What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
PD is a disorder of the nervous system. A small part of the brain, called the substantia nigra, is mainly affected. This area of the brain sends messages down nerves in the spinal cord to help control the muscles of the body. Messages are passed between brain cells, nerves and muscles by chemicals called neurotransmitters. The brain cells in the substantia nigra produce dopamine, the main neurotransmitter.
If you have PD, a number of cells in the substantia nigra become damaged and die. The exact cause of this is not known. Over time, more and more cells become damaged and die. As cells are damaged, the amount of dopamine that is produced is reduced. A combination of the reduction of cells and a low level of dopamine in the cells in this part of the brain causes nerve messages to the muscles to become slowed and abnormal.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Shooting Pain And Paraesthesia
Radicular pain is a sharp pain that shoots down a limb and often affects fingers or toes. Paraesthesia is sometimes described as a feeling of pins and needles or perhaps numbness in a limb which has fallen asleep. Such pain is usually related to trapped nerves in the spinal cord and can feel similar to an electric shock, a tingling or a burning sensation.
Treatment: Painkillers and exercise will generally settle the pain. If not your specialist may refer you for tests such as an MRI scan to check for a trapped nerve in the spinal cord.
You May Like: Does Richard Blumenthal Have Parkinson’s
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Painful Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
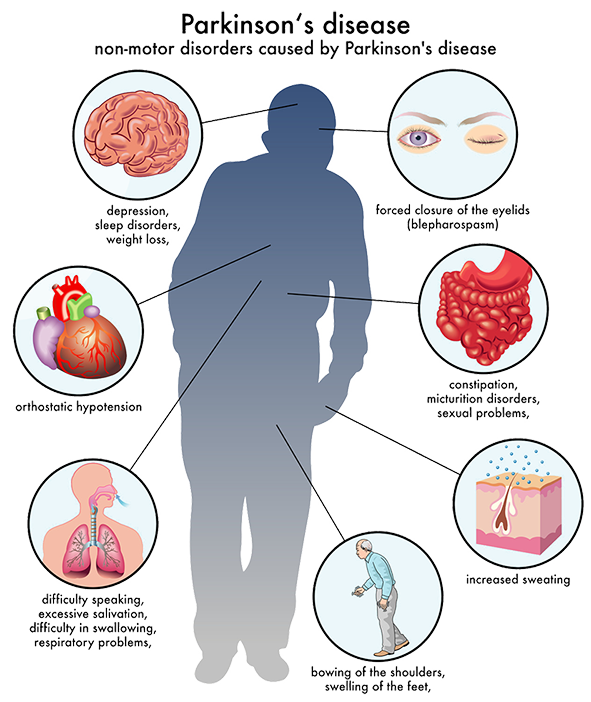
Pain can sometimes be an early symptom of PD. For example, a person may complain of a painful shoulder and be diagnosed with an orthopedic condition such as a frozen shoulder, only to develop a rest tremor on that side at a later point. The painful shoulder was in fact not a frozen shoulder after all, but rather pain due to the rigidity of PD. Now of course, sometimes a frozen shoulder is really just a frozen shoulder, so theres no need to jump to conclusions when you are experiencing pain. Not every ache and pain is a sign of PD, but it is important for you to educate yourself, be aware of the possible connections, and be proactive about seeking medical attention for any notable pain you are experiencing.
If you have PD and develop pain, it is important to first bring this to the attention of your doctor. The pain may be related to your PD, or the pain may be due to a common problem such as arthritis which is exacerbated by your PD. However, in some cases, it may be a symptom of a more serious medical problem. So do not assume that the pain is related to your PD before getting an appropriate medical workup.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
First Type Of Leg Pain Is Central Pain
This pain is described as constant burning sensation with occasional burst of sharp pain. As it was in my case, this pain is commonly exacerbated by cold and by light touch. I could not stand the sheets to touch my skin and being in a cold room sent my pain through the roof. This type is usually bilateral but it may start on the side where other Parkinsons symptoms begin. For me, it was the leg where my rest tremor began.
Sensory Profiling And The Potential For Mechanism
Since psychophysical testing offers the opportunity to explore the functionality of an individuals pain system under controlled settings, a comprehensive assessment of various pain processing and modulatory pathways for use as a surrogate measure of the mechanisms driving the development of persistent pain in a given population/patient cohort is possible. For example CPM deficiencies in patients with neuropathic pain can be targeted by manipulation of central noradrenergic and serotonergic transmission, where the pain-inhibiting impact of Tapentadol potentiates impaired CPM in persistent pain patients in a manner that back translates to animal studies,,. Psychophysical testing can also be used to predict analgesic treatment efficacy.
