Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Stages Of Parkinsons Disease & Its Early And Late Symptoms
Parkinsons disease is a common neurodegenerative disease. It is characterized by progressive loss of muscle control, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. As the disease progresses the patient presents symptoms such as difficulty in walking, talking, and completing simple tasks.
The adult onset of Parkinsons disease is very common and it is mostly seen in the people aged 60 years or elder. Early onset i.e. age between 21-40 years or juvenile onset i.e. below 21 years of age can also occur. Before knowing the early and late symptoms of Parkinsons disease, it is necessary to look at the stages of this disease.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
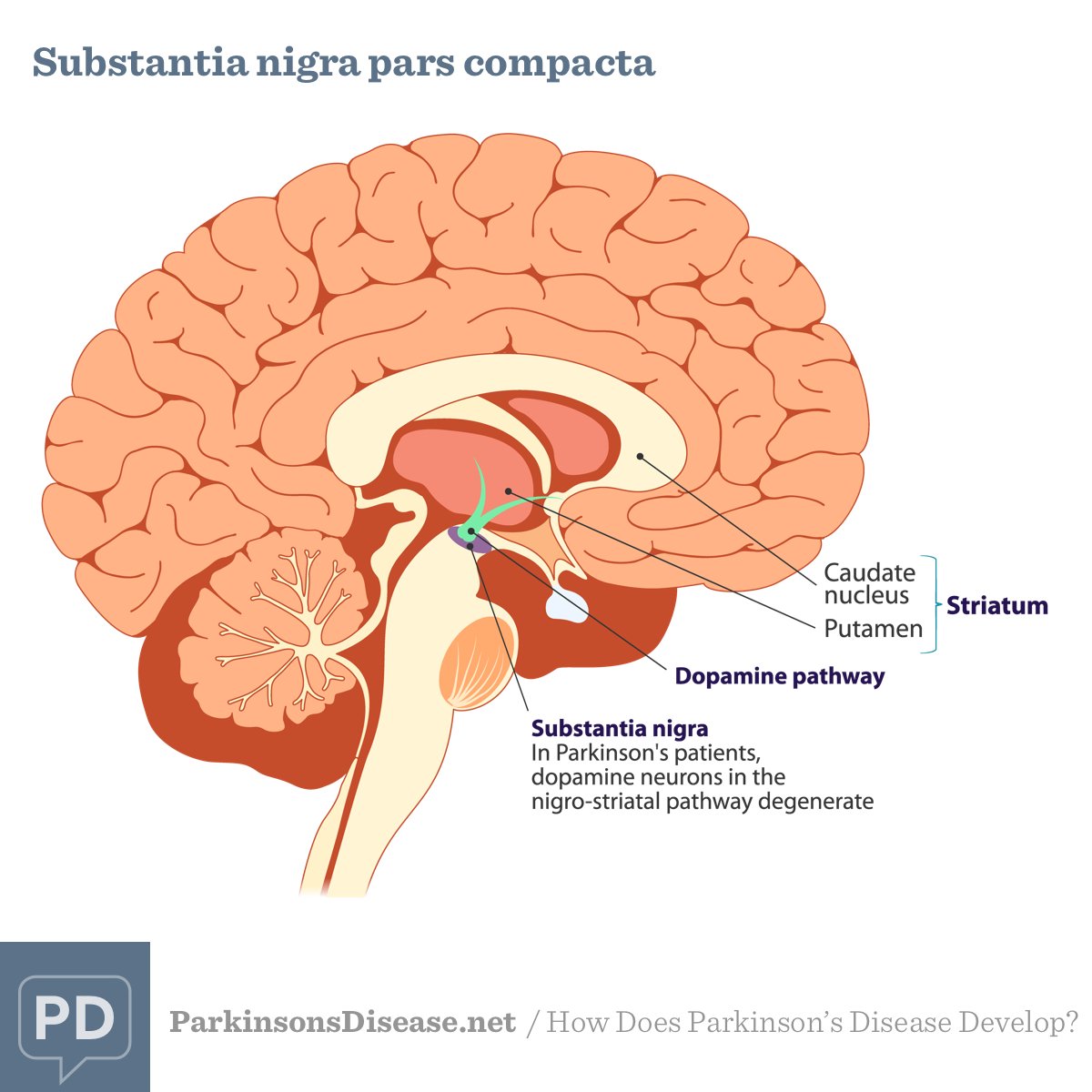
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
What Treatments Are Available
Many Parkinson’s patients enjoy an active lifestyle and a normal life expectancy. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet and staying physically active contributes to overall health and well-being. Parkinson’s disease can be managed with self-care, medication, and surgery.
