Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Other PD medications work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. One such class is the MAO-B inhibitors. As is discussed above, MAO-B is one of the main enzymes involved in the breakdown of dopamine, and reducing the activity of this enzyme therefore results in increased dopaminergic activity within the striatum, mediated by endogenous dopamine . Their use relieves motor symptoms in PD patients, and as with dopamine agonists they may be used as an initial treatment option, to delay the need for levodopa therapy, to reduce the risk of levodopa-induced motor complications . While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose.
Dyskinesia Current And New Treatment Strategies
The occurrence of dyskinesia is still common in PD notably in those individuals treated with L-dopa . However, disabling troublesome dyskinesia does not appear to be as prevalent as in previous eras and this probably reflects the more cautious treatment of early PD with an emphasis on avoiding dyskinesia induction. The exception is those individuals with a young onset variant of PD who are highly vulnerable to the early occurrence of motor complications . In contrast, non-troublesome dyskinesia remains a frequent side-effect of L-dopa therapy in the PD population but often does not require treatment while other components of motor function are adequately maintained. A lessening of the impact of dyskinesia is also a reflection of the earlier detection and treatment of PD in general as the severity or duration of disease as judged by dopaminergic nigral cell loss, is a primary factor in determining the degree of exposure to L-dopa needed to initiate involuntary movements . However, the impact of dyskinesia is in its inevitable expression by all forms of dopaminergic medication, once involuntary movements are established.
Table 1 Examples of existing and novel approaches to the treatment of dyskinesia
Common Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Recommended Reading: How Can You Diagnose Parkinson Disease
Dopaminergic Input And Organizational Features Of The Dorsal And Lateral Striatum
As reviewed above, it is generally accepted that dysfunction in PD stems from the degeneration of SNc neurons , which leads to motor dysfunction and the loss of VTA neurons , which leads to behavioral dysregulation, including demotivation, anhedonia, and depression within PD . While both pathways have been studied extensively across an array of conditions and pathologies, the modulatory mechanisms of the nigrostriatal pathway neurons have been fairly well described while the varied mechanisms and roles of VTA efferents continue to be elucidated. Within the nigrostriatal pathway, GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the dorsal/lateral striatum receive excitatory glutamatergic signals that can be modulated via dopaminergic inputs originating from the SNc. MSNs are moderately sized cells with large, multi-structured dendritic arbors that constitute a staggering 95% of all postsynaptic nigrostriatal neurons . Local circuit interneurons of the dorsal striatum are also actively involved in regulating MSN activity and can be subdivided into cholinergic interneurons and aspiny GABAergic interneurons known as low-threshold, fast-spiking neurons . Striatal cholinergic and MSNs express several neurotransmitter receptors including the -aminobutyric acid , glutamate, DA, adenosine, serotonin, opioids, and substance P receptors .
