Brain Mri Tracks Parkinsons Progression
All Science News articles summarize a research study and are not an official opinion, endorsement or position of the Parkinsons Foundations.
Researchers at a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence have found that a brain MRI that uses a special protocol can track changes that occur as Parkinsons disease progresses. This biomarker could be used in clinical trials, as an objective way to monitor whether the therapies being tested are effective. The study appears in the August 2017 issue of Brain.
Doctors currently diagnose PD based on a persons symptoms slowness, stiffness, tremor and balance difficulties. But these symptoms, and the rate at which they progress, differ from person to person. And there is no blood test, or biomarker, to definitively diagnose PD or objectively monitor underlying biological changes as PD progresses. Currently, a brain MRI may be ordered to rule out other conditions, but cannot diagnose PD or monitor its progression.
In earlier research, scientists led by David Vaillancourt, Ph.D., at the University of Florida in Gainesville a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence, used a brain scanning technique called diffusion MRI to detect changes that happen only in the brains of people with PD. The scans showed an increase in free water water outside of brain cells in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra.
Results
What Does It Mean?
Presynaptic Dopamine Transporter Imaging
A meta-analysis confirmed the utility of DAT-SPECT for the differential diagnosis of early PD from healthy controls, patients with essential tremor, and vascular parkinsonism with high accuracy . A multi-centered study evaluating the utility of visual assessment of 123I-FP-CIT SPECT reported a sensitivity of 97% for clinically-diagnosing parkinsonism and a specificity of 100% for reliably excluding essential tremor cases across institutions . In a longitudinal study, Nocker et al. reported higher rates of signal reductions in the caudate and anterior putamen in MSA-P patients relative to PD a finding consistent with faster rate of disease progression in MSA-P .
Interestingly, about 10-20% of PD patients, enrolled in neuroprotective trials of PD undergoing DAT imaging, were found to have scans without evidence of dopaminergic deficit . Follow-up studies so far have established SWEDD as a relatively heterogeneous group, with the following main conclusions: 1) most cases represented a clinical misdiagnosis of PD , 2) some cases were false-negatives with true PD, as evidenced by abnormal follow-up scan and a positive levodopa response, 3) initial imaging reports may have been inaccurate in some due to practical/methodological issues, and 4) accurate diagnoses in many cases remains unclear due to lack of neuropathological confirmation .
Is Parkinson’s Diagnosed In The Brain
Parkinson’s disease is one of the most challenging neurological disorders to diagnose and treat. If your doctor suspects you have Parkinson’s disease, you will usually be referred to a neurologist for further tests. These tests will involve certain movements and exercises to check your symptoms.
A neurologist will look for motor symptoms such as:
- A tremor that occurs at rest
- Slowed movement
- Muscle stiffness
If you have two or more of these symptoms and your doctor has taken blood tests to rule out other causes, it’s likely you will be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Your symptoms will be closely monitored to see any progression of Parkinson’s disease, which can take years.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Guidelines 2021
Detection Of Preclinical Pd
For every patient who presents with clinical PD there may be 10 subclinical cases with incidental brain stem Lewy body disease in the community . Subjects at risk of developing PD include carriers of genetic mutations known to be associated with parkinsonism , relatives of patients with the disorder, elderly subjects with idiopathic hyposmia, and patients with rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorders.
Relatives of PD patients with idiopathic hyposmia are at risk of PD. Ponsen et al. collected 40 such relatives after screening 400 subjects for hyposmia and, with 123ICIT SPECT, found that 7 of these showed reduced striatal DAT binding . Four of these 7 subsequently converted to clinical PD over a 2-y period.
Patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder are at high risk of developing parkinsonism or dementia. Using 123I-IPT SPECT, Eisensehr et al. found reduced striatal DAT binding in all 5 of their patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder . In another series, 11 patients with sleep disorders were investigated with FP-CIT SPECT, and reduced striatal DAT binding was found in 3, 1 of whom had evidence of clinical parkinsonism .
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
We do not know what causes Parkinsons disease. There is some evidence to suggest that there is a genetic factor which increases the risk of Parkinsons disease within some families. Also, there might be an increased risk if people have come into contact with a particular toxin or toxins found in the environment via pesticides and other chemicals used in agriculture. The specific toxin or toxins have not yet been identified but there is ongoing research into this possible cause.
