Does The Pet Scan Have Risks
Because radiation is part of a PET scan, there is always a small risk that cells or tissue may have received some damage following the procedure. However, the radiation levels from the tracer that is sent throughout the body are very low.
In addition, following the scan, patients may find that their arm is a little bit sore or that they experience redness where the IV was placed in the arm.
How Soon Will I Have My Pet Scan Results
PET scans are usually more extensive and detailed than similar tests that are available. Despite this, test results can usually be given within one to two days after the scan.
Show Sources
National Parkinson Foundation: “Should I get a DaT scan or PET scan to confirm my diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease?”
Radiology-Info.org: “PET Scan and Parkinson Disease.”
University of Chicago Medical Center: “How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed?”
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Its a good idea to ask questions as you and your doctor discuss a treatment. Asking questions can help you make sure you understand your condition and the benefits of treatment. Here are some sample questions to ask your doctor:
- Is it possible something other than Parkinsons is causing my symptoms?
- Do I need additional tests?
- How will my condition progress?
- What can I expect as my condition progresses?
- How will Parkinsons affect my other medical conditions?
- What treatments are available?
- Which treatments are best for me?
- How will treatments help my current symptoms?
- Will treatment slow down the progression of Parkinsons?
- What side effects do your recommended treatments have?
- What happens if these treatments dont help?
- Can you recommend any resources or educational material for me?
Read Also: What Is Bradykinesia In Parkinson’s
Mri Brain Scans Detect People With Early Parkinsons
Oxford University researchers have developed a simple and quick MRI technique that offers promise for early diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
The new MRI approach can detect people who have early-stage Parkinsons disease with 85% accuracy, according to research published in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinsons disease in the vast majority of cases, says Dr Clare Mackay of the Department of Psychiatry at Oxford University, one of the joint lead researchers. We are excited that this MRI technique might prove to be a good marker for the earliest signs of Parkinsons. The results are very promising.
Claire Bale, research communications manager at Parkinsons UK, which funded the work, explains: This new research takes us one step closer to diagnosing Parkinsons at a much earlier stage one of the biggest challenges facing research into the condition. By using a new, simple scanning technique the team at Oxford University have been able to study levels of activity in the brain which may suggest that Parkinsons is present. One person every hour is diagnosed with Parkinsons in the UK, and we hope that the researchers are able to continue to refine their test so that it can one day be part of clinical practice.
We think that our MRI test will be relevant for diagnosis of Parkinsons
Dr Michele Hu
Imaging And Differential Diagnosis
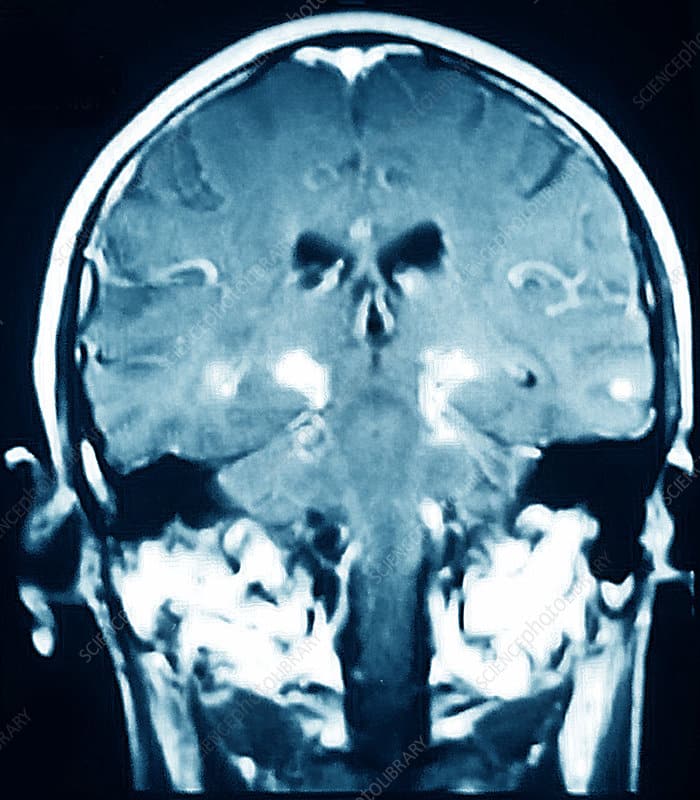
The core clinical signs of PD include resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Most patients also experience nonmotor symptoms such as cognitive and emotional changes , dysautonomia, sleep disorders, and sensory disturbances. Many experience prodromal nonmotor symptoms such as anosmia, depression, constipation, and REM sleep behavior. Clinical subtypes of the disease have been identified, including tremor dominant and postural instability gait difficulty . Atypical features may be clues that there are other etiologies that can be differentiated with imaging studies.1 Structural brain imaging is frequently ordered to investigate these cases. In addition, SPECT imaging with DaT may be useful to confirm central nervous system dopamine signaling deficiency in select cases . On DaT scans, normal radiotracer uptake in the striatum forms 2 crescent-shaped regions of activity, mirrored around the median plane. In contrast, in PD, there is asymmetrically decreased activity in the putamen, often with preserved uptake in the caudate nucleus.2,3 A DaT scan is FDA approved for differentiating essential tremor from PD, and is also frequently useful for differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from PD.