In people with PD, sensory profiling through psychophysical testing has been applied in order to provide insight of the underlying mechanisms of persistent pain. Thereafter, guidance for personalised pain medicine through mechanism-based treatments is a key goal for many chronic pain types,,,. However, a frustratingly disparate range of psychophysical trials exists in the literature for the PD patient cohort, where significant differences in the type of pain considered and methodologies employed leads to incomplete conclusions, as discussed below.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
General Aspects Of Pain Treatment In Pd
Despite the high prevalence of pain in PD, literature data suggest that only up to a maximum of 50% of PD patients receive at least some type of pain therapy .
Still, the fundament of pain therapy should be an optimized dopaminergic treatment which can improve pain related to insufficient dopaminergic supply such as akinesia and/or rigidity , pain due to dopaminergic over-supply such as dyskinesia and/or dystonia , or central pain that is dopamine-sensitive . This concept was reported to be effective in about 30% of PD patients . A standardized levodopa test can be helpful to decide whether the pain is dopaminergic responsive or not, but any result of this short-term effect must always be interpreted with caution so that the long-term assessment of pain under dopaminergic therapy over several weeks remains essential .
A systematic review and meta-analysis including databases from January 2014 until February 2018 investigated the efficacy of a variety of novel, complimentary, and conventional treatments for pain in PD and found the greatest reduction in pain for safinamide, followed by cannabinoids and opioids, multidisciplinary team care, COMT-inhibitors, and electrical and Chinese therapies, while the weakest effects were obtained for dopaminergic agonists and miscellaneous therapies . Table 1 gives an overview of larger randomized controlled trials of antiparkinsonian drugs and opioids assessing the effect on pain in PD patients.
Table 1
Fig.1
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Stages Life Expectancy
Second Type Of Leg Pain Is Caused By Dystonia
When related to levodopa, it usually occurs as a wearing off but can also occur at peak dose. In most cases this leg pain is unilateral and has direct correlation to medication intake. When pain is due to dystonia, it is more common in early morning. This type of leg pain is usually accompanied by toes curling and foot abnormally posturing.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Life Span
Pain Presentation And Assessment In Pd
Most epidemiological data are based on questionnaires which were not specifically validated for PD patients so that results have to be interpreted with caution. The Kings Parkinsons disease pain scale is to date the only questionnaire that is specifically calibrated and validated for PD and is highly recommended to qualitatively and quantitatively assess pain and to ascribe the pain pathophysiologically. The scale contains seven different pain domains comprising musculoskeletal pain, chronic pain , fluctuation-related pain, nocturnal pain, oro-facial pain, discolouration or oedema/swelling and radicular pain as well as 14 sub-categories . This assessment tool is based on the pain classification according to Ford but also considers pain types of other classifications such as motor fluctuations or visceral pain .
In addition, there are some specific pain syndromes in PD which have to be kept in mind, including the so-called coat-hanger pain that occurs in cases of pronounced orthostatic dysregulation and although it is more frequent in multisystem atrophy it can occur also in PD and is often associated with strong headache and neck pain . Furthermore, pain due to constipation which is frequent in PD can cause abdominal pain.
Dealing With Parkinson’s Disease: A Guide For Patients And Families
Parkinson’s disease is an ongoing, progressive disease of the nervous system that affects a patient’s movement. Millions of individuals worldwide are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. The cause of Parkinson’s disease is presently not known. However, research attributes the disease to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Age also plays a role. Most cases of Parkinson’s disease beginning after an individual is sixty years old.
Unfortunately, there is currently no Parkinson’s disease cure. There are, however, treatments for Parkinson’s disease. Many patients take Parkinson’s disease medications to control their symptoms. Occupational therapy is also a huge part of treating Parkinson’s disease. Overall, this condition requires intense treatment and symptom management for patients to live a full life.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Pain In Pd: Current Treatment
Pain is a multi-dimensional experience involving sensory discriminative and affective motivational descriptive axes. As such, pain perception is inherently subjective and influenced by multiple factors. While acute pain reflects an adaptive survival mechanism, persistent pain negatively impacts the quality of life of the affected individual and serves limited evolutionarily advantage. Unfortunately a large proportion of people with PD experience persistent pain and 50% of those individuals receive no or inadequate treatment,. Therapeutic strategies that offer an improved analgesic profile remain an unmet clinical need. Clearly multi-disciplinary approaches for pain management that encompass new concepts in pathogenesis and treatment are required,.