Self careExercise is as important as medication in the treatment of PD. It helps maintain flexibility and improves balance and range of motion. Patients may want to join a support group and continue enjoyable activities to improve their quality of life. Equally important is the health and well being of the family and caregivers who are also coping with PD. For additional pointers, see .
These are some practical tips patients can use:
Medications There are several types of medications used to manage Parkinson’s. These medications may be used alone or in combination with each other, depending if your symptoms are mild or advanced.
After a time on medication, patients may notice that each dose wears off before the next dose can be taken or erratic fluctuations in dose effect . Anti-Parkinsons drugs can cause dyskinesia, which are involuntary jerking or swaying movements that typically occur at peak dosage and are caused by an overload of dopamine medication. Sometimes dyskinesia can be more troublesome than the Parkinsons symptoms.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The most noticeable symptoms of PD are movement-related, and the hallmark symptoms are: bradykinesia, resting tremor, and rigidity.
Bradykinesia refers to slowness of movement—especially slowness of the initiation of movement. PD patients will often have trouble getting their body to transition from a resting state to an active state. When they finally do get moving, their movement may be much slower than a healthy patient’s.
Watch this 2-Minute Neuroscience video for a summary of Parkinsons disease symptoms, neurobiology, and treatment.
Resting tremor indicates a tremor that is worse when the patient is at rest. When the patient makes a voluntary movement, the intensity of the tremor often subsides. These tremors typically start in the hands or arms and then spread to the legs as the disease progresses.
Rigidity describes a state of generally elevated muscle tone where the patient displays inflexibility and resistance to movement .
Although these movement-related symptoms are the most familiar signs of PD, there are a number of other common symptoms that occur as well. For example, later in the disease, postural instability becomes common, making falls more likely. Some of the non-motor symptoms include constipation, deficits in the sense of smell, sleep abnormalities, mood disorders like depression and anxiety, cognitive impairment, and dementia.
The Facts About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurogenerative disease that causes nerve cells in the area of the brain that controls movement to weaken and/or die. While healthy neurons produce a chemical called dopamine, which the brain needs a certain amount of in order to regulate movement, weakened neurons produce lower levels of dopamine. What causes these neurons to weaken is currently unknown.
Some patients with Parkinson’s disease also suffer from a decline in norepinephrine, a chemical that transmits signals across nerve endings and controls various functions, such as blood pressure and heart rate.
More than 10 million people worldwide are currently living with Parkinson’s disease and nearly one million will be living with the disease in the United States this year, according to the Parkinson’s Foundation.
What Research Is Being Done
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , a component of the National Institutes of Health, is the primary funder of research on the brain and nervous system. is the leading funder of biomedical research in the world.
PSP is one of the diseases being studied as part of the NINDS Parkinsons Disease Biomarkers Program. This major initiative is aimed at discovering ways to identify individuals at risk for developing Parkinsons disease and related disorders, and to track the progression of these diseases. NINDS also supports clinical research studies to develop brain imaging that may allow for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of PSP.
Genetic studies of PSP may identify underlying genetic causes. Previous studies have linked regions of chromosomes containing multiple genes, including the gene for the tau protein , with PSP. Researchers hope to identify specific disease-causing mutation and are also studying how genetics and environment interaction may work together to contribute to disease susceptibility.
Animal models of PSP and other tau-related disorders, including fruit fly and zebrafish models, may identify basic disease mechanisms and lead to preclinical testing of potential drugs. Other studies in animal models focus on brain circuits affected by PSP, such as those involved in motor control and sleep, which may also yield insights into disease mechanisms and treatments.
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Estimates vary, but about 1 million people are living with Parkinsons disease in the U.S. Doctors diagnose about 60,000 cases a year, most in people over age 60. Younger people can also get Parkinsons. About 5-10% of patients have young-onset Parkinsons disease, diagnosed before age 50.
About 15% of patients have Parkinsons-plus syndromes, also known as atypical Parkinsons. Medications may be less effective for these syndromes, which can lead to disability sooner.