Cerebrovascular Disease
Corticobasal Degeneration
Multiple System Atrophy
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Neoplasms
Neurotoxicity
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s And Keto Diet
What Should I Expect During The Mri
As the MRI scan begins, you will hear the equipment making a variety of banging, clanging and muffled thumping sound that will last for several minutes. None of them are anything other than annoying. Other than the sound, you should experience no unusual sensations during the scanning.
Certain MRI exams require an injection of a contrast material. This helps identify certain anatomic structures on the scan images.
Please feel free to ask questions. Tell the technologist or the doctor if you have any concerns.
Preparing For A Parkinsons Mri
A Parkinsons MRI is completely painless, but you do have to lie still while being scanned. Some patients feel claustrophobic in this situation. If youre worried about that, talk with your doctor about the possibility of having an anti-anxiety medication before the procedure.
On the day of the appointment, follow any instructions provided to you by your doctor. Remove metal jewelry and dont wear make-up as that can also have metal in it. If you are in the advanced stages of Parkinsons or if you are taking a sedative, you should arrange transportation to and from the appointment.
Don’t Miss: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging takes advantage of abundant hydrogen atoms and strong magnetic fields to image brain tissues non-invasively. Conventional structural MRI uses distinct pulse sequences to obtain T1-weighted , T2-weighted , proton-density weighted, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and/or susceptibility-weighted scans. SW imaging is sensitive to magnetic inhomogeneity effects, particularly due to iron accumulation, hemorrhages, and/or slow venous blood flow, allowing for an enhanced tissue contrast. These images can be analyzed selectively or in combination to obtain volumes of brain structures, regional cortical thickness, and to identify regional tissue abnormalities. Such structural profiles, including patterns and rates of atrophy, are important areas of research from a biomarker viewpoint.
Structural MRI profiles of Parkinsons disease
Structural MRI profiles of Lewy body spectrum disorders
Structural MRI profiles of multiple system atrophy
Fig. 1
Brain Mr Contribution To The Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinsonian Syndromes: An Update
Giovanni Rizzo
1IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche, Bellaria Hospital, Bologna, Italy
2Neurology Unit, Department of Biomedical and Neuromotor Sciences, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy
3Functional MR Unit, Policlinico S.Orsola-Malpighi, Bologna, Italy
4Department of Biomedical and Neuromotor Sciences, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy
5Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Pia Fondazione di Culto e Religione Card. G. Panico, Tricase, Italy
6Department of Neurology, Kings College NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
7Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Lewisham and Greenwich NHS Trust, London, UK
8Department of Neurology and Health Science Research, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
9Department of Clinical Research in Neurology, University of Bari, Pia Fondazione di Culto e Religione Card. G. Panico, Tricase, Italy
10Department of Basic Medical Science, Neuroscience and Sense Organs, University of Bari, Bari, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
Many putative biomarkers derived from genetic-epigenetic, neurophysiological, and imaging techniques have been evaluated in order to determine their diagnostic accuracy in discriminating PD from APSs . Brain magnetic resonance represents one of the best putative sources of biomarkers in this field, because of its relative feasibility, the absence of invasiveness, and the availability in different clinical settings.