What Are Dopaminergic Antiparkinsonism Agents
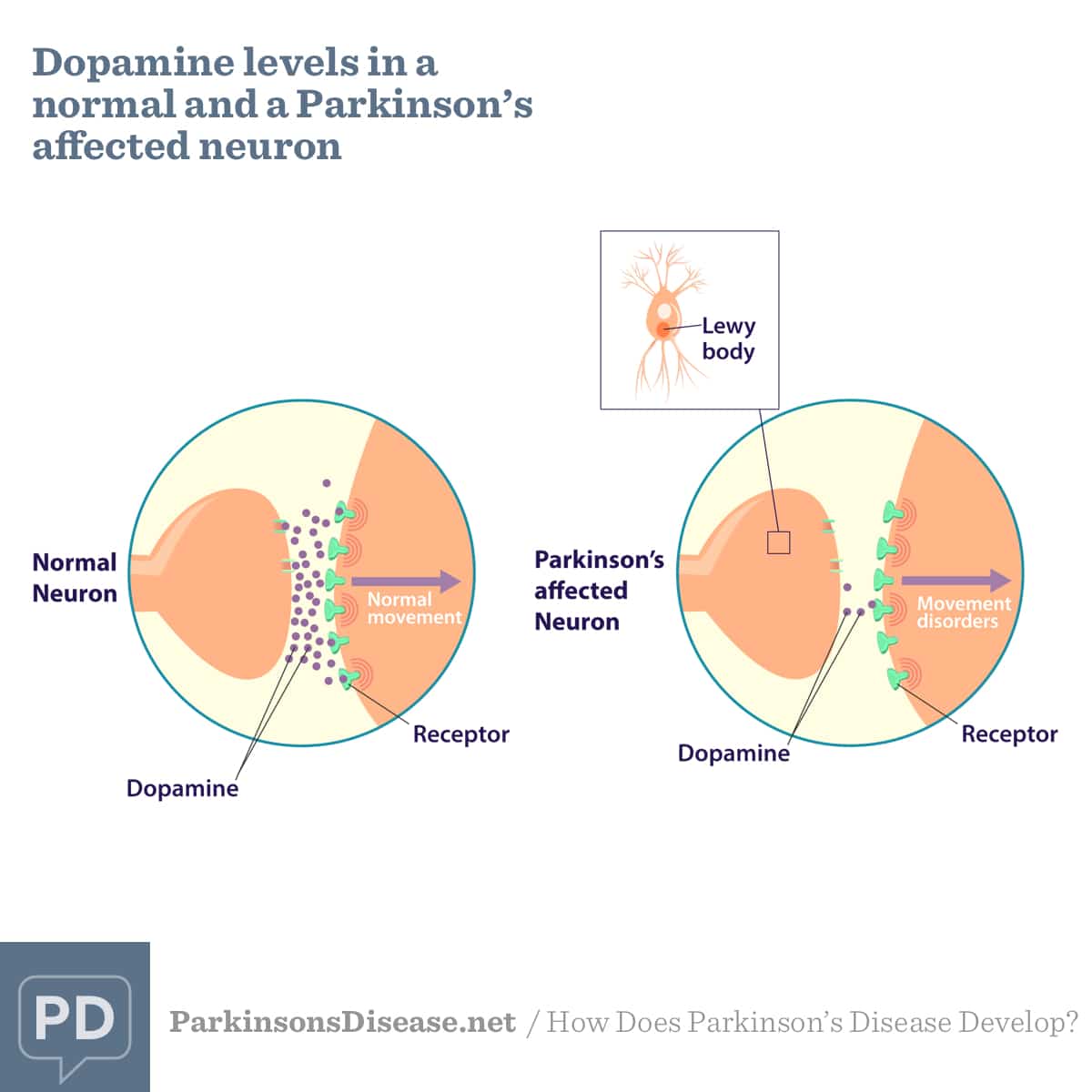
Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents aim to replace dopamine or prevent the degradation of dopamine.Antiparkinson drugs that aim to replace dopamine in the central nervous system, either release dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors, to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. Dopamine receptor agonists bind to dopamine receptors and mimic the action of dopamine.Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine from being broken down. Antiparkinson agents are used to treat Parkinsons disease, which is a degenerative disorder of movement that occurs due to dopamine deficiency in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Blood Test To Check For Parkinson’s Disease
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinsons disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patients unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinsons disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinsons disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
References
Understanding Dopamine And Parkinsons Disease
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for sending signals in the brain to coordinate movement.
- In Parkinsons disease, the cells responsible for making dopamine die off, causing movement problems and other symptoms.
- Treatments are available to increase levels of dopamine in the brain and alleviate symptoms.
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by low levels of dopamine and improper signaling in the brain, which leads to movement symptoms. Parkinsonism is a set of movement disorders characterized by tremors, muscle stiffness, coordination issues, and slowed movements .
Parkinsons is treated with medications that increase the levels of dopamine in the brain, called dopaminergic treatments. Over time, these medications may cause side effects like dyskinesia that can interfere with daily life.
You May Like: How To Help Parkinson’s Disease
How Do Dopamine Agonists Work
Symptoms of PD, especially motor symptoms, are related to a depletion of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is the neurotransmitter that is responsible for producing smooth, purposeful movement. Giving dopamine as a treatment is ineffective because it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.3
Dopamine agonists mimic dopamine. They bind to proteins on neurons called dopamine receptors. Dopamine agonists can be designed to bind to and activate specific dopamine receptors on neurons. This provides relief from symptoms of PD, especially motor symptoms like:3
- Requip® XL extended-release tablets
- Kynmobi® sublingual film
People with PD may be prescribed different dosages at different points in their disease to manage their symptoms.
New Medications For Off Time
A number of new medications approved recently are designed to reduce OFF time. These medications fall into two major categories:
- Medications that lengthen the effect of a carbidopa/levodopa dose
- Medications that are used as needed if medication effects wear off
Well give specific examples below. In general, new medications that extend the length of a carbidopa/levodopa dose are used if OFF time is somewhat predictable and occurs prior to next dose. New medications that are used as needed are most beneficial when OFF time is not predictable.