Recommended Reading: Alternative Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Brain Changes
Imaging And Differential Diagnosis
The core clinical signs of PD include resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Most patients also experience nonmotor symptoms such as cognitive and emotional changes , dysautonomia, sleep disorders, and sensory disturbances. Many experience prodromal nonmotor symptoms such as anosmia, depression, constipation, and REM sleep behavior. Clinical subtypes of the disease have been identified, including tremor dominant and postural instability gait difficulty . Atypical features may be clues that there are other etiologies that can be differentiated with imaging studies.1 Structural brain imaging is frequently ordered to investigate these cases. In addition, SPECT imaging with DaT may be useful to confirm central nervous system dopamine signaling deficiency in select cases . On DaT scans, normal radiotracer uptake in the striatum forms 2 crescent-shaped regions of activity, mirrored around the median plane. In contrast, in PD, there is asymmetrically decreased activity in the putamen, often with preserved uptake in the caudate nucleus.2,3 A DaT scan is FDA approved for differentiating essential tremor from PD, and is also frequently useful for differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from PD.
Cerebrovascular Disease
Corticobasal Degeneration
Multiple System Atrophy
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Neoplasms
Neurotoxicity
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Is The Imaging Metric Appropriate For The Question Being Asked
Neuroanatomy Relevant to Parkinsons Disease
A. Braak staging of -synuclein pathology. At death, PD patients exhibit the following stages of -Syn pathology: stage I olfactory bulb only , Stage IIa brainstem predominant , stage IIb limbic predominant , stage III brainstem and limbic and stage IV neocortical . While not all patients with pathology will exhibit clinical symptoms , the progression of neuropathology generally corresponds to the progression of both motor and non-motor symptoms . B. The SN is subdivided into the ventral pars reticulata and the dorsal pars compacta , the latter is composed of dopaminergic neurons. The SNc is further divided into the dorsal and ventral tier, with the loss of dopaminergic neurons occurring first in the caudal and ventrolateral tier . Within A9, there are five nigrosomes , with N1 exhibiting the earliest loss of dopaminergic neurons . Dopaminergic neuronal loss typically spreads to neighboring groups from the N1 in PD . C. Fronto-subcortical loops comprise the motor, associative, and limbic domains, which respectively transit through the posterior, anterior, and ventral striatum, thus segregated functionally and anatomically. GPe = globus pallidus externa. GPi = globus pallidus interna. STN = subthalamic nucleus. SNc = substantia nigra pars compacta. SNr = substantia nigra pars reticulata. Adapted with permission from: .
You May Like: What Does Amantadine Do For Parkinson’s
Metaiodobenzylguanidine Myocardial Scintigraphy In Parkinsonian Disorders
Metaiodobenzylguanidine is a radioiodinated analogue of guanethidine that is taken up by the postganglionic adrenergic neurons using cellular mechanisms identical to norepinephrine. Upon depolarization, 123I-MIBG is released into the synaptic cleft, like norepinephrine, but remains unmetabolized. This uptake and localization of 123I-MIBG provides a useful measure of postganglionic sympathetic fiber integrity and function . 123I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy has traditionally been utilized to assess sympathetic nerve damage in cardiovascular diseases. More recently, its application in the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases has emerged, especially in -synucleinopathies where profound cardiovascular dysautonomia can be observed . Uptake of 123I-MIBG in myocardial scintigraphy is often reported as a heart-to-mediastinum ratio of count densities, whereas washout rate index may also be assessed using early and delayed images.
Regional Cerebral Glucose Metabolism And Pd
18F-FDG PET can be used to assess levels of resting regional cerebral glucose metabolism. Absolute levels in the lentiform nucleus lie within the reference range in PD however, covariance analysis reveals an abnormal profile of relatively raised resting lentiform nucleus and lowered frontal and parietotemporal metabolism . The degree of expression of this PD-related profile correlates with clinical disease severity, thus providing a potential biomarker of disease progression. Successful treatment with levodopa or deep brain stimulation reduces expression of the PD-related profile . Given this, changes in treatment could result in a potential confounding factor if 18F-FDG PET were to be used as a biomarker to follow PD progression.
Eckert et al. performed 18F-FDG PET on 8 patients with suspected early parkinsonism but normal findings on 18F-dopa PET . None of these 8 patients expressed a PD-related profile of glucose metabolism, and over 3 y none of them showed any clinical progression of their disorder. This finding reinforces the viewpoint that normal dopaminergic imaging excludes the presence of a degenerative parkinsonian syndrome.
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect Eyesight
Patient And Public Involvement
The OPDC Discovery Cohort is designed by and for patients and is closely linked with the Parkinsons UK local support group. Patient representatives are also involved in the funding/renewal and strategic oversight processes, and sit on the data access panel with casting votes. Results are disseminated to the study participants through annual newsletters, the OPDC website, and series of talks at participants open days.