2. Qualitative Brain MRI
Recommended Reading: How Long Between Stages Of Parkinson’s
Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease: Motor Symptoms
The clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons disease is based on the presence of characteristic motor symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and resting tremor but neuropathology is still considered the gold standard for definite diagnosis. Differentiating PD from other movement disorders can be challenging throughout the disease course, because signs and symptoms often overlap. Indeed, neuropathology studies reveal that clinical diagnosis of PD can be confirmed with an accuracy of about 75%. Good response to levodopa is often used to support the diagnosis of PD. However, cases of pathologically proven PD with poor response to levodopa have also been reported.
Misdiagnosis of PD can occur for several reasons. In a community-based study of patients taking antiparkinsonian medication, the most common misdiagnosis were essential tremor, Alzheimers disease, and vascular parkinsonism. In addition, many of the prominent features of PD may also occur as a result of normal aging or from comorbid and multifactorial medical conditions .
R. Savica, G. Logroscino, in, 2016
A Multidisciplinary Approach To Care
Parkinsons disease is a condition that can affect different aspects of your life, including mobility, mood, and sleep. We work with a highly trained and dedicated team of specialists that are all focused on helping you live better with Parkinsons disease.
- A Nurse can help your physician provide you the best care and address concerns about medications and other Parkinsons-related symptoms.
- A Physical Therapist can evaluate and treat you to optimize your mobility, physical activity, and safety.
- An Occupational Therapist can help you stay active and independent in your daily activities.
- A Speech Therapist can evaluate you and provide recommendations and treatment if Parkinsons is affecting your speech or swallowing.
- A Social Worker can answer your questions and provide counseling about life transitions, options if you need help with your care, and financial and work-related issues.
- A Spiritual Care Provider can offer support and facilitate positive spiritual coping if you are struggling with your illness.
You have changed my life. I started using the MGH PD Exercise videos on New Years Day and have exercised every day since then even when I got my first COVID vaccine jab and had a very sore arm. Now, I actually look forward to my exercise sessions with you I am stronger, more flexible, have better stamina and am healthier both physically and emotionally because of your work.
- Medication-induced movement disorders
You May Like: Sleep Medications For Parkinson’s Patients
When People Talk About Parkinsons They May Mention The Effects It Has On The Substantia Nigra But Did You Know That There Are Other Areas Of The Brain That Are Affected By The Condition
Parkinsons is a condition that causes the gradual loss of the dopamine-producing brain cells of the substantia nigra an area of the brain located just above where the spinal cord meets the midbrain. It is these cells that produce and release the neurotransmitter dopamine, which has a key role in turning thought about movement into action.
While this definition of the condition is useful to briefly explain Parkinsons, the whole story is somewhat more complex. Over the last 30 years, it has become accepted that Parkinsons also causes a number of non-motor symptoms, such as changes in sleep, smell and even the way we think, which likely involve other areas of the brain.
Now scientists are looking at the broader effects of the condition on the brain in an attempt to better understand why people experience different symptoms. The finding could lead us to new treatments that tackle more than just the motor symptoms of the condition.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Tremor
How A Diagnosis Is Made
The bedside examination by a neurologist remains the first and most important diagnostic tool for Parkinsons disease . Researchers are working to develop a standard biological marker such as a blood test or an imaging scan that is sensitive and specific for Parkinsons disease.
A neurologist will make the diagnosis based on:
- A detailed history of symptoms, medical problems, current and past medications. Certain medical conditions, as well as some medications, can cause symptoms similar to Parkinsons.
- A detailed neurological examination during which a neurologist will ask you to perform tasks to assess the agility of arms and legs, muscle tone, gait and balance, to see if:
- Expression and speech are animated.
