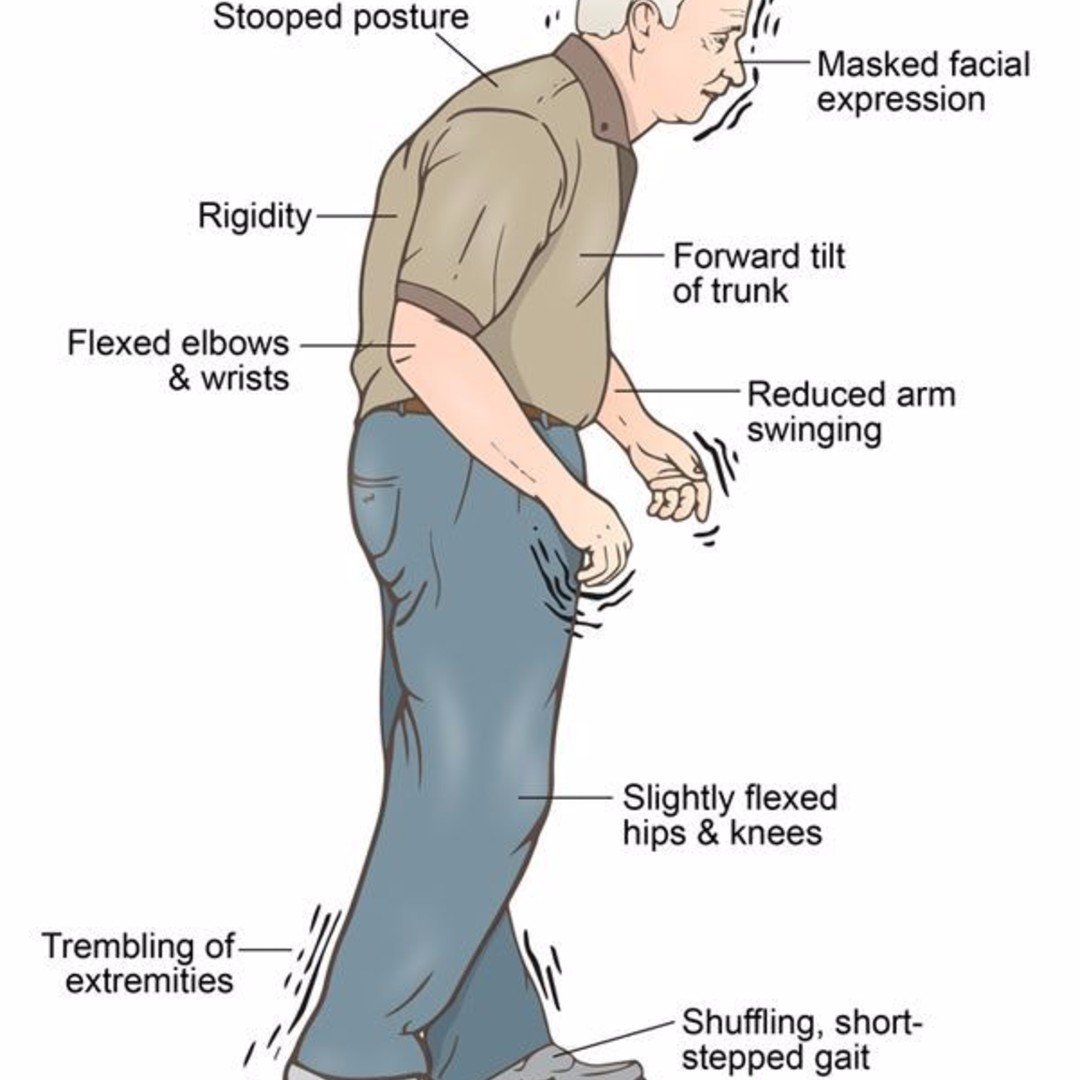
The telltale symptoms all have to do with the way you move. You usually notice problems like:
Rigid muscles. It can happen on just about any part of your body. Doctors sometimes mistake early Parkinson’s for arthritis.
Slow movements. You may find that even simple acts, like buttoning a shirt, take much longer than usual.
Tremors. Your hands, arms, legs, lips, jaw, or tongue are shaky when you’re not using them.
Walking and balance problems. You may notice your arms aren’t swinging as freely when you walk. Or you can’t take long steps, so you have to shuffle instead.
Parkinson’s can also cause a range of other issues, from depression to bladder problems to acting out dreams. It may be a while before abnormal movements start.
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Estimates vary, but about 1 million people are living with Parkinsons disease in the U.S. Doctors diagnose about 60,000 cases a year, most in people over age 60. Younger people can also get Parkinsons. About 5-10% of patients have young-onset Parkinsons disease, diagnosed before age 50.
About 15% of patients have Parkinsons-plus syndromes, also known as atypical Parkinsons. Medications may be less effective for these syndromes, which can lead to disability sooner.
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Risk increases with age. Average age at diagnosis is 65.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk.
- Environmental exposure: Lifetime exposure to well water, which may contain pesticide runoff, can increase risk. So can exposure to air particles containing heavy metals, such as in industrial areas.
- Family history: Having a close relative with the disease could increase your risk. Researchers have identified a dozen genes that may be linked to Parkinsons disease.
- Sleep disorder: People who act out their dreams are up to 12 times more likely to develop Parkinsons disease. Its not clear whether this condition, called REM sleep behavior disorder or RBD, is a cause or symptom of Parkinsons disease.
- Head trauma: Traumatic brain injury increases risk of Parkinsons, even years later.