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Risk increases with age. Average age at diagnosis is 65.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk.
- Environmental exposure: Lifetime exposure to well water, which may contain pesticide runoff, can increase risk. So can exposure to air particles containing heavy metals, such as in industrial areas.
- Family history: Having a close relative with the disease could increase your risk. Researchers have identified a dozen genes that may be linked to Parkinsons disease.
- Sleep disorder: People who act out their dreams are up to 12 times more likely to develop Parkinsons disease. Its not clear whether this condition, called REM sleep behavior disorder or RBD, is a cause or symptom of Parkinsons disease.
- Head trauma: Traumatic brain injury increases risk of Parkinsons, even years later.
We Have Choices About How This Condition Plays Out
In fact, medical scientists have proved that many people with a genetic disposition to this never get it.
While others with no genetic disposition at all still get full-on Parkinsons that ravages their mental health quickly and remorselessly.
Its not genetics. Its a basic illness with recognized causes.
Remember: the substantia nigra produces dopamine. Its the loss of substantia nigra nerve cells that leads to the loss of dopamine.
And that loss of dopamine leads to Parkinsons Disease.
So the big question is:
Why on earth is the substantia nigra losing those dopamine-producing cells in the first place?
I was shocked to discover that we already know why were losing those priceless, life-giving substantia nigra cells.
Yet still do almost nothing about it
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Other Medicines Used For Pd
- Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors are relatively new medicines. They include , and opicapone. These help to stop the breakdown of levodopa by the body, so more of each dose of levodopa can get into the brain to work. A COMT inhibitor is sometimes advised in addition to levodopa when symptoms are not well controlled by levodopa alone.
- Other medicines are sometimes used to help relieve symptoms. They have various effects which try to correct the chemical imbalance in the brain. They include beta-blockers, amantadine and anticholinergic medicines. One of these may be tried when symptoms are mild. However, you are likely to need levodopa or a dopamine agonist at some point.
Various things may influence which medicine is advised. For example, your age, severity of symptoms, how well your symptoms respond to treatment, if side-effects develop, other medicines that you may take, etc. Your specialist will advise on the best medicine for you to take. Whatever medicine or medicines you are prescribed, read the leaflet in the medicine packet for a full list of possible side-effects. Mention to your doctor if you develop a troublesome side-effect. A modification of the dose, dose schedule, or the type of medication, may be possible to help keep side-effects to a minimum.
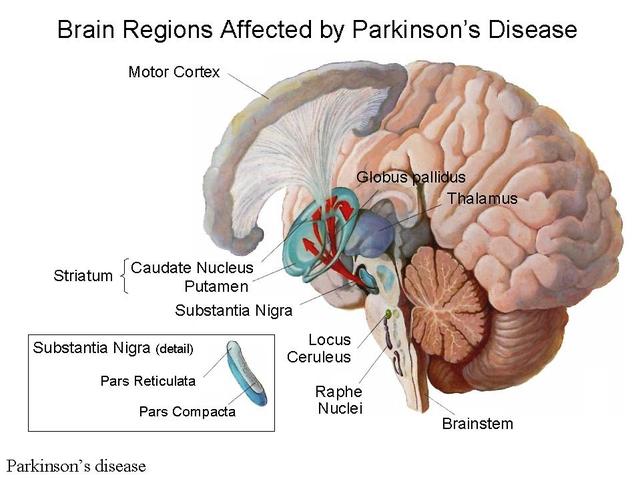
When People Talk About Parkinsons They May Mention The Effects It Has On The Substantia Nigra But Did You Know That There Are Other Areas Of The Brain That Are Affected By The Condition
Parkinsons is a condition that causes the gradual loss of the dopamine-producing brain cells of the substantia nigra an area of the brain located just above where the spinal cord meets the midbrain. It is these cells that produce and release the neurotransmitter dopamine, which has a key role in turning thought about movement into action.
While this definition of the condition is useful to briefly explain Parkinsons, the whole story is somewhat more complex. Over the last 30 years, it has become accepted that Parkinsons also causes a number of non-motor symptoms, such as changes in sleep, smell and even the way we think, which likely involve other areas of the brain.
Now scientists are looking at the broader effects of the condition on the brain in an attempt to better understand why people experience different symptoms. The finding could lead us to new treatments that tackle more than just the motor symptoms of the condition.