Q What Is The Pain Experience In Pd And Does It Differ Between Genders
Dr. Fleisher: As with almost everything else in PD, the pain experience is highly individualized, and no 2 people, regardless of gender, will have the same symptoms. Female gender appears to be an independent risk factor for chronic pain in PD, even though PD is more common in men than in women.2 Pain intensity also is higher in women than in men with PD.1
There is a lot of interesting research examining the contributions of hormones to the greater prevalence of PD in men or, conversely, the lower prevalence in women.3 Once we better understand the roles of sex hormones in the pathophysiology of PD, we may better understand whether hormones also play a role in the higher incidence of chronic pain in women with PD.
Don’t Miss: Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s
Cognitive And Psychiatric Symptoms
- depression and anxiety
- mild cognitive impairment slight memory problems and problems with activities that require planning and organisation
- dementia a group of symptoms, including more severe memory problems, personality changes, seeing things that are not there and believing things that are not true
Evaluating Lower Back Pain
When a person develops lower back pain, a neurological history and exam can help rule out serious medical conditions that may need further evaluation and intervention. The neurological history will collect information about other neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, new bowel or bladder symptoms, etc. The neurologic exam will assess strength, sensory changes and reflexes, among other things, which can shed light on spine function and help determine if a serious medical condition is present. Lower back pain caused by a serious medical condition is rare . Nevertheless, be sure to tell your neurologist about any new symptoms that you may have.
For most people, neurologic history and exam will confirm that lower back pain can be managed conservatively. When this is the case, treatment of the pain with exercise and physical therapy is the best course forward. Your neurologist may determine that imaging of the lower back will be helpful. If that is the case, he/she may order an MRI of the lower spine. An MRI will show structural changes to the lower spine but will not visualize PD-specific causes of lower back pain such as rigidity, dystonia, or central pain.
Studies have shown that MRIs can reveal structural changes that do not result in pain at all. So, it is important not to let imaging be the sole guidance of lower back pain management.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons comes under the dementia umbrella. Its adegenerative disease of the nervous system that causes a loss of motor skillsand intentional movement. When someone has Parkinsons, the part of the brainthat controls muscular movements and mood function doesnt receive enough ofthe crucial dopamine chemical. Without enough dopamine, bodily movements,learning abilities and mood levels are severely affected. So-called normalfunctions such as speaking, writing, swallowing, walking and sleeping become difficultto perform. These challenges, combined with a lowering of mood levels is whymany Parkinsons patients suffer with depression.
Natural Remedies And Treatments For Parkinsons Disease That Get Powerful Results
To successfully treat the symptoms of Parkinsons, andeven reverse this disorder, there are 4 things you must do
a) Increase your natural dopamine levels
b) Detox your body of all heavy metals andpollutants
c) Reduce all inflammation in the body,especially the brain
d) Repair the neuro pathways
These 10 natural treatments and remedies do all four. Solets not waste any more time then. Here they are in order of importance
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Pain Treated In Patients With Parkinson Disease
Pain serves as 1 of the most frequent nonmotor complaints in patients with Parkinson disease , affecting 68% to 95% of patients across all clinical stages. Published in the Journal of Parkinson Disease, researchers highlight that similar to PD, pain is complex and even has different classifications of subtypes within the disease.
While prominent, real-life pain data in PD remains scarce. Researchers sought to provide an overview on pain in PD, including classification, assessment, presentation, and the existing therapy landscape.
As researchers highlighted, todays classifications of pain in PD include musculoskeletal, radicular/neuropathic, dystonia-related, akathic discomfort/pain, and central pain. Notably, the difference in pain directly related to PD and central pain, which is attributed to objective painprocessing and pain-perception disturbance within ascending and descending pathways, was referenced. Most frequently, pain presents as musculoskeletal/nociceptive pain in PD patients, but in nearly half of the PD population, comorbid conditions, such as spine and joint arthrosis, serve as contributors.
When it comes to treating pain in PD, interventions remain a major unmet need as only approximately 50% of those with the disease receive at least some type of pain therapy. In managing pain, researchers recommend that therapy should be optimized to address dopaminergic issues, which has been shown to be effective in 30% of patients with PD.
Reference
Types Of Pain In Parkinsons

One review classified the types of PD pain as follows:
- musculoskeletal, in which the pain results from problems with the muscles , bones or joints
- dystonic, which is due to abnormal muscle contractions caused by PD or the medications used to treat it
- radicular pain or nerve pain
- central pain, which is poorly understood and thought to be due to abnormalities in the brain itself
Don’t Miss: Can Essential Tremor Turn Into Parkinson’s