New medications that lengthen the effect of a dose of carbidopa/levodopa
- Istradefylline is an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist which was approved in the US in 2019 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for treatment of OFF time in PD. Unlike many of the other medications, it has a novel mechanism of action and is the first medication in its class to be approved for PD. It acts on the adenosine receptor, which modulates the dopaminergic system, but is not directly dopaminergic. The drug was developed in Japan and underwent clinical trials both in Japan and in the US.
- Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor that is taken once a day. It was approved in the US in 2020 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for motor fluctuations.
New formulations of levodopa designed to be used as needed if medication effects wear off
Other medications used as needed if medication effects wear off
Don’t Miss: Do You Have Pain With Parkinson’s Disease
What Should I Do If I Forget A Dose
Take the missed dose of the regular tablet, orally disintegrating tablet, extended-release tablet, or extended-release capsule as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
If you are using levodopa and carbidopa enteral infusion and will be disconnecting the infusion pump for a short time , other than the normal nightly disconnection, ask your doctor if you should use an extra dose before you disconnect the pump. If the infusion pump will be disconnected for longer than 2 hours, call your doctor you probably will be advised to take levodopa and carbidopa by mouth while you are not using the suspension.
Dopamine Agonist Drugs: An Introduction
Dopamine agonist drugs trick your brain into thinking they are dopamine. This means they can mimic the way dopamine works which can reduce your symptoms.
Dopamine agonists are typically prescribed in the earlier stages of Parkinsons but everyone is different and you could be prescribed them at any time if it is right for you.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully. The dose is gradually increased until you and your specialist team are happy that your symptoms are under control.
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Foot Cramps
What Are Common Dopamine Agonists And What Do They Treat
There are two main categories of DA medications, ergoline and non-ergoline.
The first generation are ergoline type and are used less often today since they have some serious heart- and lung-related risks linked with their use. This is mainly because the older medications attach to any available dopamine receptors in the body and are not selective.
What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinsons Drugs
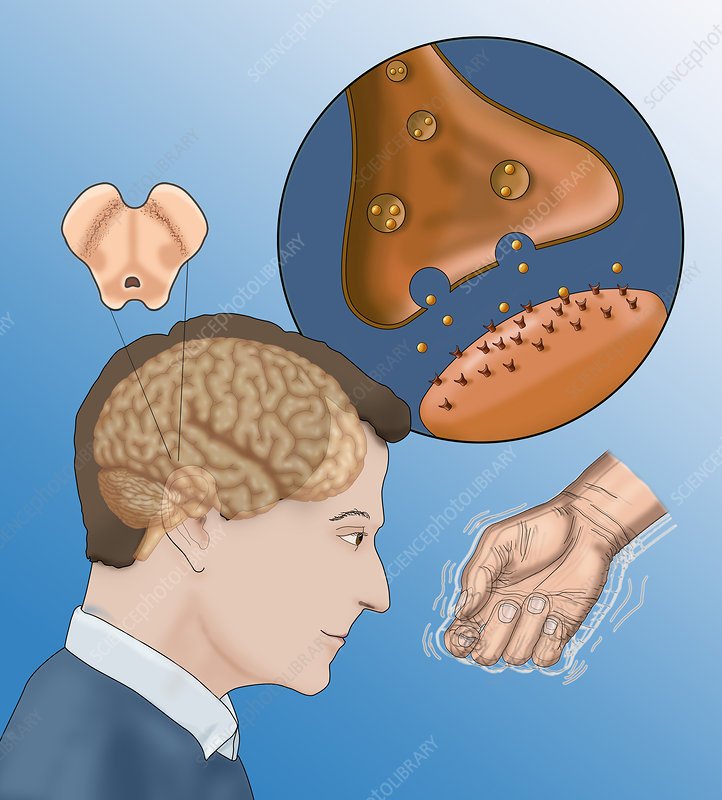
The most common reactions include nausea, vomiting, dizziness , sleepiness and visual hallucinations.
In the last few years, levodopa and dopamine agonists in particular have been associated with the emergence of behavioral changes such as impulse control disorders. These are characterized by failure to resist an impulse to perform certain actions.