Importance For Parkinsons Therapy
The researchers identified two areas of the GPe and were able to relate these areas to motor skills and cognitive skills in the mice.
Dr. Byungkook Lim is an associate professor in the Neurobiology Section of the Division of Biological Sciences at UC San Diego and corresponding author of the study.
He explains, our work demonstrates that the distinct neural circuitries in the basal ganglia are differentially involved in the motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinsonian-like behaviors that occur at different stages of the disease.
This suggests that evaluation of the detailed circuit mechanisms is needed to fully understand the changes in brain during the progression of and could provide better therapeutic strategies for the treatment of .
Dr. Byungkook Lim
The fact that specific neurons could be linked to particular changes in the brain regions of the mice means that it may be possible to develop new treatments for the symptoms of Parkinsons.
In Dr. Lims words, elective manipulation of specific changes can rescue one type of symptom without affecting other symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
The Heart Of The Matter: Cardiovascular Effects Of Parkinsons Disease
It has long been understood that Parkinsons disease does not just cause movement symptoms, but also causes a litany of non-motor symptoms with effects throughout the body. One of the organ systems that is affected is the cardiac system, encompassing the heart, as well as the major and minor blood vessels. I received this topic as a suggestion from a blog reader and we will be discussing this important issue today. Please feel free to .
Parkinsons Diseaseassociated Pathological Changes In The Cerebellum
Data Processing Of Nmr Spectra And Multivariate Pattern Recognition
NMR spectra were reduced to integrated regions with a width of 0.01 ppm corresponding to the region of ? 100.5. The regions of 4.75.2 ppm was removed to eliminate artifacts related to the residual water resonance. The remaining spectral segments were then normalized to the total sum of the spectral intensity to partially compensate for differences in the concentration of many metabolites in the samples. Before multivariate data analysis, the integral values were mean-centered and Pareto-scaled . NMR data sets were imported into SIMCA-P + 12.0 software for multivariate statistical analysis, including principal component analysis discriminant analysis and partial least squares-discriminant analysis . And another data reduced to integrated regions with a width of 0.0015 ppm width corresponding to the region of ? 100.5 were used for quantitative analysis.
Sedation And Regional Anesthesia For Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinsons Disease
Dilek Yazicioglu
1Ankara Diskapi Yildirim Beyazit Teaching and Research Hospital, Irfan Bastug Caddesi, Dskap, 06330 Ankara, Turkey
Academic Editor:
Abstract
Objective. To present the conscious sedation and the regional anesthesia technique, consisting of scalp block and superficial cervical plexus block, used in our institution for patients undergoing deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinsons disease . Methods. The study included 26 consecutive patients. A standardized anesthesia protocol was used and clinical data were collected prospectively. Results. Conscious sedation and regional anesthesia were used in all cases. The dexmedetomidine loading dose was 1gkg1 and mean infusion rate was 0.26gkg1h1 . Propofol was used to facilitate regional anesthesia. Mean propofol dose was 1.68mgkg . Scalp block and superficial cervical plexus block were used for regional anesthesia. Anesthesia related complications were minor. Postoperative pain was evaluated; mean visual analog scale pain scores were 0 at the postoperative 1st and 6th hours and 4 at the 12th and 24th hours. Values are mean . . Dexmedetomidine sedation along with scalp block and SCPB provides good surgical conditions and pain relief and does not interfere with neurophysiologic testing during DBS for PD. During DBS the SCPB may be beneficial for patients with osteoarthritic cervical pain. This trial is registered with Clinical Trials Identifier .
1. Introduction
Factors That May Make Your Symptoms Worse:
- Failure to get medications at specific times and coordinated with meals.
- Certain dopamine blocking drugs can worsen symptoms. If absolutely necessary because of hallucinations or behavior, only quetiapine or clozapine should be used.
- Anxiety, stress, and sleep deprivation
- Urinary tract, lung, or other infections
- Provide Advance Directives: Power of attorney for health care and living will. Choose an advocate who can ask questions and act as your spokesperson. Make sure this person is aware of your medical wishes so he or she can assist in speaking for you if needed.
Drugs And Medication Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
A number of different drugs can be used to treat Parkinsons.
Levodopa
Levodopa is the most common treatment for Parkinsons. It helps to replenish dopamine.