Recommended Reading: What Helps With Parkinson’s Tremors
How Is It Treated And Is There A Cure
For now, Parkinsons disease is not curable, but there are multiple ways to manage its symptoms. The treatments can also vary from person to person, depending on their specific symptoms and how well certain treatments work. Medications are the primary way to treat this condition.
A secondary treatment option is a surgery to implant a device that will deliver a mild electrical current to part of your brain . There are also some experimental options, such as stem cell-based treatments, but their availability often varies, and many aren’t an option for people with Parkinsons disease.
Treatment Of Parkinson Disease
Before people with this disease are incapacitated, they should establish advance directives Advance Directives Health care advance directives are legal documents that communicate a personâs wishes about health care decisions in the event the person becomes incapable of making health care decisions. There… read more , indicating what kind of medical care they want at the end of life.
Don’t Miss: Does John Lithgow Have Parkinson’s Disease
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
As Parkinson’s develops, a person who has it may slow down and won’t be able to move or talk quickly. Sometimes, speech therapy and occupational therapy are needed. This may sound silly, but someone who has Parkinson’s disease may need to learn how to fall down safely.
If getting dressed is hard for a person with Parkinson’s, clothing with Velcro and elastic can be easier to use than buttons and zippers. The person also might need to have railings installed around the house to prevent falls.
If you know someone who has Parkinson’s disease, you can help by being a good friend.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
You May Like: Is Restless Leg Syndrome An Early Sign Of Parkinson’s
Michael J Fox Remembers What It Was Like To First Get Parkinson’s And Here’s What To Watch For
For the last 22 years, actor Michael J. Fox has used his voice to raise awareness and an astounding 1.5 billion dollars for Parkinson’s diseasea condition he was diagnosed with at just the age of 29-years-old. Last month, Fox accepted the Academy Awards’ Jean Hersholt Humanitarian Award , which recognizes an, “individual in the motion picture industry whose humanitarian efforts have brought credit to the industry,” the Academy’s website states. During his speech, the Family Ties star reflected on his journey from high school drop out to an award-winning actor. “I did leave high school in the 11th grade, sold my guitar and moved to L.A.,” he told the audience. “I told my history teacher of my plan and he said, ‘Fox, you’re not gonna be cute forever.’ I had no idea how to respond to that, so I said, ‘Maybe just long enough, sir. Maybe just long enough.’ It turns out we were both right.”
It didn’t take long before his career took off and he made it in Hollywood, but then Fox received the shattering news he had Parkinson’s. “I was told I only had 10 years left to work,” Fox said. “That was sh***y. The hardest part of my diagnosis was grappling with the certainty of the diagnosis and the uncertainty of the situation,” he continued. “I only knew that it would get worse. The diagnosis was definite. The progress was indefinite and uncertain.”
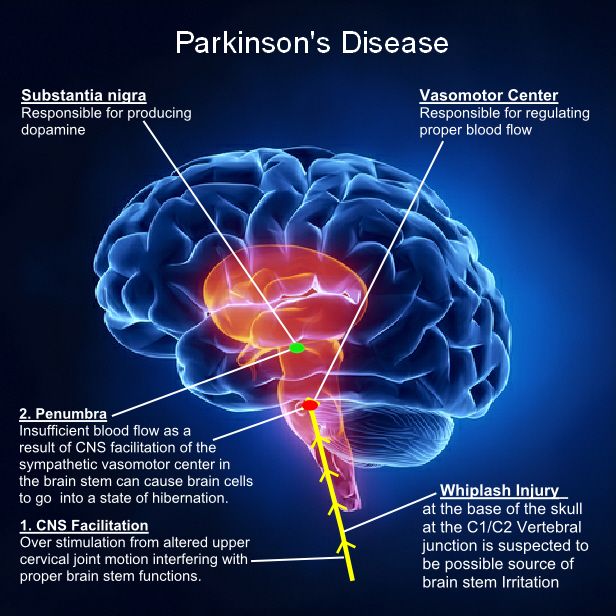
When People Talk About Parkinsons They May Mention The Effects It Has On The Substantia Nigra But Did You Know That There Are Other Areas Of The Brain That Are Affected By The Condition
Parkinsons is a condition that causes the gradual loss of the dopamine-producing brain cells of the substantia nigra an area of the brain located just above where the spinal cord meets the midbrain. It is these cells that produce and release the neurotransmitter dopamine, which has a key role in turning thought about movement into action.
While this definition of the condition is useful to briefly explain Parkinsons, the whole story is somewhat more complex. Over the last 30 years, it has become accepted that Parkinsons also causes a number of non-motor symptoms, such as changes in sleep, smell and even the way we think, which likely involve other areas of the brain.
Now scientists are looking at the broader effects of the condition on the brain in an attempt to better understand why people experience different symptoms. The finding could lead us to new treatments that tackle more than just the motor symptoms of the condition.
Also Check: Types Of Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: Michael J Fox Parkinsons Foundation
What Are The Types Of Corticobasal Degeneration
Corticobasal syndrome is a term used to specify that the symptoms, taken together, are similar to corticobasal degeneration. Many underlying neurodegenerative diseases can be caused by corticobasal syndrome, including:
- Progressive supranuclear palsy. Approximately 1 in 4 people have a type that resembles progressive supranuclear palsy. It affects balance, eye movement, speech and swallowing.
- Frontotemporal dementia. About 15% of people have frontotemporal dementia. They may struggle to organize their thoughts and behave in inappropriate, uninhibited ways.
- Dementia. An estimated 5% develop a type of dementia thats similar to Alzheimers disease. They have problems with memory and gauging spatial distances between themselves and other people or objects.
- Aphasia. Five percent have language problems or aphasia. They have trouble finding the right words to say and become unable to follow grammar rules.
Recommended Reading: Exercises For Elderly With Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s Disease And Parkinsonism
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