- Tremor can be observed in your extremities at rest or in action.
- There is stiffness in extremities or neck.
- You can maintain your balance and examine your posture.
You May Like: Brain Surgery For Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsons And How Can Mri Help
More than ten million people are living with Parkinsons disease worldwide, with about one million cases expected to be in the United States by 2020.1 This is more than the number of people with multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrigs disease combined.1 With the rising prevalence of Parkinsons disease, its important to understand the signs and symptoms of the disease. Likewise, physicians and radiology departments may need to know what role magnetic resonance imaging may play.
Dont Miss: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Mri In Parkinsons Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
Read Also: Caring For Someone With Parkinson’s Dementia
Is The Imaging Metric Appropriate For The Question Being Asked
Neuroanatomy Relevant to Parkinsons Disease
A. Braak staging of -synuclein pathology. At death, PD patients exhibit the following stages of -Syn pathology: stage I olfactory bulb only , Stage IIa brainstem predominant , stage IIb limbic predominant , stage III brainstem and limbic and stage IV neocortical . While not all patients with pathology will exhibit clinical symptoms , the progression of neuropathology generally corresponds to the progression of both motor and non-motor symptoms . B. The SN is subdivided into the ventral pars reticulata and the dorsal pars compacta , the latter is composed of dopaminergic neurons. The SNc is further divided into the dorsal and ventral tier, with the loss of dopaminergic neurons occurring first in the caudal and ventrolateral tier . Within A9, there are five nigrosomes , with N1 exhibiting the earliest loss of dopaminergic neurons . Dopaminergic neuronal loss typically spreads to neighboring groups from the N1 in PD . C. Fronto-subcortical loops comprise the motor, associative, and limbic domains, which respectively transit through the posterior, anterior, and ventral striatum, thus segregated functionally and anatomically. GPe = globus pallidus externa. GPi = globus pallidus interna. STN = subthalamic nucleus. SNc = substantia nigra pars compacta. SNr = substantia nigra pars reticulata. Adapted with permission from: .
Also Check: How Long Does Parkinsons Last
Diffusion Mri For The Study Of Parkinsons Disease
Diffusion changes in PD has been the subject of many studies over the years. They are generally based on two measures accounting for mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy . These measures describe the diffusion of water molecules in the brain, MD accounts for the their overall displacement and FA indicates the orientation of diffusion. The meta-analysis proposed by Cochrane and Ebmeier, 2013 put into evidence important discrepancies between the diffusion scans of PD patients across studies between 1946 and 2012, notably regarding acquisition parameters, analysis methods and the introduction of medication. Most studies focused on the SN as Region Of Interest and often reported FA reductions in different segments with a slight tendency towards the caudal segment. However, no significant association was detected between disease severity and FA values. The first studies were carried out on small cohorts and presented opposing results. We can notably cite the work of Schwarz et al., 2013 where, in contrast to the work of Du et al., 2011, no differences were found in SN for FA values between PD patients and controls but a significant increase of MD in the SN was reported.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Double Vision
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease In Spanish
When Brain Mri Is Recommended To Help Diagnose Parkinsonism
Differentiating atypical parkinsonism from Parkinsons disease can be a challenge in patients presenting with symptoms in early disease stages. A diagnosis cannot be made from a brain magnetic resonance imaging scan, but brain MRI can be of added value when there is uncertainty about the clinical diagnosis.
The appropriateness of and the added diagnostic value of a brain MRI scan in the work-up of parkinsonism is described in a newly published article in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease. Lead author Frederick J.A. Meijer, MD, PhD, a neuroradiologist in the department of radiology and nuclear medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, offers advice on the scanning protocol to use, and also discusses its diagnostic value with respect to specific abnormalities that can be seen.
The authors of the article, who also include neurologists from the Radboud University Medical Center and Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior, conducted a 3-year long prospective study on the contribution of routine brain MRI to the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism.1 Based on this research, the authors refuted clinical guidelines recommending standard use of cerebral MRI for all patients presenting with parkinsonism.
3T brain MRI including DTI tractography in a patient presenting with parkinsonism.