About 75 percent of cases respond to levodopa, but not all symptoms are improved. Levodopa is generally given with carbidopa.
Carbidopa delays the breakdown of levodopa which in turn increases the availability of levodopa at the blood-brain barrier.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists can imitate the action of dopamine in the brain. Theyre less effective than levodopa, but they can be useful as bridge medications when levodopa is less effective.
Drugs in this class include bromocriptine, pramipexole, and ropinirole.
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics are used to block the parasympathetic nervous system. They can help with rigidity.
Benztropine and trihexyphenidyl are anticholinergics used to treat Parkinsons.
Amantadine
Amantadine can be used along with carbidopa-levodopa. Its a glutamate-blocking drug . It offers short-term relief for the involuntary movements that can be a side effect of levodopa.
COMT inhibitors
Catechol O-methyltransferase inhibitors prolong the effect of levodopa. Entacapone and tolcapone are examples of COMT inhibitors.
Tolcapone can cause liver damage. Its usually saved for people who do not respond to other therapies.
Ectacapone does not cause liver damage.
Stalevo is a drug that combines ectacapone and carbidopa-levodopa in one pill.
MAO-B inhibitors
Who Develops Parkinson’s Disease
PD mainly develops in people over the age of 50. It becomes more common with increasing age. About 5 in 1,000 people in their 60s and about 40 in 1,000 people in their 80s have PD. It affects men and women but is a little more common in men. Rarely, it develops in people under the age of 50.
PD is not usually inherited and it can affect anyone. However, one type of PD, which appears in the small number of people who develop it before the age of 50, may be linked to inherited factors. Several family members may be affected.
Caring For Someone With Parkinsons
Practice patience and understanding when dealing with Parkinsons. You may be very frustrated and challenged as a caregiver, but those with Parkinsons are just as frustrated. Their physical and mental conditions can be debilitating, depressing, and humiliating.
Diet and nutrition can have a huge impact on the health and comfort of a Parkinson patient. Eating well, getting more rest, sleeping well, fresh air, and exercise can make a difference. Getting the right medication and complementary therapies is also important.
As Parkinsons impacts a patients motor skills, modifications to the living environment may have to be made to accommodate wheelchairs and limited mobility issues. Professional in-home assistance for Parkinsons can allow Parkinson patients to remain independent and can enhance quality of life.
Most importantly, seek help and support from family, friends, and caregiving support groups. Take advantage of the resources in your community. Shouldering all the burden can take a toll on a caregiver.