Also Check: Using Cbd For Parkinsons Disease
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Its a good idea to ask questions as you and your doctor discuss a treatment. Asking questions can help you make sure you understand your condition and the benefits of treatment. Here are some sample questions to ask your doctor:
- Is it possible something other than Parkinsons is causing my symptoms?
- Do I need additional tests?
- How will my condition progress?
- What can I expect as my condition progresses?
- How will Parkinsons affect my other medical conditions?
- What treatments are available?
- Which treatments are best for me?
- How will treatments help my current symptoms?
- Will treatment slow down the progression of Parkinsons?
- What side effects do your recommended treatments have?
- What happens if these treatments dont help?
- Can you recommend any resources or educational material for me?
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Awareness Day 2022
Is Parkinsons Diagnosed In The Brain
Parkinsons disease is one of the most challenging neurological disorders to diagnose and treat. If your doctor suspects you have Parkinsons disease, you will usually be referred to a neurologist for further tests. These tests will involve certain movements and exercises to check your symptoms.
A neurologist will look for motor symptoms such as:
- A tremor that occurs at rest
- Slowed movement
- Muscle stiffness
If you have two or more of these symptoms and your doctor has taken blood tests to rule out other causes, its likely you will be diagnosed with Parkinsons disease. Your symptoms will be closely monitored to see any progression of Parkinsons disease, which can take years.
Recommended Reading: Clinical Trials On Parkinsons Disease
What Is A Datscan And What Role Does It Play In A Parkinsons Diagnosis
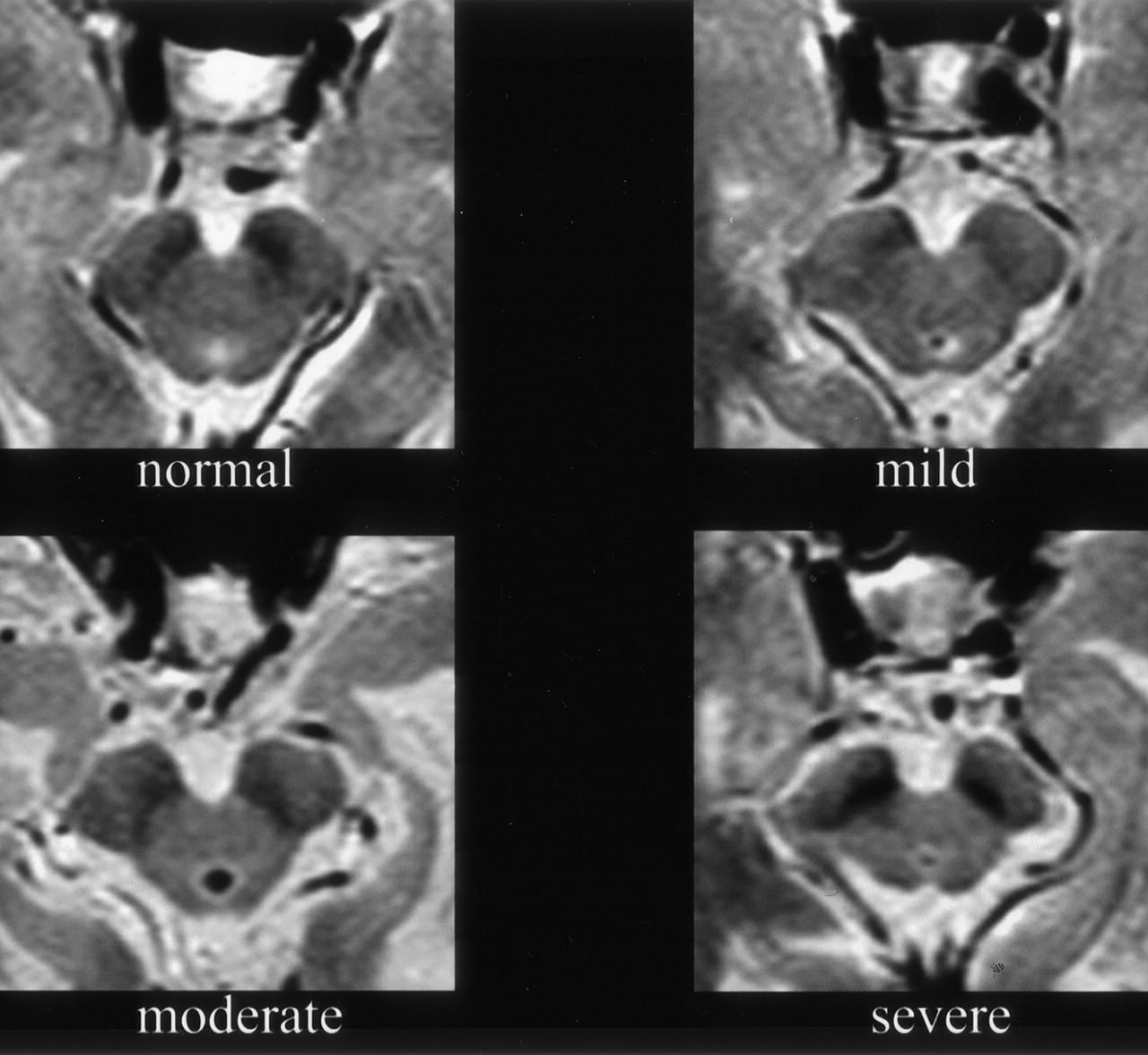
In 2011, the FDA approved the use of a scan called a dopamine transporter scan . A DaTscan is an imaging technology that allows visualization of the dopamine system in the brain. It is similar to an MRI, but looks at the function of the brain rather than the structure.