Impulse control disorders include a range of behaviors such as compulsive gambling or shopping, hypersexuality, binge eating, addiction to the Internet or to other recreational activities. These activities are often pleasant in the moment, but over time may become harmful to you or to others. If you are experiencing these behaviours, tell your neurologist/doctor. Often the medication can be adjusted which can reduce or control the behaviour.
Care partners can play an important role in helping to identify when these behaviours occur. If you are a care partner, tell the person if you have noticed a change in his/her behaviour or personality and encourage him/him/her to speak with the doctor immediately so medication can be adjusted.
Recommended Reading: When Did Michael J Fox Get Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsonâs disease can include:
- Walking slowly leaning forward with small steps
- Memory problems
People with Parkinsonâs disease often show minor symptoms at first. The symptoms may begin on only one side of the body. Symptoms often become more pronounced over time.
Parkinsonâs disease itself isnât fatal, but it has no cure. Symptoms like frequent falling can lead to injury and death.
Are There Side Effects From Dopamine Agonists
Side effects from DA medications can vary depending on the medication , dose, how long the medication is used, and individual traits.
If youre experiencing side effects which are bothersome, dont stop taking the medication on your own. Talk to your doctor about treatment options available to help improve your condition. This includes non-medication options too.
Side effects might be mild and go away after a few days or they may be important enough to need either a dose change or to stop the medication. DA medications can cause withdrawal symptoms or worsening of the condition if theyre suddenly stopped.
This is not a full list of side effects. Ask your pharmacist or doctor about specific concerns related to your medication.
side effects
Side effects for dopamine agonists include:
- heart valve problems, heart failure
- trouble with memory or concentration
- movement-related problems
Also Check: What Are The Very Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Where Is It Made In The Brain
Dopamine is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus.1 You may not remember these complicated names. That is fine! It is probably more important to know what these areas of the brain do:1,4-6
- The substantia nigra is part of the brain known as the basal ganglia. This part of the brain is responsible for making movement possible.
- The ventral tegmental area is the part of the brain that is responsible for reward and reinforcement.
- The hypothalamus has many functions. It is responsible for sleep, appetite, body temperature, and sexual arousal, among other things. The hypothalamus helps control the autonomic nervous system.
Recommended Reading: Questions About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease: Why Dopamine Replacement Therapy Has A Paradoxical Effect On Cognition
- Date:
- University of Montreal
- Summary:
- Dopamine replacement therapy, which is used to manage motor symptoms associated with Parkinsons disease, can, at times, adversely affect cognition. Now researchers have identified the reasons why.
Dopamine replacement therapy, which is used to manage motor symptoms associated with Parkinsons disease, can, at times, adversely affect cognition. Dr. Oury Monchi, Ph. D. in neuronal modeling and Head of the Neurophysiological and Neuroimaging Research theme at the Centre de recherche de lInstitut universitaire de gériatrie de Montréal , which is affiliated with the Université de Montréal, and Dr. Penny A. MacDonald, Neurologist and postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Monchis laboratory, have identified the reasons why within the framework of a clinical study recently published in Brain: A Journal of Neurology.
Until now, the effect of dopamine replacement therapy on cognition in individuals with Parkinsons disease was controversial. The purpose of this study however, was to further investigate. This led to a series of laboratory tests and neuroimaging studies that allowed researchers to clearly define the distinct cognitive functions performed by the dorsal and ventral striatum, thereby shedding some light on the issue.
Summary of the Research
Parkinsons disease
The authors are grateful for the support provided by the IUGM Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Story Source:
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Research Foundation
What Should I Know About Storage And Disposal Of This Medication
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture .
Store cassettes containing levodopa and carbidopa enteral suspension in the refrigerator in their original carton, protected from light. Do not freeze the suspension.
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage/recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your community. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers are not child-resistant and young children can open them easily. To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location â one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach.
Background Of The Disease
About 250,000 people suffer on Parkinsons disease in Germany. Another 100,000 can be assumed as not detected. Up to 180 patients per 100,000 habitants are estimated. About 1% of the 60-years old people and 3% of the 80-years old people have Parkinsons disease. 10% of the patients are younger than 40 years, 30% younger than 50 years. 40% get the disease between 50 and 60 years. Men have a double risk to get the disease then women. Incidence is increasing with age.
The clinical symptoms or Morbus Parkinson is mainly the bradykinesis, tremor , and rigor .
Dont Miss: Prayers For Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Is There A Diagnostic Test For Parkinson Disease