Take care of yourself or you wont be able to take care of your loved one. Follow the preventive advice provided above for yourself as well, and take deep breaths!
Resources
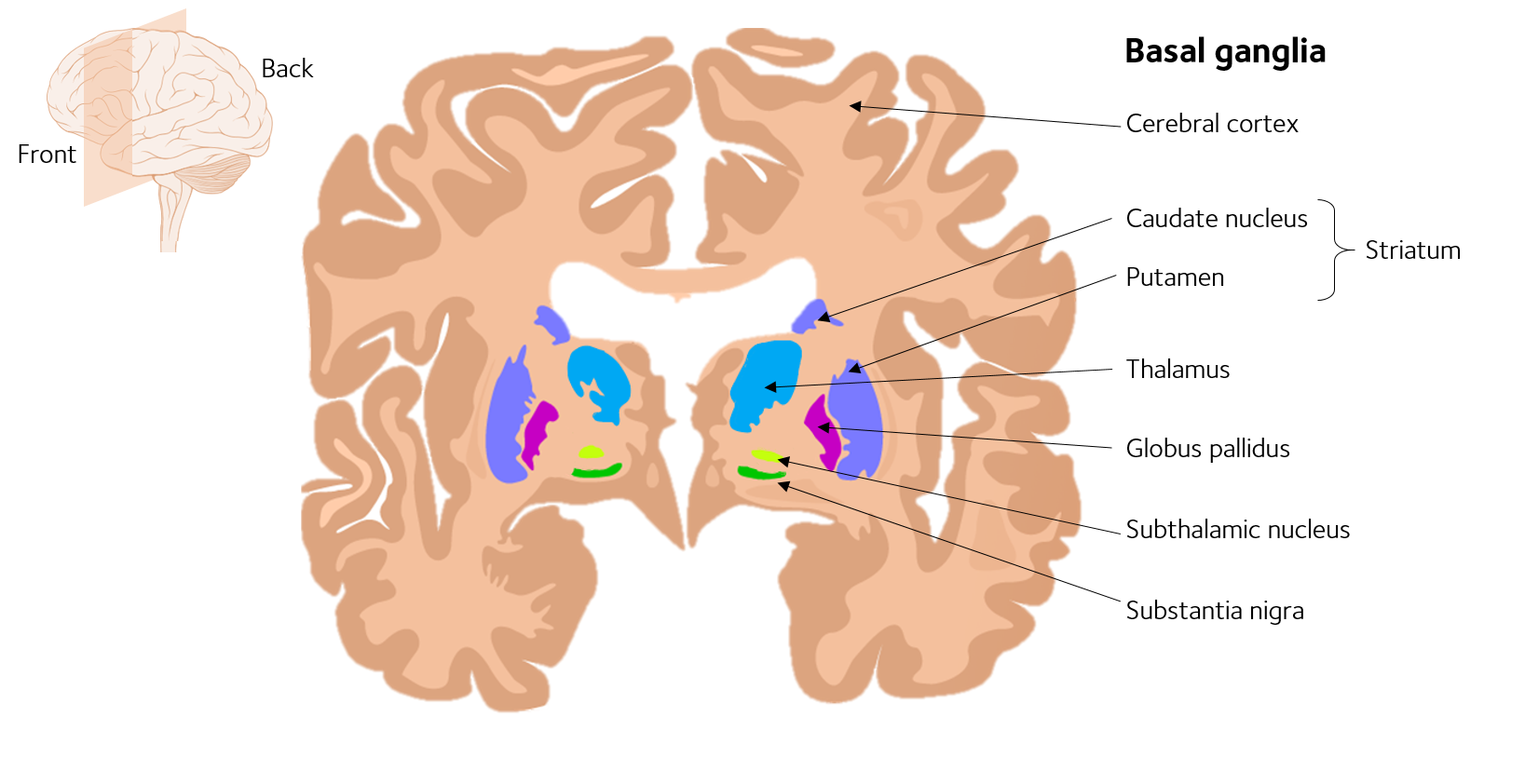
What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain. The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia; and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus .
For an illustration of the subthalamic nucleus, see the image below.
References
Hauser RA, Grosset DG. FP-CIT SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes. J Neuroimaging. 2011 Mar 16. .
Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J. Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011 Jun. 26 Suppl 1:S1-58. .
Anderson P. More Evidence Links Pesticides, Solvents, With Parkinson’s. Medscape Medical News. Available at . Accessed: June 11, 2013.
Pezzoli G, Cereda E. Exposure to pesticides or solvents and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2013 May 28. 80:2035-41. .
I Feel Wonderful And Theres A Reason Why
Actually, there are three fantastic reasons:
First and foremost: I have tackled the loss of dopamine by working on the underlying cause of that loss.
We know that cell loss in the substantia nigra is the direct cause of dopamine loss. I address that cell loss in gentle but powerful ways and so protect dopamine levels.
Second, I increase dopamine production in my brain using non-drug methods. Increasing dopamine fights this condition head-on leading to wonderfully quick improvements.
Third, I have taken each of the symptoms of my illness stiffness, shaking, anxiety and so on and addressed them directly. Ive enacted specific daily habits that make those symptoms reduce to almost nothing.
Offline Analysis Of Subthalamic Nucleus Spike Firing
Raw spike recordings from the implanted trajectories were analyzed using custom-written scripts in MATLAB R2014b . Raw recordings were visually inspected by a neurophysiologist blind to patient anesthesia group to exclude artifacts . Background spiking activity was estimated using the normalized root mean square of each subthalamic nucleus recording. The root mean square value of each recording was also normalized by the root mean square value of the baseline presubthalamic nucleus recording of each tract to control for factors such as electrode impedance and electrical noise that vary between subjects.
Single-neuron spike detection was performed using the voltage threshold method. Putative single neurons were identified offline using principal component analysis and the presence of a central trough in the autocorrelogram . Isolation of the spike train was graded by evaluating the fraction of spikes within the refractory period of 1.5 ms out of the total number of spikes in the spike train, and only spike trains with a fraction of less than 1% were processed. Spikes degraded by obvious cardiobalistic or other artefacts were excluded.
Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons. When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.