A DaTscan involves injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug that is then measured by a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner . The SPECT scanner measures the levels and location of the drug in the brain.
It is important to know that a negative DaTscan does not rule out PD, especially early in the disease, but a positive DaTscan can help confirm it. A positive DaTscan can differentiate PD from essential tremor as there is no dopamine deficiency in the latter. However, DaTscan abnormalities can be seen in PD as well as other forms of atypical parkinsonism that cause a loss of dopamine . This means that a positive result does not differentiate Parkinsons disease from other forms of atypical parkinsonism.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Happen Suddenly
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
Coming to terms with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s and living with the disease is challenging and will take a lot of adjustment. There are still things you can do that can help you to feel more in control of your situation and to stay positive. Some things that might help could include:
- choosing to lead a healthy lifestyle
- making informed decisions related to your treatment
- keeping a diary of your symptoms in preparation for meetings with health and social care professionals
- attending a self-management course
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
Read Also: Effect Of Exercise On Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: New Parkinson’s Treatment 2021
What Tests Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
There currently are no tests that can definitively diagnose Parkinsons Disease. A diagnosis is based on the clinical findings of your physician in combination with your report on the symptoms you are experiencing.
In situations where an older person presents with the typical features of Parkinsons and they are responsive to dopamine replacement therapy, there is unlikely to be any benefit to further investigation or imaging.
What Exactly Are Lewy Bodies
Lewy bodies are “clumps” of protein that accumulate in the outer layers of the brain, also known as the cortex. In addition to Parkinson’s, they are also a feature of dementia. Although we don’t know precisely what part Lewy bodies play in Parkinson’s disease or dementia, we do know that they are not the sole cause of Parkinson’s disease and its various symptoms. Some studies indicate that dopamine cells die before they even reach this part of the brain, but this is unconfirmed.
Despite the enigma of the Parkinson’s brain, many scientists have identified Lewy bodies as a potential target for new treatments. These treatments for Parkinson’s disease could be available in a matter of years, not decades.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Hand Tremors In Parkinson’s
How Can Mris Be Used To Detect Early Onset Parkinsons
MRIs use magnets to create detailed images of the inside of the body. Brain MRIs can help doctors spot tumors, brain bleeding, and other brain health conditions. Recently, medical researchers have discovered that MRIs can also spot small changes in the brain that can indicate Parkinsons disease.
A 2019 study on MRIs and Parkinsons found that people with Parkinsons often have visibly damaged brain neurons. The damage to neurons is present before any brain atrophy begins, and before symptoms are present.
Using this information, doctors can prescribe appropriate treatments, such as Deep Brain Stimulation therapy, that can slow down decline and improve the quality of life for people with Parkinsons.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: How Is Parkinson’s Disease Associated With Headaches
Positron Emission Tomography In Parkinsonian Disorders
Positron emission tomography is another in vivo functional neuroimaging technique that utilizes a variety of radionuclides to elucidate the integrity of the dopaminergic system, cerebral metabolism, pathological protein accumulation, and inflammation in the brain. Radiotracers, such as 18F-dopa and 11C-raclopride, can be employed to image the integrity of presynaptic and postsynaptic nigrostriatal projections, respectively. The functioning of the pre-synaptic monoaminergic system can be evaluated using 11C-dihydrotetrabenazine or 18F-labelled analogues. Cerebral glucose metabolism is commonly assessed using 18F-labelled fluorodeoxyglucose tracer, where reduced uptake is suggestive of lower regional tissue metabolism. Amyloid burden in the brain has been widely assessed using an 11C-labelled thioflavin analogue, known as the Pittsburgh compound B , as well as using other 18F-labelled ligands. Finally, tau imaging is a newer technique that is still in its infancy and is aimed at detecting abnormally-folded tau deposits in AD and other tauopathies.
